系列文章目录
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(1)——前言
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(2)——Player
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(3)——Timeline
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(4)——整体架构
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(5)——MediaSource
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(6)——MediaPeriod
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(7)——SampleQueue
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(8)——Loader
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(9)——TsExtractor
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(10)——H264Reader
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(11)——DataSource
ExoPlayer架构详解与源码分析(12)——Cache
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- Cache
- DataSink
- CacheDataSink
- CacheEvictor
- LeastRecentlyUsedCacheEvictor
- CachedContentIndex
- LegacyStorage
- AtomicFile
- AtomicFileOutputStream
- SimpleCache
- 动态分析
- 总结
前言
上篇介绍完基本的DataSource,现在可以开始CacheDataSource和TeeDataSource了。
先看下整体结构:

上图这里假设CacheDataSource原始的上游数据是通过OkHttpDataSource从网络获取
看完上图,是不是感觉非常复杂,没关系我们可以拆解出几个独立的结构一步步了解,可以看到底层的Cache可以作为一个独立的结构,在说CacheDataSource和TeeDataSource前,先把Cache这个基础先了解下。
Cache
可以将资源分段的缓存,资源指的是一个完整的媒体文件(如一个MP4,ts文件),每个资源都有唯一的key,一般使用资源的URI作为Key,有时候同一个资源会有不同的URI(如URI加上了失效时间)这种情况就不适合作为资源的 key了。一个资源由多个CacheSpan组成,CacheSpan包含一个数据起始位置和一个长度,代表了资源中的一段数据,CacheSpan并不一定会被Cache,当没有被Cache时叫做HoleSpan,如果被Cached CacheSpan就会对应一个缓存文件。
下面看下具体方法:
-
getUid 返回缓存的非负唯一标识符,如果在确定唯一标识符之前初始化失败,则返回UID_UNSET 。一个缓存目录对应一个UID,SimpleCache会在缓存目录下创建一个UID的文件用于下次读取UID。
-
release 释放缓存。当不再需要缓存时必须调用此方法。调用此方法后不得使用缓存。此方法可能很慢,通常不应在主线程上调用。
-
getCachedSpans 返回给定资源key的所有CacheSpan。
-
getKeys 返回所有有缓存的资源key。
-
getCacheSpace 返回所有缓存所占磁盘空间大小。
-
startReadWrite 通过传入的资源key获取资源,再通过postion和length获取指定的CacheSpan,当调用DataSource open数据源的时候应该同步调用此方法。
- 如果指定位置存在已经缓存的数据也就是CacheSpan.isCached为 true,则返回的CacheSpan.file有值,表示当前缓存的文件。
- 如果没有查询到缓存的CacheSpan则返回一个空的HoleSpan,当调用者从上游获取到数据时可以向当前的HoleSpan指定的范围写入数据,写入完成前此段HoleSpan指定的范围将会锁定,此时再通过startReadWrite会阻塞,当写入完成时,应该通过调用commitFile(File, long)会创建一个已缓存的Span提交到缓存中,此时之前阻塞的startReadWrite将会唤醒,可以获取到一个已缓存的CacheSpan,当调用者完成写入后,必须通过调用releaseHoleSpan来释放锁,此时startReadWrite可以正常获取到已缓存的CacheSpan。此方法可能会阻塞,通常不应在主线程上调用。
- 入参length表示所请求数据的长度,如果未知则为C.LENGTH_UNSET,如果存在与该postion重叠的缓存条目,则忽略该长度,也就是入参position 的查找优先级高于length,startReadWrite通常被用于后台下载器,当下载器要下载的数据段此时正在被缓存,会等待缓存完成。
-
startReadWriteNonBlocking 和startReadWrite类似,不同的是当DataSource被锁定的时候,不会阻塞会直接返回null,startReadWriteNonBlocking主要是播放器使用,因为播放器是不允许阻塞的,在缓存未获取到时会直接跳过缓存。
-
startFile 获取可写入数据的缓存文件。必须先调用startReadWrite(String, long, long)获得的相应HoleSpan时才能调用。不应在主线程上调用。
-
commitFile 将文件提交到缓存中。必须先调用startReadWrite(String, long, long)获得的相应HoleSpan时才能调用。不应在主线程上调用。
-
releaseHoleSpan 释放从startReadWrite(String, long, long)获得的 HoleSpan。
-
removeResource 删除资源的所有CacheSpans ,同时删除底层文件。
-
removeSpan 从缓存中删除缓存的CacheSpan ,从而删除底层文件。不应在主线程上调用。
-
isCached 返回资源中指定范围的数据是否已完全缓存。
-
getCachedLength 返回从资源的position开始,直到最大maxLength的连续缓存数据的长度。如果未缓存position ,则返回-holeLength ,其中holeLength是从position开始,直到最大值maxLength的连续未缓存数据的长度。
-
getCachedBytes 返回资源position (包含)和(position + length) (不包含)之间的缓存字节总数。
-
applyContentMetadataMutations 存储资源相关的Meta信息如资源的总长度 。不应在主线程上调用。
-
getContentMetadata 获取资源的Meta信息。
一个新的缓存添加时,Cache的一般执行顺序是:
- startReadWrite获取HoleSpan,同时锁定这段HoleSpan,防止其他线程再次获取这段HoleSpan。
- startFile获取CacheSpan对应的文件。
- 对2获取的文件进行写入操作。
- commitFile提交写入的文件,并创建与HoleSpan一致的已缓存的CacheSpan提交到Span索引,此时其他线程startReadWrite唤醒可以获取到一个CacheSpan供读取。
- releaseHoleSpan释放startReadWrite获取HoleSpan,此时其他线程可以再次startReadWrite获取到一个HoleSpan,并再次写入数据。
继续深挖,在讲Cache实现前说下其他几个类
DataSink
这是一个用来向其中写入数据的组件,概念上是和DataSource完全相反,提供了write供外部写入数据
看下主要方法:
- open 打开一个数据源,以用来写入指定的数据,同样传入一个DataSpec参照DataSource。
- write 消费掉传入的数据,用法上和DataSource的read类型,不过这里传入的buffer是用来读取的。
- close 关闭源。即使open调用抛出IOException 时,也必须调用此方法关闭源。
CacheDataSink
CacheDataSink是DataSink主要实现,主要目的是将数据写入文件缓存,通过Cache获取文件打开写入文件,当达到指定分段大小就获取下个文件继续写入,可以设置数据分段的长度和写入缓冲区的大小。
/** 默认文件的最大大小为5M */public static final long DEFAULT_FRAGMENT_SIZE = 5 * 1024 * 1024;/** 默认的写入流缓冲为20kb */public static final int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 20 * 1024;@Overridepublic void open(DataSpec dataSpec) throws CacheDataSinkException {...try {openNextOutputStream(dataSpec);} catch (IOException e) {throw new CacheDataSinkException(e);}}//打开下一个文件private void openNextOutputStream(DataSpec dataSpec) throws IOException {long length =dataSpec.length == C.LENGTH_UNSET? C.LENGTH_UNSET: min(dataSpec.length - dataSpecBytesWritten, dataSpecFragmentSize);file =//通过cache获取文件的路径cache.startFile(castNonNull(dataSpec.key), dataSpec.position + dataSpecBytesWritten, length);FileOutputStream underlyingFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);if (bufferSize > 0) {if (bufferedOutputStream == null) {bufferedOutputStream =//设置写入流缓冲大小new ReusableBufferedOutputStream(underlyingFileOutputStream, bufferSize);} else {bufferedOutputStream.reset(underlyingFileOutputStream);}outputStream = bufferedOutputStream;} else {outputStream = underlyingFileOutputStream;}outputStreamBytesWritten = 0;}//写入文件@Overridepublic void write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int length) throws CacheDataSinkException {@Nullable DataSpec dataSpec = this.dataSpec;if (dataSpec == null) {return;}try {int bytesWritten = 0;while (bytesWritten < length) {if (outputStreamBytesWritten == dataSpecFragmentSize) {//是否已经达到文件的分段大小closeCurrentOutputStream();//关闭当前openNextOutputStream(dataSpec);//获取下个文件}int bytesToWrite =//继续写入文件数据(int) min(length - bytesWritten, dataSpecFragmentSize - outputStreamBytesWritten);castNonNull(outputStream).write(buffer, offset + bytesWritten, bytesToWrite);bytesWritten += bytesToWrite;outputStreamBytesWritten += bytesToWrite;dataSpecBytesWritten += bytesToWrite;}} catch (IOException e) {throw new CacheDataSinkException(e);}}private void openNextOutputStream(DataSpec dataSpec) throws IOException {long length =dataSpec.length == C.LENGTH_UNSET? C.LENGTH_UNSET: min(dataSpec.length - dataSpecBytesWritten, dataSpecFragmentSize);file =cache.startFile(//这里调用了cache的startFile方法开始向文件中写入数据castNonNull(dataSpec.key), dataSpec.position + dataSpecBytesWritten, length);FileOutputStream underlyingFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);if (bufferSize > 0) {if (bufferedOutputStream == null) {bufferedOutputStream =new ReusableBufferedOutputStream(underlyingFileOutputStream, bufferSize);} else {bufferedOutputStream.reset(underlyingFileOutputStream);}outputStream = bufferedOutputStream;} else {outputStream = underlyingFileOutputStream;}outputStreamBytesWritten = 0;}private void closeCurrentOutputStream() throws IOException {if (outputStream == null) {return;}boolean success = false;try {outputStream.flush();success = true;} finally {Util.closeQuietly(outputStream);outputStream = null;File fileToCommit = castNonNull(file);file = null;if (success) {//写入完成后,提交缓存,会将当前的分段的CacheSpan添加入索引cache.commitFile(fileToCommit, outputStreamBytesWritten);} else {fileToCommit.delete();}}}
可以看到CacheDataSink主要作用是控制文件分段写入,至于文件是如何获取的则交给Cache实现。
CacheEvictor
主要用来删除缓存的CacheSpan,根据实现的移除策略调用CacheSpan.removeSpan。
这个直接看实现
LeastRecentlyUsedCacheEvictor
当缓存达到设定的最大值有限,会将最近最少使用的CacheSpan删除。
public LeastRecentlyUsedCacheEvictor(long maxBytes) {this.maxBytes = maxBytes;//将CacheSpan放入到TreeSet管理排序this.leastRecentlyUsed = new TreeSet<>(LeastRecentlyUsedCacheEvictor::compare);}//指定排序规则private static int compare(CacheSpan lhs, CacheSpan rhs) {//比较CacheSpan最后使用时间long lastTouchTimestampDelta = lhs.lastTouchTimestamp - rhs.lastTouchTimestamp;if (lastTouchTimestampDelta == 0) {// Use the standard compareTo method as a tie-break.return lhs.compareTo(rhs);}return lhs.lastTouchTimestamp < rhs.lastTouchTimestamp ? -1 : 1;}@Override//CacheSpan添加后会回调public void onSpanAdded(Cache cache, CacheSpan span) {leastRecentlyUsed.add(span);currentSize += span.length;//更新当前的总大小evictCache(cache, 0);}private void evictCache(Cache cache, long requiredSpace) {//如果超出最大值则开始cache.removeSpan超出的CacheSpanwhile (currentSize + requiredSpace > maxBytes && !leastRecentlyUsed.isEmpty()) {cache.removeSpan(leastRecentlyUsed.first());}}
可以看出CacheEvictor很简单,主要作用就是管理CacheSpan,决定哪个CacheSpan优先被移除。
CachedContentIndex
主要用于保存缓存资源的索引信息,其中包含了多个资源的信息,通过资源key查询CachedContentIndex获取到CachedContent,CachedContent又包含很多的CacheSpan,最后通过position、length查询到指定的CacheSpan。
public CachedContentIndex(@Nullable DatabaseProvider databaseProvider,@Nullable File legacyStorageDir,@Nullable byte[] legacyStorageSecretKey,boolean legacyStorageEncrypt,boolean preferLegacyStorage) {checkState(databaseProvider != null || legacyStorageDir != null);keyToContent = new HashMap<>();//资源的key和内容对于的mapidToKey = new SparseArray<>();//资源ID和资源key对应的mapremovedIds = new SparseBooleanArray();//管理移除的资源IDnewIds = new SparseBooleanArray();@NullableStorage databaseStorage =//如果databaseProvider有值直接采用数据库存储索引数据databaseProvider != null ? new DatabaseStorage(databaseProvider) : null;@NullableStorage legacyStorage =//如果legacyStorageDir有值则采用文件存储索引数据legacyStorageDir != null? new LegacyStorage(new File(legacyStorageDir, FILE_NAME_ATOMIC),//索引文件名称cached_content_index.exilegacyStorageSecretKey,//用于文件AES加密的keylegacyStorageEncrypt)//是否加密: null;if (databaseStorage == null || (legacyStorage != null && preferLegacyStorage)) {storage = castNonNull(legacyStorage);previousStorage = databaseStorage;} else {storage = databaseStorage;previousStorage = legacyStorage;}}//首先执行初始化@WorkerThreadpublic void initialize(long uid) throws IOException {storage.initialize(uid);if (previousStorage != null) {previousStorage.initialize(uid);}//如果之前有另外一种数据存储方式,先同步2种方式的数据if (!storage.exists() && previousStorage != null && previousStorage.exists()) {// Copy from previous storage into current storage.previousStorage.load(keyToContent, idToKey);storage.storeFully(keyToContent);} else {// Load from the current storage.storage.load(keyToContent, idToKey);//调用storage价值数据}if (previousStorage != null) {//删除上一种方式数据previousStorage.delete();previousStorage = null;}}@WorkerThread//如果缓存文件发生变化,更新索引文件信息public void store() throws IOException {storage.storeIncremental(keyToContent);// Make ids that were removed since the index was last stored eligible for re-use.int removedIdCount = removedIds.size();for (int i = 0; i < removedIdCount; i++) {idToKey.remove(removedIds.keyAt(i));}removedIds.clear();newIds.clear();}//通过资源key获取或添加一个CachedContentpublic CachedContent getOrAdd(String key) {@Nullable CachedContent cachedContent = keyToContent.get(key);return cachedContent == null ? addNew(key) : cachedContent;}private CachedContent addNew(String key) {int id = getNewId(idToKey);//创建一个新的资源id//实例化CachedContent,此时CachedContent中并没有CacheSpanCachedContent cachedContent = new CachedContent(id, key);keyToContent.put(key, cachedContent);//添加mapidToKey.put(id, key);newIds.put(id, true);storage.onUpdate(cachedContent);return cachedContent;}//更新新CachedContent 中的meta信息public void applyContentMetadataMutations(String key, ContentMetadataMutations mutations) {CachedContent cachedContent = getOrAdd(key);if (cachedContent.applyMetadataMutations(mutations)) {storage.onUpdate(cachedContent);}}
CachedContent 中保存了文件的Key 、Id 、CacheSpan、Meta信息,CachedContentIndex会通过storage将这些信息存储到文件或者数据库,CachedContentIndex中定义了2种存储方式DatabaseStorage和LegacyStorage,分别对应数据库存储和文件存储,这里我们以文件存储为例看下实现。
LegacyStorage
//构造函数,加密部分省略,这里主要是创建了一个可以原子操作的文件public LegacyStorage(File file, @Nullable byte[] secretKey, boolean encrypt) {...atomicFile = new AtomicFile(file);}@Override//然后是load函数读取索引文件的数据public void load(HashMap<String, CachedContent> content, SparseArray<@NullableType String> idToKey) {checkState(!changed);if (!readFile(content, idToKey)) {content.clear();idToKey.clear();atomicFile.delete();}}private boolean readFile(HashMap<String, CachedContent> content, SparseArray<@NullableType String> idToKey) {if (!atomicFile.exists()) {return true;}@Nullable DataInputStream input = null;try {InputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(atomicFile.openRead());input = new DataInputStream(inputStream);int version = input.readInt();//读取版本if (version < 0 || version > VERSION) {return false;}int flags = input.readInt();//读取是否加密的flagif ((flags & FLAG_ENCRYPTED_INDEX) != 0) {.....}int count = input.readInt();//读取CachedContent数量int hashCode = 0;for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//读取CachedContent内容CachedContent cachedContent = readCachedContent(version, input);content.put(cachedContent.key, cachedContent);idToKey.put(cachedContent.id, cachedContent.key);hashCode += hashCachedContent(cachedContent, version);}int fileHashCode = input.readInt();//hash校验boolean isEOF = input.read() == -1;if (fileHashCode != hashCode || !isEOF) {return false;}} catch (IOException e) {return false;} finally {if (input != null) {Util.closeQuietly(input);}}return true;}//读取CachedContent内容private CachedContent readCachedContent(int version, DataInputStream input) throws IOException {int id = input.readInt();//读取IDString key = input.readUTF();//读取KEYDefaultContentMetadata metadata;//获取Meta信息if (version < VERSION_METADATA_INTRODUCED) {long length = input.readLong();ContentMetadataMutations mutations = new ContentMetadataMutations();ContentMetadataMutations.setContentLength(mutations, length);metadata = DefaultContentMetadata.EMPTY.copyWithMutationsApplied(mutations);} else {metadata = readContentMetadata(input);}return new CachedContent(id, key, metadata);}//写入文件private void writeFile(HashMap<String, CachedContent> content) throws IOException {@Nullable DataOutputStream output = null;try {OutputStream outputStream = atomicFile.startWrite();if (bufferedOutputStream == null) {bufferedOutputStream = new ReusableBufferedOutputStream(outputStream);} else {bufferedOutputStream.reset(outputStream);}ReusableBufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = this.bufferedOutputStream;output = new DataOutputStream(bufferedOutputStream);output.writeInt(VERSION);//先写入版本int flags = encrypt ? FLAG_ENCRYPTED_INDEX : 0;output.writeInt(flags);//写入加密的flagif (encrypt) {...}output.writeInt(content.size());//写入长度int hashCode = 0;//写入CachedContent数据for (CachedContent cachedContent : content.values()) {writeCachedContent(cachedContent, output);hashCode += hashCachedContent(cachedContent, VERSION);}output.writeInt(hashCode);//写入校验位atomicFile.endWrite(output);output = null;} finally {Util.closeQuietly(output);}}private void writeCachedContent(CachedContent cachedContent, DataOutputStream output)throws IOException {output.writeInt(cachedContent.id);//写入IDoutput.writeUTF(cachedContent.key);//写入KEYwriteContentMetadata(cachedContent.getMetadata(), output);//写入Meta信息}
看下AtomicFile如何保证原子性操作的。
AtomicFile
AtomicFile写入数据时先调用startWrite,获取到Stream然后写入数据,写入完成后调用endWrite结束。
public OutputStream startWrite() throws IOException {// 写入文件前,先将当前已有文件重命名备份if (baseName.exists()) {if (!backupName.exists()) {if (!baseName.renameTo(backupName)) {Log.w(TAG, "Couldn't rename file " + baseName + " to backup file " + backupName);}} else {baseName.delete();}}OutputStream str;try {str = new AtomicFileOutputStream(baseName);} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {File parent = baseName.getParentFile();if (parent == null || !parent.mkdirs()) {throw new IOException("Couldn't create " + baseName, e);}// 文件夹创建好后,再次尝试创建文件try {str = new AtomicFileOutputStream(baseName);} catch (FileNotFoundException e2) {throw new IOException("Couldn't create " + baseName, e2);}}return str;}//结束写入,将备份文件删除public void endWrite(OutputStream str) throws IOException {str.close();// 流正确关闭后,删除备份文件backupName.delete();}//读取文件留public InputStream openRead() throws FileNotFoundException {restoreBackup();return new FileInputStream(baseName);}//如果备份文件存在说明上次文件写入未正确关闭,可能写入一半就终止了,这个时候恢复上次文件写入前的备份数据private void restoreBackup() {if (backupName.exists()) {baseName.delete();backupName.renameTo(baseName);}}
AtomicFileOutputStream
AtomicFileOutputStream就是对fileOutputStream的一个包装,唯一修改了close方法保证文件立即同步到物理磁盘。
@Overridepublic void close() throws IOException {if (closed) {return;}closed = true;flush();//flush只是保证java内的数据立即同步try {fileOutputStream.getFD().sync();//相当于通知操作系统立即将操作系统文件缓存同步到文件} catch (IOException e) {Log.w(TAG, "Failed to sync file descriptor:", e);}fileOutputStream.close();}
好了到这里,可以接着来看Cache的实现了。
SimpleCache
Cache的实现类,给定缓存目录只允许有一个 SimpleCache 实例。要删除 SimpleCache,请使用delete(File, DatabaseProvider) ,而不是直接删除目录及其内容。因为如果数据索引是保存在数据库中的时候,无法被删除。
先看下delete静态函数的实现:
public static void delete(File cacheDir, @Nullable DatabaseProvider databaseProvider) {if (!cacheDir.exists()) {return;}File[] files = cacheDir.listFiles();if (files == null) {cacheDir.delete();//删除子文件夹return;}if (databaseProvider != null) {// 获取UIDlong uid = loadUid(files);if (uid != UID_UNSET) {try {//删除文件信息CacheFileMetadataIndex.delete(databaseProvider, uid);} catch (DatabaseIOException e) {Log.w(TAG, "Failed to delete file metadata: " + uid);}try {//删除索引文件或者数据库CachedContentIndex.delete(databaseProvider, uid);} catch (DatabaseIOException e) {Log.w(TAG, "Failed to delete file metadata: " + uid);}}}Util.recursiveDelete(cacheDir);//删除文件夹}
SimpleCache首先要调用startReadWrite获取CacheSpan看下SimpleCache相关代码。
SimpleCache(File cacheDir,CacheEvictor evictor,CachedContentIndex contentIndex,@Nullable CacheFileMetadataIndex fileIndex) {if (!lockFolder(cacheDir)) {throw new IllegalStateException("Another SimpleCache instance uses the folder: " + cacheDir);}this.cacheDir = cacheDir;//缓存文件夹this.evictor = evictor;//缓存删除策略this.contentIndex = contentIndex;//索引文件this.fileIndex = fileIndex;//文件信息保存非必须listeners = new HashMap<>();random = new Random();touchCacheSpans = evictor.requiresCacheSpanTouches();uid = UID_UNSET;// Start cache initialization.final ConditionVariable conditionVariable = new ConditionVariable();new Thread("ExoPlayer:SimpleCacheInit") {//启动线程初始化耗时操作@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (SimpleCache.this) {conditionVariable.open();//通知父线程继续initialize();SimpleCache.this.evictor.onCacheInitialized();}}}.start();conditionVariable.block();//通过conditionVariable 阻塞线程}private void initialize() {if (!cacheDir.exists()) {try {createCacheDirectories(cacheDir);//创建缓存目录} catch (CacheException e) {initializationException = e;return;}}@Nullable File[] files = cacheDir.listFiles();if (files == null) {String message = "Failed to list cache directory files: " + cacheDir;Log.e(TAG, message);initializationException = new CacheException(message);return;}//查找.uid结尾的ID文件获取ID,个缓存目录根目录包含一个ID文件uid = loadUid(files);if (uid == UID_UNSET) {try {//没有则创建uid = createUid(cacheDir);} catch (IOException e) {String message = "Failed to create cache UID: " + cacheDir;Log.e(TAG, message, e);initializationException = new CacheException(message, e);return;}}try {//初始化contentIndex文件索引contentIndex.initialize(uid);if (fileIndex != null) {fileIndex.initialize(uid);//初始化文件信息数据库Map<String, CacheFileMetadata> fileMetadata = fileIndex.getAll();loadDirectory(cacheDir, /* isRoot= */ true, files, fileMetadata);fileIndex.removeAll(fileMetadata.keySet());} else {//遍历缓存文件夹loadDirectory(cacheDir, /* isRoot= */ true, files, /* fileMetadata= */ null);}} catch (IOException e) {String message = "Failed to initialize cache indices: " + cacheDir;Log.e(TAG, message, e);initializationException = new CacheException(message, e);return;}contentIndex.removeEmpty();//去除空的文件try {contentIndex.store();//同步到文件} catch (IOException e) {Log.e(TAG, "Storing index file failed", e);}}//遍历缓存文件夹private void loadDirectory(File directory,boolean isRoot,@Nullable File[] files,@Nullable Map<String, CacheFileMetadata> fileMetadata) {...for (File file : files) {String fileName = file.getName();if (isRoot && fileName.indexOf('.') == -1) {loadDirectory(file, /* isRoot= */ false, file.listFiles(), fileMetadata);} else {if (isRoot&& (CachedContentIndex.isIndexFile(fileName) || fileName.endsWith(UID_FILE_SUFFIX))) {// 跳过.uid文件continue;}long length = C.LENGTH_UNSET;long lastTouchTimestamp = C.TIME_UNSET;@NullableCacheFileMetadata metadata = fileMetadata != null ? fileMetadata.remove(fileName) : null;if (metadata != null) {//查询到文件信息,直接使用,后面无需再解析相关信息length = metadata.length;lastTouchTimestamp = metadata.lastTouchTimestamp;}@NullableSimpleCacheSpan span =//创建Span,file是有值的,这些CacheSpan都是已缓存的SimpleCacheSpan.createCacheEntry(file, length, lastTouchTimestamp, contentIndex);if (span != null) {addSpan(span);} else {file.delete();}}}}//向contentIndex中添加Spanprivate void addSpan(SimpleCacheSpan span) {contentIndex.getOrAdd(span.key).addSpan(span);totalSpace += span.length;notifySpanAdded(span);}//触发监听,以及evictor管理Span,删除不需要的Spanprivate void notifySpanAdded(SimpleCacheSpan span) {@Nullable ArrayList<Listener> keyListeners = listeners.get(span.key);if (keyListeners != null) {for (int i = keyListeners.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {keyListeners.get(i).onSpanAdded(this, span);}}evictor.onSpanAdded(this, span);}@Override//阻塞式获取CacheSpanpublic synchronized CacheSpan startReadWrite(String key, long position, long length)throws InterruptedException, CacheException {Assertions.checkState(!released);checkInitialization();while (true) {CacheSpan span = startReadWriteNonBlocking(key, position, length);if (span != null) {return span;} else {// 阻塞线程,一直到唤醒时继续,有2处会唤醒:// 1. 调用完commitFile文件已经写入,此时已经可以读取了// 2. 调用完releaseHoleSpan,写入的锁已经释放,此时可以被写入wait();}}}public synchronized CacheSpan startReadWriteNonBlocking(String key, long position, long length)throws CacheException {Assertions.checkState(!released);checkInitialization();//获取SpanSimpleCacheSpan span = getSpan(key, position, length);//commitFile完成,文件已经写入if (span.isCached) {// 此时可以被读取return touchSpan(key, span);}//获取或者创建资源的索引文件CachedContent cachedContent = contentIndex.getOrAdd(key);//查询当前Span是否被锁定if (cachedContent.lockRange(position, span.length)) {// 没有被锁定,可以被写入数据return span;}// 当前的Span已经锁定return null;}private SimpleCacheSpan getSpan(String key, long position, long length) {@Nullable CachedContent cachedContent = contentIndex.get(key);//当前资源索引文件不存在,直接创建一个Hole Spanif (cachedContent == null) {return SimpleCacheSpan.createHole(key, position, length);}while (true) {//cachedContent存在,通过position和length查找CacheSpanSimpleCacheSpan span = cachedContent.getSpan(position, length);if (span.isCached && span.file.length() != span.length) {// 文件的大小和Span记录的不一致,文件可能被修改,扫描其他被更改的文件然后移除removeStaleSpans();continue;}return span;}}private SimpleCacheSpan touchSpan(String key, SimpleCacheSpan span) {if (!touchCacheSpans) {return span;}String fileName = Assertions.checkNotNull(span.file).getName();long length = span.length;long lastTouchTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();boolean updateFile = false;if (fileIndex != null) {try {//将文件信息保存到数据库,下次加载后直接获取fileIndex.set(fileName, length, lastTouchTimestamp);} catch (IOException e) {Log.w(TAG, "Failed to update index with new touch timestamp.");}} else {// Updating the file itself to incorporate the new last touch timestamp is much slower than// updating the file index. Hence we only update the file if we don't have a file index.updateFile = true;}SimpleCacheSpan newSpan =contentIndex.get(key).setLastTouchTimestamp(span, lastTouchTimestamp, updateFile);notifySpanTouched(span, newSpan);//触发监听return newSpan;}public synchronized File startFile(String key, long position, long length) throws CacheException {...CachedContent cachedContent = contentIndex.get(key);//获取资源索引Assertions.checkNotNull(cachedContent);Assertions.checkState(cachedContent.isFullyLocked(position, length));//确保当前Span的起始范围在,startReadWrite锁定的HoleSpan内...evictor.onStartFile(this, key, position, length);// 这里将缓存文件放入到0-9随机命名的文件夹中File cacheSubDir = new File(cacheDir, Integer.toString(random.nextInt(SUBDIRECTORY_COUNT)));if (!cacheSubDir.exists()) {//创建文件夹createCacheDirectories(cacheSubDir);}long lastTouchTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();return SimpleCacheSpan.getCacheFile(//获取文件,供后面写入cacheSubDir, cachedContent.id, position, lastTouchTimestamp);}//缓存文件的命名方式为资源ID.起始位置position.时间戳timestamp.版本v3.exo//如1.940.1692414683255.v3.exo,资源ID为1,开始位置为940,时间戳为1692414683255public static File getCacheFile(File cacheDir, int id, long position, long timestamp) {return new File(cacheDir, id + "." + position + "." + timestamp + SUFFIX);}@Overridepublic synchronized void commitFile(File file, long length) throws CacheException {...SimpleCacheSpan span =//通过文件名称反向构建SpanAssertions.checkNotNull(SimpleCacheSpan.createCacheEntry(file, length, contentIndex));CachedContent cachedContent = Assertions.checkNotNull(contentIndex.get(span.key));//获取索引Assertions.checkState(cachedContent.isFullyLocked(span.position, span.length));//确保当前已被锁定//确保数据一致性long contentLength = ContentMetadata.getContentLength(cachedContent.getMetadata());if (contentLength != C.LENGTH_UNSET) {Assertions.checkState((span.position + span.length) <= contentLength);}if (fileIndex != null) {String fileName = file.getName();try {//文件信息记录文件信息表fileIndex.set(fileName, span.length, span.lastTouchTimestamp);} catch (IOException e) {throw new CacheException(e);}}//将当前已缓存的Span添加到索引addSpan(span);try {contentIndex.store();//同步到索引文件} catch (IOException e) {throw new CacheException(e);}//唤醒阻塞在startReadWrite里其他线程,此时startReadWrite可以返回一个可读的已缓存的SpannotifyAll();}public static SimpleCacheSpan createCacheEntry(File file, long length, long lastTouchTimestamp, CachedContentIndex index) {String name = file.getName();if (!name.endsWith(SUFFIX)) {//版本不一致,文件命名不一致,这里进行统一@Nullable File upgradedFile = upgradeFile(file, index);if (upgradedFile == null) {return null;}file = upgradedFile;name = file.getName();}//正则匹配文件名,提取资源ID,起始位置Position,时间戳Matcher matcher = CACHE_FILE_PATTERN_V3.matcher(name);if (!matcher.matches()) {return null;}int id = Integer.parseInt(Assertions.checkNotNull(matcher.group(1)));@Nullable String key = index.getKeyForId(id);if (key == null) {return null;}if (length == C.LENGTH_UNSET) {length = file.length();}if (length == 0) {return null;}long position = Long.parseLong(Assertions.checkNotNull(matcher.group(2)));if (lastTouchTimestamp == C.TIME_UNSET) {lastTouchTimestamp = Long.parseLong(Assertions.checkNotNull(matcher.group(3)));}//通过以上信息构建Spanreturn new SimpleCacheSpan(key, position, length, lastTouchTimestamp, file);}@Override//释放startReadWrite创建的Hole Spanpublic synchronized void releaseHoleSpan(CacheSpan holeSpan) {Assertions.checkState(!released);CachedContent cachedContent = Assertions.checkNotNull(contentIndex.get(holeSpan.key));cachedContent.unlockRange(holeSpan.position);//解锁Hole SpancontentIndex.maybeRemove(cachedContent.key);notifyAll();//唤醒阻塞在startReadWrite里其他线程,此时已解锁startReadWrite可以返回一个可写的Span}
SimpleCache主要作用就是针对多线程场景下,向外提供缓存文件用于外界读取或者写入,通过HoleSpan作为一个占位符锁定资源,保证并发场景下缓存文件有序的读写。
动态分析
现在假设我们的缓存目录是downloads,现在第一次使用这个缓存目录:
- 在第一次初始化缓存目录时,会创建.uid文件,用它的问价名记录当前目录的UID。
- 接着开始缓存数据SimpleCache.startFile,创建文件如下方9/1.940.1692785096322.v3.exo,其中9为随机生成的目录名称规则为0-9之间随机,第一个点号前的1代表当前文件对应的资源ID为1,940表示从资源的940byte位置开始写入数据,文件的长度为写入数据的长度,1692785096322代表文件创建的时间戳。v3为文件结构版本号,这里固定可以忽略。
- 数据写入完成后,调用SimpleCache.commitFile,通过读取文件名的id,位置,时间戳,构建出CacheSpan添加到CachedContentIndex,CachedContentIndex调用store,更新cached_content_index.exi文件,在其中添加一条当前资源的相关信息,如id,key,Metadata。
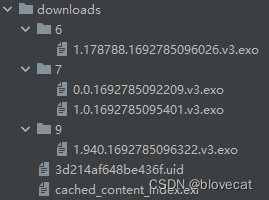
最终产生上面的目录结构,可以看到.exo文件有2种不同的资源ID,说明这里缓存了2个资源,cached_content_index.exi文件中记录了这2个资源的索引信息,现在假设我们再次使用这个缓存目录,这个时候需要重新建立内存中的所有对象CachedContentIndex,先看下文件和CachedContentIndex对象的对应关系图:

上图右侧可以看到CachedContentIndex包含多个CachedContent,而一个CachedContent又包含多个CachedSpan,这些数据都对应到左侧文件系统里的信息,文件系统构建CachedContentIndex具体过程如下:
- SimpleCache.loadUid首先读取缓存目录下的.uid文件,获取UID,用于CachedContentIndex的初始化。
- CachedContentIndex.initialize初始化时会通过Storage.load,加载目录中的cached_content_index.exi索引文件,首先获取资源总数count,然后依次读取出其中的资源数据,包括资源的id,key,meta信息(主要包含资源的长度exo_len和跳转后的URL exo_redir),最终构建所有的CachedDtaContent,此时CachedContent中的CachedSpans还未添加。
- SimpleCache.loadDirectory扫描缓存目录中的.exo文件,使用文件名字的id(查找索引文件找到对应的key),position,timestamp还有文件的长度路径,共同构建出CachedSpan,通过CachedSpan.key找到到CachedContentIndex中指定的CachedContent,向CachedContent添加CachedSpan。
- 至此CachedContentIndex就构建完成了,运行过程中如果产生新的缓存文件,则构建出此文件的CachedSpan添加入CachedContent,最终调用CachedContentIndex.store将内存中的CachedContentIndex同步到文件系统。
总结
分析完Cache这块,可以看到Cache这块就是一个单独的文件读写和管理系统,为上层的CacheDataSource提供支持,下一篇我们继续主线,正式讲下CacheDataSource。
版权声明 ©
本文为CSDN作者山雨楼原创文章
转载请注明出处
原创不易,觉得有用的话,收藏转发点赞支持


](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f77ba18b426444eb8838222d462e23ac.png)