手写Spring框架
- 准备工作
- Spring启动和扫描逻辑实现
- 依赖注入的实现
- Aware回调模拟实现和初始化机制模拟实现
- BeanPostProcessor (Bean的后置处理器) 模拟实现
- Spring AOP 模拟实现
准备工作
- 准备一个空的工程
- 创建
spring的容器类,它是Spring IOC理念的实现,负责对象的实例化、对象和对象之间依赖关系配置、对象的销毁、对外提供对象的查找等操作,对象的整个生命周期都是由容器来控制。传统使用方法是传入一个spring的配置文件或配置类根据用户的配置来创建这个容器。
package com.spring;public class EditApplicationContext {//传入配置类private Class configClass;public EditApplicationContext(Class configClass) {this.configClass = configClass;}//定义根据别名获取类的方法public Object getBean(String name){return null;}
}
- 定义一个配置类,相当于配置文件
package com.zedit;import com.spring.ComponentScan;//指定包扫描路径
@ComponentScan("com.zedit.service")
public class AppConfig {
}
- 如何定义包扫描路径,编写一个注解类
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//规定只能写在类上
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ComponentScan {//接收属性值,指定扫描路径String value() default "";
}
- 定义一个Component注解,它的作用就是将类交给spring容器,实现bean的注入
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//规定只能写在类上
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Component {//提供默认值String value() default "";
}
Spring启动和扫描逻辑实现
- 传入配置类对于spring而言 它只需要判断配置类有没有它提供的注解,获取扫描路径值,根据路径值
- 通过类加载器加载目录下的类,首先获取所有文件,然后获取全限定类名
public EditApplicationContext(Class configClass) {this.configClass = configClass;//解析配置类//Component注解->扫描路径->扫描ComponentScan declaredAnnotation = (ComponentScan)configClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);String path = declaredAnnotation.value();// 全限定类名加工成能用的路径名 "com/xuhua/service"path = path.replace(".", "/");ClassLoader classLoader = EditApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();//根据AppClassLoader加载器目录获取 classPath目录下中的‘path’目录下的资源URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);//判断是否是文件夹而不是单个文件if (file.isDirectory()) {File[] files = file.listFiles();for (File f : files) {String fileName = f.getAbsolutePath();// /Users/zhuxuhua/Desktop/project/spring-edit/target/classes/com/zedit/service/XxxUtils.class// 转换成 com.zedit.service.XxxUtilsif (fileName.endsWith(".class")) {String className = fileName.substring(fileName.indexOf("com"), fileName.indexOf(".class"));className = className.replace("/", ".");try {//根据全限定类名加载类Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(className);//判断扫描到的类是不是一个bean注解if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){}} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}}
}
- 根据
@Scope注解判断bean是单例还是原型
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Scope {String value();
}
- 定义单例池
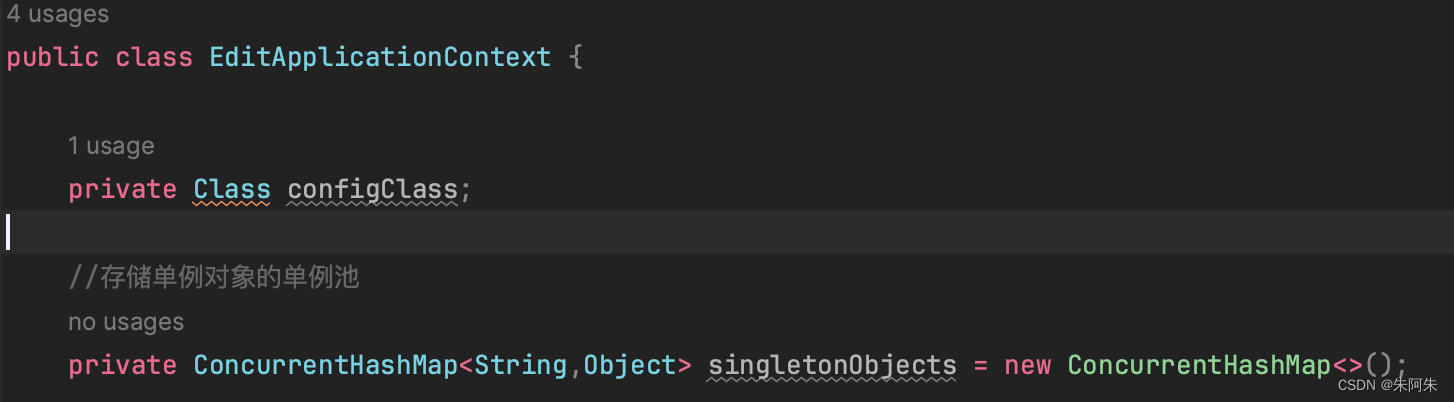
- 由于在使用bean和初始化bean时都要去解析bean的定义与他的注解,如果不做设计每次的解析就会显得冗余繁琐,所以spring在Context扫描阶段定义了一个BeanDefinition定义类,它记录了bean的各种信息,先将扫描到的bean填入BeanDefinitionMap随后处理单例对象
//存储单例对象的单例池
private ConcurrentHashMap<String,Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//存储所有bean的定义
private ConcurrentHashMap<String,BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
-------
try {Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(className);if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {//表示当前这个类有Component注解是一个bean对象//解析类,判断scope注解是单例的bean还是 prototype的bean//每扫描到一个bean就定义一个BeanDefinition对象Component componentAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();//spring bean默认为多例模式beanDefinition.setScpoe("prototype");if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){Scope annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Scope.class);String value = annotation.value();if (value.equals("singleton")){beanDefinition.setScpoe("singleton");}}beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);//扫描到的所有bean都存入这个mapbeanDefinitionMap.put(beanName,beanDefinition);}} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
- 扫描完后根据存储的beanDefinitionMap填入单例池
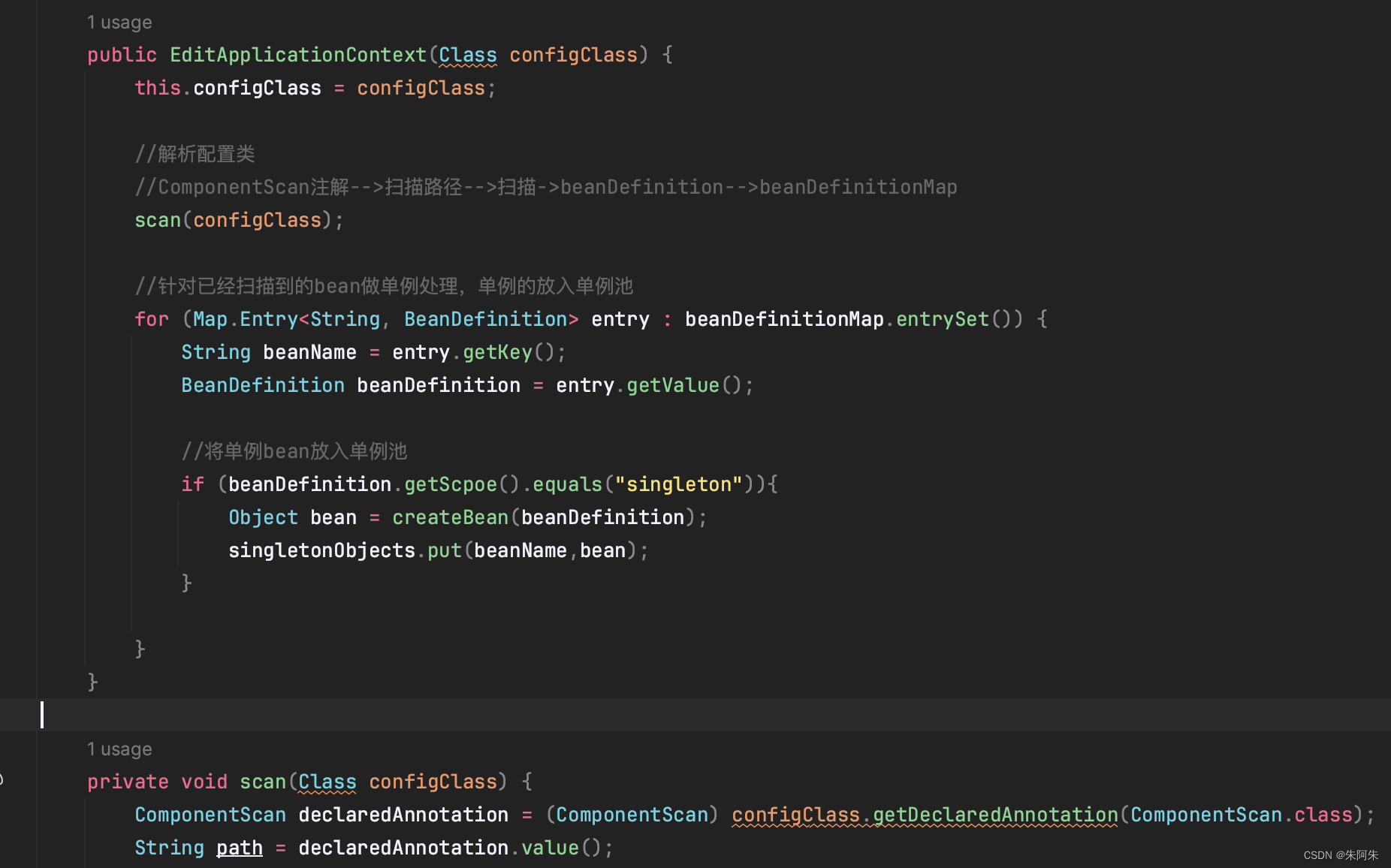
- 获取bean方法中判断是否是单例bean,如果是直接从单例池中取,如果不是则创建bean
public Object getBean(String beanName){//获取bean 如果map中没有就抛出异常,说明她不是一个bean,没有被扫描到if (beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)){BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);//判断scope值,单例直接从单例池中取if (beanDefinition.getScpoe().equals("singleton")){return singletonObjects.get(beanName);}else {//原型bean每次从新创建return createBean(beanDefinition);}}else {throw new NullPointerException();}}//用beanDefinition中的clazz信息通过反射创建bean
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition){Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();try {Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();return instance;} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
依赖注入的实现
首先注解,能标注在成员变量上
Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Autowired {}
@Component("userService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService {@Autowiredprivate OrderService orderService;public void test(){System.out.println(orderService);}
}依赖注解的实现原理就是在启动扫描初始化阶段 spring创建bean时 给@Autowired的成员变量赋值
//用beanDefinition中的clazz信息通过反射创建beanpublic Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition){Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();try {Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();//依赖注入实现原理for (Field declaredField : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)){Object bean = getBean(declaredField.getName());declaredField.setAccessible(true);declaredField.set(instance,bean);}}return instance;} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}

Aware回调模拟实现和初始化机制模拟实现
需要回调的实现接口方法,在初始化阶段bean的创建阶段将beanName通过反射设置值
//回调接口
public interface BeanNameAware {void setBeanName(String name);
}-------public interface InitializingBean {void afterPropertySet();
}
@Component("userService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService implements BeanNameAware, InitializingBean {@Autowiredprivate OrderService orderService;private String beanName;@Overridepublic void setBeanName(String name) {beanName = name;}@Overridepublic void afterPropertySet() {System.out.println("初始化");}
//用beanDefinition中的clazz信息通过反射创建beanpublic Object createBean(String beanName,BeanDefinition beanDefinition){Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();try {Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();//依赖注入for (Field declaredField : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)){Object bean = getBean(declaredField.getName());declaredField.setAccessible(true);declaredField.set(instance,bean);}}//aware 回调if (instance instanceof BeanNameAware){((BeanNameAware) instance).setBeanName(beanName);}//反射调用初始化bean的方法if (instance instanceof InitializingBean){((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertySet();}return instance;} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
BeanPostProcessor (Bean的后置处理器) 模拟实现
spring的扩展机制,在bean初始化前后调用
//定义接口 有初始化前后两种操作,也可以添加更多
public interface BeanPostProcessor {Object postProcessorBeforeInitialization(Object bean,String beanName);Object postProcessorAfterInitialization(Object bean,String beanName);
}----------------//自定义 BeanPostProcessor 实现BeanPostProcessor接口
@Component
public class ZhuZhuBanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {@Overridepublic Object postProcessorBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {System.out.println("初始化前");//定制操作if (beanName.equals("userService")) {System.out.println("userService 初始化前");}return null;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessorAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {System.out.println("初始化后");return null;}
}--------//同其他bean一样在扫描时 加载 判断是否实现了BeanPostProcessor,如果实现了就放入 专门的List存储//scan方法中 判断此类是否实现了BeanPostProcessor,并存入list
if (BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessorInstance = (BeanPostProcessor) clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();beanPostProcessorList.add(beanPostProcessorInstance);
}---------//createBean方法中//createBean 时调 初始化前调用
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {//在调用初始化方法前 重新赋值对象instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessorBeforeInitialization(instance,beanName);
}//初始化
if (instance instanceof InitializingBean){try {((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertySet();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}//createBean 时调 初始化后调用
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {//在调用初始化方法后 重新赋值对象instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessorAfterInitialization(instance, beanName);
}Spring AOP 模拟实现
使用jdk动态代理 实现
@Component("userService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{@Autowiredprivate OrderService orderService;private String beanName;@Overridepublic void setBeanName(String name) {beanName = name;}@Overridepublic void afterPropertySet() {System.out.println("初始化");}@Overridepublic void test(){System.out.println(orderService+"orderService test");System.out.println(beanName);}}--------public interface UserService {void test();
}结合 BeanPostProcessor 完成jdk动态的实现
@Overridepublic Object postProcessorAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {System.out.println("初始化后");if (beanName.equals("userService")){Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(ZhuZhuBanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {System.out.println("被代理的逻辑");return method.invoke(bean,args);}});return proxyInstance;}return bean;}
被动态代理后的类,执行类中的任意方法 都会经过 jdk的代理逻辑进行增强