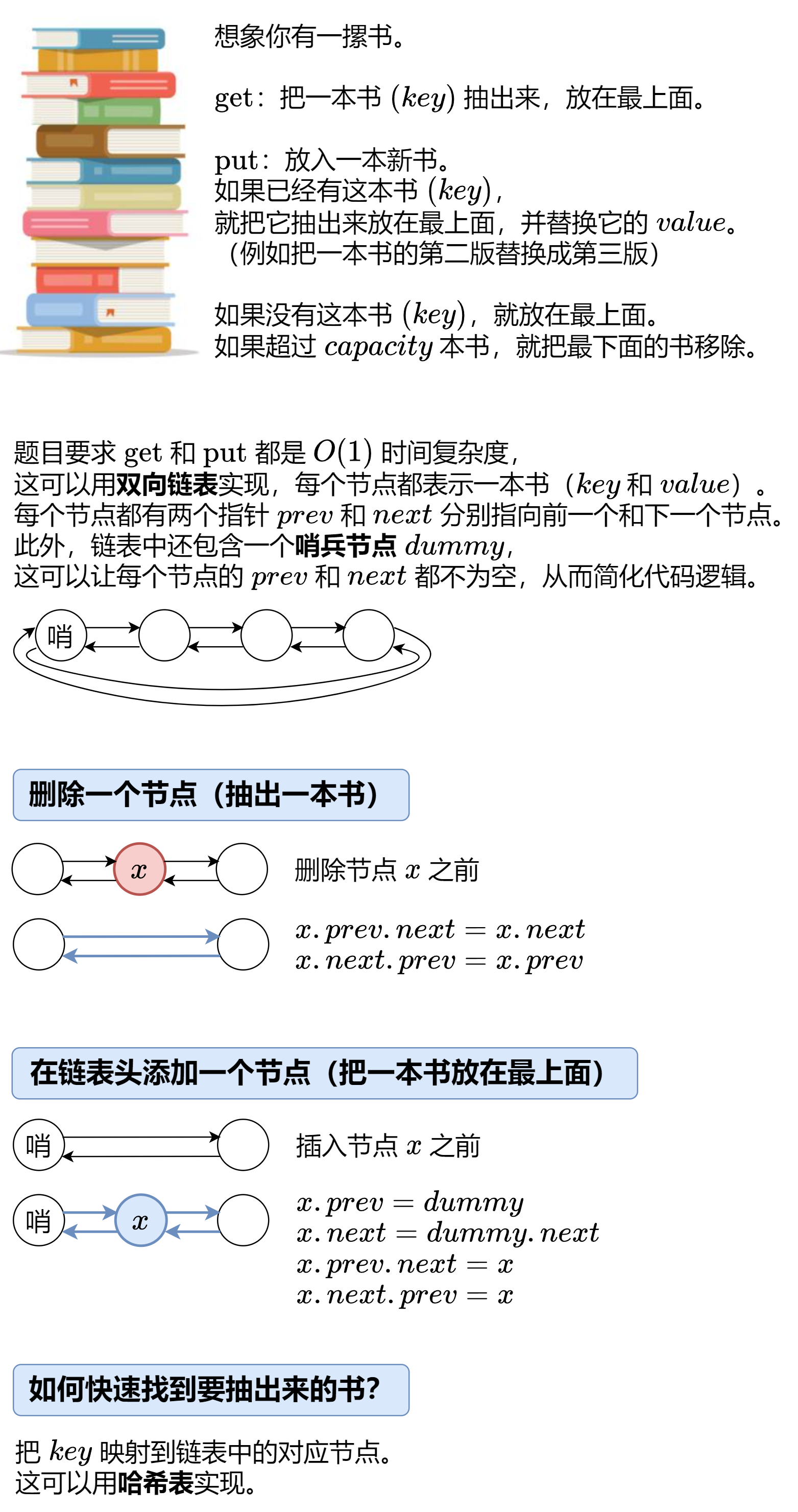
spring ioc总结-基于XML管理bean
- 前言
- 实验一 [重要]创建bean
- 1、目标和思路
- ①目标
- ②思路
- 2、创建Maven Module
- 3、创建组件类
- 4、创建spring配置文件
- 7、无参构造器
- 8、用IOC容器创建对象和自己建区别
- 实验二 [重要]获取bean
- 1、方式一:根据id获取
- 2、方式二:根据类型获取
- ①指定类型的 bean 唯一
- ②指令类型的 bean 不唯一
- ③思考
- ④结论
- 实验三 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:setter注入
- 1、给组件类添加一个属性
- 2、在配置时给属性指定值
- 3、测试
- 实验四 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:引用外部已声明的bean
- 1、声明新的组件类
- 2、原组件引用新组件
- 3、配置新组件的 bean
- 4、在原组件的 bean 中引用新组件的 bean
- 5、测试
- 6、易错点
- 实验五 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:内部bean
- 1、重新配置原组件
- 2、测试
- 实验六 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:引入外部属性文件
- 1、加入依赖
- 2、创建外部属性文件
- 3、引入
- 4、使用
- 5、测试
- 实验七 给bean的属性赋值:级联属性赋值
- 1、配置关联对象的 bean
- 2、装配关联对象并赋值级联属性
- 3、测试
- 实验八 给bean的属性赋值:构造器注入
- 1、声明组件类
- 2、配置
- 3、测试
- 4、补充
- 实验九 给bean的属性赋值:特殊值处理
- 1、声明一个类用于测试
- 2、字面量
- ①用Java代码举例说明
- ②Spring配置文件中举例
- [1]字面量举例
- [2]类似变量举例
- 3、null值
- 4、XML实体
- 5、CDATA节
- 实验十 给bean的属性赋值:使用p名称空间
- 1、配置
- 2、测试
- 实验十一 给bean的属性赋值:集合属性
- 1、给组件类添加属性
- 2、配置
- 3、测试
- 4、其他变化形式
- 实验十二 自动装配
- 1、声明组件类
- 2、配置
- 3、测试
- 实验十三 集合类型的bean
- 1、配置
- 2、测试
- 实验十四 FactoryBean机制
- 1、简介
- 2、实现FactoryBean接口
- 3、配置bean
- 4、测试获取bean
- 实验十五 bean的作用域
- 1、概念
- 2、配置
- 3、测试
- 实验十六 bean的生命周期
- 1、bean的生命周期清单
- 2、指定bean的初始化方法和销毁方法
- ①创建两个方法作为初始化和销毁方法
- ②配置bean时指定初始化和销毁方法
- 3、bean的后置处理器
- ①创建后置处理器类
- ②把bean的后置处理器放入IOC容器
- ③执行效果示例
前言
清明时节雨纷纷,路上行人欲断后。 借问酒家何处有,牧童遥指杏花村。
清明假期做个总结吧。
实验一 [重要]创建bean
1、目标和思路
①目标
由 Spring 的 IOC 容器创建类的对象。
②思路
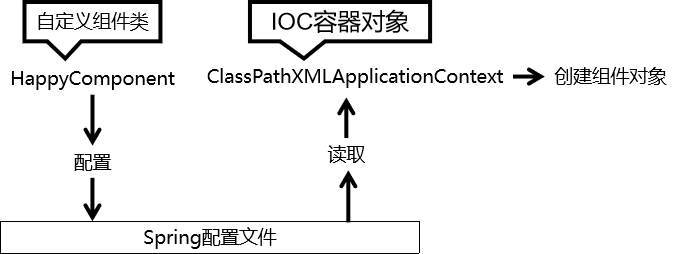
2、创建Maven Module
<dependencies><!-- 基于Maven依赖传递性,导入spring-context依赖即可导入当前所需所有jar包 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>5.3.1</version></dependency><!-- junit测试 --><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.12</version><scope>test</scope></dependency>
</dependencies>
3、创建组件类
package com.atguigu.ioc.component;public class HappyComponent {public void doWork() {System.out.println("component do work ...");}}
4、创建spring配置文件
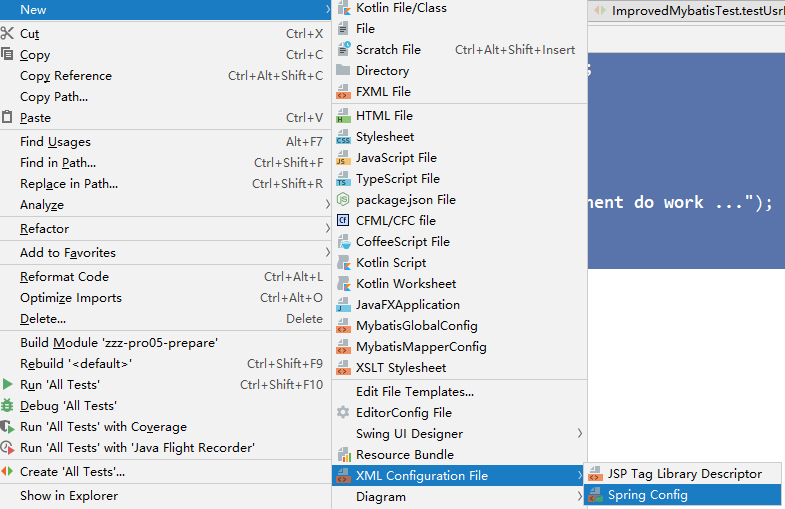
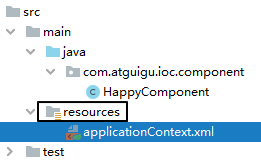
5、配置组件
<!-- 实验一 [重要]创建bean -->
<bean id="happyComponent" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"/>
bean标签:通过配置bean标签告诉IOC容器需要创建对象的组件是什么
id属性:bean的唯一标识
class属性:组件类的全类名
public class IOCTest {// 创建 IOC 容器对象,为便于其他实验方法使用声明为成员变量private ApplicationContext iocContainer = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");@Testpublic void testExperiment01() {// 从 IOC 容器对象中获取bean,也就是组件对象HappyComponent happyComponent = (HappyComponent) iocContainer.getBean("happyComponent");happyComponent.doWork();}}
7、无参构造器
Spring 底层默认通过反射技术调用组件类的无参构造器来创建组件对象,这一点需要注意。如果在需要无参构造器时,没有无参构造器,则会抛出下面的异常:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error
creating bean with name ‘happyComponent1’ defined in class path
resource [applicationContext.xml]: Instantiation of bean failed;nested exception is
org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException: Failed to
instantiate [com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent]: No default
constructor found;nested exception is java.lang.NoSuchMethodException:
com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent.()
所以对一个JavaBean来说,无参构造器和属性的getXxx()、setXxx()方法是必须存在的,特别是在框架中。
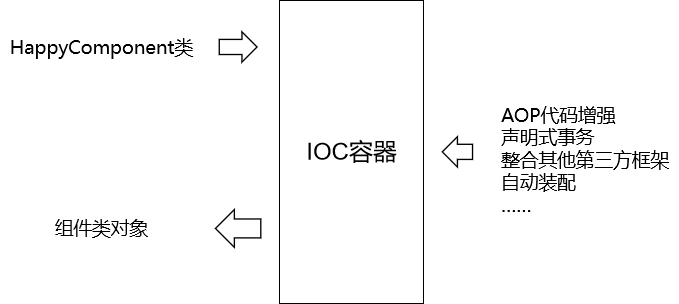
8、用IOC容器创建对象和自己建区别
实验二 [重要]获取bean
1、方式一:根据id获取
由于 id 属性指定了 bean 的唯一标识,所以根据 bean 标签的 id 属性可以精确获取到一个组件对象。上个实验中我们使用的就是这种方式。
2、方式二:根据类型获取
①指定类型的 bean 唯一
@Test
public void testExperiment02() {HappyComponent component = iocContainer.getBean(HappyComponent.class);component.doWork();}
②指令类型的 bean 不唯一
相同类型的 bean 在IOC容器中一共配置了两个:
<!-- 实验一 [重要]创建bean -->
<bean id="happyComponent" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"/><!-- 实验二 [重要]获取bean -->
<bean id="happyComponent2" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"/>
根据类型获取时会抛出异常:
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type ‘com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent’ available: expected single matching bean but found 2: happyComponent,happyComponent2
③思考
如果组件类实现了接口,根据接口类型可以获取 bean 吗?
可以,前提是bean唯一
如果一个接口有多个实现类,这些实现类都配置了 bean,根据接口类型可以获取 bean 吗?
不行,因为bean不唯一
④结论
根据类型来获取bean时,在满足bean唯一性的前提下,其实只是看:『对象 instanceof 指定的类型』的返回结果,只要返回的是true就可以认定为和类型匹配,能够获取到。
实验三 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:setter注入
1、给组件类添加一个属性
public class HappyComponent {private String componentName;public String getComponentName() {return componentName;}public void setComponentName(String componentName) {this.componentName = componentName;}public void doWork() {System.out.println("component do work ...");}}
2、在配置时给属性指定值
通过property标签配置的属性值会通过setXxx()方法注入,大家可以通过debug方式验证一下
<!-- 实验三 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:setter注入 -->
<bean id="happyComponent3" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"><!-- property标签:通过组件类的setXxx()方法给组件对象设置属性 --><!-- name属性:指定属性名(这个属性名是getXxx()、setXxx()方法定义的,和成员变量无关) --><!-- value属性:指定属性值 --><property name="componentName" value="veryHappy"/>
</bean>
3、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment03() {HappyComponent happyComponent3 = (HappyComponent) iocContainer.getBean("happyComponent3");String componentName = happyComponent3.getComponentName();System.out.println("componentName = " + componentName);}
实验四 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:引用外部已声明的bean
1、声明新的组件类
public class HappyMachine {private String machineName;public String getMachineName() {return machineName;}public void setMachineName(String machineName) {this.machineName = machineName;}
}
2、原组件引用新组件
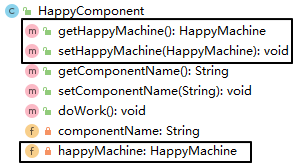
3、配置新组件的 bean
<bean id="happyMachine" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"><property name="machineName" value="makeHappy"
</bean>
4、在原组件的 bean 中引用新组件的 bean
<bean id="happyComponent4" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"><!-- ref 属性:通过 bean 的 id 引用另一个 bean --><property name="happyMachine" ref="happyMachine"/>
</bean>
这个操作在 IDEA 中有提示:
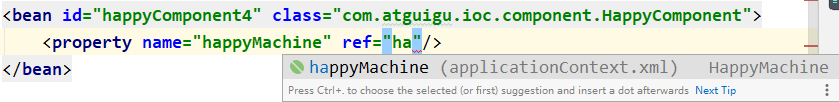
5、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment04() {HappyComponent happyComponent4 = (HappyComponent) iocContainer.getBean("happyComponent4");HappyMachine happyMachine = happyComponent4.getHappyMachine();String machineName = happyMachine.getMachineName();System.out.println("machineName = " + machineName);
}
6、易错点
如果错把ref属性写成了value属性,会抛出异常:
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot convert value of type ‘java.lang.String’ to required type ‘com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine’ for property ‘happyMachine’: no matching editors or conversion strategy found
意思是不能把String类型转换成我们要的HappyMachine类型
说明我们使用value属性时,Spring只把这个属性看做一个普通的字符串,不会认为这是一个bean的id,更不会根据它去找到bean来赋值
实验五 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:内部bean
1、重新配置原组件
在bean里面配置的bean就是内部bean,内部bean只能在当前bean内部使用,在其他地方不能使用。
<!-- 实验五 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:内部bean -->
<bean id="happyComponent5" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"><property name="happyMachine"><!-- 在一个 bean 中再声明一个 bean 就是内部 bean --><!-- 内部 bean 可以直接用于给属性赋值,可以省略 id 属性 --><bean class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"><property name="machineName" value="makeHappy"/></bean></property>
</bean>
2、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment04() {HappyComponent happyComponent4 = (HappyComponent) iocContainer.getBean("happyComponent4");HappyMachine happyMachine = happyComponent4.getHappyMachine();String machineName = happyMachine.getMachineName();System.out.println("machineName = " + machineName);
}
实验六 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:引入外部属性文件
1、加入依赖
<!-- MySQL驱动 --><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.3</version></dependency><!-- 数据源 --><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.0.31</version></dependency>
2、创建外部属性文件
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=atguigu
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.198.100:3306/mybatis-example
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
3、引入
<!-- 引入外部属性文件 --><context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
4、使用
<!-- 实验六 [重要]给bean的属性赋值:引入外部属性文件 -->
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"><property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/><property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/><property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
5、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment06() throws SQLException {DataSource dataSource = iocContainer.getBean(DataSource.class);Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();System.out.println("connection = " + connection);
}
实验七 给bean的属性赋值:级联属性赋值
1、配置关联对象的 bean
<bean id="happyMachine2" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"/>
2、装配关联对象并赋值级联属性
关联对象:happyMachine
级联属性:happyMachine.machineName
<!-- 实验七 给bean的属性赋值:级联属性赋值 -->
<bean id="happyComponent6" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"><!-- 装配关联对象 --><property name="happyMachine" ref="happyMachine2"/><!-- 对HappyComponent来说,happyMachine的machineName属性就是级联属性 --><property name="happyMachine.machineName" value="cascadeValue"/>
</bean>
3、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment07() {HappyComponent happyComponent6 = (HappyComponent) iocContainer.getBean("happyComponent6");String machineName = happyComponent6.getHappyMachine().getMachineName();System.out.println("machineName = " + machineName);}
实验八 给bean的属性赋值:构造器注入
1、声明组件类
package com.atguigu.ioc.component;public class HappyTeam {private String teamName;private Integer memberCount;private Double memberSalary;public String getTeamName() {return teamName;}public void setTeamName(String teamName) {this.teamName = teamName;}public Integer getMemberCount() {return memberCount;}public void setMemberCount(Integer memberCount) {this.memberCount = memberCount;}public Double getMemberSalary() {return memberSalary;}public void setMemberSalary(Double memberSalary) {this.memberSalary = memberSalary;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "HappyTeam{" +"teamName='" + teamName + '\'' +", memberCount=" + memberCount +", memberSalary=" + memberSalary +'}';}public HappyTeam(String teamName, Integer memberCount, Double memberSalary) {this.teamName = teamName;this.memberCount = memberCount;this.memberSalary = memberSalary;}public HappyTeam() {}
}
2、配置
<!-- 实验八 给bean的属性赋值:构造器注入 -->
<bean id="happyTeam" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyTeam"><constructor-arg value="happyCorps"/><constructor-arg value="10"/><constructor-arg value="1000.55"/>
</bean>
3、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment08() {HappyTeam happyTeam = iocContainer.getBean(HappyTeam.class);System.out.println("happyTeam = " + happyTeam);}
4、补充
constructor-arg标签还有两个属性可以进一步描述构造器参数:
- index属性:指定参数所在位置的索引(从0开始)
- name属性:指定参数名
实验九 给bean的属性赋值:特殊值处理
1、声明一个类用于测试
package com.atguigu.ioc.component;public class PropValue {private String commonValue;private String expression;public String getCommonValue() {return commonValue;}public void setCommonValue(String commonValue) {this.commonValue = commonValue;}public String getExpression() {return expression;}public void setExpression(String expression) {this.expression = expression;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "PropValue{" +"commonValue='" + commonValue + '\'' +", expression='" + expression + '\'' +'}';}public PropValue(String commonValue, String expression) {this.commonValue = commonValue;this.expression = expression;}public PropValue() {}
}
2、字面量
①用Java代码举例说明
字面量是相对于变量来说的。看下面的代码:
int a = 10;
声明一个变量a,初始化为10,此时a就不代表字母a了,而是作为一个变量的名字。当我们引用a的时候,我们实际上拿到的值是10。
而如果a是带引号的:‘a’,那么它现在不是一个变量,它就是代表a这个字母本身,这就是字面量。所以字面量没有引申含义,就是我们看到的这个数据本身。
②Spring配置文件中举例
[1]字面量举例
<!-- 使用value属性给bean的属性赋值时,Spring会把value属性的值看做字面量 -->
<property name="commonValue" value="hello"/>
[2]类似变量举例
<!-- 使用ref属性给bean的属性复制是,Spring会把ref属性的值作为一个bean的id来处理 -->
<!-- 此时ref属性的值就不是一个普通的字符串了,它应该是一个bean的id -->
<property name="happyMachine" ref="happyMachine"/>
3、null值
<property name="commonValue"><!-- null标签:将一个属性值明确设置为null --><null/></property>
4、XML实体
<!-- 实验九 给bean的属性赋值:特殊值处理 -->
<bean id="propValue" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.PropValue"><!-- 小于号在XML文档中用来定义标签的开始,不能随便使用 --><!-- 解决方案一:使用XML实体来代替 --><property name="expression" value="a < b"/>
</bean>
5、CDATA节
<!-- 实验九 给bean的属性赋值:特殊值处理 -->
<bean id="propValue" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.PropValue"><property name="expression"><!-- 解决方案二:使用CDATA节 --><!-- CDATA中的C代表Character,是文本、字符的含义,CDATA就表示纯文本数据 --><!-- XML解析器看到CDATA节就知道这里是纯文本,就不会当作XML标签或属性来解析 --><!-- 所以CDATA节中写什么符号都随意 --><value><![CDATA[a < b]]></value></property>
</bean>
实验十 给bean的属性赋值:使用p名称空间
1、配置
使用 p 名称空间的方式可以省略子标签 property,将组件属性的设置作为 bean 标签的属性来完成。
<!-- 实验十 给bean的属性赋值:使用p名称空间 -->
<bean id="happyMachine3"class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"p:machineName="goodMachine"
/>
使用 p 名称空间需要导入相关的 XML 约束,在 IDEA 的协助下导入即可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
具体操作时,输入p:稍微等一下,等IDEA弹出下面的提示:
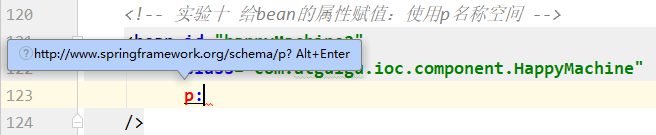
按Alt+Enter即可导入。
2、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment10() {HappyMachine happyMachine3 = (HappyMachine) iocContainer.getBean("happyMachine3");String machineName = happyMachine3.getMachineName();System.out.println("machineName = " + machineName);
}
实验十一 给bean的属性赋值:集合属性
1、给组件类添加属性
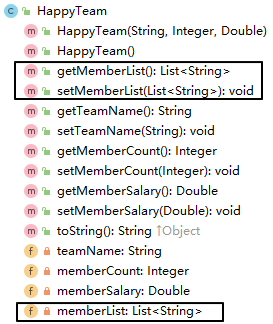
2、配置
<!-- 实验十三 集合类型的bean -->
<bean id="happyTeam2" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyTeam"><property name="memberList"><list><value>member01</value><value>member02</value><value>member03</value></list></property>
</bean>
3、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment13() {HappyTeam happyTeam2 = (HappyTeam) iocContainer.getBean("happyTeam2");List<String> memberList = happyTeam2.getMemberList();for (String member : memberList) {System.out.println("member = " + member);}}
4、其他变化形式
<!-- 实验十一 给bean的属性赋值:集合属性 -->
<bean id="happyTeam2" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyTeam"><property name="memberNameList"><!-- list标签:准备一组集合类型的数据,给集合属性赋值 --><!--<list><value>member01</value><value>member02</value><value>member03</value></list>--><!-- 使用set标签也能实现相同效果,只是附带了去重功能 --><!--<set><value>member01</value><value>member02</value><value>member02</value></set>--><!-- array也同样兼容 --><array><value>member01</value><value>member02</value><value>member02</value></array></property><property name="managerList"><!-- 给Map类型的属性赋值 --><!--<map><entry key="财务部" value="张三"/><entry key="行政部" value="李四"/><entry key="销售部" value="王五"/></map>--><!-- 也可以使用props标签 --><props><prop key="财务部">张三2</prop><prop key="行政部">李四2</prop><prop key="销售部">王五2</prop></props></property>
</bean>
实验十二 自动装配
1、声明组件类
其中HappyController需要用到HappyService。所谓自动装配就是一个组件需要其他组件时,由 IOC 容器负责找到那个需要的组件,并装配进去。
public class HappyController {private HappyService happyService;public HappyService getHappyService() {return happyService;}public void setHappyService(HappyService happyService) {this.happyService = happyService;}
}
public class HappyService {
}
2、配置
<!-- 实验十二 自动装配 -->
<bean id="happyService3" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyService"/>
<bean id="happyService2" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyService"/><!-- 使用bean标签的autowire属性设置自动装配效果 -->
<!-- byType表示根据类型进行装配,此时如果类型匹配的bean不止一个,那么会抛NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException -->
<!-- byName表示根据bean的id进行匹配。而bean的id是根据需要装配组件的属性的属性名来确定的 -->
<bean id="happyController"class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyController"autowire="byName"
><!-- 手动装配:在property标签中使用ref属性明确指定要装配的bean --><!--<property name="happyService" ref="happyService"/>-->
</bean>
3、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment12() {HappyController happyController = iocContainer.getBean(HappyController.class);HappyService happyService = happyController.getHappyService();System.out.println("happyService = " + happyService);
}
实验十三 集合类型的bean
1、配置
<!-- 实验十一 给bean的属性赋值:集合属性 -->
<util:list id="machineList"><bean class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"><property name="machineName" value="machineOne"/></bean><bean class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"><property name="machineName" value="machineTwo"/></bean><bean class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"><property name="machineName" value="machineThree"/></bean>
</util:list>
2、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment11() {List<HappyMachine> machineList = (List<HappyMachine>) iocContainer.getBean("machineList");for (HappyMachine happyMachine : machineList) {System.out.println("happyMachine = " + happyMachine);}
}
实验十四 FactoryBean机制
1、简介
FactoryBean是Spring提供的一种整合第三方框架的常用机制。和普通的bean不同,配置一个FactoryBean类型的bean,在获取bean的时候得到的并不是class属性中配置的这个类的对象,而是getObject()方法的返回值。通过这种机制,Spring可以帮我们把复杂组件创建的详细过程和繁琐细节都屏蔽起来,只把最简洁的使用界面展示给我们。
将来我们整合Mybatis时,Spring就是通过FactoryBean机制来帮我们创建SqlSessionFactory对象的。
/** Copyright 2002-2020 the original author or authors.** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.* You may obtain a copy of the License at** https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and* limitations under the License.*/package org.springframework.beans.factory;import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;/*** Interface to be implemented by objects used within a {@link BeanFactory} which* are themselves factories for individual objects. If a bean implements this* interface, it is used as a factory for an object to expose, not directly as a* bean instance that will be exposed itself.** <p><b>NB: A bean that implements this interface cannot be used as a normal bean.</b>* A FactoryBean is defined in a bean style, but the object exposed for bean* references ({@link #getObject()}) is always the object that it creates.** <p>FactoryBeans can support singletons and prototypes, and can either create* objects lazily on demand or eagerly on startup. The {@link SmartFactoryBean}* interface allows for exposing more fine-grained behavioral metadata.** <p>This interface is heavily used within the framework itself, for example for* the AOP {@link org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean} or the* {@link org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean}. It can be used for* custom components as well; however, this is only common for infrastructure code.** <p><b>{@code FactoryBean} is a programmatic contract. Implementations are not* supposed to rely on annotation-driven injection or other reflective facilities.</b>* {@link #getObjectType()} {@link #getObject()} invocations may arrive early in the* bootstrap process, even ahead of any post-processor setup. If you need access to* other beans, implement {@link BeanFactoryAware} and obtain them programmatically.** <p><b>The container is only responsible for managing the lifecycle of the FactoryBean* instance, not the lifecycle of the objects created by the FactoryBean.</b> Therefore,* a destroy method on an exposed bean object (such as {@link java.io.Closeable#close()}* will <i>not</i> be called automatically. Instead, a FactoryBean should implement* {@link DisposableBean} and delegate any such close call to the underlying object.** <p>Finally, FactoryBean objects participate in the containing BeanFactory's* synchronization of bean creation. There is usually no need for internal* synchronization other than for purposes of lazy initialization within the* FactoryBean itself (or the like).** @author Rod Johnson* @author Juergen Hoeller* @since 08.03.2003* @param <T> the bean type* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory* @see org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean* @see org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean*/
public interface FactoryBean<T> {/*** The name of an attribute that can be* {@link org.springframework.core.AttributeAccessor#setAttribute set} on a* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition} so that* factory beans can signal their object type when it can't be deduced from* the factory bean class.* @since 5.2*/String OBJECT_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "factoryBeanObjectType";/*** Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) of the object* managed by this factory.* <p>As with a {@link BeanFactory}, this allows support for both the* Singleton and Prototype design pattern.* <p>If this FactoryBean is not fully initialized yet at the time of* the call (for example because it is involved in a circular reference),* throw a corresponding {@link FactoryBeanNotInitializedException}.* <p>As of Spring 2.0, FactoryBeans are allowed to return {@code null}* objects. The factory will consider this as normal value to be used; it* will not throw a FactoryBeanNotInitializedException in this case anymore.* FactoryBean implementations are encouraged to throw* FactoryBeanNotInitializedException themselves now, as appropriate.* @return an instance of the bean (can be {@code null})* @throws Exception in case of creation errors* @see FactoryBeanNotInitializedException*/@NullableT getObject() throws Exception;/*** Return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates,* or {@code null} if not known in advance.* <p>This allows one to check for specific types of beans without* instantiating objects, for example on autowiring.* <p>In the case of implementations that are creating a singleton object,* this method should try to avoid singleton creation as far as possible;* it should rather estimate the type in advance.* For prototypes, returning a meaningful type here is advisable too.* <p>This method can be called <i>before</i> this FactoryBean has* been fully initialized. It must not rely on state created during* initialization; of course, it can still use such state if available.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Autowiring will simply ignore FactoryBeans that return* {@code null} here. Therefore it is highly recommended to implement* this method properly, using the current state of the FactoryBean.* @return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates,* or {@code null} if not known at the time of the call* @see ListableBeanFactory#getBeansOfType*/@NullableClass<?> getObjectType();/*** Is the object managed by this factory a singleton? That is,* will {@link #getObject()} always return the same object* (a reference that can be cached)?* <p><b>NOTE:</b> If a FactoryBean indicates to hold a singleton object,* the object returned from {@code getObject()} might get cached* by the owning BeanFactory. Hence, do not return {@code true}* unless the FactoryBean always exposes the same reference.* <p>The singleton status of the FactoryBean itself will generally* be provided by the owning BeanFactory; usually, it has to be* defined as singleton there.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> This method returning {@code false} does not* necessarily indicate that returned objects are independent instances.* An implementation of the extended {@link SmartFactoryBean} interface* may explicitly indicate independent instances through its* {@link SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype()} method. Plain {@link FactoryBean}* implementations which do not implement this extended interface are* simply assumed to always return independent instances if the* {@code isSingleton()} implementation returns {@code false}.* <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}, since a* {@code FactoryBean} typically manages a singleton instance.* @return whether the exposed object is a singleton* @see #getObject()* @see SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype()*/default boolean isSingleton() {return true;}}
2、实现FactoryBean接口
// 实现FactoryBean接口时需要指定泛型
// 泛型类型就是当前工厂要生产的对象的类型
public class HappyFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<HappyMachine> {private String machineName;public String getMachineName() {return machineName;}public void setMachineName(String machineName) {this.machineName = machineName;}@Overridepublic HappyMachine getObject() throws Exception {// 方法内部模拟创建、设置一个对象的复杂过程HappyMachine happyMachine = new HappyMachine();happyMachine.setMachineName(this.machineName);return happyMachine;}@Overridepublic Class<?> getObjectType() {// 返回要生产的对象的类型return HappyMachine.class;}
}
3、配置bean
<!-- 实验十四 FactoryBean机制 -->
<!-- 这个bean标签中class属性指定的是HappyFactoryBean,但是将来从这里获取的bean是HappyMachine对象 -->
<bean id="happyMachine3" class="com.atguigu.ioc.factory.HappyFactoryBean"><!-- property标签仍然可以用来通过setXxx()方法给属性赋值 --><property name="machineName" value="iceCreamMachine"/>
</bean>
4、测试获取bean
- 配置的bean:HappyFactoryBean
- 获取bean后得到的bean:HappyMachine
@Test
public void testExperiment14() {HappyMachine happyMachine3 = (HappyMachine) iocContainer.getBean("happyMachine3");String machineName = happyMachine3.getMachineName();System.out.println("machineName = " + machineName);
}
实验十五 bean的作用域
1、概念
在Spring中可以通过配置bean标签的scope属性来指定bean的作用域范围,各取值含义参加下表:
| 取值 | 含义 | 创建对象的时机 |
|---|---|---|
| singleton | 在IOC容器中,这个bean的对象始终为单实例 | IOC容器初始化时 |
| prototype | 这个bean在IOC容器中有多个实例 | 获取bean时 |
如果是在WebApplicationContext环境下还会有另外两个作用域(但不常用):
| 取值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| request | 在一个请求范围内有效 |
| session | 在一个会话范围内有效 |
2、配置
<!-- 实验十五 bean的作用域 -->
<!-- scope属性:取值singleton(默认值),bean在IOC容器中只有一个实例,IOC容器初始化时创建对象 -->
<!-- scope属性:取值prototype,bean在IOC容器中可以有多个实例,getBean()时创建对象 -->
<bean id="happyMachine4" scope="prototype" class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyMachine"><property name="machineName" value="iceCreamMachine"/>
</bean>
3、测试
@Test
public void testExperiment15() {HappyMachine happyMachine01 = (HappyMachine) iocContainer.getBean("happyMachine4");HappyMachine happyMachine02 = (HappyMachine) iocContainer.getBean("happyMachine4");System.out.println(happyMachine01 == happyMachine02);System.out.println("happyMachine01.hashCode() = " + happyMachine01.hashCode());System.out.println("happyMachine02.hashCode() = " + happyMachine02.hashCode());
}
实验十六 bean的生命周期
1、bean的生命周期清单
- bean对象创建(调用无参构造器)
- 给bean对象设置属性
- bean对象初始化之前操作(由bean的后置处理器负责)
- bean对象初始化(需在配置bean时指定初始化方法)
- bean对象初始化之后操作(由bean的后置处理器负责)
- bean对象就绪可以使用
- bean对象销毁(需在配置bean时指定销毁方法)
- IOC容器关闭
2、指定bean的初始化方法和销毁方法
①创建两个方法作为初始化和销毁方法
用com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent类测试:
public void happyInitMethod() {System.out.println("HappyComponent初始化");
}public void happyDestroyMethod() {System.out.println("HappyComponent销毁");
}
②配置bean时指定初始化和销毁方法
<!-- 实验十六 bean的生命周期 -->
<!-- 使用init-method属性指定初始化方法 -->
<!-- 使用destroy-method属性指定销毁方法 -->
<bean id="happyComponent"class="com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent"init-method="happyInitMethod"destroy-method="happyDestroyMethod"
><property name="happyName" value="uuu"/>
</bean>
3、bean的后置处理器
①创建后置处理器类
package com.atguigu.ioc.process;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;// 声明一个自定义的bean后置处理器
// 注意:bean后置处理器不是单独针对某一个bean生效,而是针对IOC容器中所有bean都会执行
public class MyHappyBeanProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("☆☆☆" + beanName + " = " + bean);return bean;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("★★★" + beanName + " = " + bean);return bean;}
}
②把bean的后置处理器放入IOC容器
<!-- bean的后置处理器要放入IOC容器才能生效 -->
<bean id="myHappyBeanProcessor" class="com.atguigu.ioc.process.MyHappyBeanProcessor"/>
③执行效果示例
HappyComponent创建对象
HappyComponent要设置属性了
☆☆☆happyComponent = com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent@ca263c2
HappyComponent初始化
★★★happyComponent = com.atguigu.ioc.component.HappyComponent@ca263c2
HappyComponent销毁