参考:
BV1zE411s77Z
[南京大学]-[软件分析]课程学习笔记(一)-introduction_南京大学软件分析笔记-CSDN博客
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. program language and static analysis
背景:在过去的十年中,语言的核心基本没有变化,但是程序变得显著的更大和更复杂。
挑战:如何确保大规模复杂程序的可靠性、安全性和其他承诺。
2. why we learn static analysis
2.1 程序的可靠性 reliability:
- null pointer dereference 空指针引用
- 去引用的时候没有 define,就会带来很多 bug
- memory leak 内存泄漏
- malloc 没有 free,内存占用过多会导致 crash
2.2 程序的安全性 security:
- private information leak 私有信息的泄露
- injection attack 注入攻击
2.3 编译器优化
- dead code elimination 死代码消除
- code motion 代码移动
2.4 程序理解
- IDE call hierarchy 调用层次
- type indication 类型指示
3. what is static analysis
静态分析通过分析程序 P 来推理其行为,并在运行 P 之前确定其是否满足某些属性。
Does P contain any private information leaks?
Does P dereference any null potinters?
Are all the cast operations in P safe? 类型转换操作符
Can v1 and v2 in P point to the same memory location?
Will certain assert statements in P fail?
Is this piece of code in P dead(so that it could be eliminated)?
一个 perfect static analysis 是不存在的。
从学术的角度来看,一个 perfect 的 static analysis 需要满足以下两个条件:
- sound: over approximate
- complete: under approximate

所以并不追求完美的静态分析,而是追求 useful static analysis:
- Compromise soundness (false negatives)
- Compromise completeness (false positives)
绝大多数静态分析追求的都是追求Soundness,会造成误报;在确保soundness的同时,在分析精度和分析速度之间做好权衡。
4. static analysis features and examples
Abstraction + Over-approximation(抽象和过近似)
- abstraction
- over-approximation
- transfer function
- control flows
Example:
判断给定的程序中所有变量的符号:正、负或者是0.
- T(Top):unknow 可正可负(over-approximation 过近似)
- bottom:undefined,除零操作,抛出异常操作

transfer function 定义了如何在抽象值上评估不同的程序状态,并且应该根据分析问题和不同程序状态的语义去定义。

图:Transfer functions
- 1问题是除零、抛出异常,则应该为 undefined;
- 2问题是下标为负,抛出异常,也应该为 undefined
- 3问题则是 over-approximated,也即是误报,在实际的程序中 a=x+y=9,所以并不会报错,而在抽象化为符号的过程中会模糊这个界限,导致产生误报
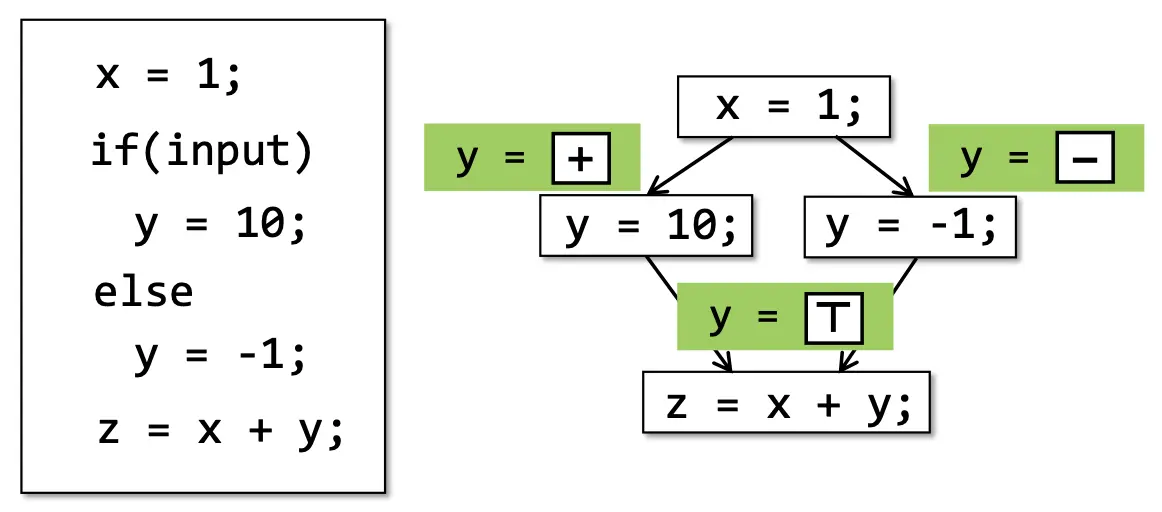
图:Control Flows
控制流分析,y 的两个值是两个branch,执行分支不同会使 z 的值产生变化。并且在实际中枚举所有路径是不可能的,空间特别庞大,因此 flow merging 则被很多静态分析采用。