1、演示
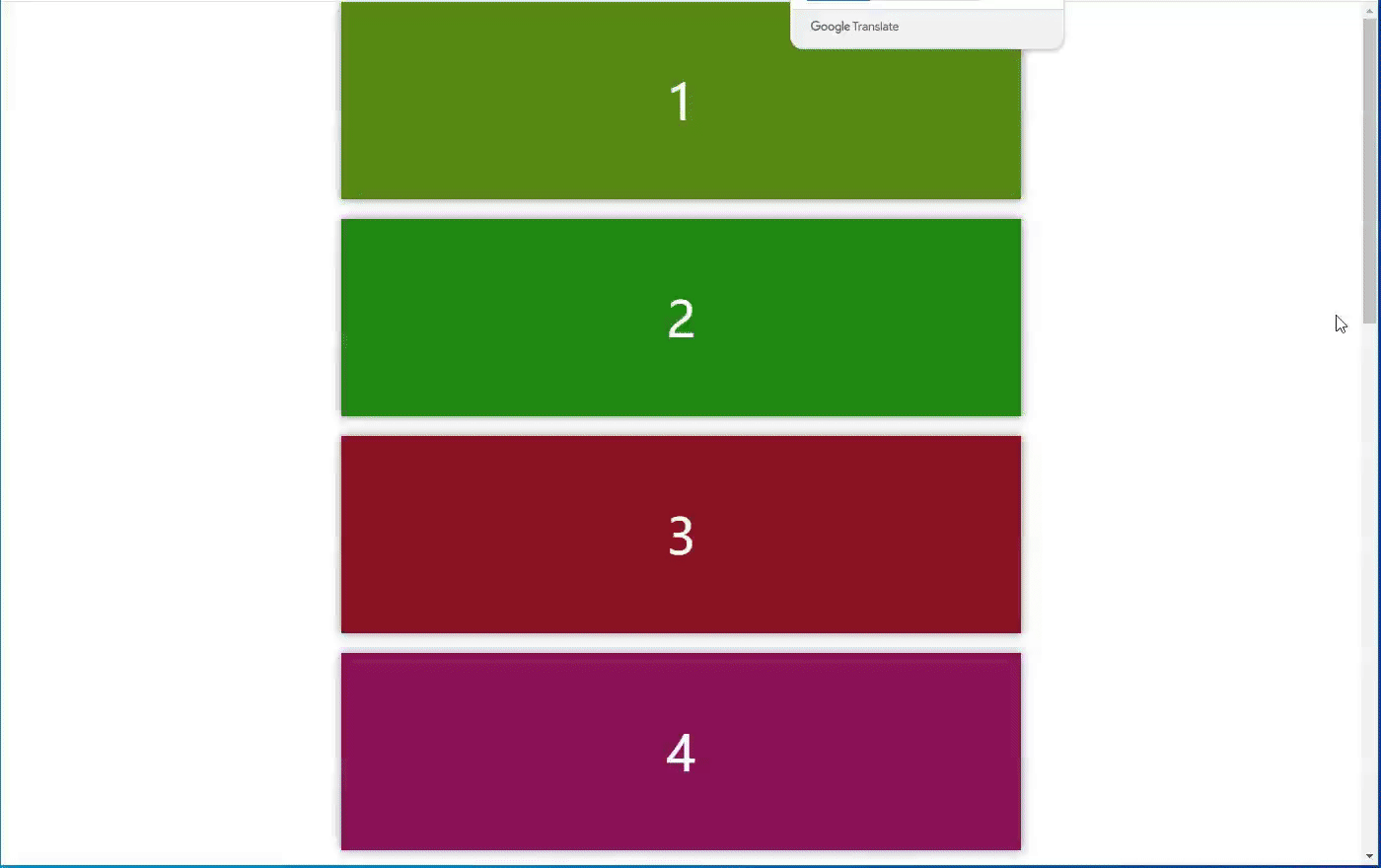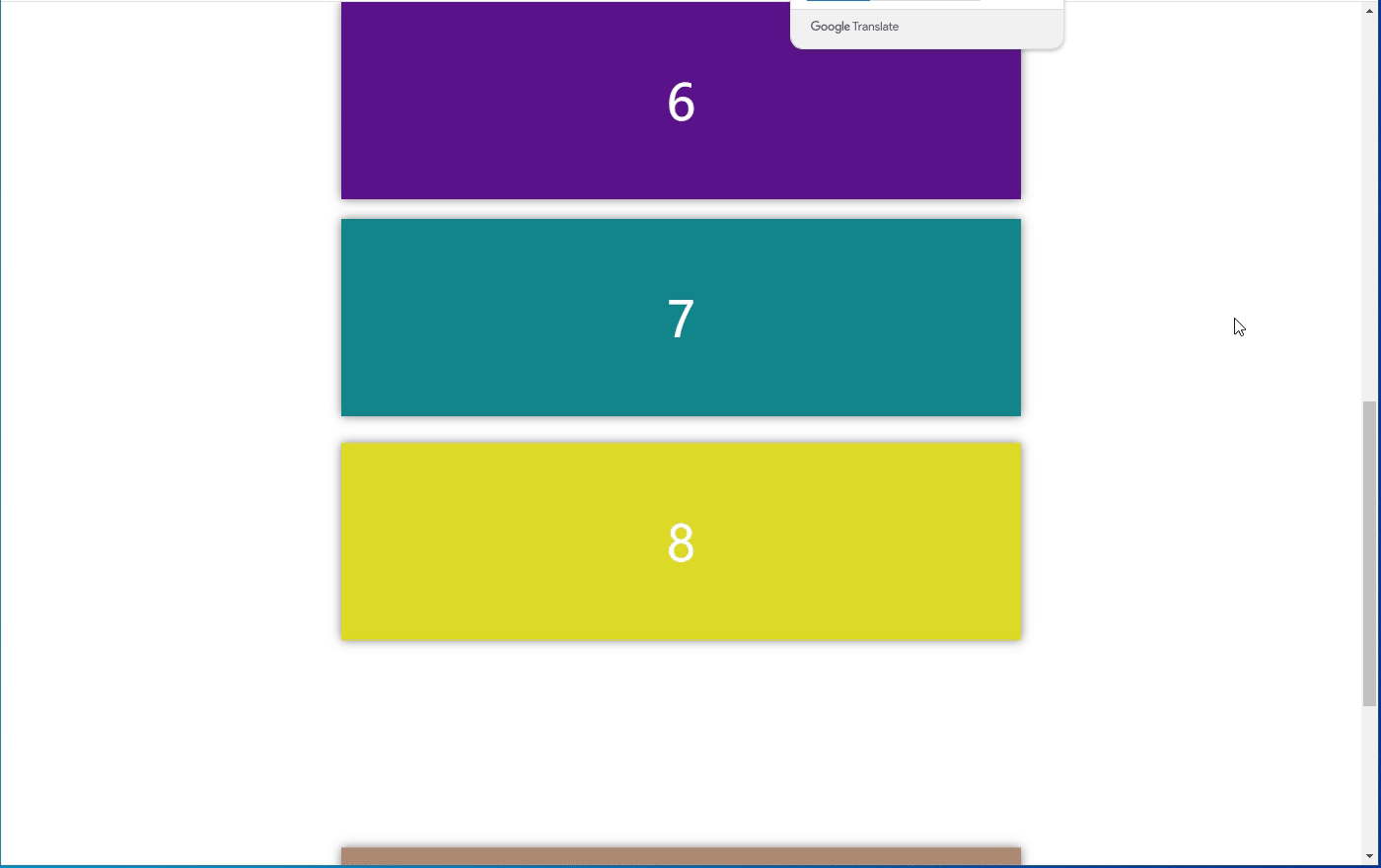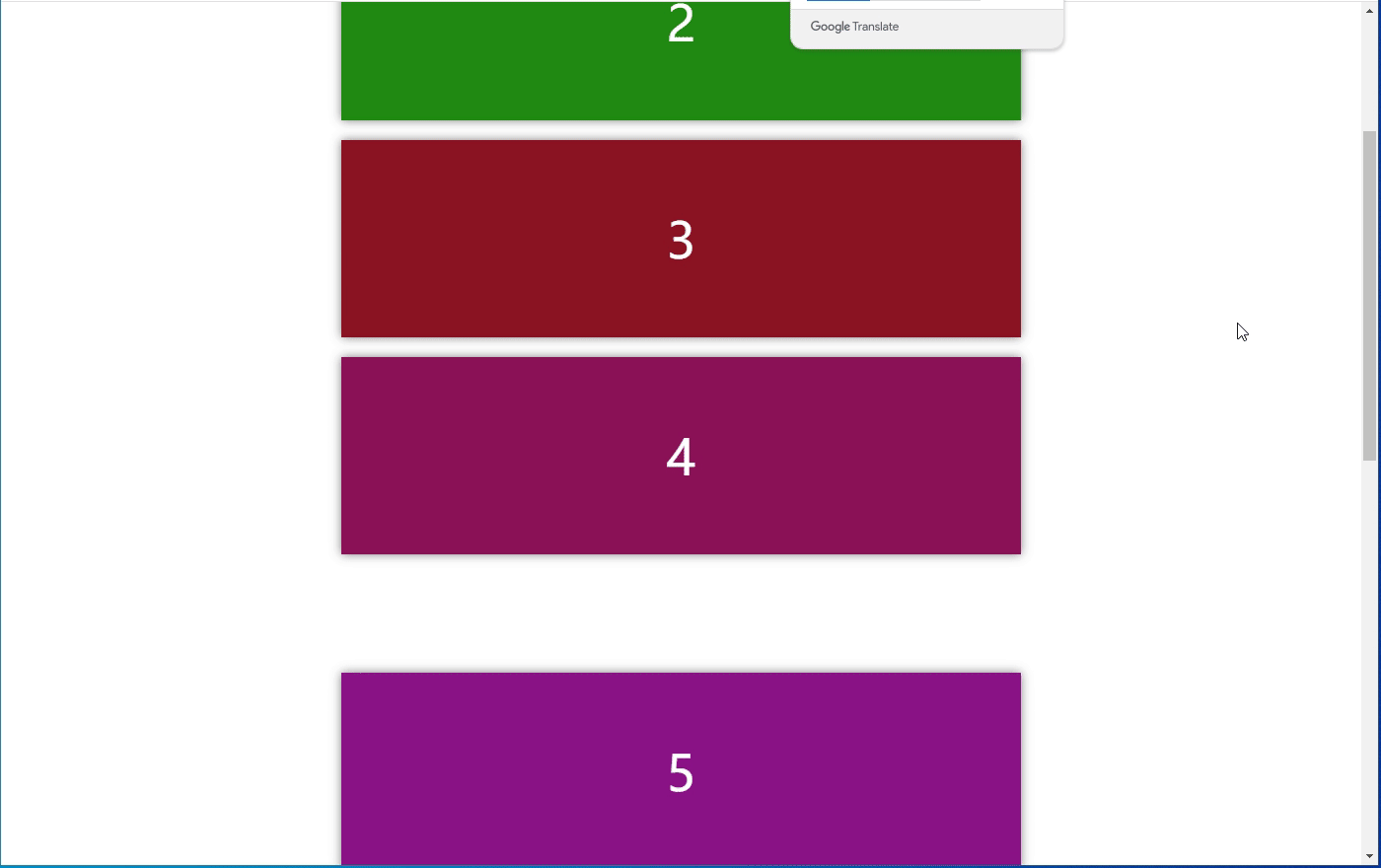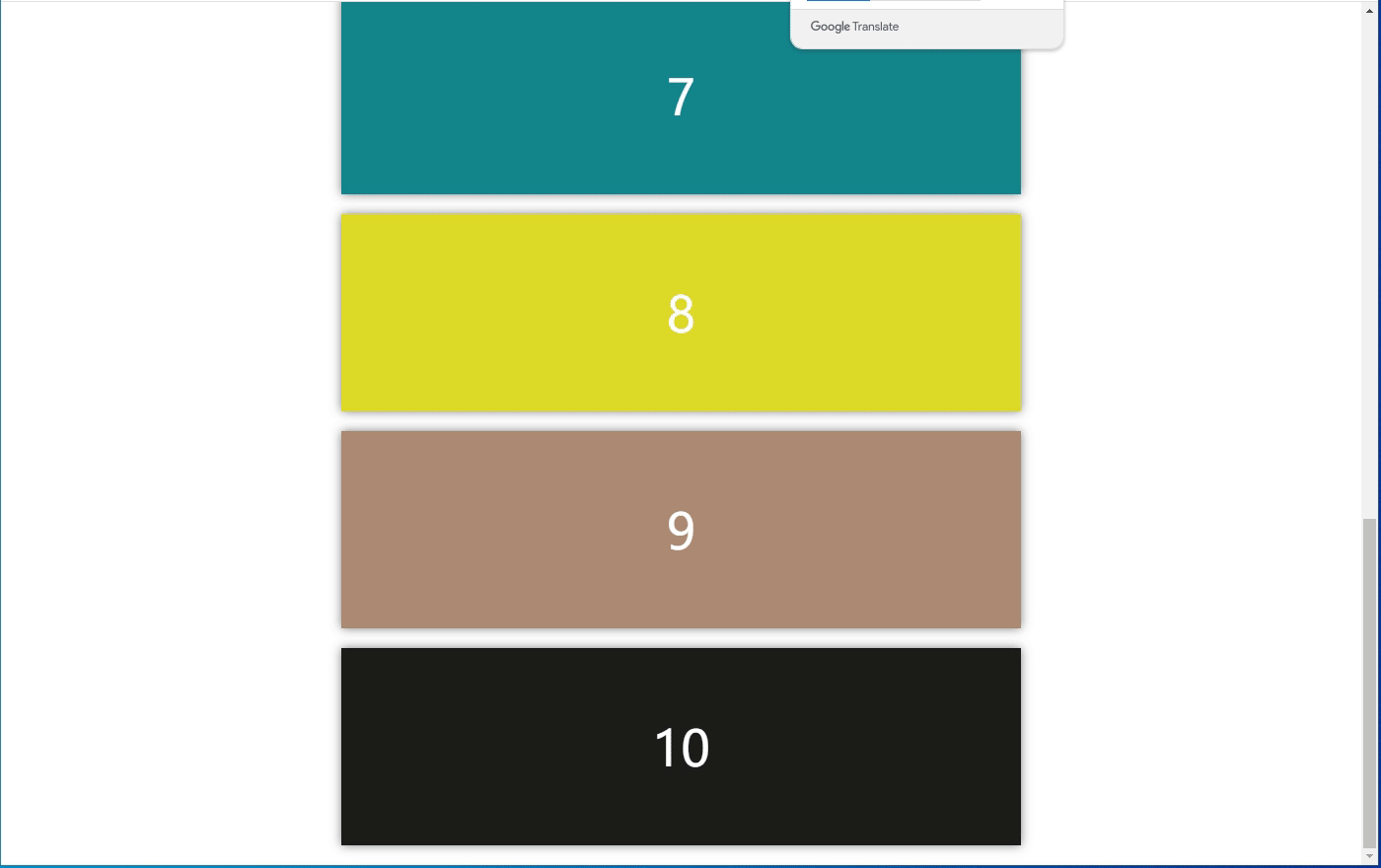
2、介绍
这个指令不是原生自带的,需要手动去书写,但是这辈子只需要编写这一次就好了,后边可以反复利用。
3、关键API
IntersectionObserver
IntersectionObserver 是一个用于监测元素是否进入或离开视口(viewport)的 API。它可以帮助你在页面滚动时或者元素位置改变时进行回调操作,这样你就可以根据元素是否可见来触发动作或者动画效果。
使用 IntersectionObserver 的基本步骤如下:
创建一个 IntersectionObserver 对象,并指定一个回调函数。这个回调函数会在被观察的元素进入或离开视口时被调用。
使用 observe() 方法开始观察指定的元素。你可以同时观察多个元素。
在回调函数中处理元素的可见状态变化。根据元素的可见性状态来执行相应的操作,比如触发动画、加载内容等。
在不需要观察元素时,使用 unobserve() 方法停止观察。
以下是一个简单的示例代码,演示了如何使用 IntersectionObserver 来监测元素的可见性:
// 创建一个 IntersectionObserver 对象 const observer = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {// 遍历观察到的所有元素entries.forEach(entry => {// 如果当前元素进入视口if (entry.isIntersecting) {// 执行相应的操作,比如触发动画entry.target.classList.add('animate');// 停止观察当前元素,可根据需求决定是否停止观察observer.unobserve(entry.target);}}); });// 要观察的目标元素 const targetElement = document.querySelector('.target');// 开始观察目标元素 observer.observe(targetElement);
4、Vue文件代码
<template><div class="container"><div v-slide-in class="item" v-for="item in 10">{{ item }}</div></div> </template><script setup> import { ref, reactive } from 'vue' </script><style scoped lang="scss"> .container {width: 100%;display: flex;flex-direction: column;align-items: center; } .item {width: 50%;height: 200px;margin-bottom: 20px;text-align: center;line-height: 200px;font-size: 50px;color: #fff;box-shadow: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5) 0px 0px 10px 0px; } .item:nth-child(1) {background-color: rgb(87, 139, 19); } .item:nth-child(2) {background-color: rgb(33, 139, 19); } .item:nth-child(3) {background-color: rgb(139, 19, 35); } .item:nth-child(4) {background-color: rgb(139, 19, 87); } .item:nth-child(5) {background-color: rgb(139, 19, 135); } .item:nth-child(6) {background-color: rgb(91, 19, 139); } .item:nth-child(7) {background-color: rgb(19, 133, 139); } .item:nth-child(8) {background-color: rgb(221, 218, 40); } .item:nth-child(9) {background-color: rgb(173, 139, 115); } .item:nth-child(10) {background-color: rgb(29, 28, 27); } </style>
5、指令文件及代码注释(清晰明了)
// WeakMap是一种键值对的集合 // 这里用来将一个dom元素和一种动画对应起来 const map = new WeakMap()// 创建一个观察对象 const ob = new IntersectionObserver(entries => {// 遍历所有被观察的元素 entries为一个数组for (const entry of entries) {// 判断该元素是否与视口相交(出现在视口里面了)if (entry.isIntersecting) {// 判断目标元素是出现在上视口还是下视口if (entry.boundingClientRect.top > entry.rootBounds.top) {// 找出这个元素对应的动画const animation = map.get(entry.target)if (animation) {// 播放该元素的动画animation.play()}}}} }) // 辅助函数,用来判断页面上的元素是否在视口外 function isBelowViewport(el) {const rect = el.getBoundingClientRect()return rect.top > window.innerHeight }export default function (app) {app.directive('slideIn', {mounted(el, bindings) {// 如果元素已经在视口内了,直接return 不加动画if (!isBelowViewport(el)) return// 创建一个动画 animate是Vue自带的const animation = el.animate([// 数组的每一个对象都表示关键帧 相当于css中的 @keyframes 这里想写多少个就写多少个{transform: `translateY(${200}px)`,},{transform: `translateY(0px)`,},],// duration:执行时间 easing:动画效果,fill:动画结束过后的行为 这些跟css中的一样{ duration: 1000, easing: 'ease-in-out', fill: 'forwards' })// 一开始的时候让动画暂停,这里只是先定义好animation.pause()// 当元素进入视口的时候在进行动画播放ob.observe(el)// 存储键值map.set(el, animation)},// 在元素卸载时,取消观察unmounted(el) {ob.unobserve(el)},}) }