本文首发于公众号:机器感知

CameraCtrl、EDTalk、Sketch3D、Diffusion^2、FashionEngine
NVINS: Robust Visual Inertial Navigation Fused with NeRF-augmented Camera Pose Regressor and Uncertainty Quantification

In recent years, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have emerged as a powerful tool for 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, the computational cost of NeRF rendering and degradation in quality due to the presence of artifacts pose significant challenges for its application in real-time and robust robotic tasks, especially on embedded systems. This paper introduces a novel framework that integrates NeRF-derived localization information with Visual-Inertial Odometry(VIO) to provide a robust solution for robotic navigation in a real-time. By training an absolute pose regression network with augmented image data rendered from a NeRF and quantifying its uncertainty, our approach effectively counters positional drift and enhances system reliability. We also establish a mathematically sound foundation for combining visual inertial navigation with camera localization neural networks, considering uncertainty under a Bayesian framework. Experimental validation in the photore......
Is Model Collapse Inevitable? Breaking the Curse of Recursion by Accumulating Real and Synthetic Data

The proliferation of generative models, combined with pretraining on web-scale data, raises a timely question: what happens when these models are trained on their own generated outputs? Recent investigations into model-data feedback loops discovered that such loops can lead to model collapse, a phenomenon where performance progressively degrades with each model-fitting iteration until the latest model becomes useless. However, several recent papers studying model collapse assumed that new data replace old data over time rather than assuming data accumulate over time. In this paper, we compare these two settings and show that accumulating data prevents model collapse. We begin by studying an analytically tractable setup in which a sequence of linear models are fit to the previous models' predictions. Previous work showed if data are replaced, the test error increases linearly with the number of model-fitting iterations; we extend this result by proving that if data instead acc......
Octopus: On-device language model for function calling of software APIs

In the rapidly evolving domain of artificial intelligence, Large Language Models (LLMs) play a crucial role due to their advanced text processing and generation abilities. This study introduces a new strategy aimed at harnessing on-device LLMs in invoking software APIs. We meticulously compile a dataset derived from software API documentation and apply fine-tuning to LLMs with capacities of 2B, 3B and 7B parameters, specifically to enhance their proficiency in software API interactions. Our approach concentrates on refining the models' grasp of API structures and syntax, significantly enhancing the accuracy of API function calls. Additionally, we propose \textit{conditional masking} techniques to ensure outputs in the desired formats and reduce error rates while maintaining inference speeds. We also propose a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the effectiveness of LLMs in API interactions, establishing a foundation for subsequent research. Octopus, the fine-tuned model, is ......
EDTalk: Efficient Disentanglement for Emotional Talking Head Synthesis

Achieving disentangled control over multiple facial motions and accommodating diverse input modalities greatly enhances the application and entertainment of the talking head generation. This necessitates a deep exploration of the decoupling space for facial features, ensuring that they a) operate independently without mutual interference and b) can be preserved to share with different modal input, both aspects often neglected in existing methods. To address this gap, this paper proposes a novel Efficient Disentanglement framework for Talking head generation (EDTalk). Our framework enables individual manipulation of mouth shape, head pose, and emotional expression, conditioned on video or audio inputs. Specifically, we employ three lightweight modules to decompose the facial dynamics into three distinct latent spaces representing mouth, pose, and expression, respectively. Each space is characterized by a set of learnable bases whose linear combinations define specific motions.......
FashionEngine: Interactive Generation and Editing of 3D Clothed Humans

We present FashionEngine, an interactive 3D human generation and editing system that allows us to design 3D digital humans in a way that aligns with how humans interact with the world, such as natural languages, visual perceptions, and hand-drawing. FashionEngine automates the 3D human production with three key components: 1) A pre-trained 3D human diffusion model that learns to model 3D humans in a semantic UV latent space from 2D image training data, which provides strong priors for diverse generation and editing tasks. 2) Multimodality-UV Space encoding the texture appearance, shape topology, and textual semantics of human clothing in a canonical UV-aligned space, which faithfully aligns the user multimodal inputs with the implicit UV latent space for controllable 3D human editing. The multimodality-UV space is shared across different user inputs, such as texts, images, and sketches, which enables various joint multimodal editing tasks. 3) Multimodality-UV Aligned Sampler ......
GEARS: Local Geometry-aware Hand-object Interaction Synthesis

Generating realistic hand motion sequences in interaction with objects has gained increasing attention with the growing interest in digital humans. Prior work has illustrated the effectiveness of employing occupancy-based or distance-based virtual sensors to extract hand-object interaction features. Nonetheless, these methods show limited generalizability across object categories, shapes and sizes. We hypothesize that this is due to two reasons: 1) the limited expressiveness of employed virtual sensors, and 2) scarcity of available training data. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a novel joint-centered sensor designed to reason about local object geometry near potential interaction regions. The sensor queries for object surface points in the neighbourhood of each hand joint. As an important step towards mitigating the learning complexity, we transform the points from global frame to hand template frame and use a shared module to process sensor features of each individual......
Sketch3D: Style-Consistent Guidance for Sketch-to-3D Generation

Recently, image-to-3D approaches have achieved significant results with a natural image as input. However, it is not always possible to access these enriched color input samples in practical applications, where only sketches are available. Existing sketch-to-3D researches suffer from limitations in broad applications due to the challenges of lacking color information and multi-view content. To overcome them, this paper proposes a novel generation paradigm Sketch3D to generate realistic 3D assets with shape aligned with the input sketch and color matching the textual description. Concretely, Sketch3D first instantiates the given sketch in the reference image through the shape-preserving generation process. Second, the reference image is leveraged to deduce a coarse 3D Gaussian prior, and multi-view style-consistent guidance images are generated based on the renderings of the 3D Gaussians. Finally, three strategies are designed to optimize 3D Gaussians, i.e., structural optimiz......
Co-Speech Gesture Video Generation via Motion-Decoupled Diffusion Model

Co-speech gestures, if presented in the lively form of videos, can achieve superior visual effects in human-machine interaction. While previous works mostly generate structural human skeletons, resulting in the omission of appearance information, we focus on the direct generation of audio-driven co-speech gesture videos in this work. There are two main challenges: 1) A suitable motion feature is needed to describe complex human movements with crucial appearance information. 2) Gestures and speech exhibit inherent dependencies and should be temporally aligned even of arbitrary length. To solve these problems, we present a novel motion-decoupled framework to generate co-speech gesture videos. Specifically, we first introduce a well-designed nonlinear TPS transformation to obtain latent motion features preserving essential appearance information. Then a transformer-based diffusion model is proposed to learn the temporal correlation between gestures and speech, and performs gener......
CameraCtrl: Enabling Camera Control for Text-to-Video Generation

Controllability plays a crucial role in video generation since it allows users to create desired content. However, existing models largely overlooked the precise control of camera pose that serves as a cinematic language to express deeper narrative nuances. To alleviate this issue, we introduce CameraCtrl, enabling accurate camera pose control for text-to-video(T2V) models. After precisely parameterizing the camera trajectory, a plug-and-play camera module is then trained on a T2V model, leaving others untouched. Additionally, a comprehensive study on the effect of various datasets is also conducted, suggesting that videos with diverse camera distribution and similar appearances indeed enhance controllability and generalization. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of CameraCtrl in achieving precise and domain-adaptive camera control, marking a step forward in the pursuit of dynamic and customized video storytelling from textual and camera pose inputs. Our proje......
Diffusion$^2$: Dynamic 3D Content Generation via Score Composition of Orthogonal Diffusion Models
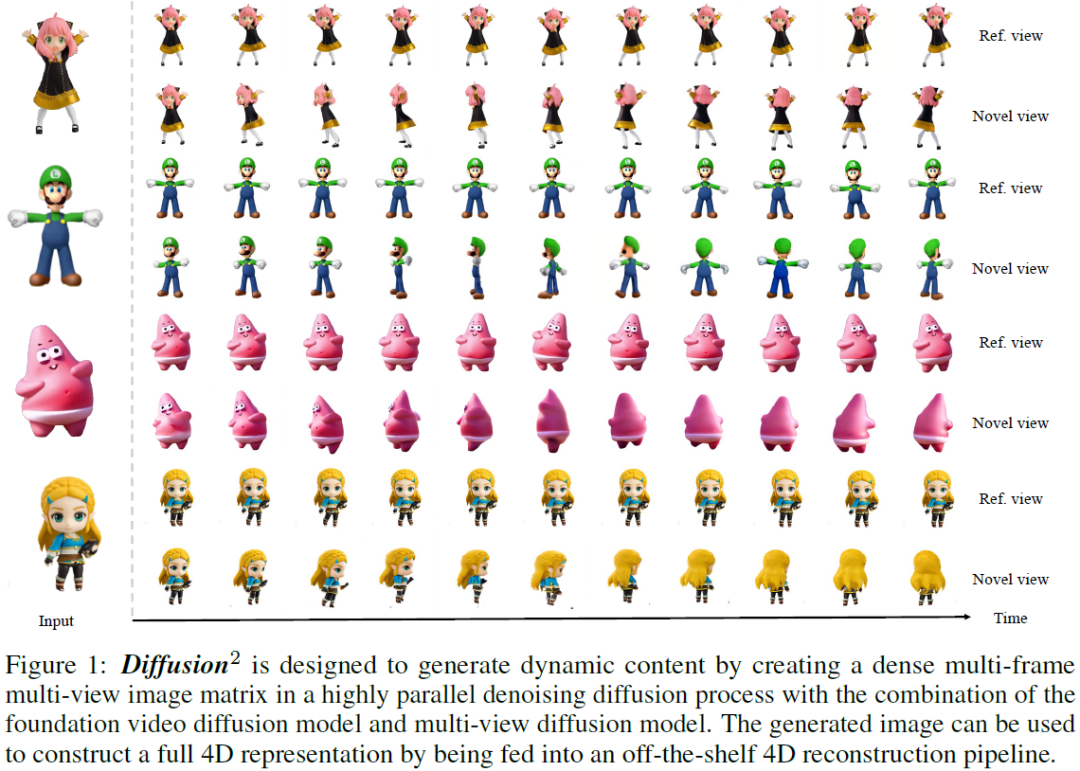
Recent advancements in 3D generation are predominantly propelled by improvements in 3D-aware image diffusion models which are pretrained on Internet-scale image data and fine-tuned on massive 3D data, offering the capability of producing highly consistent multi-view images. However, due to the scarcity of synchronized multi-view video data, it is impractical to adapt this paradigm to 4D generation directly. Despite that, the available video and 3D data are adequate for training video and multi-view diffusion models that can provide satisfactory dynamic and geometric priors respectively. In this paper, we present Diffusion$^2$, a novel framework for dynamic 3D content creation that leverages the knowledge about geometric consistency and temporal smoothness from these models to directly sample dense multi-view and multi-frame images which can be employed to optimize continuous 4D representation. Specifically, we design a simple yet effective denoising strategy via score composi......