1,翻转一个单链表
 建立变量cur指向第二个节点,curN指向cur.next,将第二个节点的next改为head,head=cur这样实现,前两个节点顺序的翻转,第二个节点指向了第一个节点,之后cur向后移(cur=curN),curN也向后移,进行循环,直到所以节点的顺序都翻转
建立变量cur指向第二个节点,curN指向cur.next,将第二个节点的next改为head,head=cur这样实现,前两个节点顺序的翻转,第二个节点指向了第一个节点,之后cur向后移(cur=curN),curN也向后移,进行循环,直到所以节点的顺序都翻转
问:curN的作用是什么,为什么要这样定义?
答:因为进行反转时,这个节点的next要改为前一个节点的地址,所以这个节点和后一个节点就没有关系了,但是我们还需要找到后一个节点,依次进行翻转,所以设置变量,将后一个节点的地址提前记录下来
public void reverseList(){if (head==null){return;}ListNode cur=head.next;ListNode curNext=head.next.next;head.next=null;while (cur!=null){cur.next=head;head=cur;cur=curNext;if (curNext!=null){curNext=curNext.next;}}}
2.给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
用快慢指针法:快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,所以快指针走的是慢指针的两倍路程,所以慢指针指向的是链表的中间值
链表的节点分两种情况,一种为单数,另一种为双数,第一种,fast指向最后一个节点,slow指向中间节点,第二种,fast指向空,slow指向中间的靠右的节点

public ListNode returnMid(){if (head==null){return null;}ListNode slow=head;ListNode fast=head;while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;}return slow;
}
3, 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
用快慢指针法:快指针先走k-1个节点,然后快指针和慢指针一起向后走,直到快指针的下一个为null,则慢指针指向倒数第k个结点
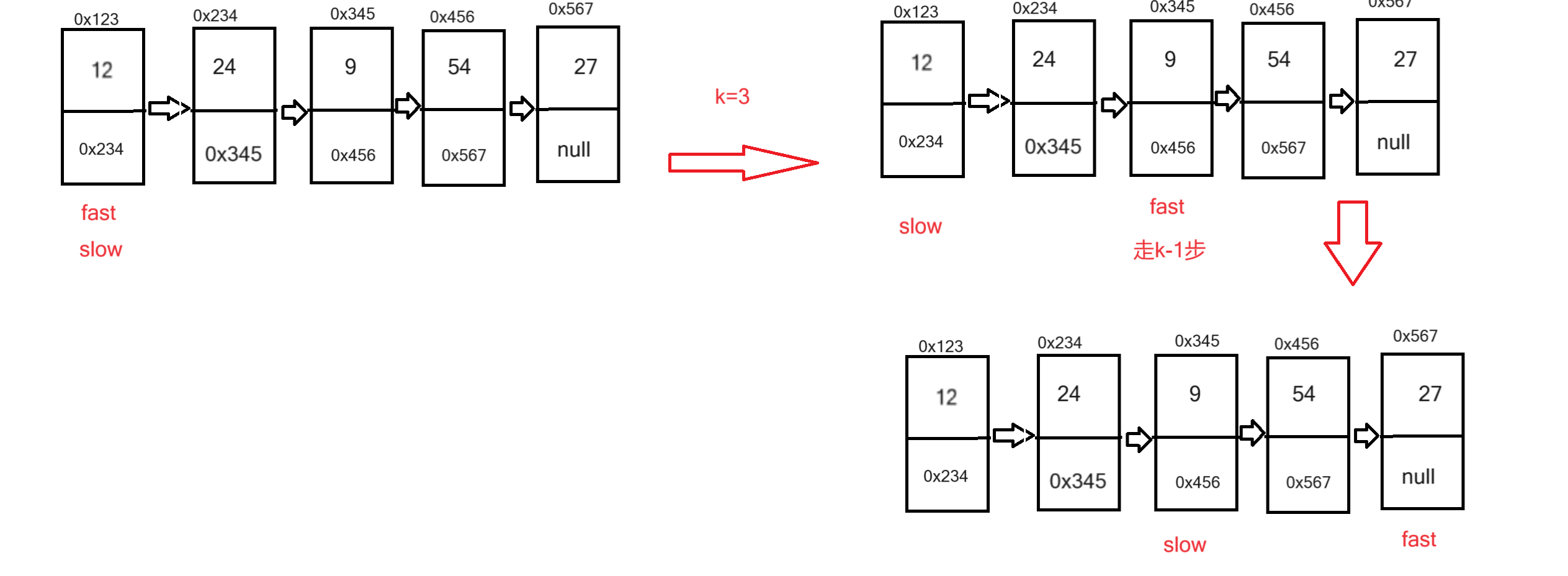
首先要判断输入坐标的合法性,和链表为空的情况
private void KLegal(int k){if (k<=0||k>size()){throw new IndexException("输入的第k个节点,k输入异常");}
}
private void heedIsNull(){if (head==null){throw new IndexException("head为空,该链表没有节点");}
}
public int kthToLast(int k){try {KLegal(k);}catch (IndexException e){e.printStackTrace();}try {heedIsNull();}catch (IndexException e){e.printStackTrace();}ListNode slow=head;ListNode fast=head;while ((k-1)!=0){fast=fast.next;k--;}while (fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next;slow=slow.next;}return slow.val;
}
4,将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
建立一个空节点,比较链表1,和链表2,的值将比较大的值的节点放到空节点的后面
然后再将p1与p2的val进行比较重复上述操作,知道一个链表的节点为0,直接将另一个链表剩余的节点直接放到新建的链表后面,最后将建立的空节点删除
public ListNode mergeTowLists(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){ListNode node=new ListNode(0);ListNode cur=node;ListNode b1=head1;ListNode p1=head2;while (b1!=null&&p1!=null){if (b1.val<p1.val){cur.next=b1;cur=cur.next;b1=b1.next;}else {cur.next=p1;cur=cur.next;p1=p1.next;}}if (b1==null){cur.next=p1;}else {cur.next=b1;}return node.next;}
5,编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
以x为界限,创立两个分区,遍历链表,将小于x的放到第一个分区,大于x的放到第二个分区,采用尾插法放置

public ListNode partition(int k) {ListNode b1 = null;ListNode b2 = null;ListNode p1 = null;ListNode p2 = null;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val < k) {if (b1 == null) {b1 = b2 = cur;} else {b2.next=cur;b2 = cur;}} else {if (p1 == null) {p1 = p2 = cur;} else {p2.next = cur;p2 = cur;}}cur = cur.next;}if (b1==null){return p1;}b2.next = p1;if (p1!=null){p2.next=null;}return b1;
}
6,判断回文
1,先用快慢指针,找到中间值,然后将中间值后面的节点翻转,然后,中间值以前的节点从前往后遍历,中间值以后的节点从后往前遍历,并对比节点的val是否相同,如果完全相同,则为回文,如果不相同,则不是

public boolean chkPalindrome(){if (head==null){return true;}ListNode slow=head;ListNode fast=head;while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;}ListNode cur=slow.next;ListNode curNext=cur.next;while (cur!=null){cur.next=slow;slow=cur;cur=curNext;if (curNext!=null){curNext=curNext.next;}}ListNode head1=head;while (slow!=head1&&head1.next!=slow){if (slow.val!=head1.val){return false;}slow=slow.next;head1=head1.next;}return true;
}
7, 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
先判断两个链表的长度,算出差值k,将长的链表向后走k步,然后,两个链表同时遍历,直到两个链表节点的next相等是,这next指向的节点就是公共节点
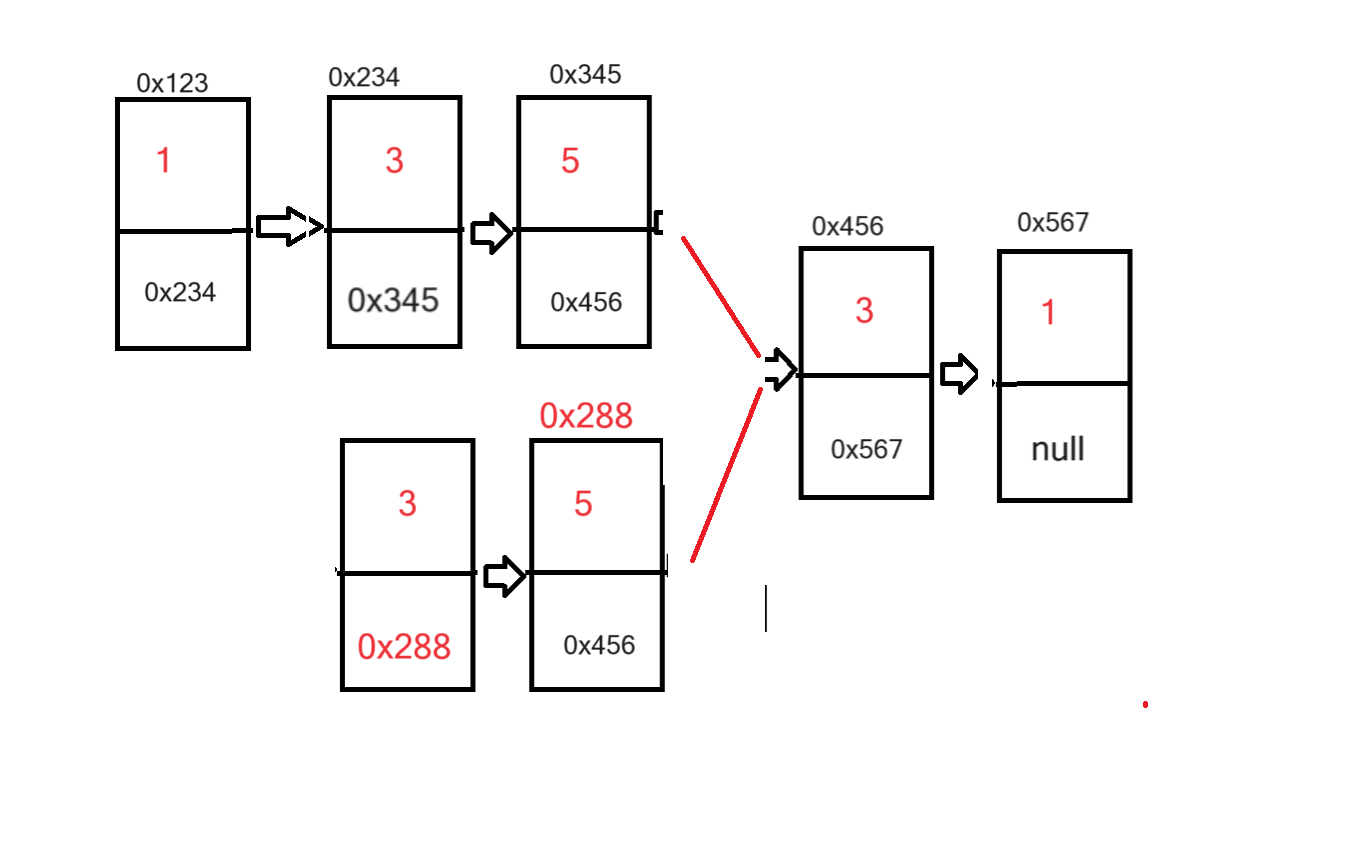
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){ListNode p1=head1;//longListNode p2=head2;int len1=0;int len2=0;while (p1!=null){p1=p1.next;len1++;}while (p2!=null){p2=p2.next;len2++;}int len=len1-len2;p1=head1;p2=head2;if (len1<len2){p1=head2;p2=head1;len=len2-len1;}while (len!=0){p1=p1.next;len--;}while (p1!=p2){p1=p1.next;p2=p2.next;}return p1;}
8,成环的判断和成环的节点
成环的判断:快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果成环,快指针与慢指针总会相遇,所以当快指针等于慢指针时,则有环,如果遍历之后没有相遇,则没有环
public boolean isDetectCycle(){ListNode slow=head;ListNode fast=head;while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;if (fast==slow){return true;}}return false;
}
成环的节点:

有公式可推从头节点到成环节点的路程等于快指针与慢指针相遇的节点到成环节点的距离,所以将slow=head,快指针和慢指针同时走相遇的节点就是成环节点
public ListNode detectCycle(){ListNode slow=head;ListNode fast=head;while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;if (fast==slow){break;}}if (fast==null||fast.next==null){return null;}//排除没有环的情况slow=head;while (slow!=fast){slow=slow.next;fast=fast.next;}return slow;}