导 读
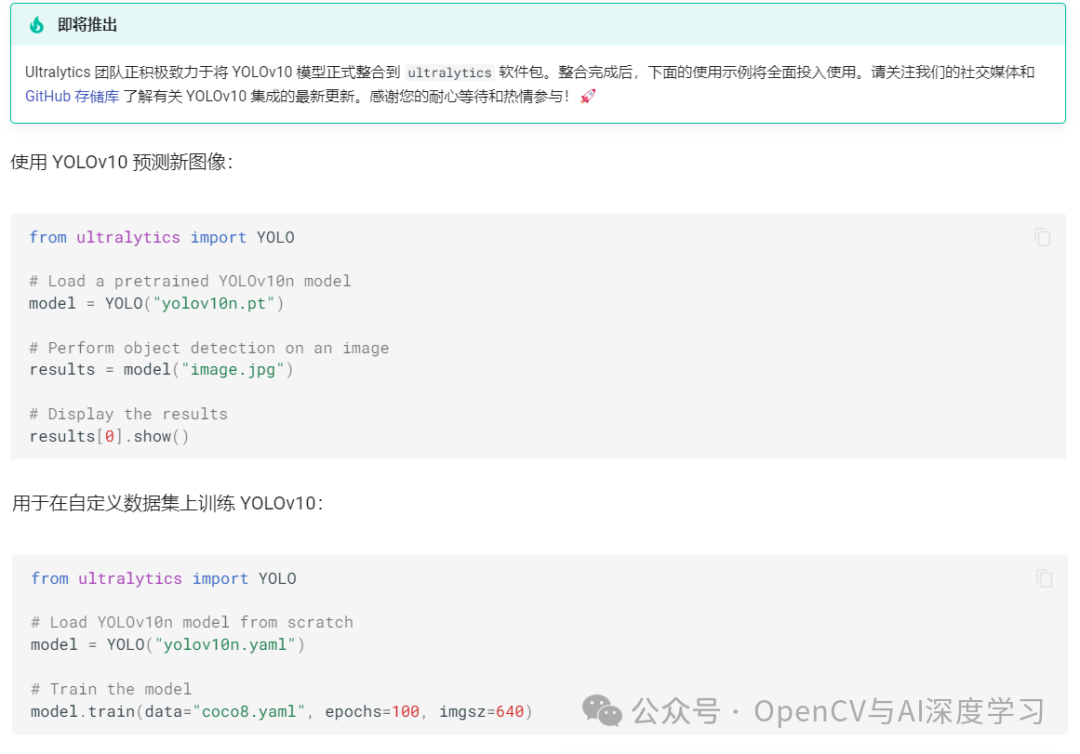
本文主要对YOLOv10做简单介绍并给出推理图片和视频的步骤演示。
YOLOv10简介
YOLOv10是清华大学的研究人员在Ultralytics Python包的基础上,引入了一种新的实时目标检测方法,解决了YOLO 以前版本在后处理和模型架构方面的不足。通过消除非最大抑制(NMS)和优化各种模型组件,YOLOv10 在显著降低计算开销的同时实现了最先进的性能。大量实验证明,YOLOv10 在多个模型尺度上实现了卓越的精度-延迟权衡。

概述
实时目标检测旨在以较低的延迟准确预测图像中的物体类别和位置。YOLO 系列在性能和效率之间取得了平衡,因此一直处于这项研究的前沿。然而,对 NMS 的依赖和架构上的低效阻碍了最佳性能的实现。YOLOv10 通过为无 NMS 训练引入一致的双重分配和以效率-准确性为导向的整体模型设计策略,解决了这些问题。
网络架构
YOLOv10 的结构建立在以前YOLO 模型的基础上,同时引入了几项关键创新。模型架构由以下部分组成:
-
-
主干网:YOLOv10 中的主干网负责特征提取,它使用了增强版的 CSPNet(跨阶段部分网络),以改善梯度流并减少计算冗余。
-
颈部:颈部设计用于汇聚不同尺度的特征,并将其传递到头部。它包括 PAN(路径聚合网络)层,可实现有效的多尺度特征融合。
-
一对多头:在训练过程中为每个对象生成多个预测,以提供丰富的监督信号并提高学习准确性。
-
一对一头:在推理过程中为每个对象生成一个最佳预测,无需 NMS,从而减少延迟并提高效率。
-
主要功能
-
-
无 NMS 训练:利用一致的双重分配来消除对 NMS 的需求,从而减少推理延迟。
-
整体模型设计:从效率和准确性的角度全面优化各种组件,包括轻量级分类头、空间通道去耦向下采样和等级引导块设计。
-
增强的模型功能:纳入大核卷积和部分自注意模块,在不增加大量计算成本的情况下提高性能。
-
模型支持:
YOLOv10 有多种模型,可满足不同的应用需求:
-
-
YOLOv10-N:用于资源极其有限环境的纳米版本。
-
YOLOv10-S:兼顾速度和精度的小型版本。
-
YOLOv10-M:通用中型版本。
-
YOLOv10-B:平衡型,宽度增加,精度更高。
-
YOLOv10-L:大型版本,精度更高,但计算资源增加。
-
YOLOv10-X:超大型版本可实现最高精度和性能。
-
性能
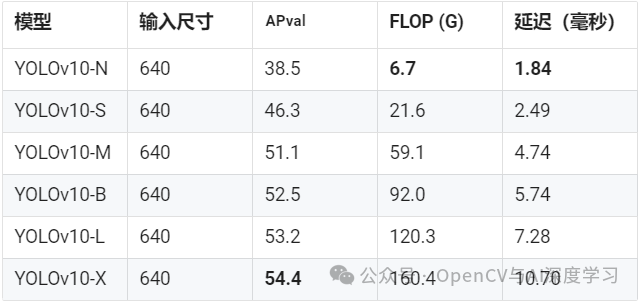
在准确性和效率方面,YOLOv10 优于YOLO 以前的版本和其他最先进的模型。例如,在 COCO 数据集上,YOLOv10-S 的速度是RT-DETR-R18 的 1.8 倍,而 YOLOv10-B 与 YOLOv9-C 相比,在性能相同的情况下,延迟减少了 46%,参数减少了 25%。下图是使用TensorRT FP16 在T4 GPU上的测试结果:
实验和结果
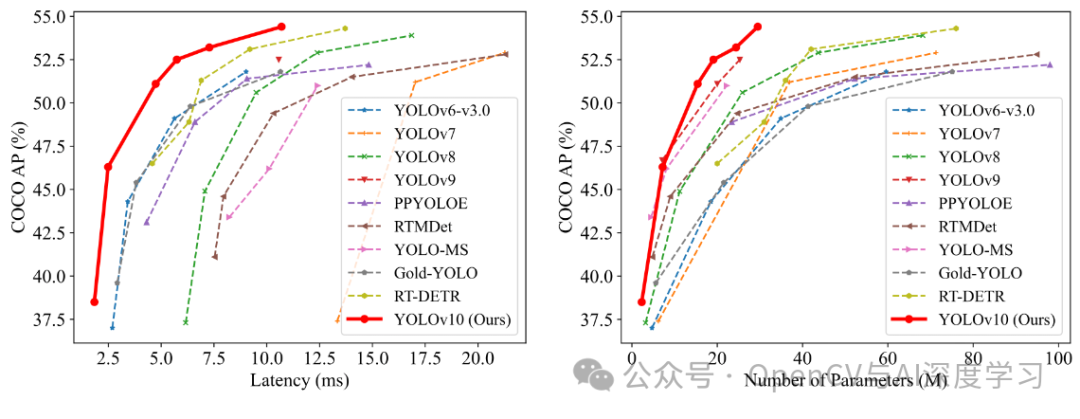
YOLOv10 在 COCO 等标准基准上进行了广泛测试,显示出卓越的性能和效率。与以前的版本和其他当代探测器相比,YOLOv10 在延迟和准确性方面都有显著提高。
推理演示
官方实现代码地址:
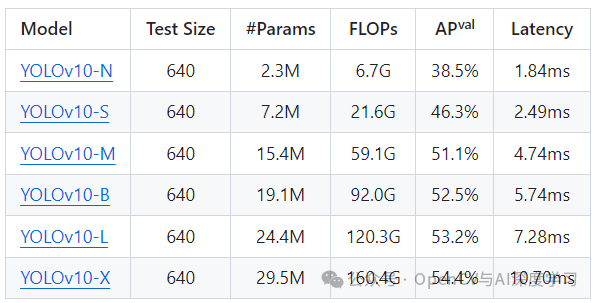
https://github.com/THU-MIG/yolov10?tab=readme-ov-file包含不同版本模型下载:
安装配置可参考官方文档:
conda create -n yolov10 python=3.9conda activate yolov10pip install -r requirements.txtpip install -e .
或:
pip install supervision git+https://github.com/THU-MIG/yolov10.git上述方法如果报错可以尝试下面方法:
【1】先将github项目代码下载到本地;
【2】安装supervision:
pip install supervision -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple图片推理预测:
from ultralytics import YOLOv10import supervision as svimport cv2classes = {0: 'person', 1: 'bicycle', 2: 'car', 3: 'motorcycle', 4: 'airplane', 5: 'bus',6: 'train', 7: 'truck', 8: 'boat', 9: 'traffic light', 10: 'fire hydrant',11: 'stop sign', 12: 'parking meter', 13: 'bench', 14: 'bird', 15: 'cat',16: 'dog', 17: 'horse', 18: 'sheep', 19: 'cow', 20: 'elephant', 21: 'bear',22: 'zebra', 23: 'giraffe', 24: 'backpack', 25: 'umbrella', 26: 'handbag',27: 'tie', 28: 'suitcase', 29: 'frisbee', 30: 'skis', 31: 'snowboard',32: 'sports ball', 33: 'kite', 34: 'baseball bat', 35: 'baseball glove',36: 'skateboard', 37: 'surfboard', 38: 'tennis racket', 39: 'bottle',40: 'wine glass', 41: 'cup', 42: 'fork', 43: 'knife', 44: 'spoon', 45: 'bowl',46: 'banana', 47: 'apple', 48: 'sandwich', 49: 'orange', 50: 'broccoli',51: 'carrot', 52: 'hot dog', 53: 'pizza', 54: 'donut', 55: 'cake',56: 'chair', 57: 'couch', 58: 'potted plant', 59: 'bed', 60: 'dining table',61: 'toilet', 62: 'tv', 63: 'laptop', 64: 'mouse', 65: 'remote', 66: 'keyboard',67: 'cell phone', 68: 'microwave', 69: 'oven', 70: 'toaster', 71: 'sink',72: 'refrigerator', 73: 'book', 74: 'clock', 75: 'vase', 76: 'scissors',77: 'teddy bear', 78: 'hair drier', 79: 'toothbrush'}model = YOLOv10('yolov10s.pt')image = cv2.imread('5.jpg')results = model(source=image, conf=0.25, verbose=False)[0]detections = sv.Detections.from_ultralytics(results)box_annotator = sv.BoxAnnotator()labels = [f"{classes[class_id]} {confidence:.2f}"for class_id, confidence in zip(detections.class_id, detections.confidence)]annotated_image = box_annotator.annotate(image.copy(), detections=detections, labels=labels)cv2.imshow('result', annotated_image)cv2.waitKey()cv2.destroyAllWindows()cv2.imwrite('annotated_dog.jpeg', annotated_image)
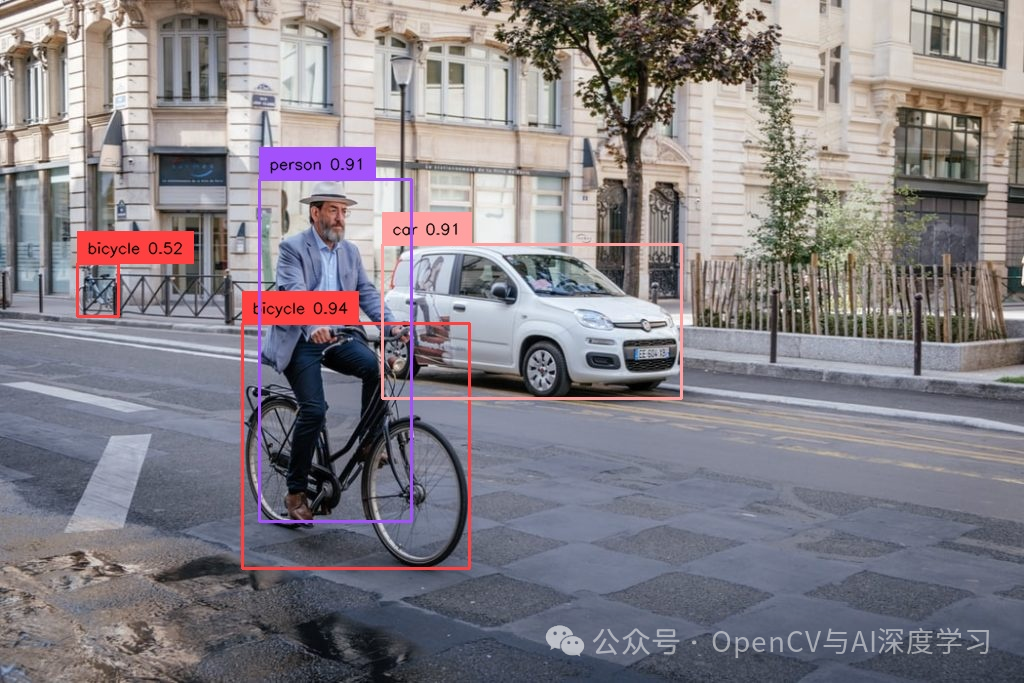
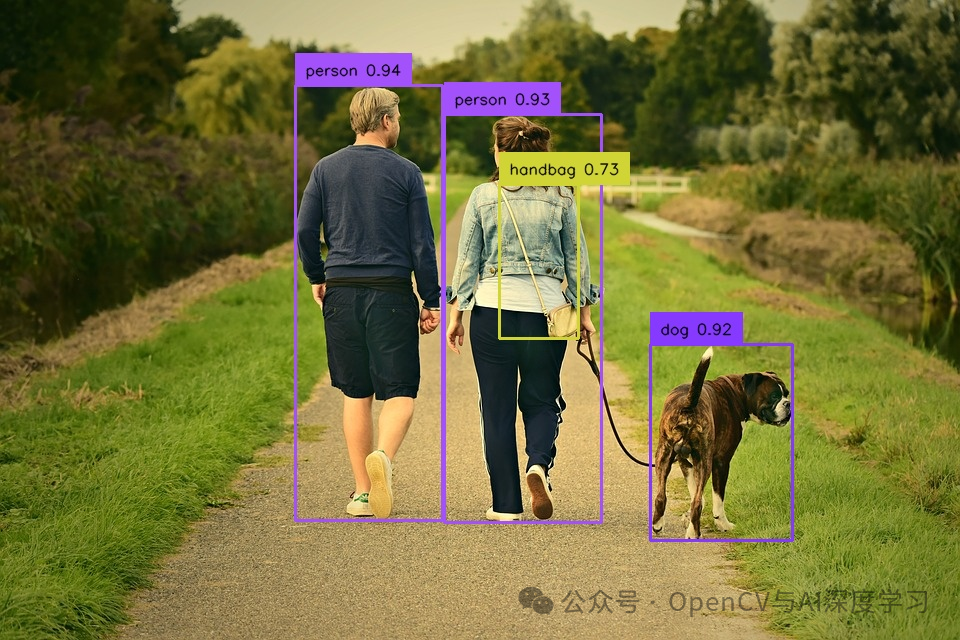
视频推理预测:
from ultralytics import YOLOv10import supervision as svimport cv2classes = {0: 'person', 1: 'bicycle', 2: 'car', 3: 'motorcycle', 4: 'airplane', 5: 'bus',6: 'train', 7: 'truck', 8: 'boat', 9: 'traffic light', 10: 'fire hydrant',11: 'stop sign', 12: 'parking meter', 13: 'bench', 14: 'bird', 15: 'cat',16: 'dog', 17: 'horse', 18: 'sheep', 19: 'cow', 20: 'elephant', 21: 'bear',22: 'zebra', 23: 'giraffe', 24: 'backpack', 25: 'umbrella', 26: 'handbag',27: 'tie', 28: 'suitcase', 29: 'frisbee', 30: 'skis', 31: 'snowboard',32: 'sports ball', 33: 'kite', 34: 'baseball bat', 35: 'baseball glove',36: 'skateboard', 37: 'surfboard', 38: 'tennis racket', 39: 'bottle',40: 'wine glass', 41: 'cup', 42: 'fork', 43: 'knife', 44: 'spoon', 45: 'bowl',46: 'banana', 47: 'apple', 48: 'sandwich', 49: 'orange', 50: 'broccoli',51: 'carrot', 52: 'hot dog', 53: 'pizza', 54: 'donut', 55: 'cake',56: 'chair', 57: 'couch', 58: 'potted plant', 59: 'bed', 60: 'dining table',61: 'toilet', 62: 'tv', 63: 'laptop', 64: 'mouse', 65: 'remote', 66: 'keyboard',67: 'cell phone', 68: 'microwave', 69: 'oven', 70: 'toaster', 71: 'sink',72: 'refrigerator', 73: 'book', 74: 'clock', 75: 'vase', 76: 'scissors',77: 'teddy bear', 78: 'hair drier', 79: 'toothbrush'}model = YOLOv10('yolov10m.pt')def predict_and_detect(image):results = model(source=image, conf=0.5, verbose=False)[0]detections = sv.Detections.from_ultralytics(results)box_annotator = sv.BoxAnnotator()labels = [f"{classes[class_id]} {confidence:.2f}"for class_id, confidence in zip(detections.class_id, detections.confidence)]annotated_image = box_annotator.annotate(image.copy(), detections=detections, labels=labels)return annotated_imagedef create_video_writer(video_cap, output_filename):# grab the width, height, and fps of the frames in the video stream.frame_width = int(video_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))frame_height = int(video_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))fps = int(video_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))# initialize the FourCC and a video writer objectfourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'MP4V')writer = cv2.VideoWriter(output_filename, fourcc, fps,(frame_width, frame_height))return writervideo_path = 'cars.MP4'cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)output_filename = "out.mp4"writer = create_video_writer(cap, output_filename)while True:success, img = cap.read()if not success:breakframe = predict_and_detect(img)writer.write(frame)cv2.imshow("frame", frame)if cv2.waitKey(1)&0xFF ==27: #按下Esc键退出breakcap.release()writer.release()
,时长00:02
后续ultralytics也将添加YOLOv10的支持,部署训练将会更便捷。