一.Shell概述
1)Linux提供的Shell解析器有:sudo cat /etc/shells
/bin/sh
/bin/bash
/usr/bin/sh
/usr/bin/bash
/bin/tcsh
/bin/csh2)bash和sh的关系
cd /bin
ll | grep bash 或者使用:ls -l /bin/ | grep bash3)Centos默认的解析器是bash
echo $SHELL二.Shell脚本入门
1)脚本格式
脚本以#!/bin/bash开头(指定解析器)。
案例一:第一个Shell脚本:helloworld
需求:创建一个Shell脚本,输出helloworld
创建文件夹:mkdir scripts
创建脚本:touch hello.sh
vim hello.sh
在helloworld.sh中输入如下内容
#!/bin/bash
echo "helloworld"
打印输入:bash /scripts/hello.sh 对应的绝对路径
第二章方式打印:sh /scripts/hello.sh 一样效果
给脚本增加执行命令:chmod +x /scripts/hello.sh
直接绝对路径:./hello.sh
第三种:脚本的常用执行方式(source 是 shell 内嵌)
source /scripts/hello.sh
source hello.sh
. hello.sh
第二个Shell脚本:多命令处理
直接输入hello.sh
bash: hello.sh: 未找到命令...
cp hello.sh /bin/
sudo cp hello.sh /bin/(一般不要使用)
(方法:不改变bin目录,正常执行)
1.脚本参数用法:
三.变量
1.$n
./hello.sh 参数(xiaoming)
' ===$n============'原封不动的输出
#!/bin/bash
echo '================$n===================='
echo script name:0
echo 1st parameter:$1
echo 2nd parameter:$2
输出:./parameter.sh abc def
================$n====================
script name:0
1st parameter:abc
2nd parameter:def
2.$#
用于循环中,次数
#!/bin/bash
echo '================$n===================='
echo script name:0
echo 1st parameter:$1
echo 2nd parameter:$2echo '================$n===================='
echo parameter numbers:$#
./parameter.sh abc def
================$n====================
script name:0
1st parameter:abc
2nd parameter:def
================$n====================
parameter numbers:2
3.$*和$@用法
$*:代表命令行中所有的参数,$*把所有的参数看做一个整体
$@:代表命令行中所有的参数,$@把这个参数区分对待
1st parameter:abc
2nd parameter:def
================$n====================
parameter numbers:2
================$*====================
abc def
================$@====================
abc def
4.$?
功能描述:最后一次执行的命令的返回状态。变量为0,上个命令正确执行;
变量的值为非0(具体数值,由自己命令决定)证明上个命令执行不正确;
四、运算符
基本语法:“$((运算式))”或“$[运算式]”
expr:表达式
expr 1 + 2
expr 5 - 2
直接写乘报错:
应写:echo $[5 * 2]或者使用echo $((5*2))
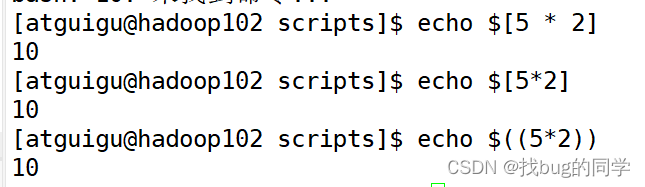
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ expr 1 + 2
3
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ expr 5 - 2
3
命令替换:
赋值给a=$[8*2]
echo $a
另外写法:
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ a=$(expr 5 \* 2) (一般不用)
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ echo $a
10
使用expr写法:乘法
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ a=`expr 5 \* 2`
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ echo $a
10
五.条件判断
语法:[ condition ]
1.常用判断条件
(1)两个整数之间比较
= 字符串比较
-lt 小于(less than) -le 小于等于(less equal)
-eq 等于(equal) -gt 大于(greater than)
-ge 大于等于(greater equal) -ne 不等于(Not equal)
(2)按照文件权限进行判断
-r 有读的权限(read) -w 有写的权限(write)
-x 有执行的权限(execute)
(3)按照文件类型进行判断
-f 文件存在并且是一个常规的文件(file)
-e 文件存在(existence) -d 文件存在并是一个目录(directory)
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ a=15
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ [ $a -lt 20 ] && echo "$a < 20" || echo "$a >=20"
15 < 20
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ a=27
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ [ $a -lt 20 ] && echo "$a < 20" || echo "$a >=20"
27 >=20
六、流程控制(重点)
1 if 判断
1.基本语法
if [ 条件判断式 ];then
程序
fi
或者
if [ 条件判断式 ]
then
程序
fi
注意事项:
(1)[ 条件判断式 ],中括号和条件判断式之间必须有空格
(2)if后要有空格
举个例子:
a=25
if [ $a -gt 18 ]; then echo OK;fi
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ if [ $a -gt 18 ] && [ $a -lt 35 ];then echo OK;fi
OK
2 case 语句
基本语法
case $变量名 in
"值1")
如果变量的值等于值1,则执行程序1
;;
"值2")
如果变量的值等于值2,则执行程序2
;;
…省略其他分支…
*)
如果变量的值都不是以上的值,则执行此程序
;;
esac
注意事项:
- case行尾必须为单词“in”,每一个模式匹配必须以右括号“)”结束。
- 双分号“;;”表示命令序列结束,相当于java中的break。
- 最后的“*)”表示默认模式,相当于java中的default。
3.for 循环
1.基本语法1
for (( 初始值;循环控制条件;变量变化 ))
do
程序
done
例如:创建脚本:parameter_for_test.sh
给予权限:chmod 777 parameter_for_test.sh执行
echo '===================$*===================='
for para in "$*"
doecho $para
doneecho '==================$@====================='
for para in "$@"
doecho $para
done执行:./parameter_for_test.sh a b c d e
结果输出:
===================$*====================
a b c d e
==================$@=====================
a
b
c
d
e
备注:“$*”把所有元素当成整体输出
“$@”把数据当成独立数据输出,依次打印
4.while 循环
1.基本语法
while [ 条件判断式 ]
do
程序
done
七、read读取控制台的输入
1.基本语法
read(选项)(参数)
选项:
-p:指定读取值时的提示符;
-t:指定读取值时等待的时间(秒)。
参数
变量:指定读取值的变量名
八、函数(一段代码的集合)
1.系统函数(也叫:命令替换)
basename:
创建脚本:cmd_test.sh
#!/bin/bash
filename="$1"_log_$( date +%s)
echo $filename
执行权限:chmod +x cmd_test.sh
备注:$( date +%s)
1).basename基本语法
basename [string / pathname] [suffix] (功能描述:basename命令会删掉所有的前缀包括最后一个(‘/’)字符,然后将字符串显示出来。
选项:
suffix为后缀,如果suffix被指定了,basename会将pathname或string中的suffix去掉。
例如:
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ basename /home/atguigu/scripts/parameter.sh
parameter.sh
本质上路径可以随便写(不需要确定是否存在具体路径):找最后一个目录/ 相当于做字符串剪切
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ basename /home/atguigu/helo/parameter.sh
parameter.sh
剪切最后一个/后缀
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ basename /home/atguigu/scripts/parameter.sh .sh
parameter
2).dirname基本语法
dirname 文件绝对路径 (功能描述:从给定的包含绝对路径的文件名中去除文件名(非目录的部分),然后返回剩下的路径(目录的部分))
截取最后一个斜杠 /之前的路径:
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ dirname /home/atguigu/scripts/parameter.sh
/home/atguigu/scripts
截取最后一个斜杠前的相对路径:
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ dirname ../atguigu/scripts/parameter.sh
../atguigu/scripts
截取路径:仅值切割 最后一个斜杠前路径 /
2.自定义函数
九、综合案例
1.归档文件
归档命令:tar
自动归档:crontab -l
十、正则表达式
正则表达式用来检索,替换,符合某个模式的文本。
1.常规匹配
不含特殊字符的表达式匹配它自己。(存文本匹配)如筛选
cat /etc/passwd | grep xx
2.特殊匹配
1)使用^号配置开头
atguigu@hadoop102 ~]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep ^a
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
2)$匹配一行的结束
例如:匹配出所有以t结尾的行。
[atguigu@hadoop102 ~]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep t$
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
匹配出空格:cat /etc/passwd | grep ^$
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ cat daily_achive.sh |grep -n ^$
2:
9:
22:
25:
29:
33:
35:
38:
49:
3. .匹配一个任意的字符
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ cat daily_achive.sh |grep r..t
DEST=/home/atguigu/scripts/archive/$FILE
4. *不单独使用
他和上一个字符连用,表示匹配上一个字符0次或多次。
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ cat daily_achive.sh |grep r..t
DEST=/home/atguigu/scripts/archive/$FILE
5. .*
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep ^a.*bash$
atguigu:x:1003:1003::/home/atguigu:/bin/bash
6.字符区间使用(中括号):[ ]

[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ echo "rbtadfasf" | grep r[a,b]t
rbtadfasf
[atguigu@hadoop102 scripts]$ echo "23ddratadfasf" | grep r[a,b]t
23ddratadfasf
7. \
十一、文本处理工具
1.cut
1.基本用法
cut [选项参数] filename