文章目录
- 前言
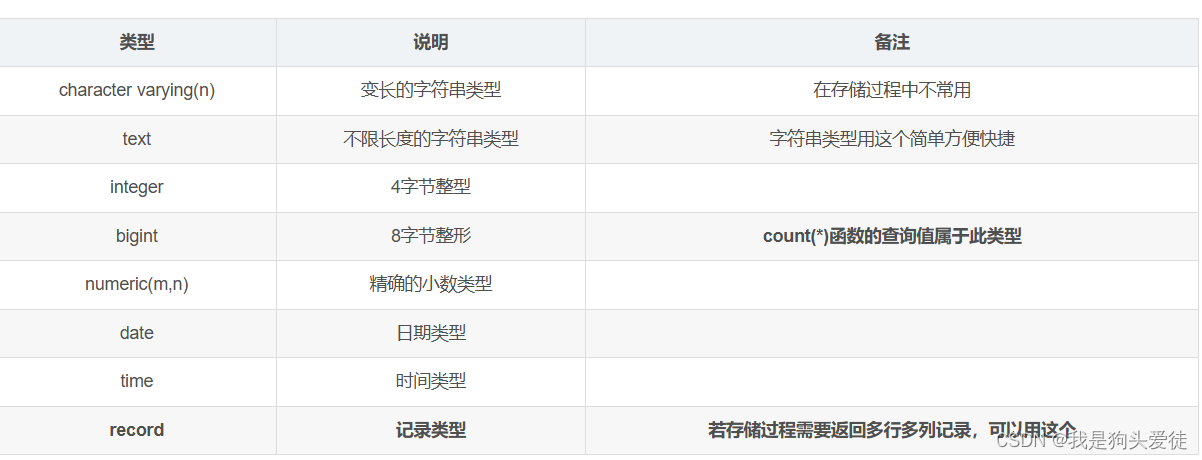
- 日期类Date的接口设计
- 构造函数和打印函数
- 获取日期并判断日期是否合法
- 日期类的大小比较关系
- <运算符重载 判断小于
- ==运算符重载 判断相等
- <=运算符重载 判断小于等于
- >运算符重载 判断大于
- >= 运算符重载 判断大于等于
- != 运算符重载 不等于
- 日期类计算
- 日期+=天数
- 日期+天数
- 日期-=天数
- 日期-天数
- 前置++
- 后置++
- 前置--
- 后置--
- 日期-日期
- 完整代码
- Date.h
- Date.cpp
- Test.cpp
前言
日期类Date的接口设计
我们把函数的声明放到类中,定义在类的外边,实现声明与定义分离
以下是日期类中所包含的成员函数和成员变量
🗨️Date.h
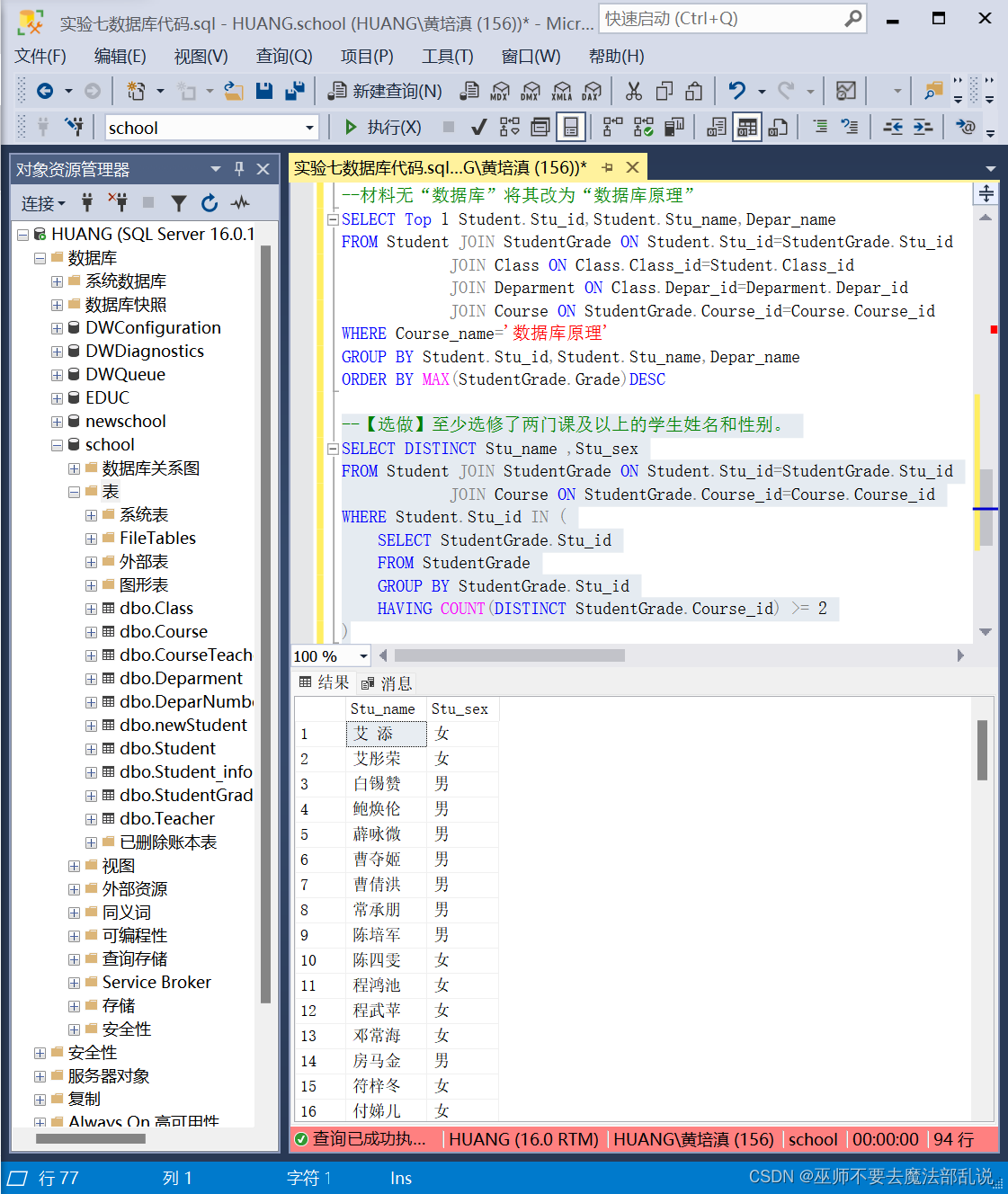
class Date
{
public:// 判断日期是否合法bool CheckInvalid() const;// 构造函数Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);// 日期类的大小关系比较bool operator<(const Date& d) const;bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;bool operator>(const Date& d) const;bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;bool operator==(const Date& d) const;bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;// d1 + 100Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day) const;// d1 - 100Date operator-(int day) const;Date& operator-=(int day);// ++d1Date& operator++();// 特殊处理:解决语法逻辑不自洽,自相矛盾的问题// d1++// 为了跟前置++区分,强行增加一个int形参,够成重载区分Date operator++(int);Date operator--(int);Date& operator--();// d1 - d2int operator-(const Date& d) const;// 本质就是inlineint GetMonthDay(int year, int month) const{assert(month > 0 && month < 13);static int monthDays[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return monthDays[month];}void Print() const{cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
构造函数和打印函数
函数声明写到Date.h文件中
函数定义写到Date.cpp 中
🗨️Date.h
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:// 全缺省构造函数Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);// 打印函数void Print() const{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
🗨️Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"// 缺省值在声明和定义中不能同时出现
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}
运行结果
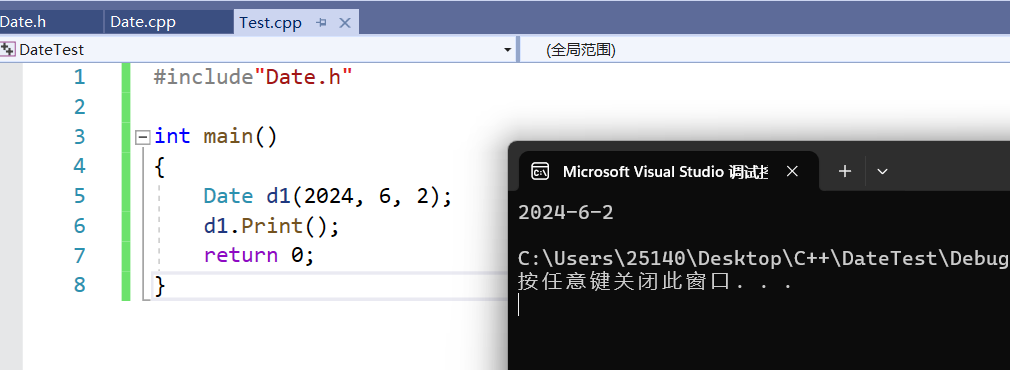
在上面的代码中,构造函数我们使用全缺省,在调用的时候给了指定日期,通过打印函数把日期打印出来,这里的打印函数可以用const来修饰,const修饰成员函数,不能修改里面状态,而构造函数需要修改成员变量,所以不能加const。
获取日期并判断日期是否合法
比如说,我输入日期:
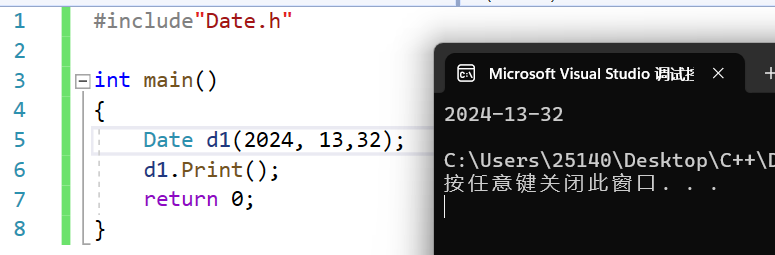
我们大家都知道,这日期哪来的13月啊,哪来的32天?是不是很离谱,是不是相当的不合理😅😅😅
所以我们设计一个自动获取日期天数并帮助我们判断该日期是否合法的函数功能。
获取天数int GetMonthDay 我们将该函数封装在类内,方便访问私有成员,提高效率。
注意:内联函数不要声明和定义分离!否则会出现链接错误,所以我们定义在类内
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) const{assert(month > 0 && month < 13);static int monthDay[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };// 判断是否为闰年// 非整百年:能被4整除而不能被100整除的为闰年// 整百年:能被400整除的是闰年。if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return monthDay[month];}
我们将数组设置成13,因为数组下标是从0开始访问的,这样设方便我们返回时直接返回月份。
判断日期是否有效
月数:小于等于0或者大于12就无效
天数:可以依靠我们刚刚写的GetMonthDay函数,获取不同月份的天数,再去判断是否有效。
bool Date::CheckInvalid() const
{if (_year <= 0 || _month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){return false;}else{return true;}
}
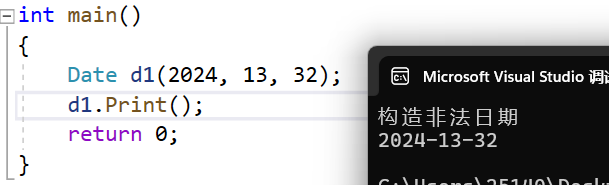
利用该函数每次构造日期判断日期是否合法。
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (!CheckInvalid()){cout << "构造非法日期" << endl;}
}
测试:
日期类的拷贝构造和析构我们可以不写,让编译器自己生成就行了。
日期类的大小比较关系
日期类的大小关系看着挺多,实际上有些是可以复用的,实现了两个剩下的都可以复用
比较日期类的大小是不会修改传入对象的值的,所以我们把比较大小关系的成员函数都加上const修饰
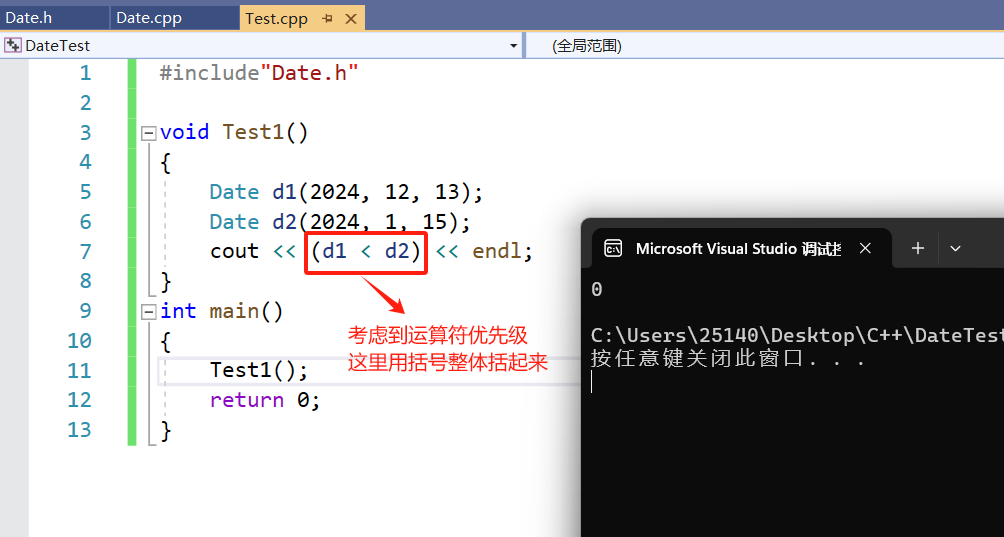
<运算符重载 判断小于
先比较年是否小于,再判断月是否小于,最后判断日是否小于,其中一条满足则返回真true,反之返回假false。
Date.h
bool operator<(const Date& d) const;
Date.cpp
// d1 < d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year){if (_month < d._month){return true;}else if (_month == d._month){if (_day < d._day){return true;}}}return false;
}
运行结果
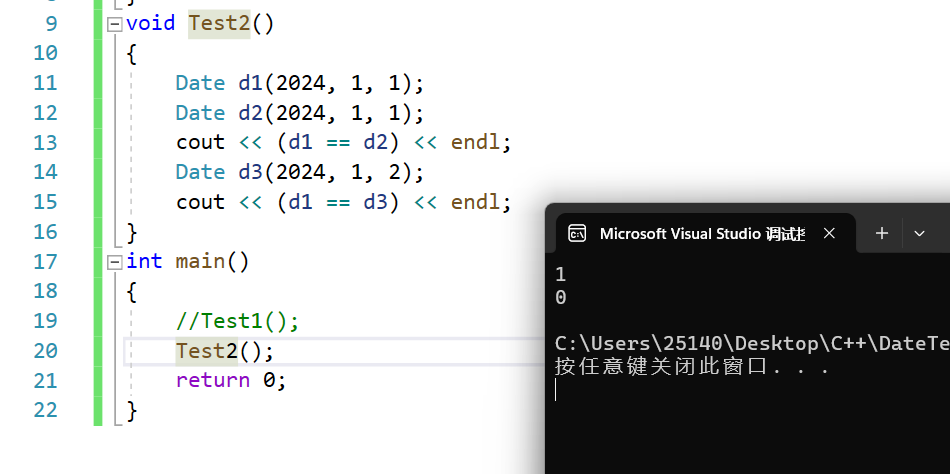
==运算符重载 判断相等
判断年月日是否都相等
Date.h
bool operator==(const Date& d) const;
Date.cpp
// d1 == d2
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}
运行结果
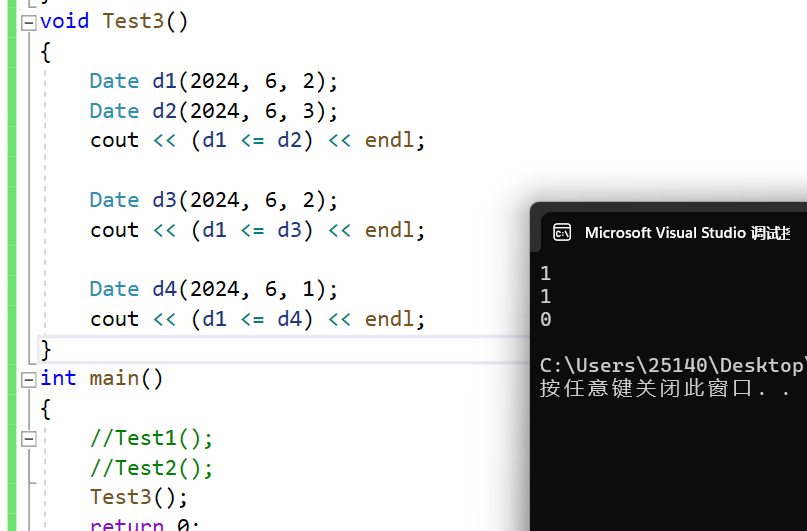
<=运算符重载 判断小于等于
小于等于,即小于或等于,两者满足一个即可
这里就可以展现出复用的魅力了,已知我们已经实现了小于和等于,那小于或等于就不用自己实现了,直接复用
Date.h
bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;
Date.cpp
// d1 <= d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{return *this < d || *this == d;
}
运行结果
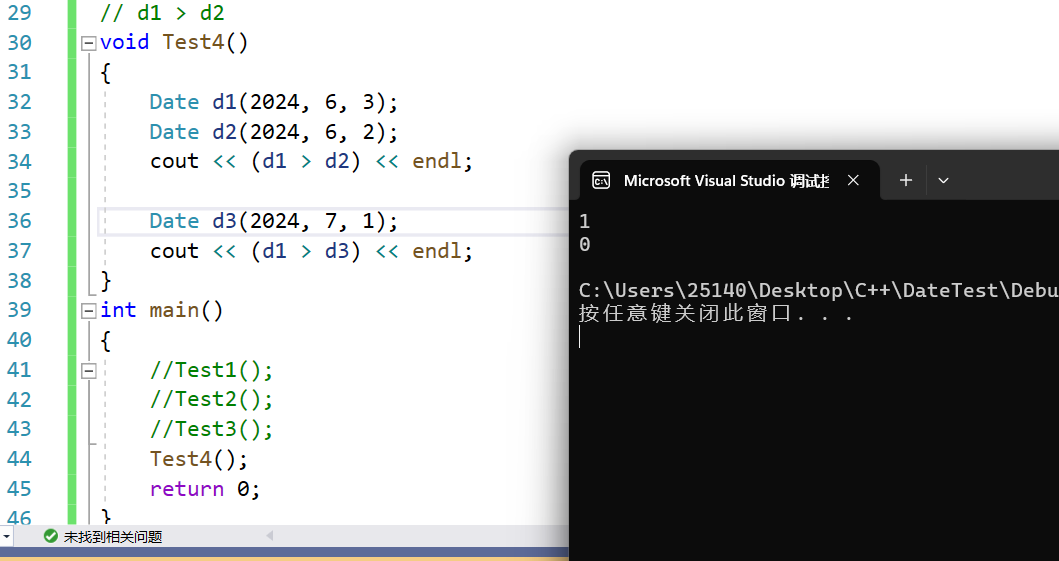
>运算符重载 判断大于
你也可以用判断语句 if else if 来判断 但是这样太矬了,我们已经实现了小于等于了,那大于不就是非大于等于吗,继续复用!能坐着咱绝不站着🏄♀️
Date.h
bool operator>(const Date& d) const;
Date.cpp
// d1 > d2
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this <= d);
}
运行结果
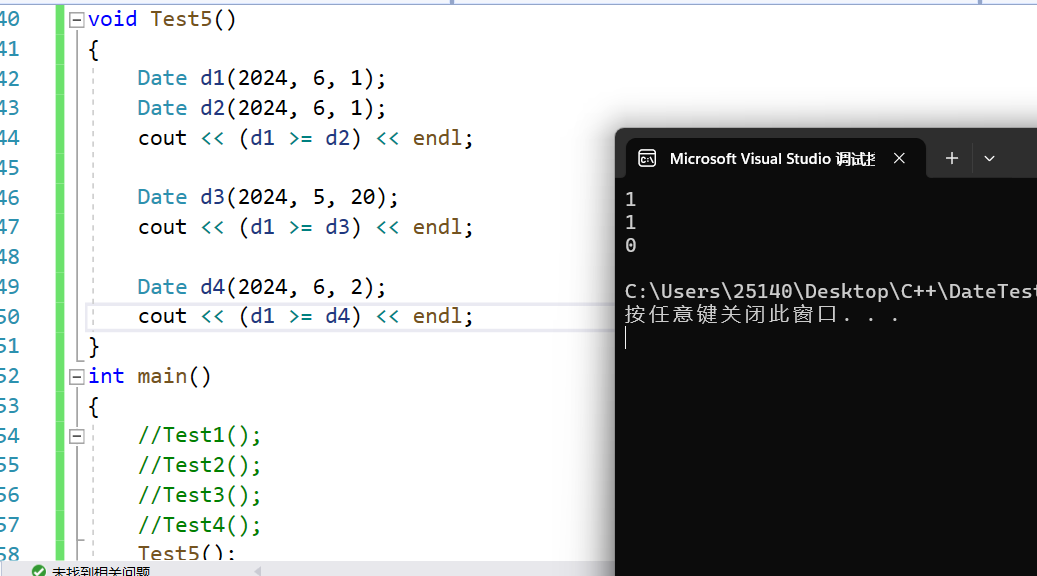
>= 运算符重载 判断大于等于
大于等于,即大于或者等于,两者满足一个即可,或者直接非小于(!<)
Date.h
bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;
Date.cpp
以下两种方法都可
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{return *this > d || *this == d;
}
or
// d1 >= d2
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this < d);
}
运行结果
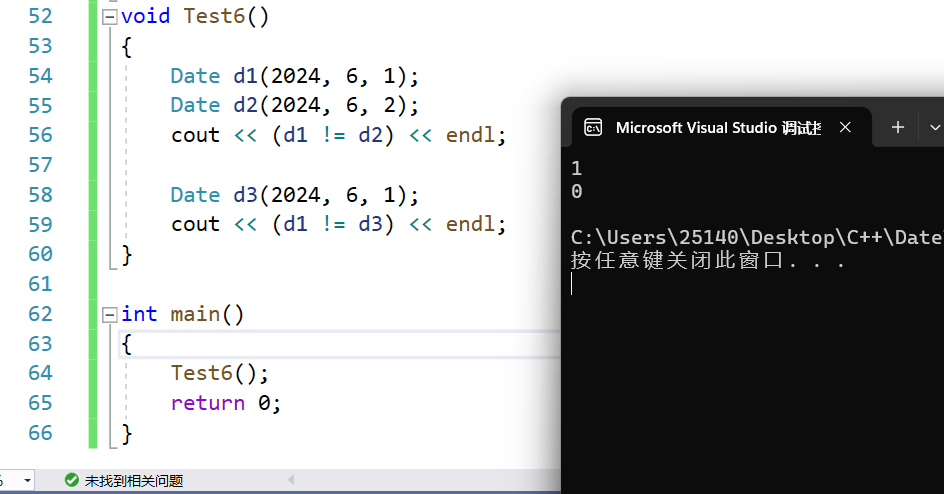
!= 运算符重载 不等于
字面意思很好理解,我们实现了等于,直接判断不等于即可
Date.h
bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;
Date.cpp
// d1 != d2
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this == d);
}
运行结果
日期类计算
我们认为,日期+日期是没有意义的,但是+天数就很有意义了,假设我们想计算当前日期+100天之后的日期,+1000天呢何年何月何日?我们下面就来实现这个功能。
日期+=天数
+=运算符重载
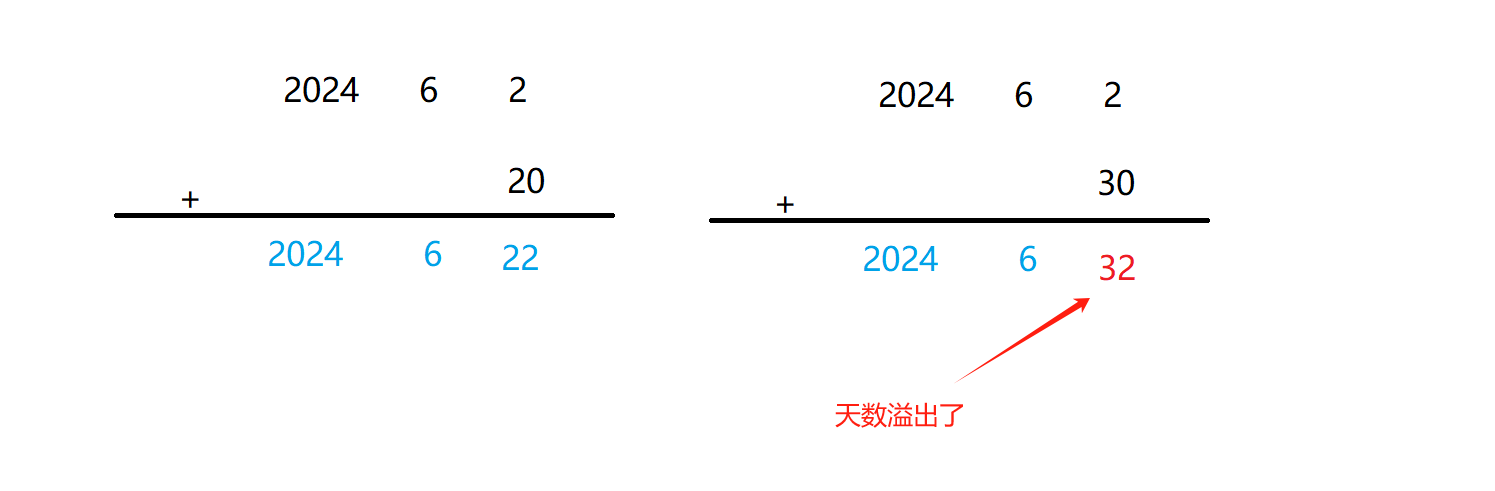
由上图可见,无脑把天数叠上去肯定是不合理的,这里需要用到我们上面实现过的函数 GetMonthDay 了
思路:先将天数加到日(day)上面去,再判断是否合法,是否超出该月的天数,若不合法,则不断调整,直到合法为止。
调整日期步骤:
1.日+天数,若日超出当前月的天数,则日-当前月的天数,然后月+1;
2.若月加满,即超出12,则年+1,然后月重新置为1;
3.不断执行以上步骤进行调整,直到日期合法;
Date.h
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date.cpp
// d1 += 100
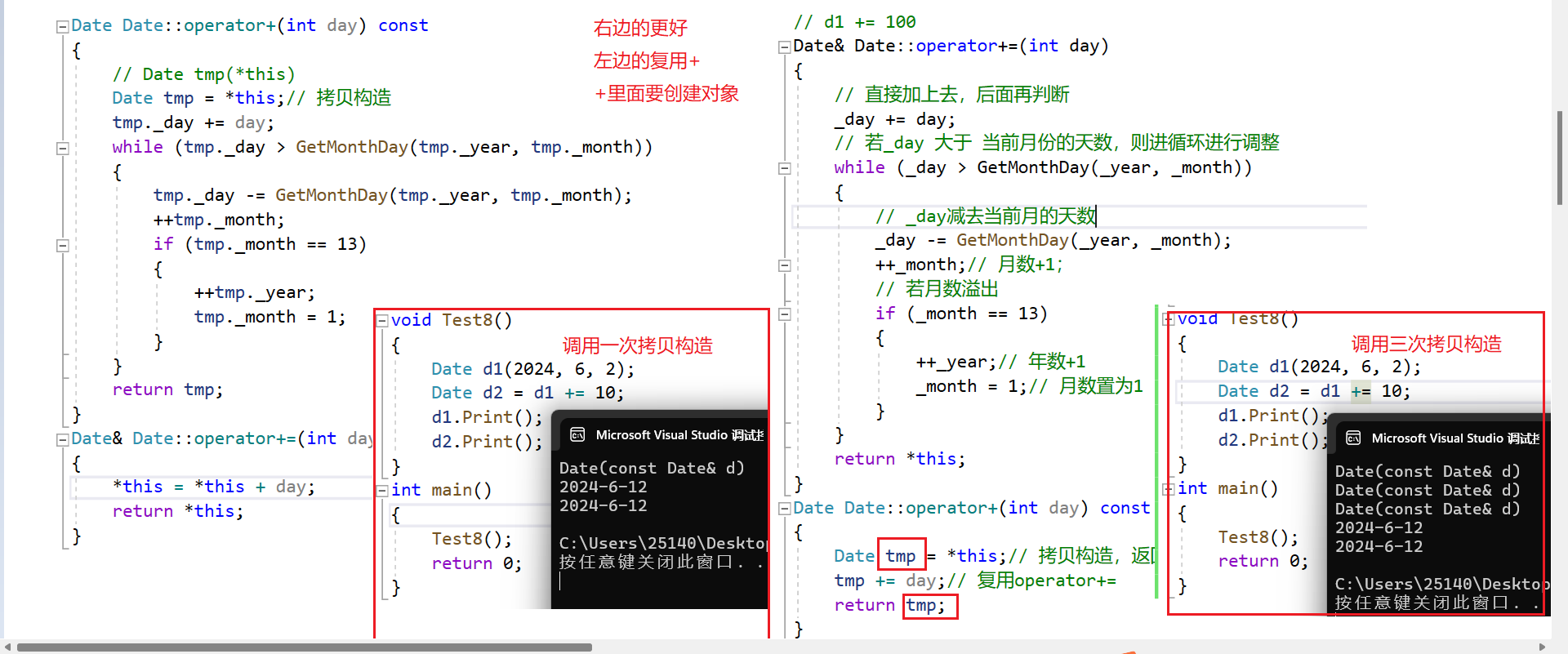
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{// 直接加上去,后面再判断_day += day;// 若_day 大于 当前月份的天数,则进循环进行调整while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){// _day减去当前月的天数_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;// 月数+1;// 若月数溢出if (_month == 13){++_year;// 年数+1_month = 1;// 月数置为1}}return *this;
}
运行结果
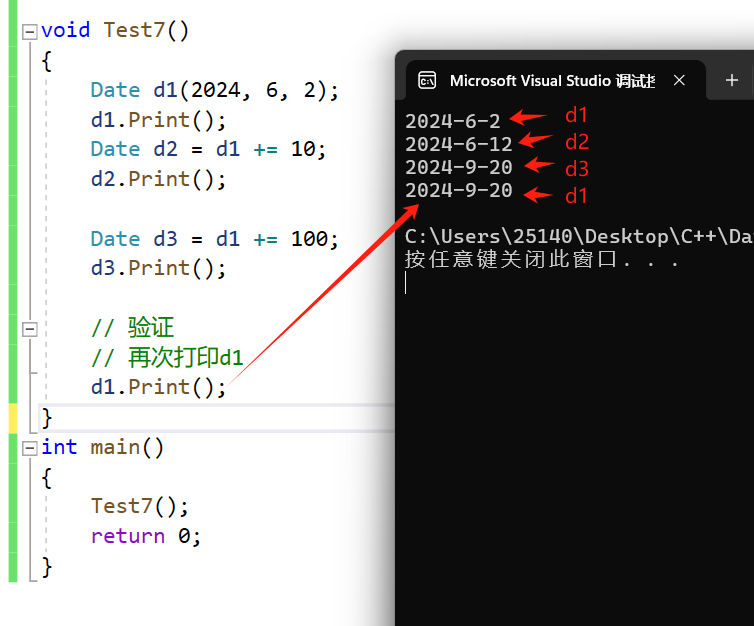
注意:因为我们传引用返回,传的是d1的别名,实际上我们+=的是d1本身,d1原始值会发生改变,如下测试样例实际上是先加上了10,再把+10后的结果+100,这和我们接下来要讲的+是不一样的。
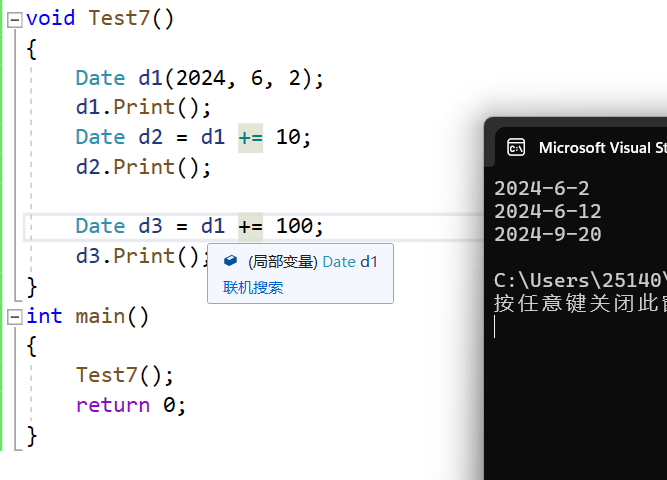
验证:此时d1原始数据发生改变
日期+天数
+运算符重载
对于+运算符来说,我们可以复用刚刚实现的operator+=运算符。
方法一:
先看结果:
Date.h
Date operator+(int day) const;
Date.cpp
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{Date tmp = *this;// 拷贝构造,返回tmptmp += day;// 复用operator+=return tmp;
}
运行结果
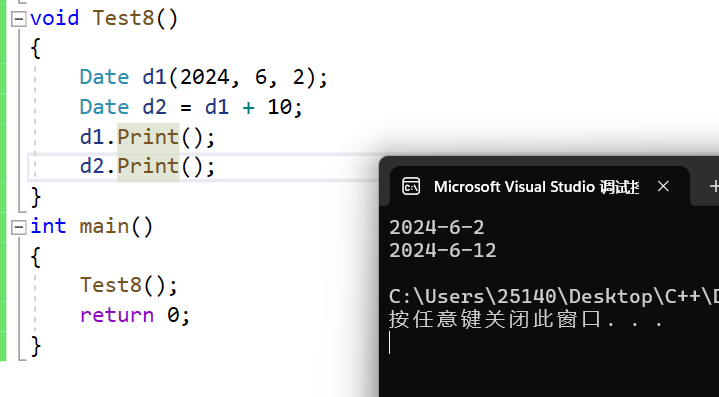
这里得注意,虽然我们对天数进行了加,并且返回的是加之后的值,但是d1本身并不会发生改变,这便是与+=运算符不同的地方,由代码可见,我们创建了个Date类的临时变量tmp,所以我们改变的是临时变量,并返回临时变量,这里我们还可以用const来修饰一下函数,防止内部改变this指针的指向。
对于+=和+,这里我们是先实现+=后实现+的,当然也可以先实现+后实现+=,它们有什么区别吗?
实现方法是类似的
我们简单看一下:
方法二:
Date.cpp
// d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{// Date tmp(*this)Date tmp = *this;// 拷贝构造tmp._day += day;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);++tmp._month;if (tmp._month == 13){++tmp._year;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;
}
Date.cpp
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{*this = *this + day;return *this;
}
区别:
日期-=天数
和+=思路一样的,先用日减去需要减的天数day,再判断结果是否合法,若不合法,则进行调整,直到合法为止
步骤:
1若减完结果得负,则像月借,即月-1;
2.如果月减到0,则像年借,年-1;
3.日加上借的天数
4.重复以上步骤,直到日期合法为止;
Date.h
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date.cpp
// d1 -= 100
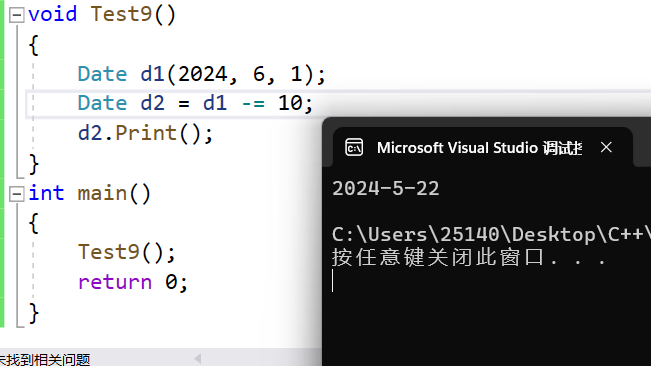
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}
运行结果
-=和+=一样的会改变d1本身,即改变原始值
日期-天数
Date.h
Date operator-(int day) const;
Date.cpp
// d1 -100
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= day;return tmp;
}
运行结果
注意:-=运算符的重载采用了引用返回,但是-运算符重载的返回却只能是传值返回,因为-运算符重载函数中的tmp对象出了作用域被销毁了,所以不能用引用返回。
前置++
我们可以服用+=运算符的重载
因为前置++返回的是++之后的值,所以我们使用引用返回
加不加引用就取决于它出了作用域还在不在
Date.h
Date& operator++();
Date.cpp
// 前置++ ——》d.operator++()
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}
因为是复用+=,所以++的值就是this,直接返回this即可
运行结果
后置++
前置++和后置++都operator++,那要怎么让编译器方便识别它们呢,它怎么知道到底是前置++还是后置++。
这里我们要做特殊处理:解决语法逻辑自洽,自相矛盾问题
为了跟前置++区分,强行增加了一个int形参,构成重载区分
Date.h
Date operator++(int);
Date.cpp
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{// Date tmp(*this) 为了能返回++之前的值,所以拷贝构造d1;Date tmp = *this;*this += 1; // 复用+= ,return tmp;
}
运行结果
 注意:后置++也是需要返回加之前的值,所以我们用tmp保存之前的值,然后再+1,最后返回tmp,因为tmp是临时对象,出了作用域销毁了,所以后置++只能使用传值返回,前置++可以使用引用返回
注意:后置++也是需要返回加之前的值,所以我们用tmp保存之前的值,然后再+1,最后返回tmp,因为tmp是临时对象,出了作用域销毁了,所以后置++只能使用传值返回,前置++可以使用引用返回
前置–
前置–和前置++是一模一样的,参照前置++
Date.h
// 前置--Date& operator--();
Date.cpp
// --d1
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}
后置–
后置–和后置++一样的
Date.h
// 后置--Date operator--(int);
Date.cpp
// d1--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= 1;return tmp;
}
日期-日期
计算两个传入日期相差的天数,一直让较小的日期++,一直加到和另一个日期相等即可,在加的过程中,小日期所加的天数,就是两个日期的差值
Date.h
// d1 - d2int operator-(const Date& d) const;
Date.cpp
// d1 - d2
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{// 立个flag,若左边的日期大于右边的日期,则返回真int flag = 1;Date max = *this;// 假设左边的日期大Date min = d;// 假设右边的日期小// 假设错误,进行更正if (*this < d){int flag = -1;max = d;// 令大的为右边的日期min = *this;// 小的为左边的日期}int n = 0;//记录加的天数while (min != max){++min;// 小日期++++n;// 总天数++}return n * flag;
}
运行结果
完整代码
Date.h
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:// 全缺省构造函数Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);Date(const Date& d);bool CheckInvalid() const;// 判断日期大小bool operator<(const Date& d) const;bool operator==(const Date& d) const;bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;bool operator>(const Date& d) const;bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;// d1 += 100Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day) const;// d1 - 100Date& operator-=(int day);Date operator-(int day) const;// 前置++Date& operator++();// 后置++Date operator++(int);// 前置--Date& operator--();// 后置--Date operator--(int);// d1 - d2int operator-(const Date& d) const;// 本质就是内联inlineint GetMonthDay(int year, int month) const{assert(month > 0 && month < 13);static int monthDay[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return monthDay[month];}// 打印函数void Print() const{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"// 缺省值在声明和定义中不能同时出现
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (!CheckInvalid()){cout << "构造非法日期" << endl;}
}
Date::Date(const Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;//cout << "Date(const Date& d)" << endl;
}
// d1 < d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year){if (_month < d._month){return true;}else if (_month == d._month){if (_day < d._day){return true;}}}return false;
}
// d1 == d2
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}
// d1 <= d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{return *this < d || *this == d;
}
// d1 > d2
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this <= d);
}
// d1 >= d2
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{//return !(*this < d);return *this > d || *this == d;
}
// d1 != d2
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this == d);
}// d1 += 100
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{// 直接加上去,后面再判断_day += day;// 若_day 大于 当前月份的天数,则进循环进行调整while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){// _day减去当前月的天数_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;// 月数+1;// 若月数溢出if (_month == 13){++_year;// 年数+1_month = 1;// 月数置为1}}return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{Date tmp = *this;// 拷贝构造,返回tmptmp += day;// 复用operator+=return tmp;
}//Date Date::operator+(int day) const
//{
// // Date tmp(*this)
// Date tmp = *this;// 拷贝构造
// tmp._day += day;
// while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
// {
// tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
// ++tmp._month;
// if (tmp._month == 13)
// {
// ++tmp._year;
// tmp._month = 1;
// }
// }
// return tmp;
//}
//Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
//{
// *this = *this + day;
// return *this;
//}// d1 -= 100
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}
// d1 -100
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= day;return tmp;
}// 前置++ ——》d.operator++()
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}
// d++ ->d.operator++(0)
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this += 1;return tmp;
}
// --d1
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}
// d1--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= 1;return tmp;
}
// d1 - d2
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{// 立个flag,若左边的日期大于右边的日期,则返回真int flag = 1;Date max = *this;// 假设左边的日期大Date min = d;// 假设右边的日期小// 假设错误,进行更正if (*this < d){int flag = -1;max = d;// 令大的为右边的日期min = *this;// 小的为左边的日期}int n = 0;//记录加的天数while (min != max){++min;// 小日期++++n;// 总天数++}return n * flag;
}
bool Date::CheckInvalid() const
{if (_year <= 0 || _month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){return false;}else{return true;}
}
Test.cpp
#include"Date.h"void Test1()
{Date d1(2024, 12, 13);Date d2(2024, 1, 15);cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;
}
void Test2()
{Date d1(2024, 1, 1);Date d2(2024, 1, 1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;Date d3(2024, 1, 2);cout << (d1 == d3) << endl;
}
void Test3()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 2);Date d2(2024, 6, 3);cout << (d1 <= d2) << endl;Date d3(2024, 6, 2);cout << (d1 <= d3) << endl;Date d4(2024, 6, 1);cout << (d1 <= d4) << endl;
}
// d1 > d2
void Test4()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 3);Date d2(2024, 6, 2);cout << (d1 > d2) << endl;Date d3(2024, 7, 1);cout << (d1 > d3) << endl;
}
// d1 >= d2
void Test5()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 1);Date d2(2024, 6, 1);cout << (d1 >= d2) << endl;Date d3(2024, 5, 20);cout << (d1 >= d3) << endl;Date d4(2024, 6, 3);cout << (d1 >= d4) << endl;
}
void Test6()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 1);Date d2(2024, 6, 2);cout << (d1 != d2) << endl;Date d3(2024, 6, 1);cout << (d1 != d3) << endl;
}void Test7()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 2);d1.Print();Date d2 = d1 += 10;d2.Print();Date d3 = d1 += 100;d3.Print();// 验证// 再次打印d1d1.Print();
}
void Test8()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 2);Date d2 = d1 += 10;d1.Print();d2.Print();
}
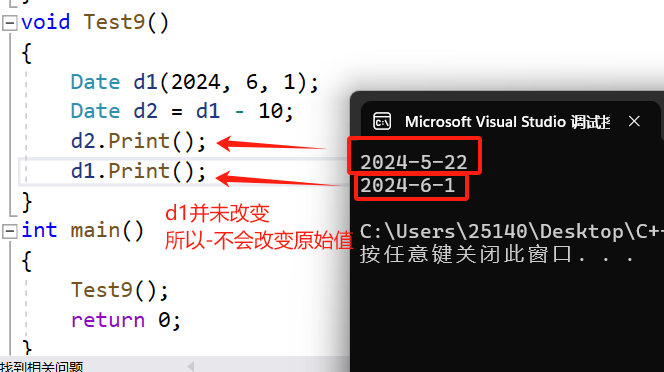
void Test9()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 1);Date d2 = d1 - 10;d2.Print();d1.Print();
}
// ++d1
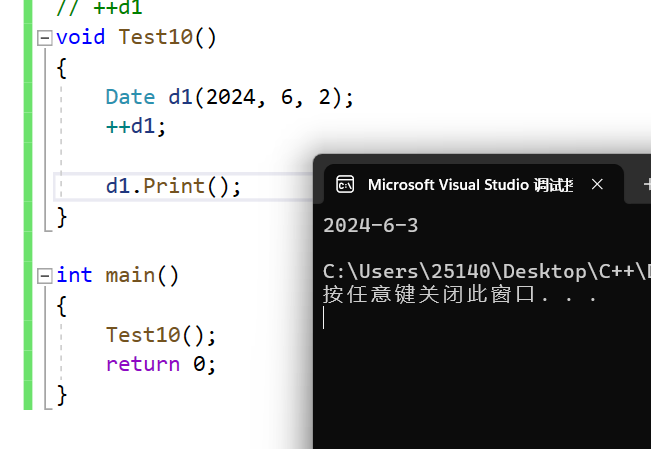
void Test10()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 2);++d1;d1.Print();//d1++;//d1.operator++(10);//d1.Print();
}
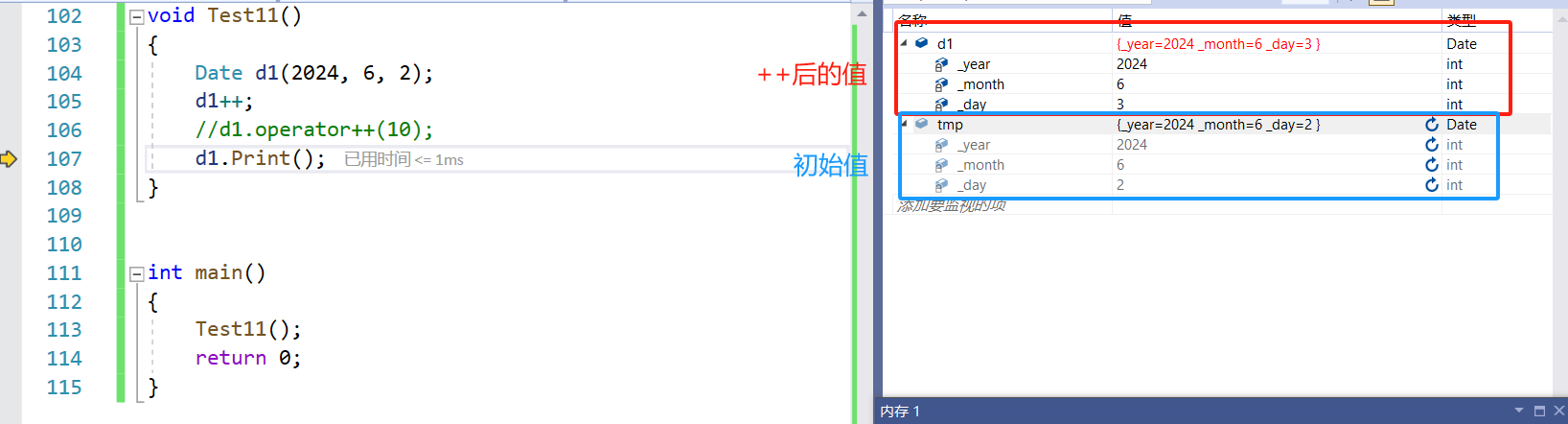
void Test11()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 2);d1++;//d1.operator++(10);d1.Print();
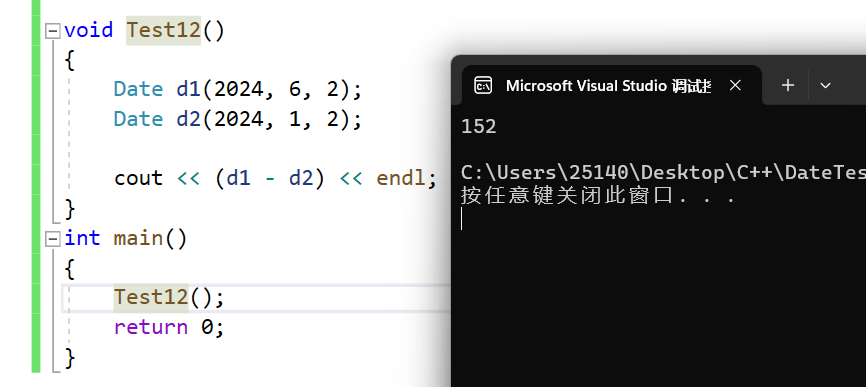
}void Test12()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 2);Date d2(2024, 1, 2);cout << (d1 - d2) << endl;
}
int main()
{Test12 ();return 0;
}