1.二叉树的概念及结构
1.1 概念
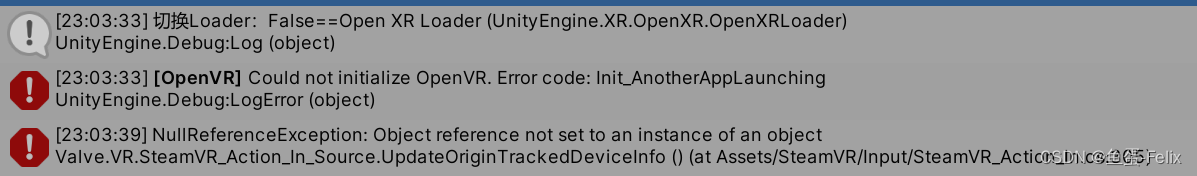
一棵二叉树是结点的一个有限集合,该集合:
1.或者为空
2.由一个根结点加上两棵别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成
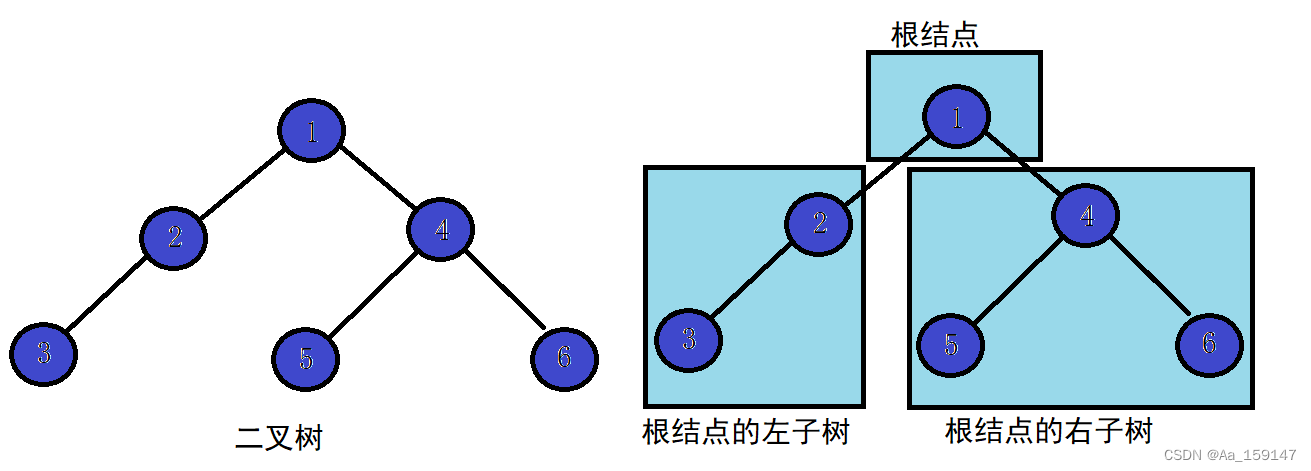
从上图可以看出:
1.二叉树不存在度大于2的结点
2.二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒,因此二叉树是有序树
1.2 特殊二叉树
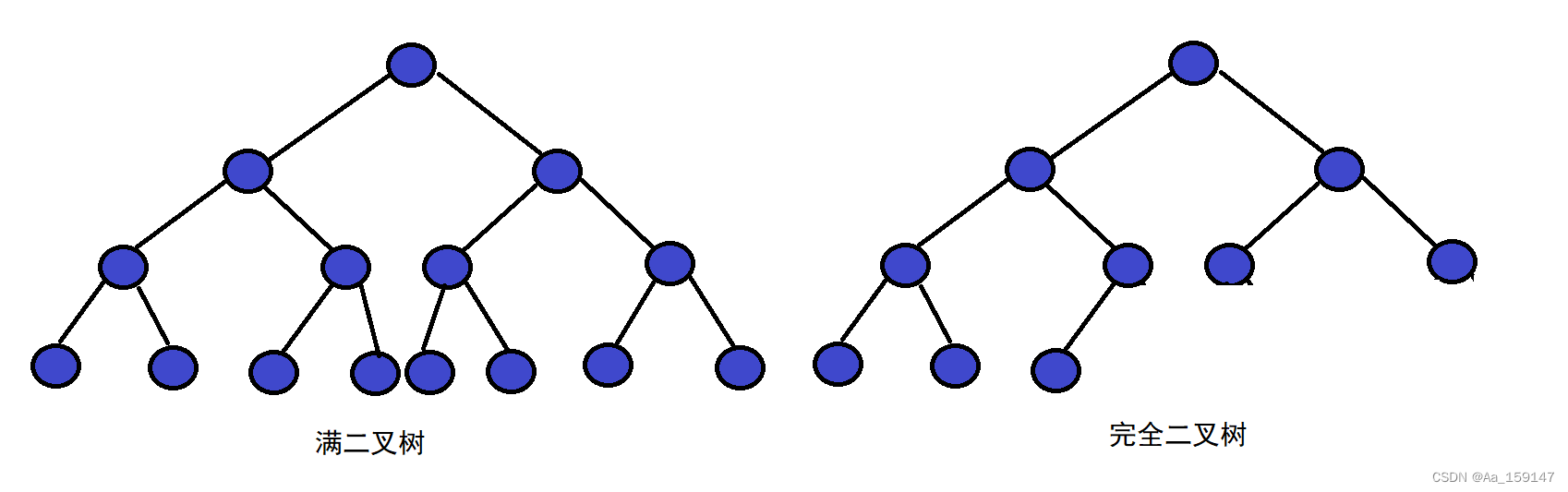
1.满二叉树:一个二叉树,如果每一个层的结点数都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉树,也就是说没如果一个二叉树的层数为K,且结点总数是2^k-1,则它就是满二叉树。
2.完全二叉树:完全二叉树是效率很高的数据结构,完全二叉树是由满二叉树而引出来的。对于深度为K的,有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当每一个结点都与深度为K的满二叉树中编号从1至n的结点——对应时称之为完全二叉树,要注意的是满二叉树是一中特殊的完全二叉树。
1.3二叉树的性质
1.若规定根结点的层数为1,则一棵非空二叉树的第i层上最多有2^(i-1)个结点。
2.若规定根结点的层数为1,则深度为h的二叉树的最大结点数是2^h-1。
3.对任何一棵二叉树,如果度为0其叶子结点个数为a,度为2的分支个数为b,则有a=b+1。
4.若规定根结点的层数为1,具有n个结点的满二叉树的深度,h=log2(n+1).(ps:以2为底,n+1为对数)
5.对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从左至右的数组顺序对所有结点从0开始编号,则对于序号为i的结点有:
1.若i>0,i的位置结点的双亲序号:(i-1)/2;i=0,i为根结点编号,无双亲结点
2.2i+1<n,左孩子序号:2i+1,2i+1>=n否则无左孩子
3.2i+2<n,右孩子序号:2i+2,2i+2>=n否则无右孩子
1.4二叉树的存储结构
二叉树一般可以使用两种结构存储,一种顺序结构,一种链式结构。
1.顺序存储
顺序结构村塾就是使用数组来存储,一般使用数组只适合表示完全二叉树,因为不是完全二叉树会有空间的浪费,而现实中使用只有堆才会使用数组来存储,二叉树顺序存储在物理上是一个数组,在逻辑上是一棵二叉树。

2.链式存储
二叉树的链式存储结构是指用链表来表示一棵二叉树,即用链来指示元素的逻辑关系。通常的方法是链表中每个结点由三个域组成,数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别用来给出该结点左孩子和右孩子所在的链结点的存储地址。链式结构又分为二叉链和三叉链。
2.二叉树的实现
#pragma once#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef char BTDataType;typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{BTDataType _data;struct BinaryTreeNode* _left;struct BinaryTreeNode* _right;
}BTNode;// 通过前序遍历的数组"ABD##E#H##CF##G##"构建二叉树
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int n, int* pi);
// 二叉树销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root);
// 二叉树节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k);
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);
// 二叉树前序遍历
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树中序遍历
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树后序遍历
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root);
// 层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root);
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root);
//二叉树的高度
int TreeHigh(BTNode* root);2.1创建新的结点
调用函数BuyNode来创建新的结点
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}node->_data = x;node->_left = NULL;node->_right = NULL;return node;
}2.2通过前序遍历数组来构建二叉树
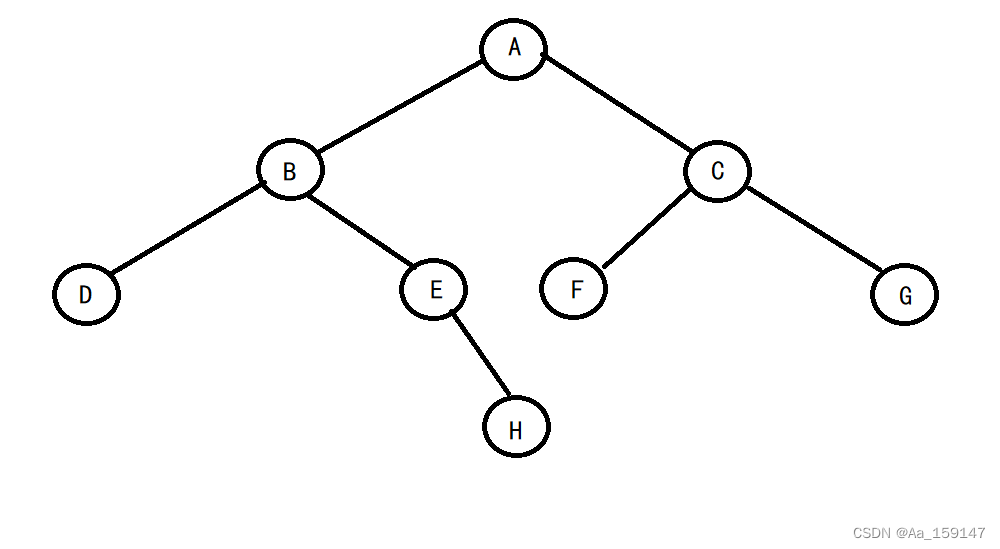
// 通过前序遍历的数组"ABD##E#H##CF##G##"构建二叉树
//a为我们所要遍历的数组
//n是最大数组的长度
//pi是我们用来遍历数组的指针
//当遍历是遇到‘#’或者指针超出了数组的范围就返回NULL
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int n, int* pi)
{if (a[*pi] == '#' || *pi >= n){printf("NULL ");(*pi)++;return NULL;}//创建一个新的二叉树的节点BTNode* dst = BuyNode(a[*pi]); printf("%c ", dst->_data);(*pi)++;dst->_left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, pi);dst->_right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, pi);return dst;
}
构建出来的二叉树如下:
2.3二叉树的销毁
实现二叉树的销毁时,我们要正确选择以哪种遍历的方式,这里使用后序遍历,从底层叶子层开始,先释放左子树和右子树的空间,再释放根结点的空间,如果先对根结点释放,就找不到它所对应的左子树和右子树了。
//二叉树的销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root)
{if (*root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->_left));BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->_right));free(*root);*root = NULL;return;}2.4计算二叉树的结点个数
这里我罗列了两种方法:
一种是用一个静态变量通过size++的形式来计算结点的个数(局部的静态变量只能初始化一次)
另一种是递归遍历二叉树通过放回: 左子树+右子树+1
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{//方法一://用静态变量(在堆上,不在栈上)改变局部变量 -> 使得递归的size可以累加起来,但是局部的静态只能初始化一次/*static int size = 0;if (root == NULL){return 0;}else++size;BinaryTreeSize(root->_left);BinaryTreeSize(root->_right);*///方法二://如果我们当前的节点为空,也就是说我们已经到了叶子节点的左右节点,也就是没有节点//所以我们需要返回0if (root == NULL){return 0;}//如果我们当前的节点的左指针和右指针都是空的话,也就是说这是我们的叶子节点//就返回1,也就是只有一个节点if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL){return 1;}//使用递归遍历我们的二叉树,即分别统计我们左子树的节点个数再加上右子树中的节点个数再加上1//因为我们需要将我们当前所指的节点算上return BinaryTreeSize(root->_left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->_right) + 1;}2.5计算二叉树叶子结点的个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}//如果我们的节点的左右指针全部都为空,那就是我们的叶子节点if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL){return 1;}//返回我们左子树中的叶子节点和右子树中的叶子节点之和return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->_left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->_right);
}2.6二叉树第k层的结点个数
二叉树第一层结点个数为1,第k层结点是第一层结点往下找k-1层,第二层的结点往下找k-2层,当k为1的时候返回的结果就是找的k层的结点的个数的总和。
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (k == 1){return 1;}//分别遍历我们的左右子树,并且将我们的k的参数--,当我们的k为1时,就到达了我们所想要查找对应的层return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->_left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->_right, k - 1);
}2.7查找值为x的结点
查找第一个指定值为x的结点,同过前序遍历的方法来寻找第一个值为x的结点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->_data == x){return root;}BTNode* ret1 = BinaryTreeFind(root->_left, x);if (ret1){return ret1;}/*BTNode* ret2 = BinaryTreeFind(root->_right, x);if (ret2){return ret2;}return NULL;*/return BinaryTreeFind(root->_right, x);
}
2.8二叉树前序遍历
前序遍历的顺序是根 - 左子树 - 右子树
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return;}printf("%c ", root->_data);BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->_left);BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->_right);}2.9二叉树中序遍历
中序遍历的顺序是左子树 - 根 - 右子树
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeInOrder(root->_left);printf("%c ", root->_data);BinaryTreeInOrder(root->_right);}2.10二叉树后序遍历
后序遍历的顺序是左子树 - 右子树 - 根
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreePostOrder(root->_left);BinaryTreePostOrder(root->_right);printf("%c ", root->_data);}
2.11二叉树层序遍历
需要使用一个队列实现层序遍历,先将指向根结点的指针入队,当根结点出队列的时候,将它的左右子树的结点的指针入队,就达到了层层遍历的效果
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%c ", front->_data);if (front->_left)QueuePush(&q, front->_left);if (front->_right)QueuePush(&q, front->_right);}QueueDestroy(&q);
}2.12判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
思路是通过层序遍历的方法,二叉树的叶子结点的下一层节点全部都是NULL,那么在根出队列,左右子树进队列的情况下:
当出队列出到空的时候,判断队列里面的结点是否有非空结点,如果有则证明不是完全二叉树,
反之队列里面都是空结点,则是完全二叉树。
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//遇到第一个空,就可以开始判断,如果队列中还有非空,就不是完全二叉树if (front == NULL){break; }QueuePush(&q, front->_left);QueuePush(&q, front->_right);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//如果有非空,就不是完全二叉树if (front){QueueDestroy(&q);printf("不是完全二叉树\n");return 0;}}QueueDestroy(&q);printf("是完全二叉树\n");return 1;
}2.13求二叉树的高度
int TreeHigh(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int lefthigh = TreeHigh(root->_left);int righthigh = TreeHigh(root->_right);return lefthigh > righthigh ? lefthigh + 1 : righthigh + 1;//return TreeHigh(root->_left) > TreeHigh(root->_right) ? TreeHigh(root->_left) + 1 : TreeHigh(root->_right) + 1;
}3.二叉树总代码
3.1 Tree.h
#pragma once#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef char BTDataType;typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{BTDataType _data;struct BinaryTreeNode* _left;struct BinaryTreeNode* _right;
}BTNode;// 通过前序遍历的数组"ABD##E#H##CF##G##"构建二叉树
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int n, int* pi);
// 二叉树销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root);
// 二叉树节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k);
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);
// 二叉树前序遍历
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树中序遍历
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树后序遍历
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root);
// 层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root);
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root);
//二叉树的高度
int TreeHigh(BTNode* root);3.2 Tree.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"Tree.h"
#include"Queue.h"BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}node->_data = x;node->_left = NULL;node->_right = NULL;return node;
}// 通过前序遍历的数组"ABD##E#H##CF##G##"构建二叉树
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int n, int* pi)
{//这里我们的a为我们的数组//n为我们数组的最大长度//pi为我们遍历数组的指针//这里我们使用'#'来表示NULL//当我们所指向的位置的元素为#或者我们的指针已经超过了数组的范围的时候,我们就需要返回NULL//并且将我们的指针后移if (a[*pi] == '#' || *pi >= n){printf("NULL ");(*pi)++;return NULL;}//创建一个新的二叉树的节点BTNode* dst = BuyNode(a[*pi]); printf("%c ", dst->_data);(*pi)++;//将我们之前开创的节点的左右指针指向数组中所对应的节点//如果我们的对应数组中的数据不为空的话,我们的左右指针都会指向新的对应的节点//如果我们的节点为空的话,我们会得到的返回值为NULLdst->_left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, pi);dst->_right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, pi);return dst;
}//二叉树的销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root)
{if (*root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->_left));BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->_right));free(*root);*root = NULL;return;}//计算二叉树的节点个数int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{//用静态变量(在堆上,不在栈上)改变局部变量 -> 使得递归的size可以累加起来,但是局部的静态只能初始化一次/*static int size = 0;if (root == NULL){return 0;}else++size;BinaryTreeSize(root->_left);BinaryTreeSize(root->_right);*///如果我们当前的节点为空,也就是说我们已经到了叶子节点的左右节点,也就是没有节点//所以我们需要返回0if (root == NULL){return 0;}//如果我们当前的节点的左指针和右指针都是空的话,也就是说这是我们的叶子节点//就返回1,也就是只有一个节点if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL){return 1;}//使用递归遍历我们的二叉树,即分别统计我们左子树的节点个数再加上右子树中的节点个数再加上1//因为我们需要将我们当前所指的节点算上return BinaryTreeSize(root->_left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->_right) + 1;}//统计二叉树叶子节点的个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}//如果我们的节点的左右指针全部都为空,那就是我们的叶子节点if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL){return 1;}//返回我们左子树中的叶子节点和右子树中的叶子节点之和return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->_left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->_right);
}// 二叉树第k层节点个数int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (k == 1){return 1;}//分别遍历我们的左右子树,并且将我们的k的参数--,当我们的k为1时,就到达了我们所想要查找对应的层return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->_left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->_right, k - 1);
}// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->_data == x){return root;}BTNode* ret1 = BinaryTreeFind(root->_left, x);if (ret1){return ret1;}/*BTNode* ret2 = BinaryTreeFind(root->_right, x);if (ret2){return ret2;}return NULL;*/return BinaryTreeFind(root->_right, x);
}// 二叉树前序遍历
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return;}printf("%c ", root->_data);BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->_left);BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->_right);}// 二叉树中序遍历
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeInOrder(root->_left);printf("%c ", root->_data);BinaryTreeInOrder(root->_right);}// 二叉树后序遍历
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreePostOrder(root->_left);BinaryTreePostOrder(root->_right);printf("%c ", root->_data);}// 层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%c ", front->_data);if (front->_left)QueuePush(&q, front->_left);if (front->_right)QueuePush(&q, front->_right);}QueueDestroy(&q);
}// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//遇到第一个空,就可以开始判断,如果队列中还有非空,就不是完全二叉树if (front == NULL){break; }QueuePush(&q, front->_left);QueuePush(&q, front->_right);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//如果有非空,就不是完全二叉树if (front){QueueDestroy(&q);printf("不是完全二叉树\n");return 0;}}QueueDestroy(&q);printf("是完全二叉树\n");return 1;
}int TreeHigh(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int lefthigh = TreeHigh(root->_left);int righthigh = TreeHigh(root->_right);return lefthigh > righthigh ? lefthigh + 1 : righthigh + 1;//return TreeHigh(root->_left) > TreeHigh(root->_right) ? TreeHigh(root->_left) + 1 : TreeHigh(root->_right) + 1;
}3.3 Queue.h
#pragma once#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType val;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
//队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
3.4 Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"Queue.h"void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;if (pq->ptail == NULL){pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}//队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(QueueSize(pq) != 0);//一个节点if (pq->phead == pq->ptail){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}//多个节点else{QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->phead);return pq->phead->val;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->ptail);return pq->ptail->val;
}bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;
}3.5 Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "Tree.h"int main()
{char a[] = { 'A','B','D','#','#','E','#','H','#','#','C','F','#','#','G','#','#' };int b = 0;int* pi = &b;BTNode* Btree = BinaryTreeCreate(a, 16, pi);printf("\n");//前序遍历BinaryTreePrevOrder(Btree);printf("\n");//中序遍历BinaryTreeInOrder(Btree);printf("\n");//后序遍历BinaryTreePostOrder(Btree);printf("\n");//层次遍历BinaryTreeLevelOrder(Btree);printf("\n");int number = BinaryTreeSize(Btree);printf("%d", number);printf("\n");//查找为x的节点BTNode* find = BinaryTreeFind(Btree, 'A');printf("%c", find->_data);printf("\n");//查询第K层的节点个数int W = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(Btree, 3);printf("%d\n", W);//查询叶子节点的个数int count = BinaryTreeLeafSize(Btree);printf("%d\n", count);//判断当前是否为一颗完全二叉树int ret = BinaryTreeComplete(Btree);int x = TreeHigh(Btree);printf("%d\n", x);BinaryTreeDestory(&Btree);return 0;
}






![[office] Excel教学:Excel通配符怎么用? #其他#职场发展](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/66894084aebd2321ee9dd516f6e31f3e.gif)