文章目录
- 第1章 重构,第一个示例
- 1.1 重构前
- 1.2 重构后
- 第2章 重构原则
- 2.1 何谓重构
- 2.2 两顶帽子
- 2.3 为何重构
- 2.4 何时重构
- 2.5 重构和开发过程
第1章 重构,第一个示例
我这里使用的IDE是IntelliJ IDEA
1.1 重构前
- plays.js
export const plays = {"hamlet": {"name": "Hamlet", "type": "tragedy"},"as-like": {"name": "As You Like It", "type": "comedy"},"othello": {"name": "Othello", "type": "tragedy"}
};
- invoice.js
export const invoice = {"customer": "BigCo","performances": [{"playID": "hamlet","audience": 55},{"playID": "as-like","audience": 35},{"playID": "othello","audience": 40}]
}
- statement.js
import {plays} from "./plays.js";
import {invoice} from "./invoice.js";function statement(invoice, plays) {let totalAmount = 0;let volumeCredits = 0;let result = `Statement for ${invoice.customer}\n`;const format = new Intl.NumberFormat("en-US",{style: "currency", currency: "USD",minimumFractionDigits: 2}).format;for (let perf of invoice.performances) {const play = plays[perf.playID];let thisAmount = 0;switch (play.type) {case "tragedy":thisAmount = 40000;if (perf.audience > 30) {thisAmount += 1000 * (perf.audience - 30);}break;case "comedy":thisAmount = 30000;if (perf.audience > 20) {thisAmount += 10000 + 500 * (perf.audience - 20);}thisAmount += 300 * perf.audience;break;default:throw new Error(`unknown type: ${play.type}`);}// add volume creditsvolumeCredits += Math.max(perf.audience - 30, 0);// add extra credit for every ten comedy attendeesif ("comedy" === play.type) volumeCredits += Math.floor(perf.audience / 5);// print line for this orderresult += ` ${play.name}: ${format(thisAmount / 100)} (${perf.audience} seats)\n`;totalAmount += thisAmount;}result += `Amount owed is ${format(totalAmount / 100)}\n`;result += `You earned ${volumeCredits} credits\n`;return result;
}let res = statement(invoice, plays);
console.log(res);
- package.json
{"name": "untitled","version": "1.0.0","type": "module","dependencies": {}
}
运行结果
Statement for BigCoHamlet: $650.00 (55 seats)As You Like It: $580.00 (35 seats)Othello: $500.00 (40 seats)
Amount owed is $1,730.00
You earned 47 credits
1.2 重构后
- plays.js
export const plays = {"hamlet": {"name": "Hamlet", "type": "tragedy"},"as-like": {"name": "As You Like It", "type": "comedy"},"othello": {"name": "Othello", "type": "tragedy"}
};
- invoice.js
export const invoice = {"customer": "BigCo","performances": [{"playID": "hamlet","audience": 55},{"playID": "as-like","audience": 35},{"playID": "othello","audience": 40}]
}
- package.json
{"name": "untitled","version": "1.0.0","type": "module","dependencies": {}
}
- createStatementData.js
class PerformanceCalculator {constructor(aPerformance, aPlay) {this.performance = aPerformance;this.play = aPlay;}get volumeCredits() {return Math.max(this.performance.audience - 30, 0);}get amount() {throw new Error("subclass responsibility");}
}class TragedyCalculator extends PerformanceCalculator {get amount() {let result = 40000;if (this.performance.audience > 30) {result += 1000 * (this.performance.audience - 30);}return result;}
}class ComedyCalculator extends PerformanceCalculator {get amount() {let result = 30000;if (this.performance.audience > 20) {result += 10000 + 500 * (this.performance.audience - 20);}result += 300 * this.performance.audience;return result;}get volumeCredits() {return super.volumeCredits + Math.floor(this.performance.audience / 5);}
}function createPerformanceCalculator(aPerformance, aPlay) {switch (aPlay.type) {case "tragedy":return new TragedyCalculator(aPerformance, aPlay);case "comedy":return new ComedyCalculator(aPerformance, aPlay);default:throw new Error(`unknown type: ${aPlay.type}`);}
}export function createStatementData(invoice, plays) {const statementData = {};statementData.customer = invoice.customer;statementData.performances = invoice.performances.map(enrichPerformances);statementData.totalAmount = totalAmount(statementData);statementData.totalVolumeCredits = totalVolumeCredits(statementData);return statementData;function enrichPerformances(aPerformance) {const calculator = createPerformanceCalculator(aPerformance, playFor(aPerformance));const result = Object.assign({}, aPerformance);result.play = calculator.play;result.amount = calculator.amount;result.volumeCredits = calculator.volumeCredits;return result;}function playFor(aPerformance) {return plays[aPerformance.playID];}function totalAmount(data) {return data.performances.reduce((total, p) => total + p.amount, 0);}function totalVolumeCredits(data) {return data.performances.reduce((total, p) => total + p.volumeCredits, 0);}
}
- statement.js
import {plays} from "./plays.js";
import {invoice} from "./invoice.js";
import {createStatementData} from "./createStatementData.js";function statement(invoice, plays) {return renderPlainText(createStatementData(invoice, plays));
}function renderPlainText(data) {let result = `Statement for ${data.customer}\n`;for (let perf of data.performances) {result += ` ${perf.play.name}: ${usd(perf.amount)} (${perf.audience} seats)\n`;}result += `Amount owed is ${usd(data.totalAmount)}\n`;result += `You earned ${(data.totalVolumeCredits)} credits\n`;return result;
}function htmlStatement (invoice, plays) {return renderHtml(createStatementData(invoice, plays));
}
function renderHtml (data) {let result = `<h1>Statement for ${data.customer}</h1>\n`;result += "<table>\n";result += "<tr><th>play</th><th>seats</th><th>cost</th></tr>";for (let perf of data.performances) {result += ` <tr><td>${perf.play.name}</td><td>${perf.audience}</td>`;result += `<td>${usd(perf.amount)}</td></tr>\n`;}result += "</table>\n";result += `<p>Amount owed is <em>${usd(data.totalAmount)}</em></p>\n`;result += `<p>You earned <em>${data.totalVolumeCredits}</em> credits</p>\n`;return result;
}function usd(aNumber) {return new Intl.NumberFormat("en-US",{style: "currency", currency: "USD",minimumFractionDigits: 2}).format(aNumber / 100);
}let res = statement(invoice, plays);
console.log(res);
let assert_res = "Statement for BigCo\n" +" Hamlet: $650.00 (55 seats)\n" +" As You Like It: $580.00 (35 seats)\n" +" Othello: $500.00 (40 seats)\n" +"Amount owed is $1,730.00\n" +"You earned 47 credits\n"console.log(res === assert_res)
第2章 重构原则
2.1 何谓重构
重构(名词):在不改变软件可观察行为的前提下,提高其可理解性,降低其修改成本。
重构(动词):使用重构手法,在不改变软件可观察行为的前提下,调整其结构。
重构的过程中,代码必须保持可用。如果重构导致代码不可用,那么它不可以称之为重构。
重构与性能优化的对比
| 重构 | 性能优化 |
|---|---|
| 都修改代码,都不改变系统功能 | 都修改代码,都不改变系统功能 |
| 为了可读性,为了可扩展性 | 为了提升系统性能 |
2.2 两顶帽子
- 添加新功能:不应该修改已有代码,只关注新功能。增加新测试,通过测试衡量工作进度
- 重构:只改变程序内部结构,不应该添加测试(存在遗漏),不修改测试(除非接口发生变化)
- 软件开发在这两者之间切换
2.3 为何重构
- 改进软件设计:程序的设计在没有重构的情况下逐渐腐败变质,功能的增加或者修改可能使代码越来越难以理解。
- 软件更容易理解:提高代码可读性。
- 帮助找出bug:这个是建立在代码容易理解之上的。
- 提高编程速度:良好设计降低开发和理解成本。
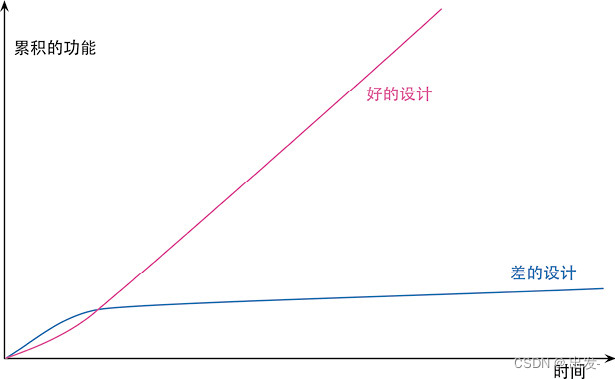
2.4 何时重构
- 事不过三,三则重构:重复性问题若出现三次,就应该考虑重构。
见机行事重构
- 预备性重构:最佳时机是在添加新功能之前进行,磨刀不误砍柴工。
- 阅读时重构:遇到难以理解的代码时,考虑是否可以通过重构使其更清晰。
- 人的思考资源宝贵:重构就是把理解转移到代码中,沉淀知识。
- 捡垃圾式重构:“童子军军规”——至少让营地比你来时更干净。
有计划的重构
-
日常编程中的重构:重构应是为了自己,而非单独排期。
-
长期重构:大型重构应由整个团队共同参与,逐步推进。
-
CodeReview时的重构:考虑他人的理解,提高代码和设计的可读性。
-
添加功能时重构:一方面可能是需要理解需要修改的代码,另一方面是使增加新特性更加容易。
-
修补错误时重构:出现bug的时候,难以找出问题所在的时候,很有可能是代码不清晰导致查找bug的困难。
何时不应重构
- 不需人理解的抽象代码:不需人常常修改,可放任自流。
- 重写成本低于重构:若从头开始更经济,无需重构。
2.5 重构和开发过程
重构中不断集成,基于主干开发,保证自测试用例的完整性,CI(持续集成)、自动化测试和重构是不可分割的三位一体。





![拓扑排序[讲课留档]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/0b8cfc92ecea4441b8020b2bd6d8c1cb.png)