- Request 存东西
- Response
- Session 存东西
- Application [ SerlvetContext ] 存东西
- config [ SerlvetConfig ]
- out/target
- page 不用了解
- exception
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head><title>Title</title>
</head>
<body><%-- 内置对象--%>
<%pageContext.setAttribute("name1","葱1");//保存的数据只在一个页面有效request.setAttribute("name2","葱2");//保存的数据只在一次请求中有效,请求转化会携带这个数据session.setAttribute("name3","葱3");//保存的数据只在一次会话中有效,从打开浏览器到关闭浏览器application.setAttribute("name4","葱4");//保存的数据只在服务器中有效,从打开服务器到关闭服务器
%>
<%--脚本片段中的代码,会被原封不动生成到......jsp.java文件中....--%>
<%--要求:这里的代码:必须保证java语法的正确性--%>
<%
// 通过pageContext取出我们保存的值pageContext.getAttribute();request.getAttribute();session.getAttribute();application.getAttribute();
%>
<%//从pageContext取出,我们通过寻找的方式来//从底层到高层(作用域)String name1 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("name1");String name2 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("name2");String name3 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("name3");String name4 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("name4");
%>
<h1>取出的值为:</h1>
<h3>${name1}</h3>
<h3>${name2}</h3>
<h3>${name3}</h3>
<h3>${name4}</h3>
</body>
</html>
层级结构
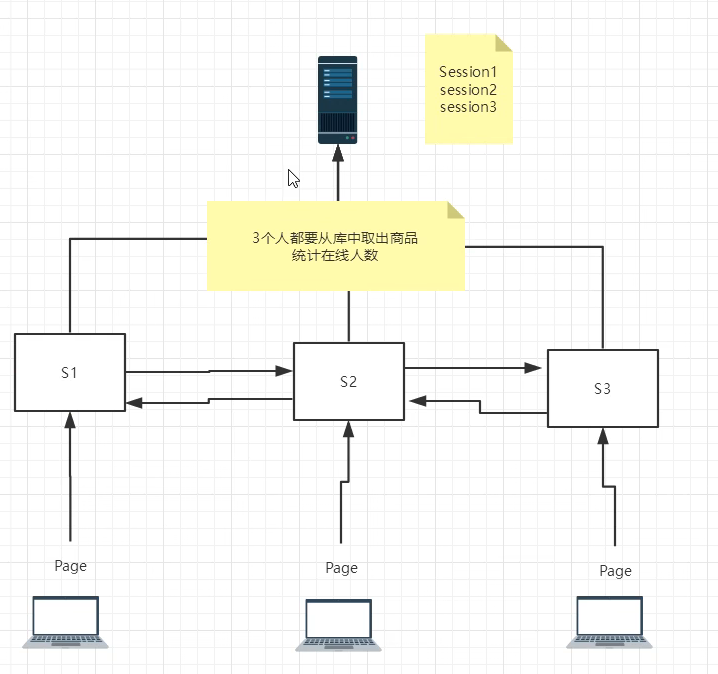
//scope:作用域
public void setattribute(string name, object attribute, int scope) t
switch(scope){
case 1:
this.mpage.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 2:
this.mrequest.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 3:
this.msession.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 4:
this.mapp.put(name, attribute);
break;
default:
throw new illegalargumentexception("bad scope " + scope);request:客户端向服务端发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,比如新闻,用户看完没用的
session:客户端向服务端发送请求,产生的数据,用户用完一会还有用,比如购物车
application:客户端向服务端发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户用完了,其他用户还可能使用,比如聊天数据