【基本内容】
二、Set接口(接上一章)
Set是Java集合框架中不允许有重复元素的无序集合,其典型的实现类是HashSet,它完全是遵循Set接口特性规范实现的,无序且不允许元素重复;而Set接口下的实现类还有LinkedHashSet和TreeSort,两者实现了有序的Set。Set接口及其实现类的完整继承关系如下图:
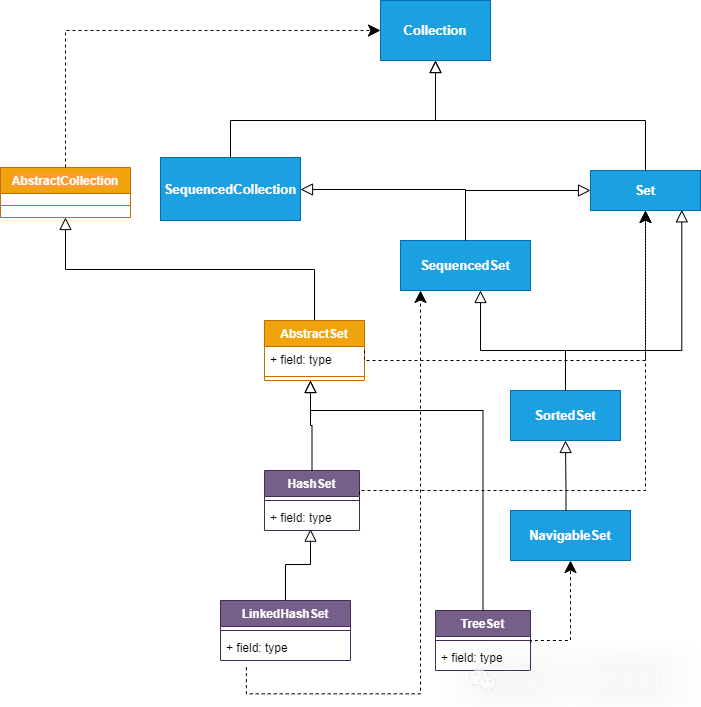
从上述继承图可以看出,HashSet只是继承了抽象类AbastractSet和实现了Set接口,是比较典型的Set接口的实现,而LinkedHashSet和TreeSet则都实现了SequencedSet接口,以此保证元素的有序。下面对三个实现类作具体介绍。
HashSet
HashSet的特性基本上等同Set接口的特性:无序且不能元素重复。从HashSet的命名来看,其底层存储实现和哈希表有关,那HashSet实现类是如何实现元素不能重复的呢?我们不妨看看HashSet的源代码:
public class HashSet<E>extends AbstractSet<E>implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{@java.io.Serialstatic final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;transient HashMap<E,Object> map;// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Mapstatic final Object PRESENT = new Object();/*** Constructs a new, empty set; the backing {@code HashMap} instance has* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).*/public HashSet() {map = new HashMap<>();}/*** Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified* collection. The {@code HashMap} is created with default load factor* (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to contain the elements in* the specified collection.** @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this set* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {map = HashMap.newHashMap(Math.max(c.size(), 12));addAll(c);}......HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);}} 从上述HashSet的源代码定义可以看出,HashSet底层是采用Java集合框架双列集合HashMap来存储数据元素的,而我们知道HashMap底层是主要采用哈希表实现,那HashSet是如何通过HashMap实现元素不能重复的呢?我们继续看源代码:
public Iterator<E> iterator() {return map.keySet().iterator();}......public boolean contains(Object o) {return map.containsKey(o);}/*** Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.* More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if* this set contains no element {@code e2} such that* {@code Objects.equals(e, e2)}.* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set* unchanged and returns {@code false}.** @param e element to be added to this set* @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified* element*/public boolean add(E e) {return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;}/*** Removes the specified element from this set if it is present.* More formally, removes an element {@code e} such that* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)},* if this set contains such an element. Returns {@code true} if* this set contained the element (or equivalently, if this set* changed as a result of the call). (This set will not contain the* element once the call returns.)** @param o object to be removed from this set, if present* @return {@code true} if the set contained the specified element*/public boolean remove(Object o) {return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;}从上述HashSet增删元素的方法实现中,我们可以看到HashSet是把元素作为内部HashMap的键,把一个不可变的常量对象PRESENT作为内部HashMap的值;我们都知道HashMap的键是哈希值是唯一的,如果HashSet添加的新元素和HashMap的某个键重复,HashMap的键自然会被覆盖,因而不会出现重复;而HashSet获取元素的时候,也是获取内部HashMap的键的列表。至于HashMap的键如何保持唯一性,不是还会有哈希冲突吗?相关知识请看后续Java集合框架相关文章。
总之,HashSet通过内部HashMap的键实现了元素的唯一性和不重复,同时因为底层采用哈希表实现,通过哈希键值能快速定位元素,因而具有高效的随机访问和快速查找能力。
LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类,所以自然具备HashSet快速查找元素和不允许重复元素的特性,但是为了保证元素的有序性,LinkedHashSet通过内置了一个双向链表来维护所有元素,从而可以利用迭代器快速遍历元素和保证元素存取的有序性。那LinkedHashSet内部是如何实现这样一个双向链表的呢?其实双向链表的实现不在LinkedHashSet的源代码中,双向链表的功能是通过其内部的LinkedHashMap来实现的,我们看LinkedHashSet的源代码:
public class LinkedHashSet<E>extends HashSet<E>implements SequencedSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {....../*** Constructs a new, empty linked hash set with the specified initial* capacity and load factor.** @apiNote* To create a {@code LinkedHashSet} with an initial capacity that accommodates* an expected number of elements, use {@link #newLinkedHashSet(int) newLinkedHashSet}.** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the linked hash set* @param loadFactor the load factor of the linked hash set* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive*/public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, true);}/*** Constructs a new, empty linked hash set with the specified initial* capacity and the default load factor (0.75).** @apiNote* To create a {@code LinkedHashSet} with an initial capacity that accommodates* an expected number of elements, use {@link #newLinkedHashSet(int) newLinkedHashSet}.** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the LinkedHashSet* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less* than zero*/public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity) {super(initialCapacity, .75f, true);}/*** Constructs a new, empty linked hash set with the default initial* capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).*/public LinkedHashSet() {super(16, .75f, true);}......}从上述代码中可以看出,LinkedHashSet的构造函数都调用了基类的构造函数,这个基类正是HashSet,我们再回头看看HashSet的构造函数代码,其实现如下:
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);}HashSet的构造函数之一正是新创建了一个LinkedHashMap,正是这个LinkedHashMap实现了双向链表的功能从而有效地支持了LinkedHashSet元素存取的有效性,同时也保留了基于哈希键值快速定位元素的特性以及唯一性。从后续的代码也可以看出,LinkedHashSet的其他操作都是通过这个内部的LinkedHashMap来进行的。代码如下:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")LinkedHashMap<E, Object> map() {return (LinkedHashMap<E, Object>) map;}/*** {@inheritDoc}* <p>* If this set already contains the element, it is relocated if necessary so that it is* first in encounter order.** @since 21*/public void addFirst(E e) {map().putFirst(e, PRESENT);}/*** {@inheritDoc}* <p>* If this set already contains the element, it is relocated if necessary so that it is* last in encounter order.** @since 21*/public void addLast(E e) {map().putLast(e, PRESENT);}/*** {@inheritDoc}** @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}* @since 21*/public E getFirst() {return map().sequencedKeySet().getFirst();}/*** {@inheritDoc}** @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}* @since 21*/public E getLast() {return map().sequencedKeySet().getLast();}/*** {@inheritDoc}** @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}* @since 21*/public E removeFirst() {return map().sequencedKeySet().removeFirst();}/*** {@inheritDoc}** @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}* @since 21*/public E removeLast() {return map().sequencedKeySet().removeLast();}/*** {@inheritDoc}* <p>* Modifications to the reversed view are permitted and will be propagated to this set.* In addition, modifications to this set will be visible in the reversed view.** @return {@inheritDoc}* @since 21*/public SequencedSet<E> reversed() {class ReverseLinkedHashSetView extends AbstractSet<E> implements SequencedSet<E> {public int size() { return LinkedHashSet.this.size(); }public Iterator<E> iterator() { return map().sequencedKeySet().reversed().iterator(); }public boolean add(E e) { return LinkedHashSet.this.add(e); }public void addFirst(E e) { LinkedHashSet.this.addLast(e); }public void addLast(E e) { LinkedHashSet.this.addFirst(e); }public E getFirst() { return LinkedHashSet.this.getLast(); }public E getLast() { return LinkedHashSet.this.getFirst(); }public E removeFirst() { return LinkedHashSet.this.removeLast(); }public E removeLast() { return LinkedHashSet.this.removeFirst(); }public SequencedSet<E> reversed() { return LinkedHashSet.this; }public Object[] toArray() { return map().keysToArray(new Object[map.size()], true); }public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { return map().keysToArray(map.prepareArray(a), true); }}return new ReverseLinkedHashSetView();}包括实现SequencedSet接口的反向操作,间接都是通过内部的LinkedHashMap来最终完成的。至于LinkedHashMap内部如何实现双向链表的功能,我们暂时把它当做一个黑盒,在后面的Java集合框架章节中去深入了解。
总之,LinkedHashSet是通过内部的LinkedHashMap保留了基类HashSet的特性,同时又实现了元素存取的有序性,但是因为维护内部的双向链表,在性能上逊色HashSet。
它的应用场景:1. 在一个流式处理数据的应用中,需要对元素进行去重和排序操作;2. 在一个多线程爬虫程序中,需要对爬取到的URL进行去重操作,就可以使用LinkedHashSet来避免并发修改异常。
TreeSet
TreeSet是Set接口家族中的一员,它和HashSet以及LinkedHashSet一样,不允许元素重复,同样无法保证线程安全,具体区别如下表:
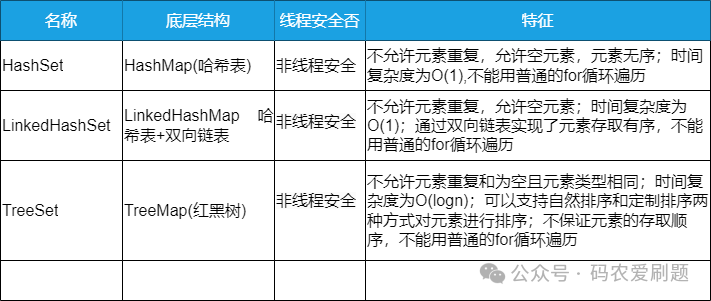
TreeSet底层是通过红黑树实现了对元素的排序,但是是通过内部的TreeMap来实现的,红黑树的具体逻辑在TreeMap代码中实现,这点HashSet、LinkedHashSet和TreeSet三者都是一样的,依赖的都是对应的Map集合类。
TreeSet默认是自然排序,按元素的大小进行排序,具体规则如下:
1.对于数值类型:Integer、Double,默认按照从小到大的顺序进行排序。2.对于字符、字符串类型:按照字符在ASCII码表中的数字升序进行排序。
参考代码如下:
import java.util.TreeSet;public class TreeSetExample {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();// 添加元素set.add(20);set.add(10); set.add(30);set.add(40);// 尝试添加重复元素boolean isAdded = set.add(20); // 返回 false// 获取第一个和最后一个元素int first = set.first(); // 返回 10int last = set.last(); // 返回 40// 遍历 TreeSetfor (Integer num : set) {System.out.println(num);} // 输出顺序为:10 ,20, 30 ,40}
}自然排序主要应用于Jdk内置的数据类型,对于用户自定义类型需要采用定制排序,定制排序有两种方式:方法一、放入TreeSet集合的元素需要实现接口java.lang.Comparable接口,例如以下代码:
public class TreeSetTest04 {public static void main(String[] args) {Person1 p1 = new Person1(32);Person1 p2 = new Person1(20);Person1 p3 = new Person1(25);TreeSet<Person1> ts = new TreeSet<>();ts.add(p1);ts.add(p2);ts.add(p3);for (Person1 x:ts) {System.out.println(x);}}}/*** 放在TreeSet集合中的元素需要实现java.lang.Comparable接口* 并且实现compareTo方法。equals可以不写*/
class Person1 implements Comparable<Person1>{int age;public Person1(int age){this.age = age;}// 重写toString方法@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person1{" +"age=" + age +'}';}/*** 需要在这个比较的方法中编写比较的逻辑或者比较的规则,按照什么进行比较* 拿着参数k和集合中的每一个key进行比较,返回值可能是大于0 小于0 或者等于0* 比较规则最终还是由程序员指定的; 例如按照年龄升序,或者按照年龄降序。* @param o* @return*/@Overridepublic int compareTo(Person1 o) { // c1.compareTo(c2)return this.age-o.age; // >0 =0 <0 都有可能}
}方法二,在构造器TreeSet的时候给它传一个实现了Comparator比较器接口的对象,例如以下代码:
public class TreeSetTest06 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 此时创建TreeSet集合的时候,需要使用这个比较器。// TreeSet<WuGui> wuGui = new TreeSet<>(); // 这样不行,没有通过构造方法传递一个比较器进去。// 给构造方法传递一个比较器TreeSet<WuGui> wuGui = new TreeSet<>(new WuGuiComparator()); // 底层源码可知其中一个构造方法的参数为比较器// 大家可以使用匿名内部类的方式wuGui.add(new WuGui(100));wuGui.add(new WuGui(10));wuGui.add(new WuGui(1000));for (WuGui wugui:wuGui) {System.out.println(wugui);}}
}
class WuGui {int age;public WuGui(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "WuGui{" +"age=" + age +'}';}
}
// 单独再这里编写一个比较器
// 比较器实现java.util.Comparator接口 (Comparable是java.lang包下的。Comparator是java.util包下的。)
class WuGuiComparator implements Comparator<WuGui>{@Overridepublic int compare(WuGui o1, WuGui o2) {// 指定比较规则// 按照年龄排序return o1.age-o2.age;}
}
两种方法适应场景如下:
1.比较规则经常变换: Comparator 接口的设计符合OCP原则(可切换)2.比较规则较固定: Comparable如果一个TreeSet集合两种比较方法都实现了,则以方法二比较器接口优先。
【注意事项】
1.自然排序的注意事项:如果字符串里的字符比较多,那么它就是从首字母开始,挨个比较的,要注意的是,此时跟字符串的长度是没有什么关系的,例如 "aaa" 和 "ab",在比较的时候,首先比第一个字母,发现第一个字母都是 a;继续往后来比第二个字母,第二个字母就不一样了,这个时候就已经能确定大小关系了,'a' 比 b 大,此时后面的就不会再看了。

码农爱刷题
为计算机编程爱好者和从业人士提供技术总结和分享 !为前行者蓄力,为后来者探路!