comments: true
difficulty: 简单
edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcof/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E9%A2%9868%20-%20I.%20%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E7%A5%96%E5%85%88/README.md
面试题 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
题目描述
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
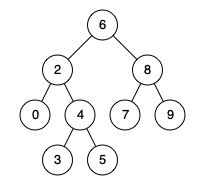
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 输出: 6 解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 输出: 2 解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
注意:本题与主站 235 题相同:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
解法
方法一:一次遍历
从上到下遍历二叉树,找到第一个值位于 [ p . v a l , . . q . v a l ] [p.val,.. q.val] [p.val,..q.val] 之间的结点即可【核心】。既可以用迭代实现,也可以用递归实现。
时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n 是二叉树的结点数。空间复杂度方面,迭代实现的空间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),递归实现的空间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = Noneclass Solution:def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:while 1:if root.val < p.val and root.val < q.val: # 说明p,q节点在右子树,因此公共祖先节点也应该向右边找root = root.rightelif root.val > p.val and root.val > q.val: # 反之,亦然root = root.leftelse:return root
Java
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {while (true) {if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {root = root.right;} else if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {root = root.left;} else {return root;}}}
}
C++
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if (root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);}if (root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);}return root;}
};
Go
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* type TreeNode struct {* Val int* Left *TreeNode* Right *TreeNode* }*/func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {if root.Val < p.Val && root.Val < q.Val {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)}if root.Val > p.Val && root.Val > q.Val {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q)}return root
}
TypeScript
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* class TreeNode {* val: number* left: TreeNode | null* right: TreeNode | null* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }* }*/
function lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode | null,p: TreeNode | null,q: TreeNode | null,
): TreeNode | null {if (root == null) {return root;}if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);}if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);}return root;
}
Rust
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {pub fn lowest_common_ancestor(mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {let p = p.unwrap().borrow().val;let q = q.unwrap().borrow().val;loop {let mut cur = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().val;match (cur.cmp(&p), cur.cmp(&q)) {(Ordering::Less, Ordering::Less) => {root = root.unwrap().borrow().right.clone();}(Ordering::Greater, Ordering::Greater) => {root = root.unwrap().borrow().left.clone();}(_, _) => {break root;}}}}
}
JavaScript
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val) {* this.val = val;* this.left = this.right = null;* }*/
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {TreeNode} p* @param {TreeNode} q* @return {TreeNode}*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) {if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);} else if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);}return root;
};
方法二:递归
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = Noneclass Solution:def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':if root.val < p.val and root.val < q.val:return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)if root.val > p.val and root.val > q.val:return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)return root
Java
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);}if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);}return root;}
}
C++
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {while (1) {if (root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val) {root = root->right;} else if (root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val) {root = root->left;} else {return root;}}}
};
Go
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* type TreeNode struct {* Val int* Left *TreeNode* Right *TreeNode* }*/func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {for {if root.Val < p.Val && root.Val < q.Val {root = root.Right} else if root.Val > p.Val && root.Val > q.Val {root = root.Left} else {return root}}
}
TypeScript
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* class TreeNode {* val: number* left: TreeNode | null* right: TreeNode | null* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }* }*/
function lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode | null,p: TreeNode | null,q: TreeNode | null,
): TreeNode | null {if (root == null) {return root;}while (true) {if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {root = root.left;} else if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {root = root.right;} else {return root;}}
}
Swift
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* public var val: Int* public var left: TreeNode?* public var right: TreeNode?* public init(_ val: Int) {* self.val = val* self.left = nil* self.right = nil* }* }*/class Solution {func lowestCommonAncestor(_ root: TreeNode?, _ p: TreeNode?, _ q: TreeNode?) -> TreeNode? {guard let p = p, let q = q else {return nil}var node = rootwhile let current = node {if current.val < p.val && current.val < q.val {node = current.right} else if current.val > p.val && current.val > q.val {node = current.left} else {return current}}return nil}
}