更多SpringBoot3内容请关注我的专栏:《SpringBoot3》
期待您的点赞👍收藏⭐评论✍
重学SpringBoot3-集成Redis(三)之注解缓存策略设置
- 1. 引入 Redis 依赖
- 2. 配置 RedisCacheManager 及自定义过期策略
- 2.1 示例代码:自定义过期策略
- 3. 配置说明
- 4. 使用自定义的缓存区域
- 5. 验证
- 6. 总结
书接上回,重学SpringBoot3-集成Redis(二), Spring Boot 提供了对缓存的简便支持,使得开发者能够通过简单的注解实现缓存操作,减少重复代码的编写。本文将继续介绍如何在 Spring Boot 3 中通过注解驱动的方式针对不同缓存区域设置不同缓存策略。
在 Spring Boot 3 中,使用 RedisCacheManager 可以为不同的缓存区域(缓存名称)设置自定义的过期策略。通过为每个缓存区域创建不同的 RedisCacheConfiguration,你可以指定不同的过期时间(TTL)和其他缓存行为。以下是如何为不同的缓存区域设置自定义过期策略的详细说明。
1. 引入 Redis 依赖
首先确保你的 pom.xml 或 build.gradle 文件中已经引入了 Redis 相关的依赖。以 Maven 为例:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency>
2. 配置 RedisCacheManager 及自定义过期策略
通过创建自定义的 CacheManager,你可以为不同的缓存名称指定不同的 RedisCacheConfiguration,每个配置可以有不同的过期时间或序列化规则。
2.1 示例代码:自定义过期策略
package com.coderjia.boot310redis.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;/*** @author CoderJia* @create 2024/10/5 下午 12:36* @Description**/
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {// @Bean// public RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration() {// return RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()// .prefixCacheNameWith("coderjia:") // 设置缓存 Key 前缀// .entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10)) // 设置缓存过期时间为 10 分钟// .disableKeyPrefix()// .enableTimeToIdle()// .serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())) // 自定义 Key 序列化器// .serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer())); // 自定义 Value 序列化器// }@Beanpublic RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {// 创建默认的 RedisCacheConfiguration,并设置全局缓存过期时间RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(5)) // 默认全局缓存过期时间为5分钟.disableCachingNullValues(); // 禁止缓存 null 值// 为特定缓存配置不同的过期策略Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> cacheConfigurations = new HashMap<>();// 配置名为 "shortLivedCache" 的缓存,设置过期时间为1分钟cacheConfigurations.put("shortLivedCache",RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(1)) // 设置缓存的TTL为1分钟.disableCachingNullValues()); // 禁止缓存 null 值// 配置名为 "longLivedCache" 的缓存,设置过期时间为1小时cacheConfigurations.put("longLivedCache",RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)) // 设置缓存的TTL为1小时.disableCachingNullValues()); // 禁止缓存 null 值// 配置名为 "jsonCache" 的缓存,使用 JSON 序列化器cacheConfigurations.put("jsonCache",RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 30分钟过期.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())).serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer())).disableCachingNullValues()); // 禁止缓存 null 值// 创建 RedisCacheManager,加载自定义的缓存配置return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(defaultCacheConfig) // 设置默认的缓存配置.withInitialCacheConfigurations(cacheConfigurations) // 加载不同缓存区域的配置.build();}
}
3. 配置说明
-
defaultCacheConfig:这是默认的缓存配置,用于所有未显式定义的缓存区域。在上面的例子中,默认的 TTL 是 5 分钟。 -
cacheConfigurations.put("shortLivedCache", ...):为缓存名为"shortLivedCache"的区域设置了特定的过期时间为 1 分钟。这意味着,当你使用@Cacheable指定该缓存时,它的 TTL 将为 1 分钟。 -
cacheConfigurations.put("longLivedCache", ...):为缓存名为"longLivedCache"的区域设置了 1 小时的 TTL。这非常适合需要长时间保留的数据。 -
cacheConfigurations.put("jsonCache", ...):这个缓存区域使用 JSON 序列化器。这样可以确保键和值的序列化与反序列化是通过 JSON 格式完成的。
4. 使用自定义的缓存区域
在代码中使用这些自定义的缓存区域时,你可以通过 @Cacheable 注解指定不同的缓存名称。
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class UserService {// 当方法第一次调用时,结果将被缓存起来,之后相同参数的调用将直接从缓存中获取数据@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#p0")public User getUserById(Long id) {// 模拟数据库查询操作System.out.println("Fetching user with id: " + id);return new User(id, "User" + id);}// 使用短生命周期的缓存配置(1分钟)@Cacheable(value = "shortLivedCache", key = "#p0")public User getShortLivedUserById(Long id) {return findUserInDatabase(id);}// 使用长生命周期的缓存配置(1小时)@Cacheable(value = "longLivedCache", key = "#p0")public User getLongLivedUserById(Long id) {return findUserInDatabase(id);}// 使用 JSON 序列化的缓存(30分钟)@Cacheable(value = "jsonCache", key = "#p0")public User getJsonSerializedUserById(Long id) {return findUserInDatabase(id);}private User findUserInDatabase(Long userId) {// 模拟数据库查找return new User(userId, "John Doe");}
}
5. 验证
当调用 getUserById 时,缓存数据会存储在默认的缓存区域,数据会在 5 分钟后过期。
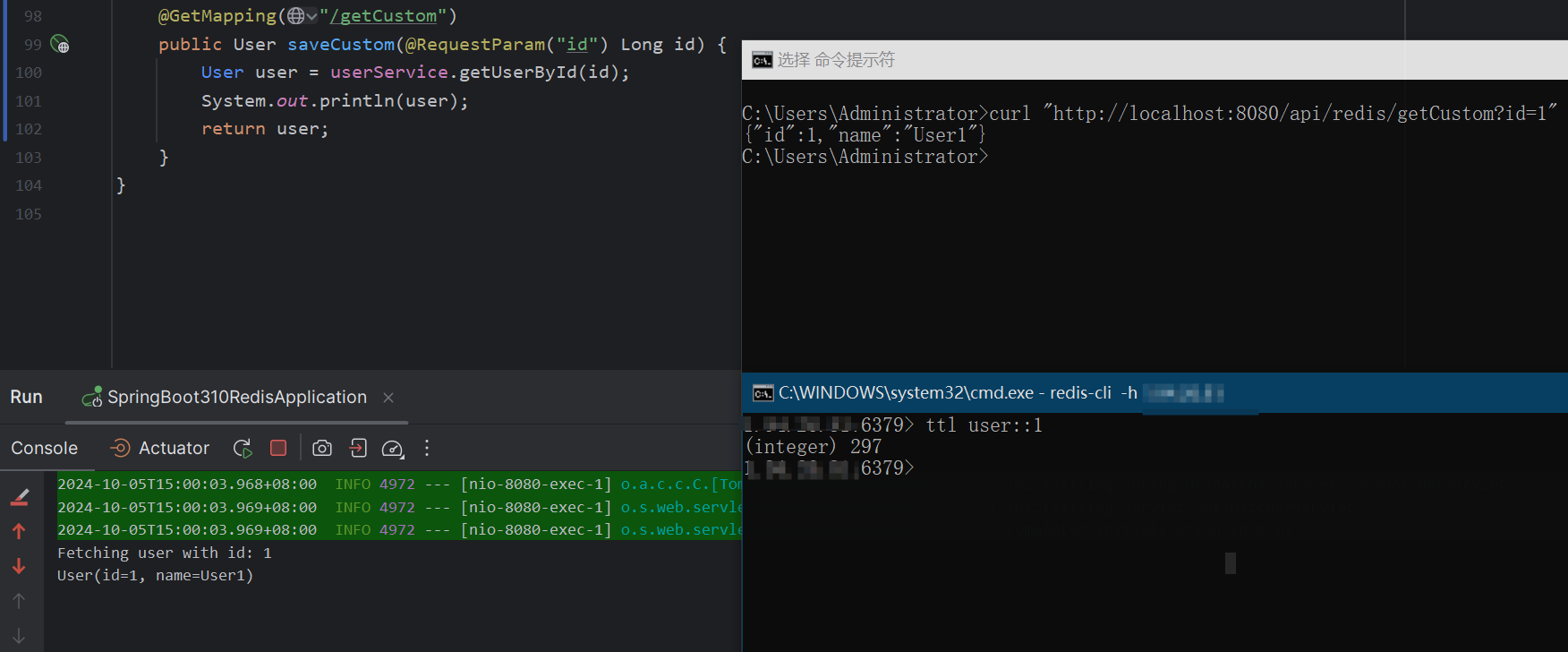
调用 getShortLivedUserById 时,数据会在 1 分钟后自动失效。
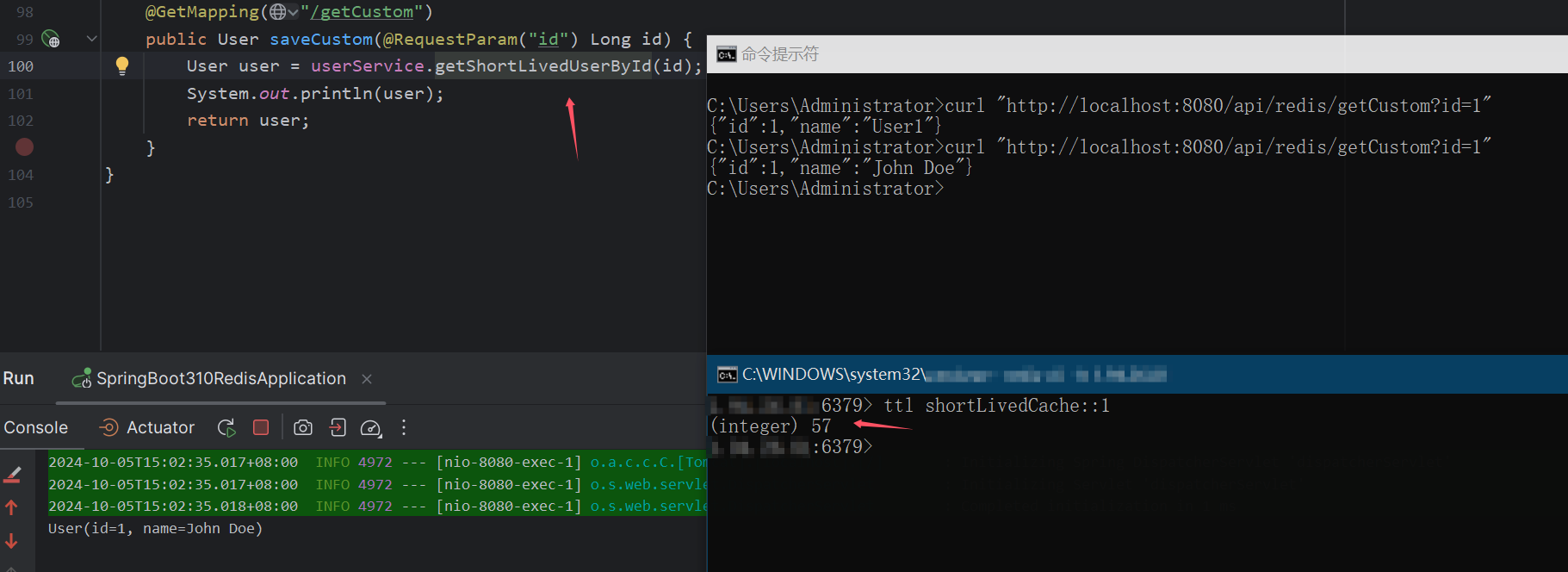
调用 getLongLivedUserById 时,缓存数据会在 1 小时后失效。
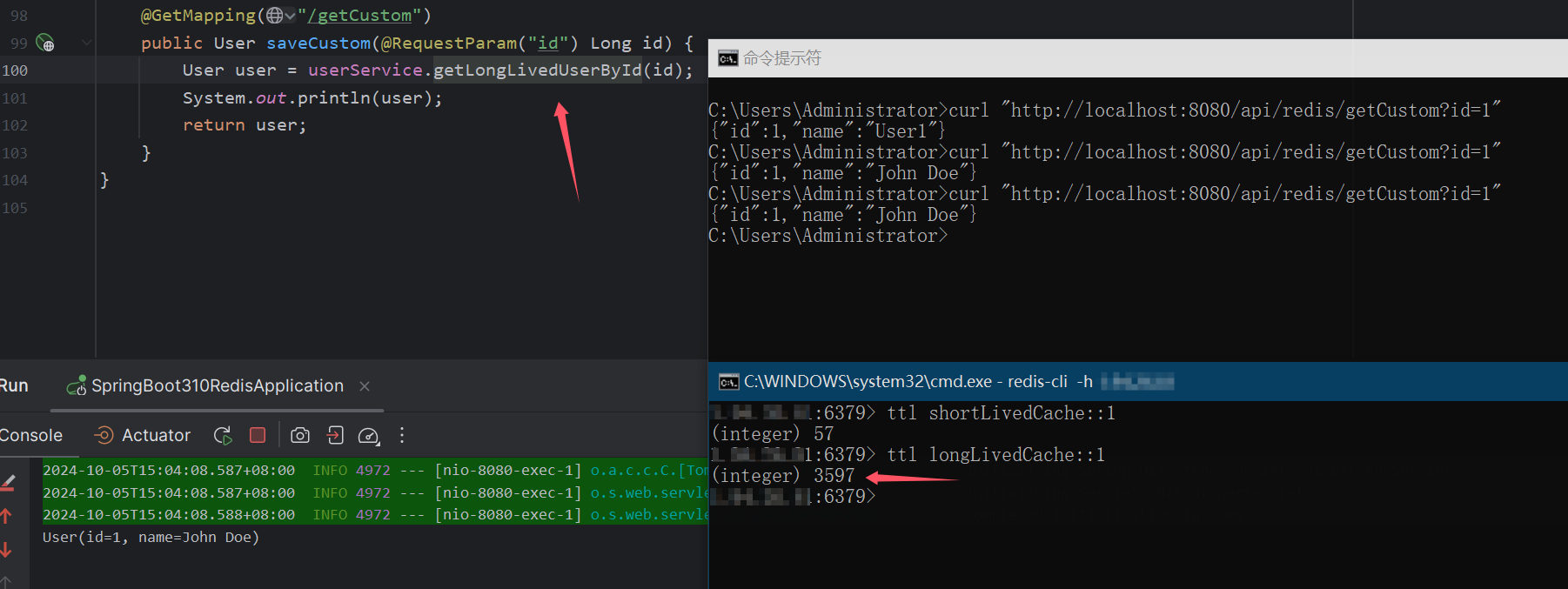
getJsonSerializedUserById 方法将数据以 JSON 格式序列化,并在 30 分钟后过期。

6. 总结
通过 RedisCacheManager 和 RedisCacheConfiguration,你可以为不同的缓存区域设置不同的 TTL、序列化策略、以及缓存行为。这样可以根据不同的业务场景调整缓存的生命周期,优化应用的性能。
为了更进一步完整代码,可以将缓存名称和对应有效期放入都配置文件中,更有利于线上环境根据实际情况调整缓存有效期,示例如下:
@Value("${cache.shortLiveCache.name}")
private String shortLiveCacheName;@Value("${cache.shortLiveCache.ttl}")
private long shortLiveCacheTtl;RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().cacheName(shortLiveCacheName).enableTimeToIdle(true).tti(Duration.ofSeconds(shortLiveCacheTtl));