一、题目
给 定 两 个 单 词 ( beginWord 和 endWord ) 和 一 个 字 典 , 找 到 从 beginWord 到
endWord 的最短转换序列的长度。转换需遵循如下规则:
1. 每次转换只能改变一个字母。
2. 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典中的单词。
说明 :
1、如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
2、 所有单词具有相同的长度。
3、所有单词只由小写字母组成。
4、 字典中不存在重复的单词。
5、你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
示例 1:

示例 2:

二、解题思路
解决方式一(一圈一圈往外扩散):
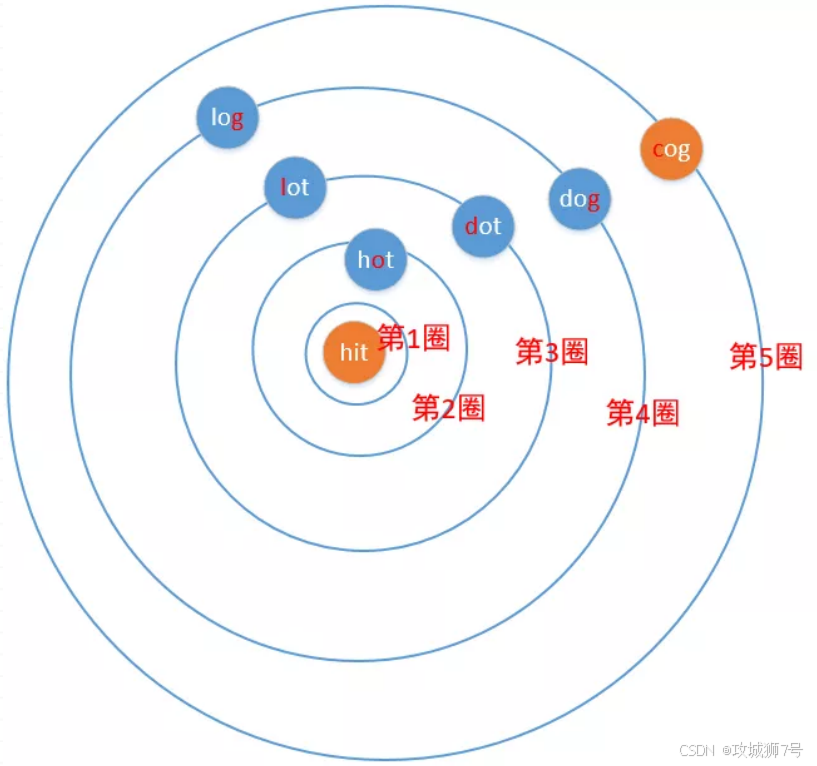
以beginWord为起点,将其视为第一圈。接着,将字典中与beginWord仅有一个字符差异的单词归入第二圈。随后,将与第二圈单词仅有一个字符差异且在字典中存在的单词纳入第三圈……以此类推。在扩展过程中,需确保不重复纳入已出现的单词,并且在遇到endWord时立即返回。
这里以示例1为例画个图看看
解决方式二(从两边往中间开始计算):
上述方法是从start开始向外扩散,但也可以采用双向扩散的策略:同时从start和end向中间推进。在每一步中,优先遍历元素较少的圈,这样可以减少循环的次数。如果在某个圈中相遇,则立即返回结果。
三、代码实现
方式一代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <queue>using namespace std;int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {// 把字典中的单词放入到set中,主要是为了方便查询unordered_set<string> dictSet(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());// 创建一个新的单词,记录单词是否被访问过,如果没被访问过就加入进来unordered_set<string> visit;// BFS中常见的队列,我们可以把它想象成为一颗二叉树,记录每一层的节点。// 或者把它想象成为一个图,记录挨着的节点,也就是每一圈的节点。这里我们把它想象成为一个图queue<string> queue;queue.push(beginWord);// 这里的图是一圈一圈往外扩散的,这里的minlen可以看做扩散了多少圈,// 也就是最短的转换序列长度int minlen = 1;while (!queue.empty()) {// 这里找出每个节点周围的节点数量,然后都遍历他们int levelCount = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < levelCount; i++) {// 出队string word = queue.front();queue.pop();// 这里遍历每一个节点的单词,然后修改其中一个字符,让他成为一个新的单词,// 并查看这个新的单词在字典中是否存在,如果存在并且没有被访问过,就加入到队列中for (int j = 0; j < word.length(); j++) {char ch[word.length()];strcpy(ch, word.c_str());for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {if (c == word[j])continue;ch[j] = c;// 修改其中的一个字符,然后重新构建一个新的单词string newWord(ch);// 查看字典中有没有这个单词,如果有并且没有被访问过,就加入到队列中// (unordered_set的insert方法表示把单词加入到队列中,如果set中没有这个单词// 就会添加成功,返回true。如果有这个单词,就会添加失败,返回false)if (dictSet.find(newWord) != dictSet.end() && visit.insert(newWord).second) {// 如果新单词是endWord就返回,这里访问的是第minlen圈的节点,然后// 新建的节点就是第minlen+1层if (newWord == endWord)return minlen + 1;queue.push(newWord);}}}}// 每往外扩一圈,长度就加1minlen++;}return 0;
}int main() {string beginWord = "hit";string endWord = "cog";vector<string> wordList = {"hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"};int result = ladderLength(beginWord, endWord, wordList);cout << "The shortest transformation sequence length is: " << result << endl;return 0;
}方式二代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <queue>using namespace std;int find(int minlen, queue<string>& startQueue, queue<string>& endQueue, unordered_set<string>& dictSet, unordered_set<string>& visit) {int startCount = startQueue.size();int endCount = endQueue.size();bool start = startCount <= endCount;int count = start ? startCount : endCount;// 哪个量少,遍历哪个for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {// 出队string word;if (start)word = startQueue.front();elseword = endQueue.front();if (start)startQueue.pop();elseendQueue.pop();// 这里遍历每一个节点的单词,然后修改其中一个字符,让他成为一个新的单词,// 并查看这个新的单词在字典中是否存在,如果存在并且没有被访问过,就加入到队列中for (int j = 0; j < word.length(); j++) {char ch[word.length() + 1];strcpy(ch, word.c_str());for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {if (c == word[j])continue;ch[j] = c;// 修改其中的一个字符,然后重新构建一个新的单词string newWord(ch);if (dictSet.find(newWord) != dictSet.end()) {if (start) { // 从前往后if (find(endQueue.begin(), endQueue.end(), newWord) != endQueue.end())return minlen + 1;if (visit.insert(newWord).second)startQueue.push(newWord);} else { // 从后往前if (find(startQueue.begin(), startQueue.end(), newWord) != startQueue.end())return minlen + 1;if (visit.insert(newWord).second)endQueue.push(newWord);}}}}}// 如果没有相遇就返回-1return -1;
}int main() {string beginWord = "hit";string endWord = "cog";vector<string> wordList = {"hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"};unordered_set<string> dictSet(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());unordered_set<string> visit;queue<string> startQueue;queue<string> endQueue;startQueue.push(beginWord);endQueue.push(endWord);int minlen = 1;int result = find(minlen, startQueue, endQueue, dictSet, visit);cout << "The shortest transformation sequence length is: " << result << endl;return 0;
} 这道题上两种方式都能解决,第2种方式比第一种稍微要复杂一些,但运行效率要比第1种高。