Title
题目
CoD-MIL: Chain-of-Diagnosis Prompting Multiple Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Classification
CoD-MIL: 基于诊断链提示的多实例学习用于全切片图像分类
01
文献速递介绍
病理检查被广泛视为肿瘤诊断的金标准,因为它为治疗决策和患者管理提供了关键信息。数字切片扫描仪的快速发展使得将传统病理切片高通量转换为全切片图像(WSI)成为可能。该研究得到了宁夏回族自治区重点研发项目资助(项目编号:2023BEG02023),部分资金来自中国工程科技知识中心项目。
Jiangbo Shi、Chen Li(通讯作者)和 Tieliang Gong 隶属于西安交通大学计算机科学与技术学院,地址:中国陕西省西安市,邮编 710049(电子邮件shijiangbo@stu.xjtu.edu.cn;cli@xjtu.edu.cn;gongtl@xjtu.edu.cn)。Chunbao Wang 隶属于西安交通大学第一附属医院病理科,地址:中国陕西省西安市,邮编 710061(电子邮件:bingliziliao2012@163.com)。Huazhu Fu(通讯作者)隶属于新加坡科学技术研究局(ASTAR)高性能计算研究所(IHPC),地址:新加坡,邮编 138632(电子邮件:hzfu@ieee.org)。
全切片图像(WSI)具有金字塔结构和巨大的尺寸,通常在最高放大倍率下包含数十亿像素(0.25 µm/像素)。因此,WSI 的像素级标注非常耗时且劳动密集 。目前,多实例学习(MIL) 已成为处理 WSI 的主要方法,仅利用切片级别的标注。
Aastract
摘要
Multiple instance learning (MIL) has emergedas a prominent paradigm for processing the whole slideimage with pyramid structure and giga-pixel size in digitalpathology. However, existing attention-based MIL methodsare primarily trained on the image modality and a predefined label set, leading to limited generalization and interpretability. Recently, vision language models (VLM) haveachieved promising performance and transferability, offering potential solutions to the limitations of MIL-based methods. Pathological diagnosis is an intricate process thatrequires pathologists to examine the WSI step-by-step. Inthe field of natural language process, the chain-of-thought(CoT) prompting method is widely utilized to imitate thehuman reasoning process. Inspired by the CoT promptand pathologists’ clinic knowledge, we propose a chainof-diagnosis prompting multiple instance learning (CoDMIL) framework for whole slide image classification. Specifically, the chain-of-diagnosis text prompt decomposes thecomplex diagnostic process in WSI into progressive subprocesses from low to high magnification. Additionally,we propose a text-guided contrastive masking module toaccurately localize the tumor region by masking the mostdiscriminative instances and introducing the guidance ofnormal tissue texts in a contrastive way. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world subtyping datasetsdemonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of CoD-MIL.
多实例学习(MIL)已成为数字病理学中处理具有金字塔结构和超大像素大小的全切片图像的主要方法。然而,现有基于注意力的 MIL 方法主要在图像模态和预定义的标签集上进行训练,导致其泛化性和可解释性受限。最近,视觉语言模型(VLM)取得了令人鼓舞的性能和可迁移性,为 MIL 方法的局限性提供了潜在解决方案。病理诊断是一个复杂的过程,需要病理学家逐步检查全切片图像(WSI)。在自然语言处理中,链式思维(CoT)提示方法被广泛用于模拟人类的推理过程。受 CoT 提示和病理学家临床知识的启发,我们提出了一种用于全切片图像分类的基于诊断链提示的多实例学习(CoD-MIL)框架。具体来说,诊断链文本提示将 WSI 中的复杂诊断过程分解为从低倍到高倍放大的渐进子过程。此外,我们提出了一种文本引导的对比掩模模块,通过掩盖最具辨别力的实例并引入正常组织文本的对比性指导,以准确定位肿瘤区域。在三个真实世界的亚型数据集上进行的大量实验表明了 CoD-MIL 的有效性和优越性。
Method
方法
A. Attention-based Multiple Instance Learning
In MIL, a WSI (i.e., bag) W = {Wl , Wh} is croppedinto a series of patches (i.e., instances) P = {Pl ∈R Nl×N0×N0×3 , Ph ∈ R Nh×N0×N0×3} by the non-overlappingsliding window method. Wl and Wh denote the slides at lowand high magnifications; Pl and Ph represent the corresponding patches to Wl and Wh; Nl and Nh denote the patchnumber of Pl and Ph; and N0 is the patch size. To identifythe corresponding spatial relations of patches between twomagnifications, we define an alignment matrix M ∈ R Nl×Nh .
A. 基于注意力的多实例学习
在多实例学习(MIL)中,全切片图像(WSI,即包)W = {Wl, Wh} 被通过无重叠滑动窗口方法裁剪为一系列小块(即实例)P = {Pl ∈ R Nl×N0×N0×3, Ph ∈ R Nh×N0×N0×3}。其中,Wl 和 Wh 分别表示低倍和高倍放大倍率下的切片;Pl 和 Ph 分别代表与 Wl 和 Wh 对应的小块;Nl 和 Nh 表示 Pl 和 Ph 的小块数量;N0 为小块的尺寸。为了识别两个放大倍率之间小块的对应空间关系,我们定义了一个对齐矩阵 M ∈ R Nl×Nh。
Conclusion
结论
In this work, we proposed a chain-of-diagnosis promptingmultiple instance learning framework (CoD-MIL) for wholeslide image classification. Inspired by the chain-of-thoughtprompt in NLP and the diagnostic prior of pathologists,our chain-of-diagnosis text prompt decomposed the complexdiagnostic process into a series of progressive sub-processesin WSI from low to high magnification. Moreover, we alsoproposed a text-guide contrastive masking module to improvethe model’s ability to accurately locate the tumor region byintroducing the normal tissue texts as the negative corpusin a contrastive way. Extensive comparative and ablationexperiments demonstrated that CoD-MIL achieved new stateof-the-art results for whole slide image classification.
在本研究中,我们提出了一种用于全视野图像分类的链式诊断提示多实例学习框架 (CoD-MIL)。受自然语言处理中的链式思维提示和病理学家诊断先验的启发,我们的链式诊断文本提示将复杂的诊断过程分解为在全视野图像中从低倍到高倍的系列渐进子过程。此外,我们还提出了一种文本引导的对比遮罩模块,通过引入正常组织的文本作为对比中的负样本,提升模型准确定位肿瘤区域的能力。大量的对比实验和消融实验表明,CoD-MIL 在全视野图像分类中达到了新的最先进结果。
Figure
图
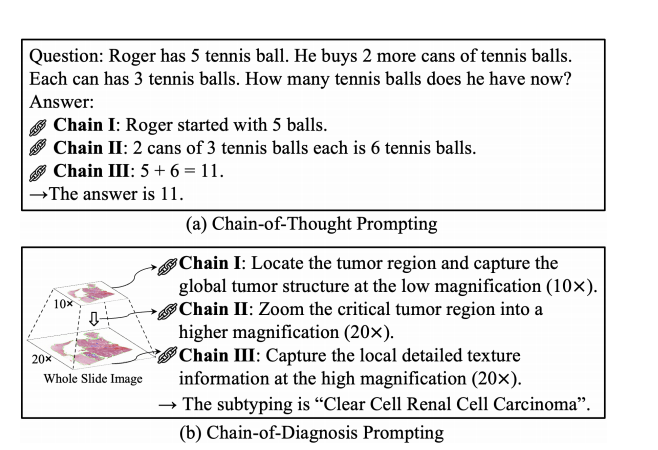
Fig. 1. Illustration on chain-of-thought (CoT) and our chain-of-diagnosis (CoD) prompting methods.
图1. 链式思维(CoT)和我们提出的诊断链(CoD)提示方法的示意图。
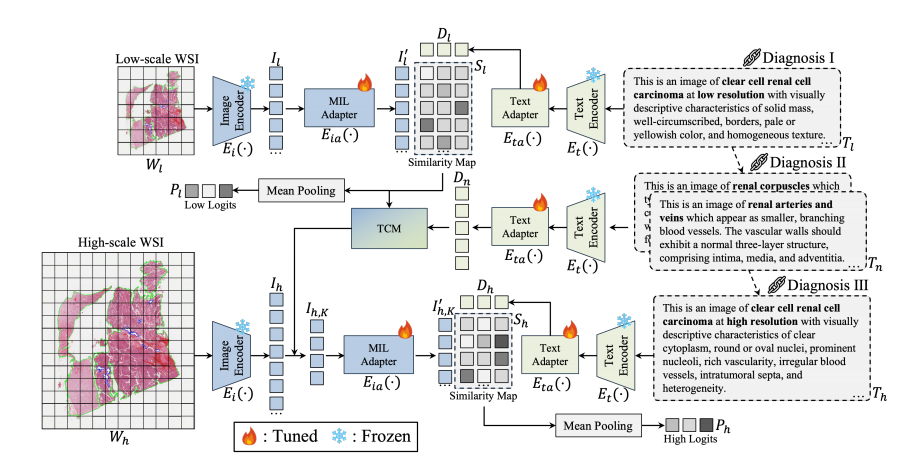
Fig. 2. Illustration of the proposed CoD-MIL framework. The input of the CoD-MIL is the multi-scale WSIs and the chain-of-diagnosis text prompt.TCM is the text-guided contrastive masking module to improve the model’s performance and interpretability. The output is the summation of twoscale slide logits.
图2. 所提出的 CoD-MIL 框架示意图。CoD-MIL 的输入包括多尺度全切片图像(WSIs)和诊断链文本提示。TCM 是文本引导的对比掩模模块,用于提升模型的性能和可解释性。输出是两个尺度切片 logits 的总和。
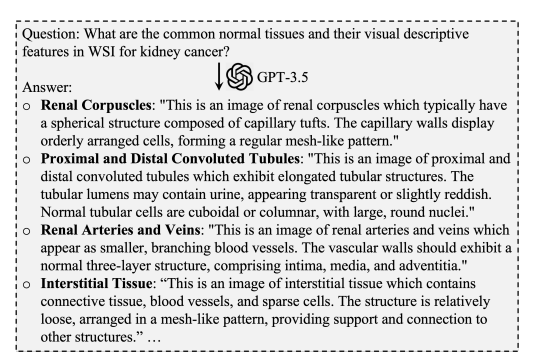
Fig. 3. The second diagnostic chain text prompts of the normal tissues.
图3. 正常组织的第二条诊断链文本提示。
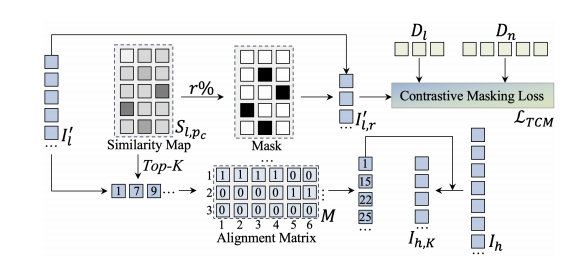
Fig. 4. Text-guided Contrastive Masking Module.
图4. 文本引导的对比掩模模块。
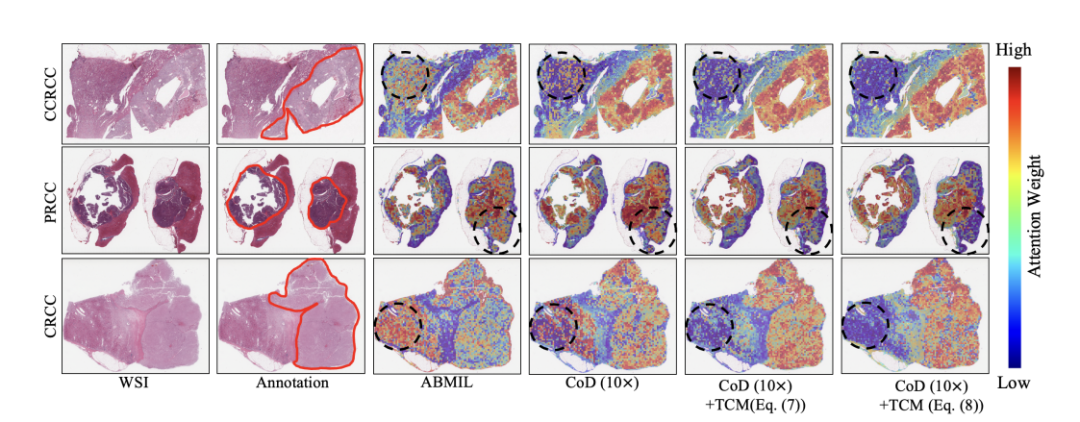
Fig. 5. Visualization results of each ablation setting on TCGA-RCC dataset. The second column represents the tumor area outlined in a red line.
图 5. TCGA-RCC 数据集上各消融设置的可视化结果。第二列表示用红线勾勒的肿瘤区域。
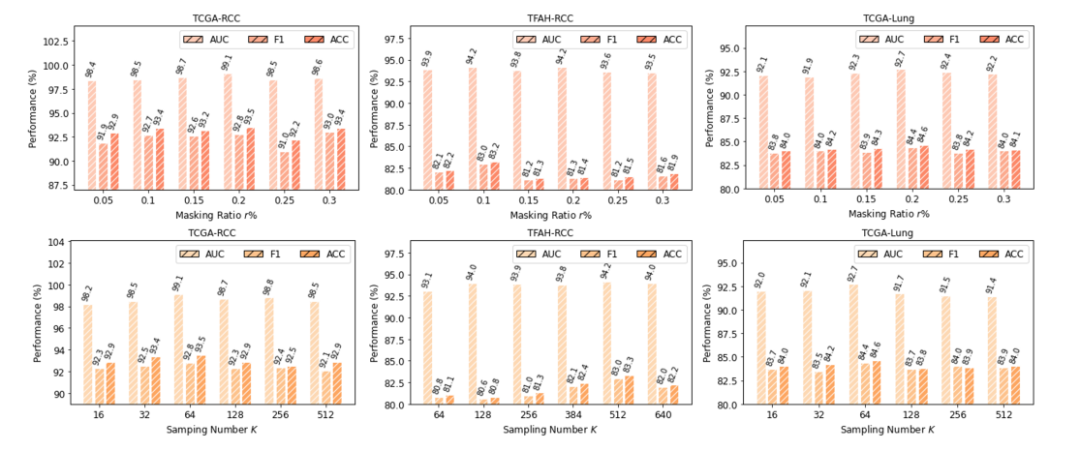
Fig. 6. Parameter analysis: the number of masking ratio r% (first row) and the number of sampling number K (second row) on three datasets.
图 6. 参数分析:在三个数据集上遮罩比例 r%(第一行)和采样数量 K(第二行)的分析。
Table
表
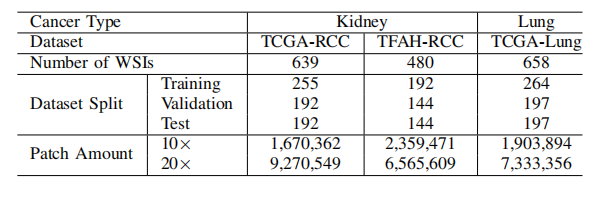
TABLE I dataset statics
表1 数据集统计。
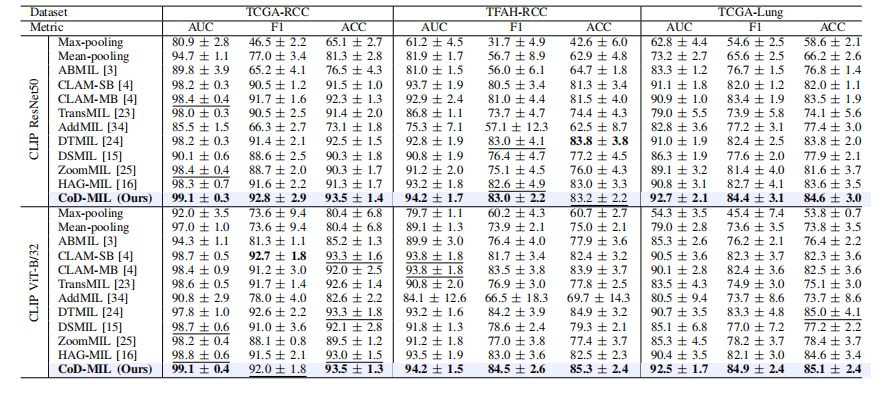
TABLE II table ii results (presented in %) on tcga-rcc, tfah-rcc, and tcga-lung datasets. the best results are in bold, and its comparable performance is denoted by underlining based on a paired t-test (p-value>0.05)
表2 TCGA-RCC、TFAH-RCC 和 TCGA-LUNG 数据集的结果(以%表示)。最佳结果以粗体显示,基于配对 t 检验(p 值 > 0.05)的相近性能以下划线标出。
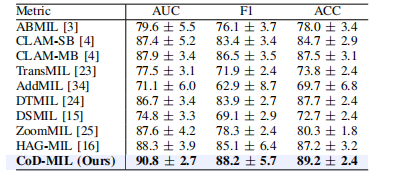
TABLE III results (presented in %) on the camelyon16 dataset. the best results are in bold, and its comparable performance is denoted by underlining based on a paired t-test (p-value>0.05).
表3 CAMELYON16 数据集的结果(以%表示)。最佳结果以粗体显示,基于配对 t 检验(p 值 > 0.05)的相近性能以下划线标出。
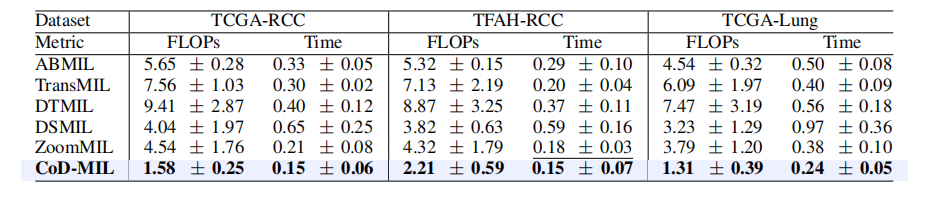
TABLE IVtable iv comparison of flops (g) and inference time (s) on three datasets. the top result is in bold, and its comparable performance is denoted by underlining based on a paired t-test (p-value>0.05).
表 IV 三个数据集上的 FLOPs(G)和推理时间(s)比较。最优结果以加粗显示,基于配对 T 检验的可比性能(P 值 > 0.05)以下划线标注。
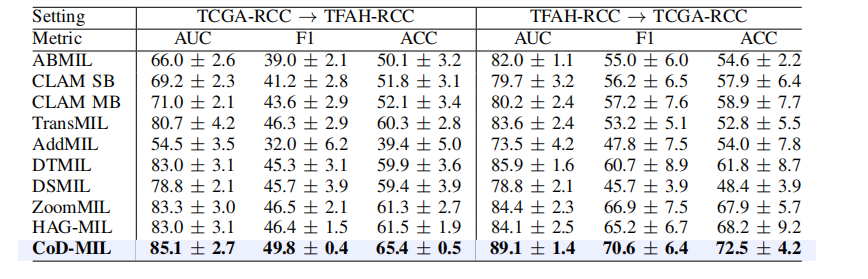
TABLE Vresults (presented in %) of multi-center cross-evaluation between tcga-rcc and tfah-rcc dataset. the best results are in bold, and its comparable performance is denoted by underlining based on a paired t-test (p-value>0.05).
表 VTCGA-RCC 和 TFAH-RCC 数据集之间的多中心交叉评估结果(以 % 表示)。最佳结果以加粗显示,基于配对 T 检验的可比性能(P 值 > 0.05)以下划线标注。
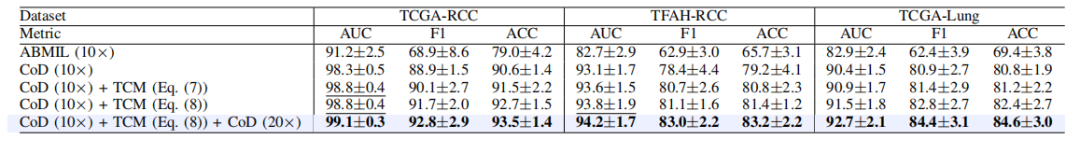
TABLE VI ablation experiment results (presented in %) on tcga-rcc, tfah-rcc, and tfah-rcc datasets. the best result
表 VI在 TCGA-RCC、TFAH-RCC 和 TFAH-RCC 数据集上的消融实验结果(以 % 表示)。最佳结果
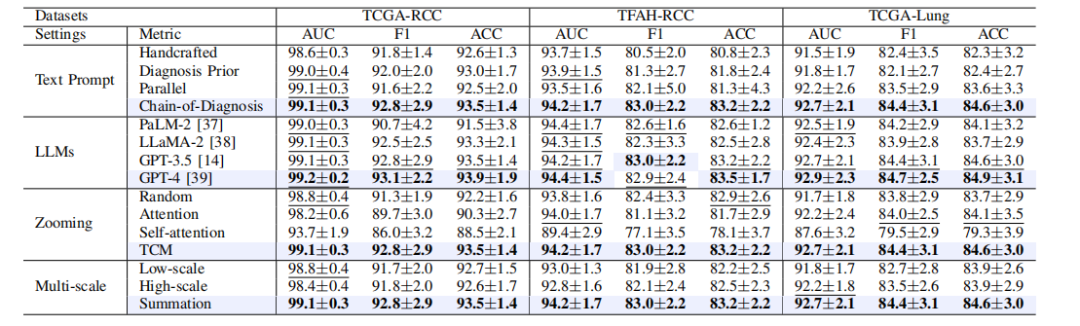
TABLE VII results (presented in %) of different ablation factors on three datasets. the best results are in bold, and its comparable performance is denoted by underlining based on a paired t-test (p-value>0.05).
表 VII三个数据集上不同消融因素的结果(以 % 表示)。最佳结果以加粗显示,基于配对 T 检验的可比性能(P 值 > 0.05)以下划线标注。
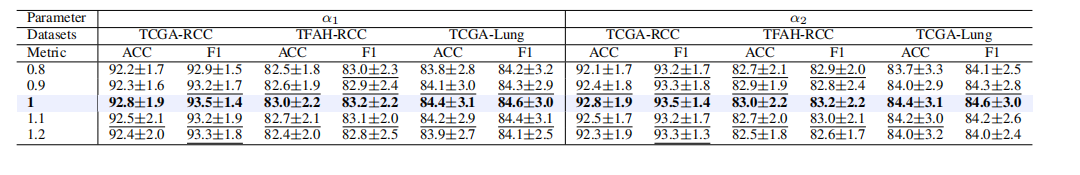
TABLE VIII parameter analysis: the number of α1 and α2 on three datasets. the best results are in bold, and its comparableperformance is denoted by underlining based on a paired t-test (p-value>0.05).
表 VIII参数分析:三个数据集上的 α1 和 α2 数值。最佳结果以加粗显示,基于配对 T 检验的可比性能(P 值 > 0.05)以下划线标注。
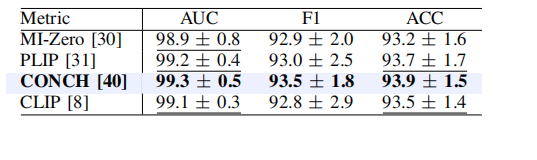
TABLE IXresults (presented in %) of vlms on the tcga-rcc dataset.the best results are in bold, and its comparableperformance is denoted by underlining based on a pairedt-test (p-value>0.05).
表 IXTCGA-RCC 数据集上 VLMS 的结果(以 % 表示)。最佳结果以加粗显示,基于配对 T 检验的可比性能(P 值 > 0.05)以下划线标注。