Python 代码加速通常是为了提高计算性能、减少运行时间。以下是一些常见的 Python 加速方法,适用于不同场景:
1、问题背景
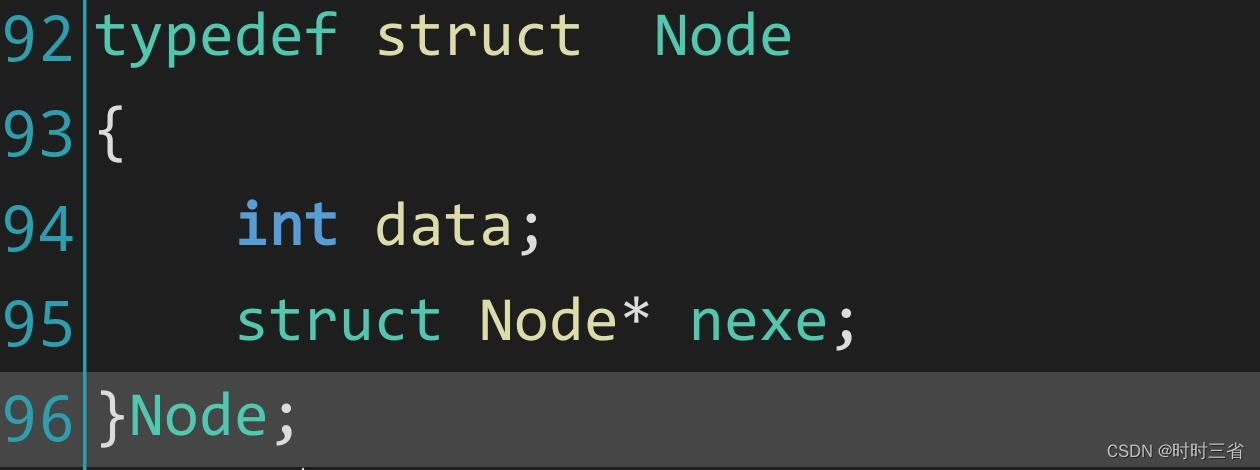
def novo (infile, seqList, out) :uDic = dict()rDic = dict()nmDic = dict()with open(infile, 'r') as infile, open(seqList, 'r') as RADlist :samples = [line.strip() for line in RADlist]lines = [line.strip() for line in infile]#Create dictionaires with all the samplesfor i in samples:uDic[i.replace(" ","")] = 0rDic[i.replace(" ","")] = 0nmDic[i.replace(" ","")] = 0for k in lines:l1 = k.split("\t")l2 = l1[0].split(";")l3 = l2[0].replace(">","")if len(l1)<2:continueif l1[4] == "U":for k in uDic.keys():if k == l3:uDic[k] += 1if l1[4] == "R":for j in rDic.keys():if j == l3:rDic[j] += 1if l1[4] == "NM":for h in nmDic.keys():if h == l3:nmDic[h] += 1f = open(out, "w")f.write("Sample"+"\t"+"R"+"\t"+"U"+"\t"+"NM"+"\t"+"TOTAL"+"\t"+"%R"+"\t"+"%U"+"\t"+"%NM"+"\n")for i in samples:U = int()R = int()NM = int ()for k, j in uDic.items():if k == i:U = jfor o, p in rDic.items():if o == i:R = pfor y,u in nmDic.items():if y == i:NM = uTOTAL = int(U + R + NM)try:f.write(i+"\t"+str(R)+"\t"+str(U)+"\t"+str(NM)+"\t"+str(TOTAL)+"\t"+str(float(R) / TOTAL)+"\t"+str(float(U) / TOTAL)+"\t"+str(float(NM) / TOTAL)+"\n")except:continuef.close()
上面是一个 Python 代码,它从文本文件中读取字符串并将其搜索一个输入文件中,并将这些字符串在输出文件中出现的次数打印出来。问题是,该代码在处理大文件时速度很慢。
2、解决方案
方法一
一个提高代码速度的方法是使用迭代器来逐行读取文件,而不是一次性将整个文件读入内存。这可以节省大量的内存,并允许代码处理更大的文件。
from collections import Counter
import csv# Count
counts = Counter()
with open(infile, 'r') as infile:for line in infile:l1 = line.strip().split("\t")l2 = l1[0].split(";")l3 = l2[0].replace(">","")if len(l1)<2:continuecounts[(l1[4], l3)] += 1# Produce output
types = ['R', 'U', 'NM']
with open(seqList, 'r') as RADlist, open(out, 'w') as outfile:f = csv.writer(outfile, delimiter='\t')f.writerow(types + ['TOTAL'] + ['%' + t for t in types])for sample in RADlist:sample = sample.strip()countrow = [counts((t, sample)) for t in types]total = sum(countrow)f.writerow([sample] + countrow + [total] + [c/total for c in countrow])
方法二
另一个提高代码速度的方法是使用并行处理。这可以利用多核 CPU 的优势,同时处理多个任务。
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor
from collections import Counter# Count
def count_sample(sample, infile):counts = Counter()with open(infile, 'r') as infile:for line in infile:l1 = line.strip().split("\t")l2 = l1[0].split(";")l3 = l2[0].replace(">","")if len(l1)<2:continuecounts[(l1[4], l3)] += 1return sample, counts# Produce output
types = ['R', 'U', 'NM']
with ProcessPoolExecutor() as executor, open(seqList, 'r') as RADlist, open(out, 'w') as outfile:f = csv.writer(outfile, delimiter='\t')f.writerow(types + ['TOTAL'] + ['%' + t for t in types])for sample, counts in executor.map(count_sample, RADlist, [infile] * len(RADlist)):countrow = [counts[(t, sample)] for t in types]total = sum(countrow)f.writerow([sample] + countrow + [total] + [c/total for c in countrow])
通过这些方法,可以显著加快 Python 代码的执行速度。