文章目录
- 报错
- 解决方案
- 1. 后端未配置跨域支持
- 2. 后端响应的 Content-Type 或 CORS 配置问题
- 3. 前端 request 配置问题
- 4. 浏览器缓存或代理问题
- 5. 后端端口未被正确映射
报错
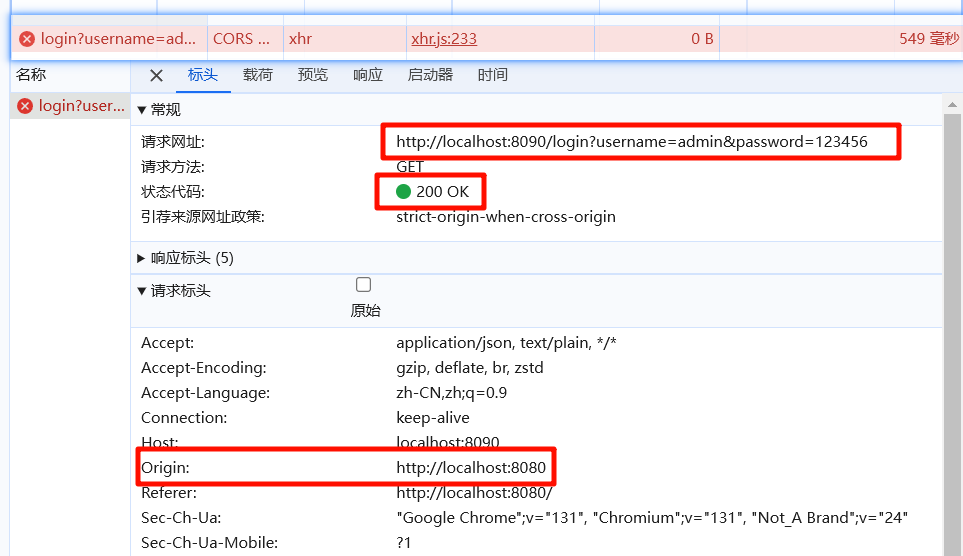
如下图,后端显示请求成功,前端显示失败

解决方案
1. 后端未配置跨域支持
默认情况下,不同源(域名、端口、协议)的请求会受到浏览器的跨域限制(CORS)。前端 http://localhost:8080 和后端 http://localhost:8090 被视为不同源,因此会导致请求被阻止。
解决方法:在后端添加跨域支持
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {registry.addMapping("/**") // 匹配所有路径.allowedOrigins("http://localhost:8080") // 允许前端域名.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "OPTIONS") // 允许的请求方法.allowCredentials(true) // 允许携带凭证.maxAge(3600); // 缓存时间}
}如果项目中使用了 Spring Boot,可以直接在控制器方法上添加注解:
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:8080")
@GetMapping("/login")
public class UserController {public Result login(@RequestParam String username, @RequestParam String password) {// 登录逻辑return Result.success(1);}
}
2. 后端响应的 Content-Type 或 CORS 配置问题
如果后端的返回头缺少正确的内容类型或跨域响应头,浏览器也可能拒绝请求。
解决方法:确保后端返回头正确设置
@GetMapping("/login")
public Result login(@RequestParam String username, @RequestParam String password, HttpServletResponse response) {// 设置响应头response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://localhost:8080");response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, POST, OPTIONS");response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type, Authorization");response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");// 登录逻辑int result = userService.login(username, password);return Result.success(result);
}
3. 前端 request 配置问题
检查前端是否正确发起了请求,包括 baseURL 是否正确,是否携带了其他额外的头。
确保前端 axios 配置正确
import axios from "axios";const request = axios.create({baseURL: "http://localhost:8090", // 后端服务地址timeout: 5000, // 超时时间headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json", // 确保类型正确},
});export default request;
调用接口时,应传递 params 而不是 data,因为是 GET 请求:
request({method: "get",url: "/login",params: {username: this.user.username,password: this.user.password,},
}).then((resp) => {console.log(resp.data);}).catch((error) => {console.error(error);});
4. 浏览器缓存或代理问题
某些情况下,浏览器缓存或代理工具可能导致请求异常。
解决方法:
解决方法:
- 清除浏览器缓存并重试。
- 检查是否有代理工具拦截了请求(如 Charles 或 Fiddler)。
- 在请求中加上时间戳避免缓存问题:
params: {username: this.user.username,password: this.user.password,_t: new Date().getTime(), // 避免缓存
}5. 后端端口未被正确映射
如果你运行的后端服务(如 Spring Boot)监听的端口未正确绑定到网络,前端可能无法访问。
解决方法:
- 确认后端服务启动成功且端口未被占用。
- 使用工具(如 Postman)单独测试后端 API,确认后端可用。