ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

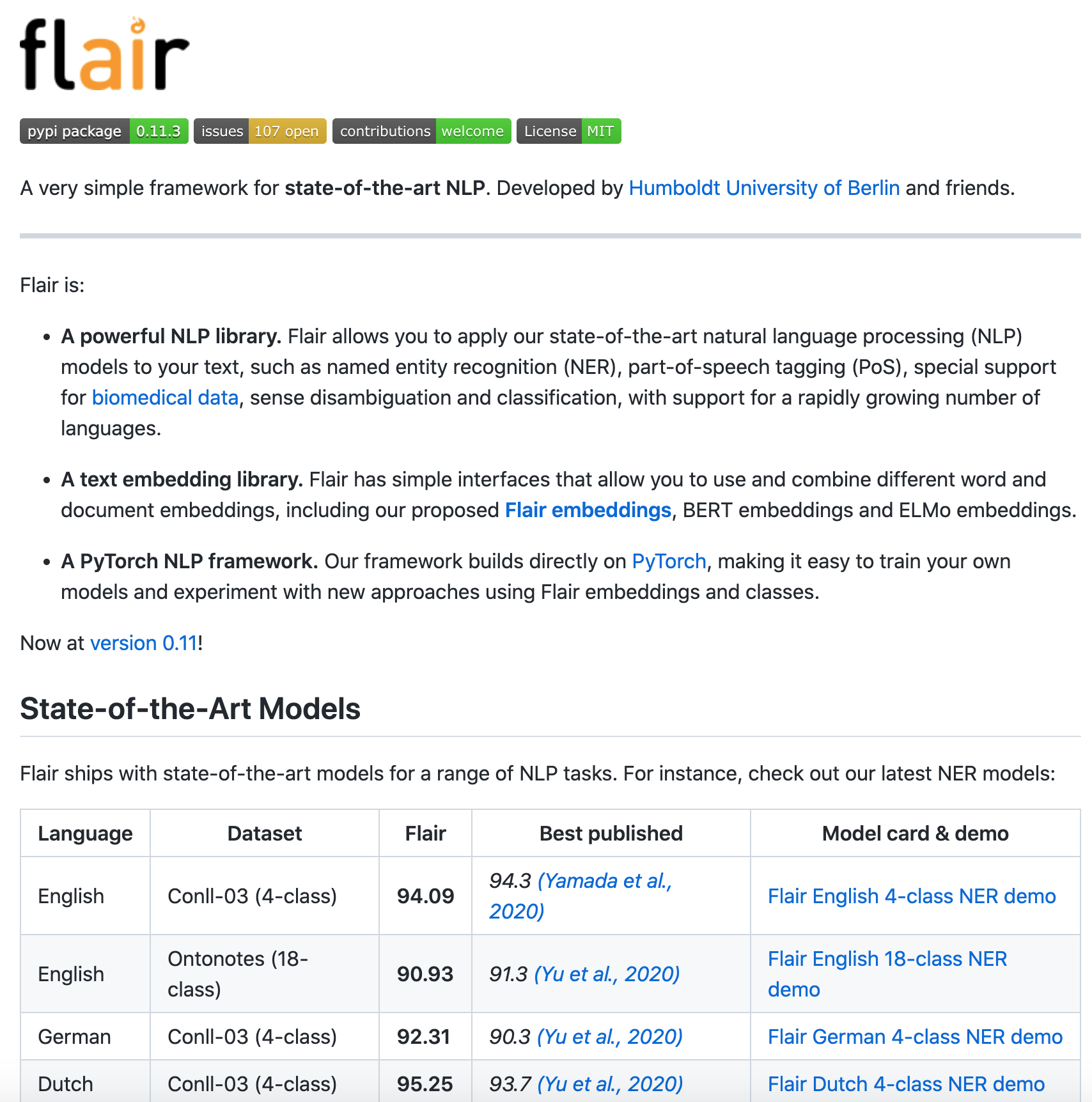
工具框架:flair - 集成最先进NLP技术的简单框架(Python)
tags: [NLP技术,NLP应用]
‘flair - A very simple framework for state-of-the-art NLP’ by Zalando Research
GitHub: https://github.com/flairNLP/flair
工具库:cleanlab - 机器学习数据集错误自动发现修复工具包
tags: [机器学习,数据集错误,错误修复]
‘cleanlab - The standard data-centric AI package for data quality and machine learning with messy, real-world data and labels.’
GitHub: https://github.com/cleanlab/cleanlab


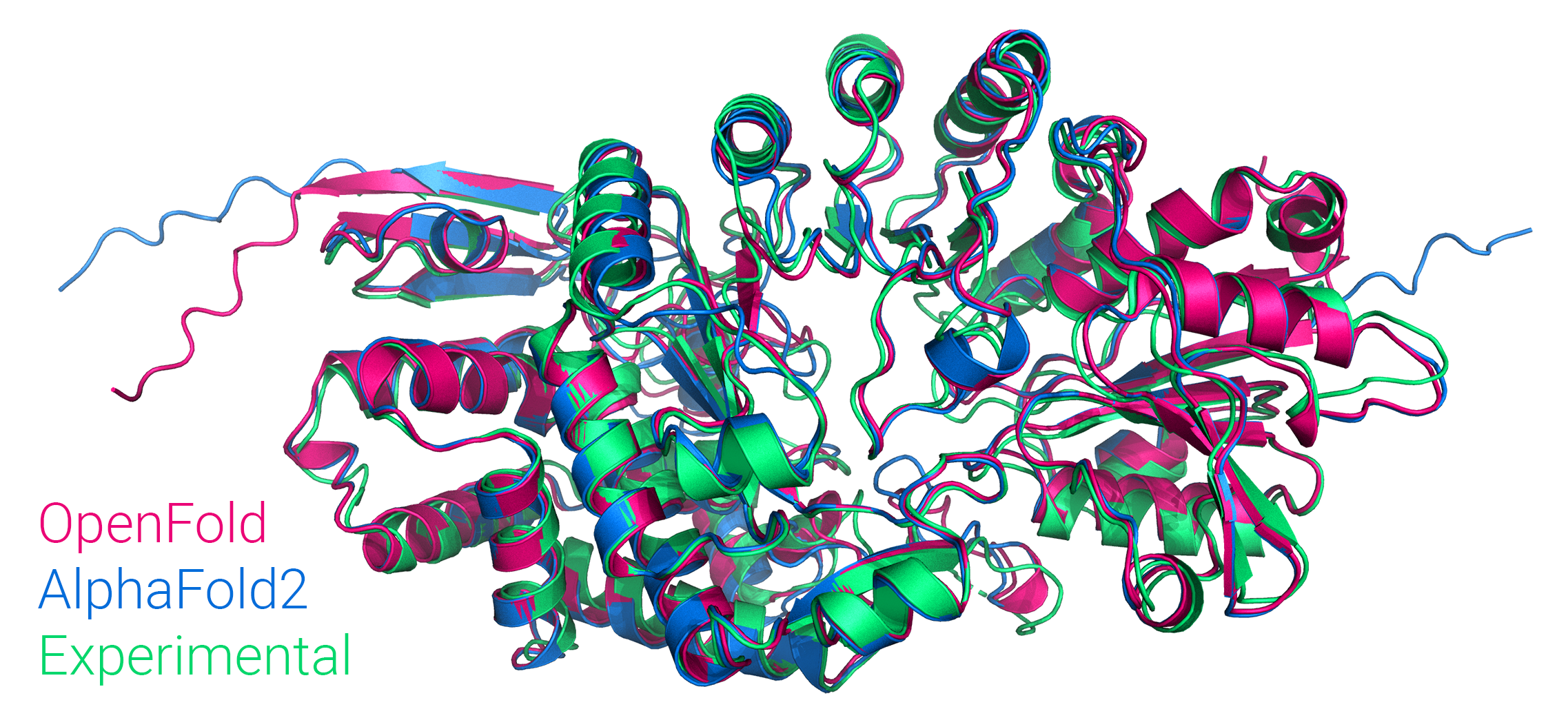
工具库:OpenFold - AlphaFold 2的PyTorch版开源复现
tags: [AlphaFold 2,pytorch]
‘OpenFold - Trainable PyTorch reproduction of AlphaFold 2’ by AQ Laboratory
GitHub: https://github.com/aqlaboratory/openfold
工具库:darts - Python时序处理与预测库
tags: [时间序列]
‘darts - A python library for easy manipulation and forecasting of time series.’ by Unit8 SA
GitHub: https://github.com/unit8co/darts


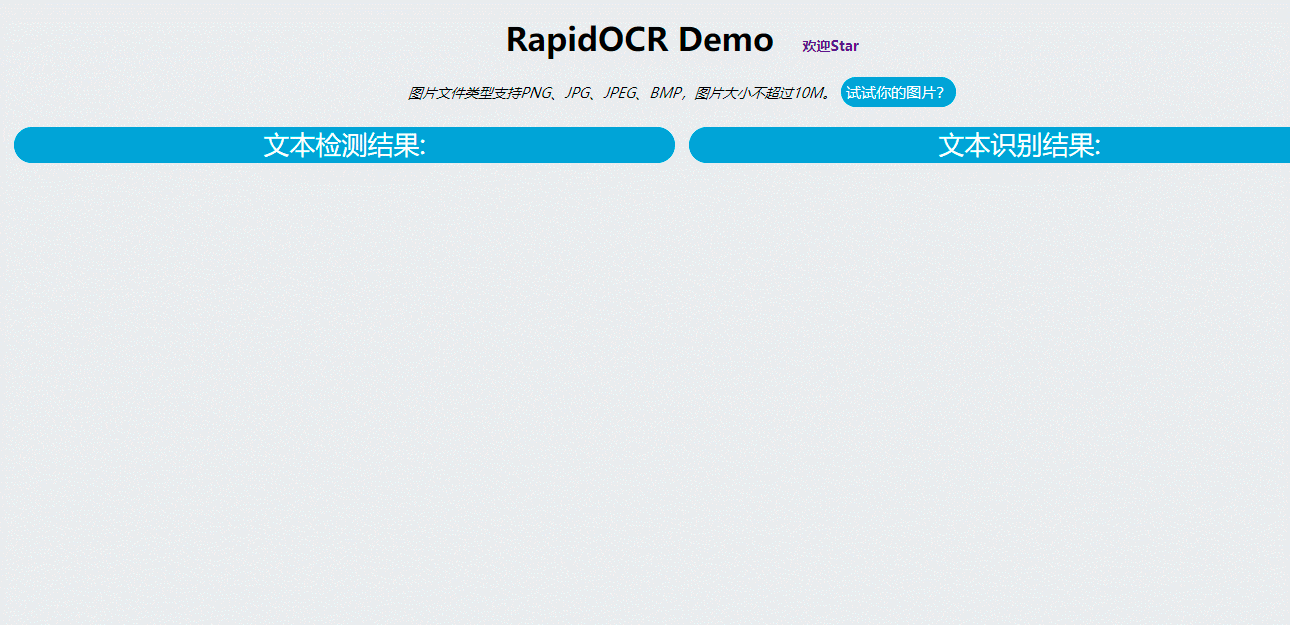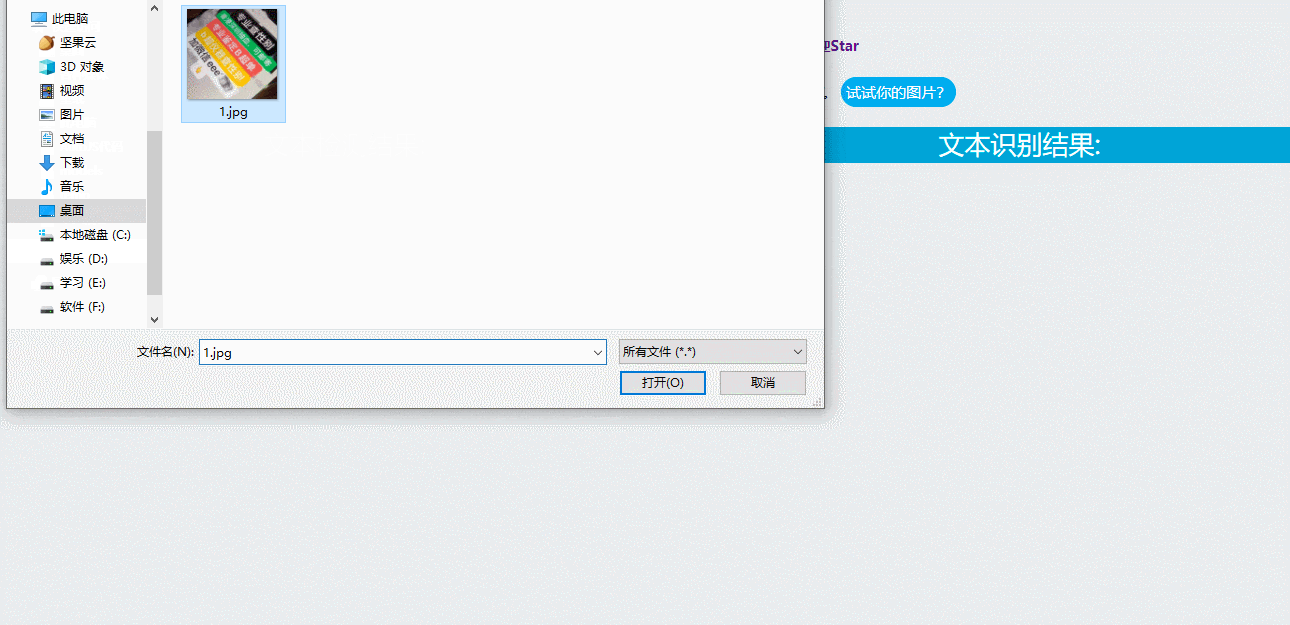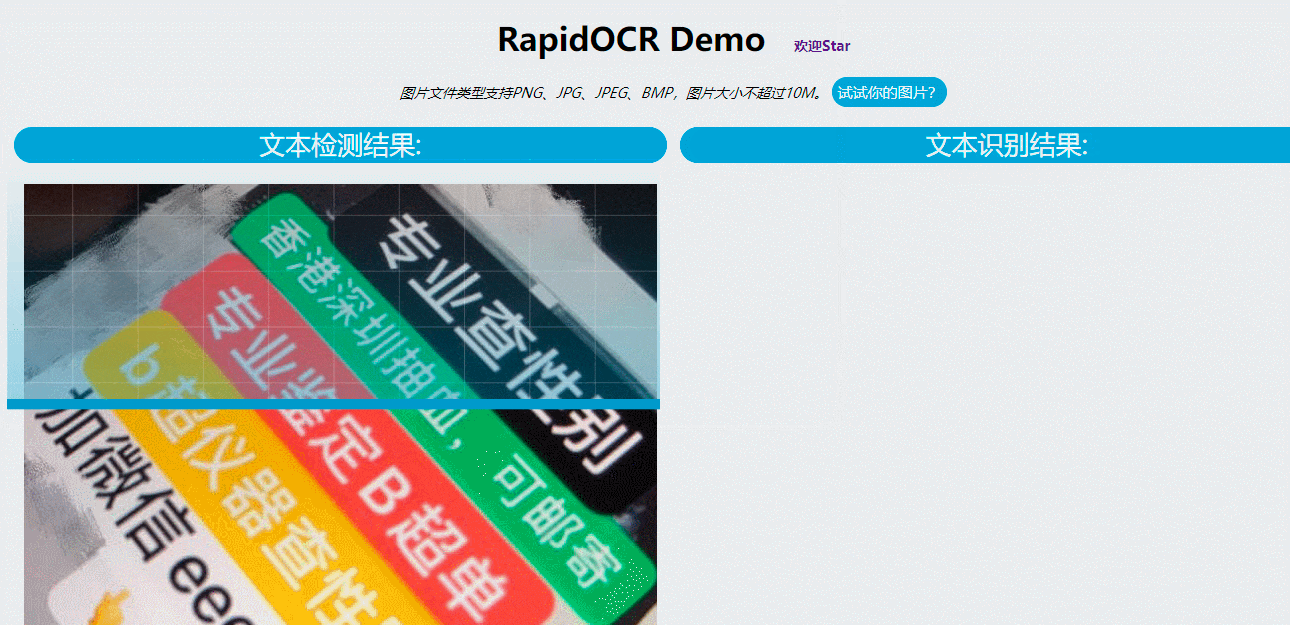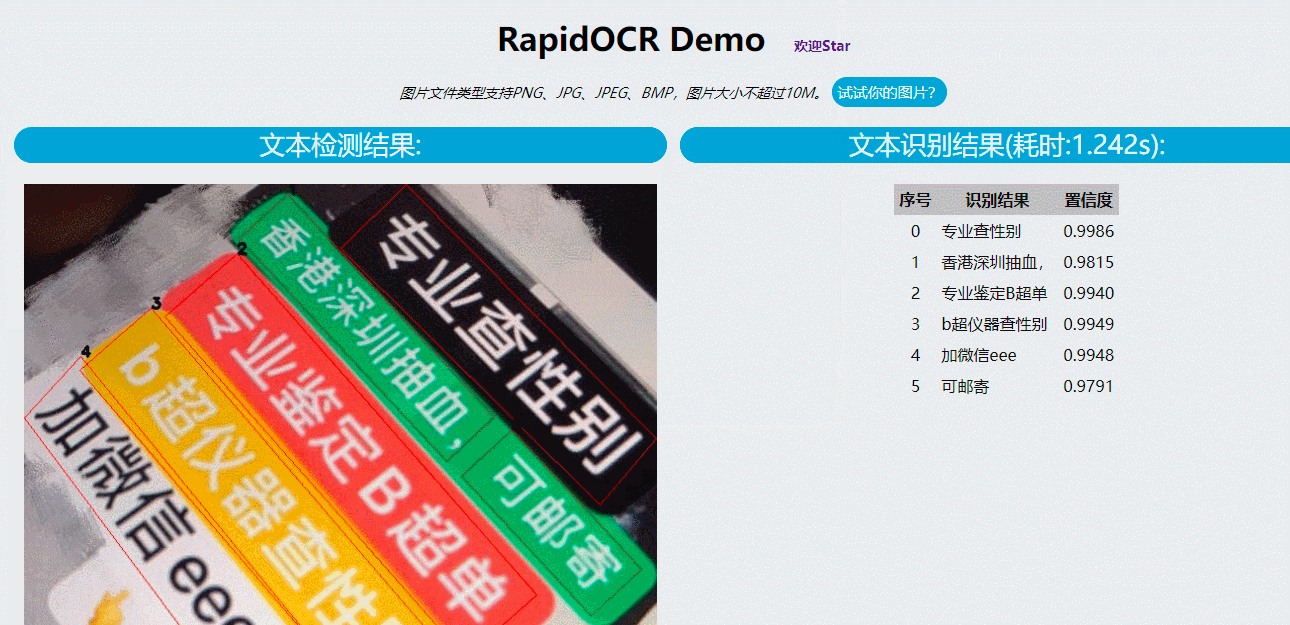
工具库:RapidOCR - 基于PaddleOCR & OnnxRuntime的跨平台OCR库
tags: [OCR,跨平台]
‘RapidOCR (捷智OCR) - A cross platform OCR Library based on PaddleOCR & OnnxRuntime’
GitHub: https://github.com/RapidAI/RapidOCR


2.博文&分享

分享:读博申请攻略
Tutorial on PhD Application’ by Lijin Zhang
GitHub: https://github.com/zhanglj37/Tutorial-on-PhD-Application

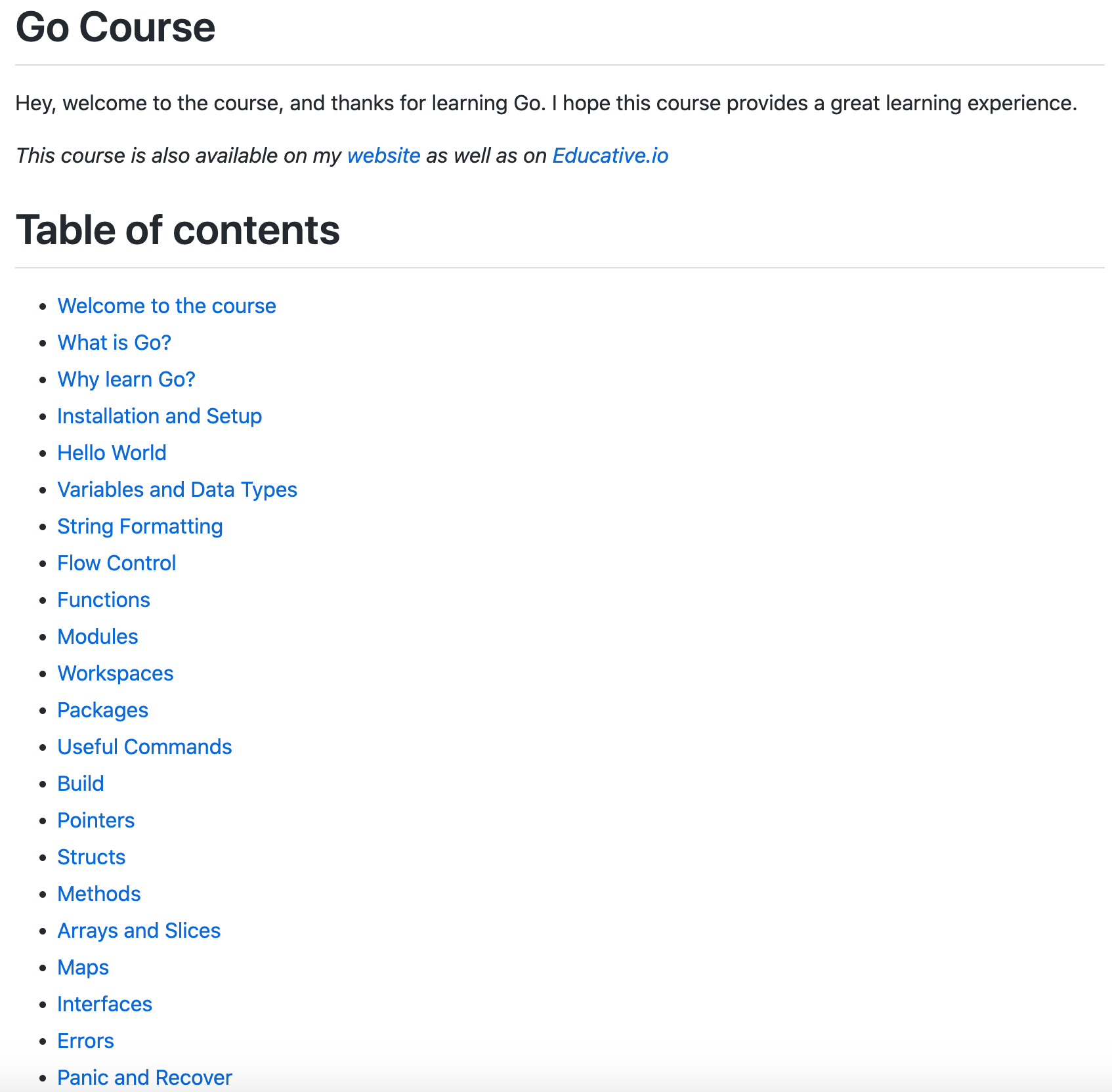
课程:Go语言入门与进阶课程
‘Go Course - Master the fundamentals and advanced features of the Go programming language’ by Karan Pratap Singh
GitHub: https://github.com/karanpratapsingh/go-course
3.数据&资源

资源列表:时序AI相关资源大列表
‘AI for Time Series (AI4TS) Papers, Tutorials, and Surveys - A professional list of Papers, Tutorials, and Surveys on AI for Time Series in top AI conferences and journals.’ by Qingsong Wen
GitHub: https://github.com/qingsongedu/awesome-AI-for-time-series-papers

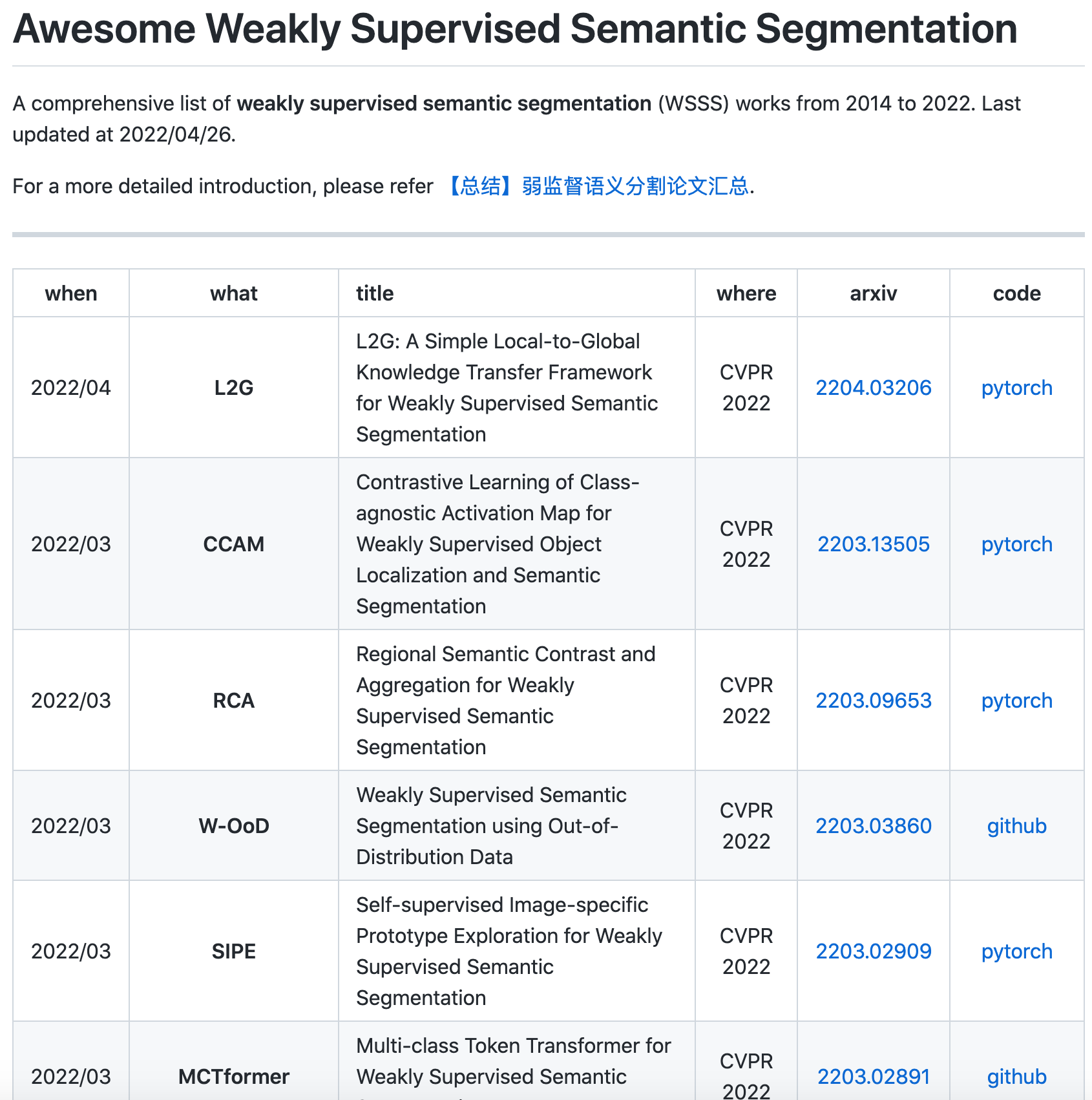
资源列表:弱监督语义分割论文汇总
‘Awesome Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation - A comprehensive list of weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) works from 2014 to 2022.’ by Xiaojian Zhong
GitHub: https://github.com/xiaojianzhong/awesome-weakly-supervised-semantic-segmentation
4.研究&论文

可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
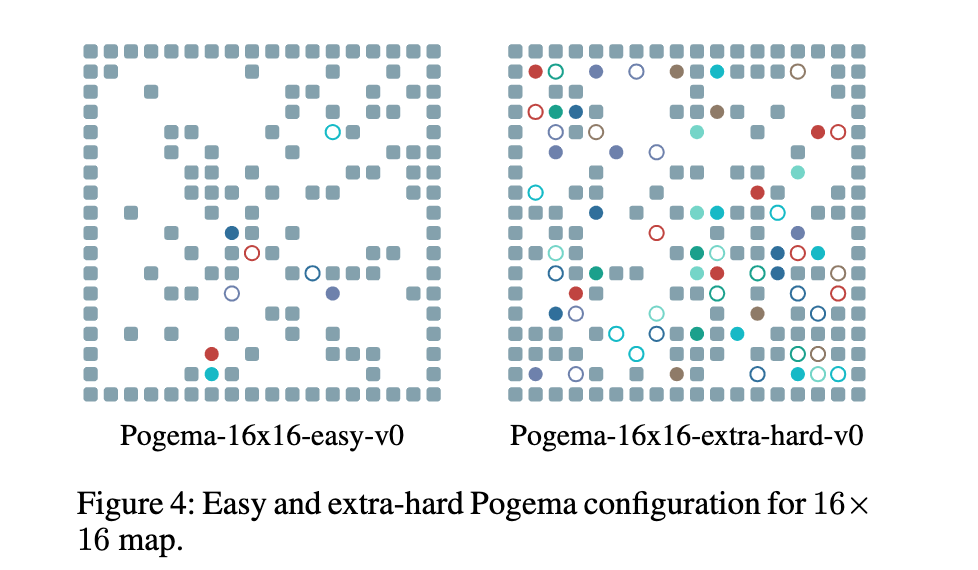
论文:POGEMA: Partially Observable Grid Environment for Multiple Agents
论文标题:POGEMA: Partially Observable Grid Environment for Multiple Agents
论文时间:22 Jun 2022
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.10944
代码实现:https://github.com/airi-institute/pogema
论文作者:Alexey Skrynnik, Anton Andreychuk, Konstantin Yakovlev, Aleksandr I. Panov
论文简介:We introduce POGEMA (https://github. com/AIRI-Institute/pogema) a sandbox for challenging partially observable multi-agent pathfinding (PO-MAPF) problems ./我们推出的POGEMA(https://github. com/AIRI-Institute/pogema)是一个用于挑战部分可观察的多Agent寻路(PO-MAPF)问题的沙盒。
论文摘要:We introduce POGEMA (https://github.com/AIRI-Institute/pogema) a sandbox for challenging partially observable multi-agent pathfinding (PO-MAPF) problems . This is a grid-based environment that was specifically designed to be a flexible, tunable and scalable benchmark. It can be tailored to a variety of PO-MAPF, which can serve as an excellent testing ground for planning and learning methods, and their combination, which will allow us to move towards filling the gap between AI planning and learning.
我们推出了POGEMA(https://github.com/AIRI-Institute/pogema),这是一个用于挑战部分可观察的多代理寻路(PO-MAPF)问题的沙盒。这是一个基于网格的环境,专门设计成一个灵活、可调整和可扩展的基准。它可以为各种PO-MAPF量身定做,这可以作为规划和学习方法的一个很好的试验场,以及它们的组合,这将使我们能够朝着填补人工智能规划和学习之间的空白前进。


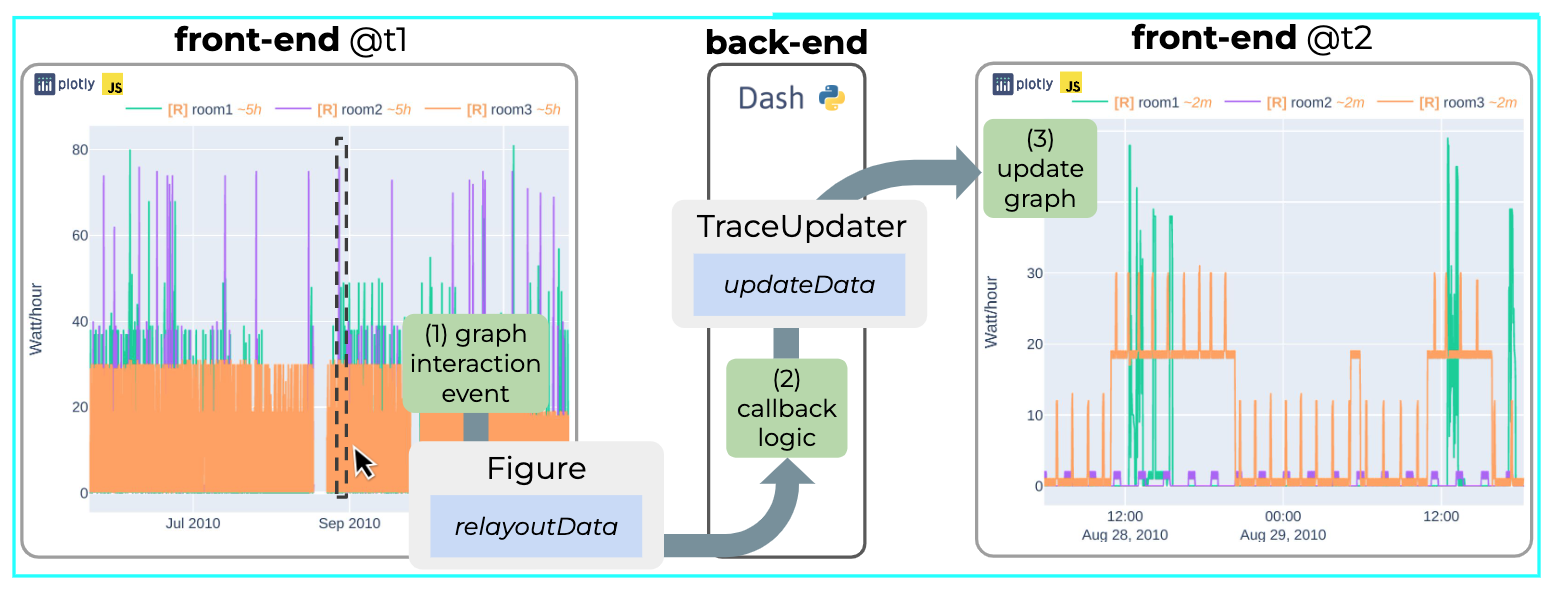
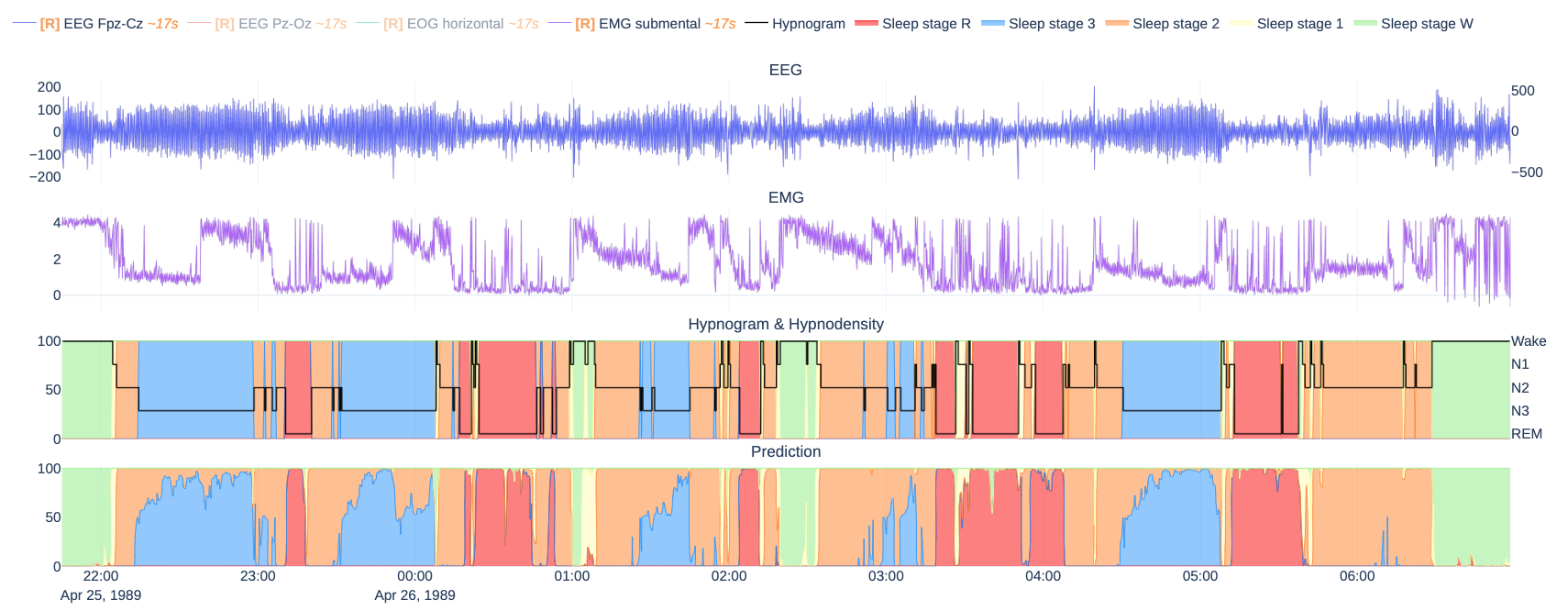
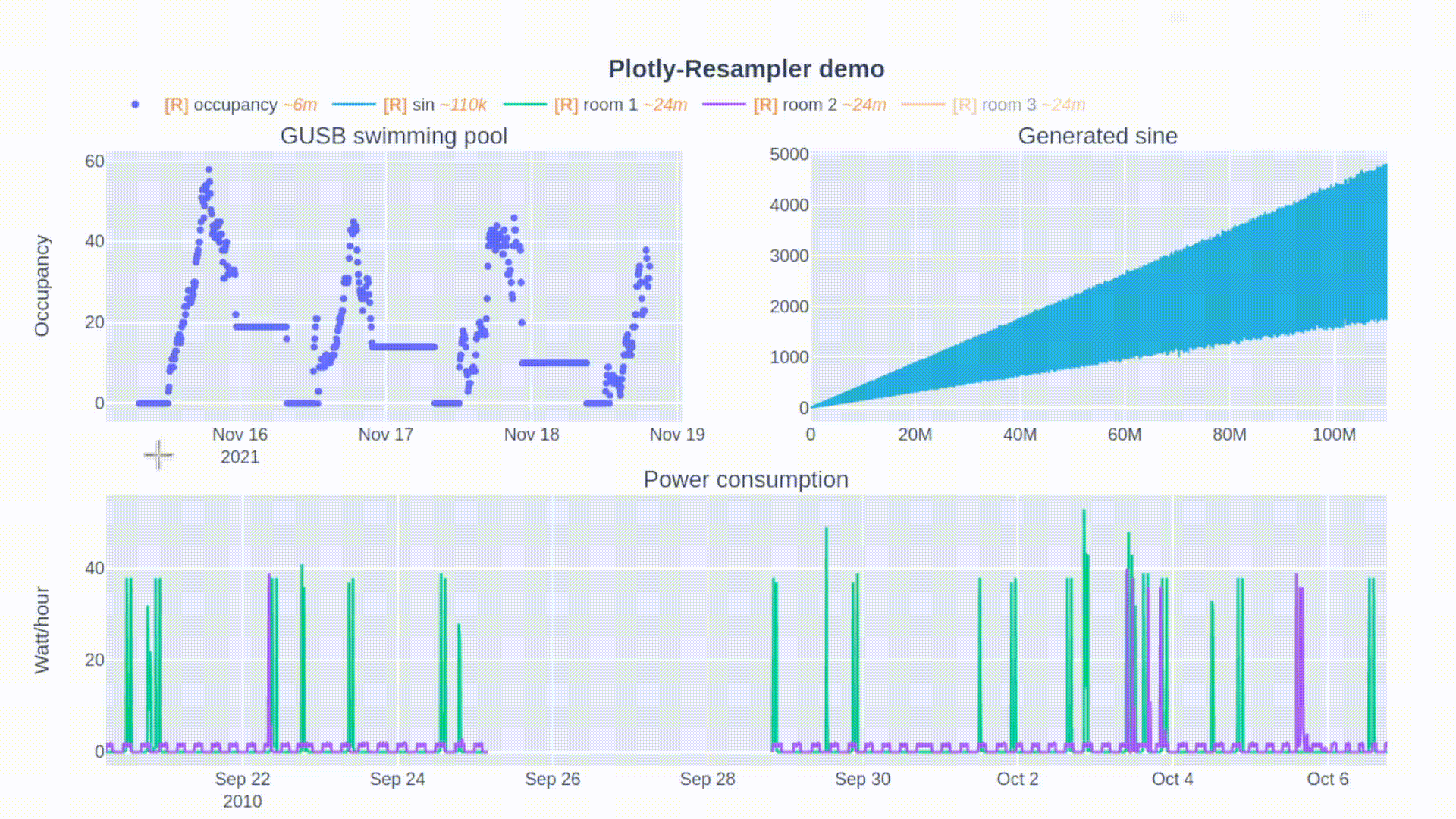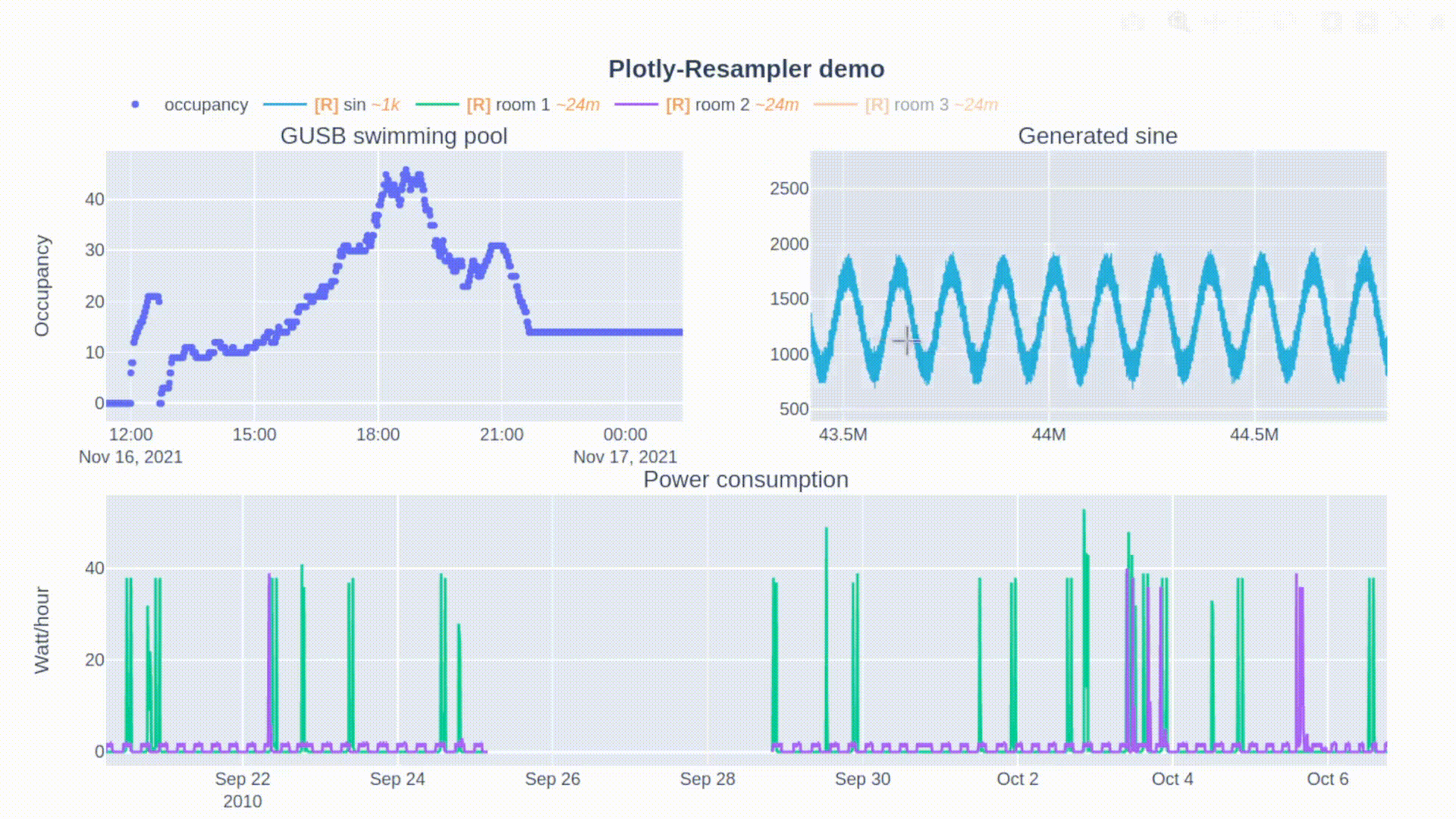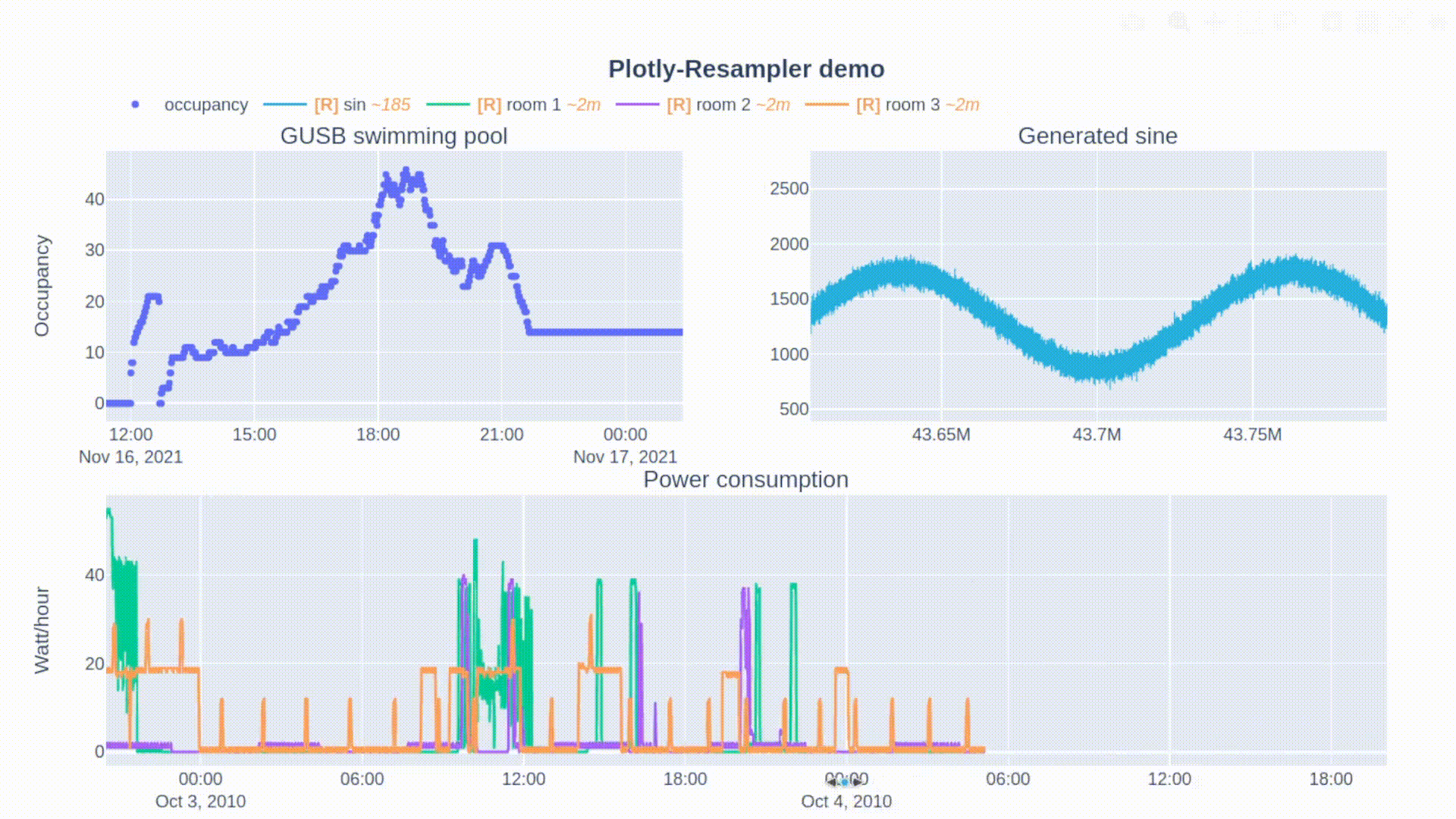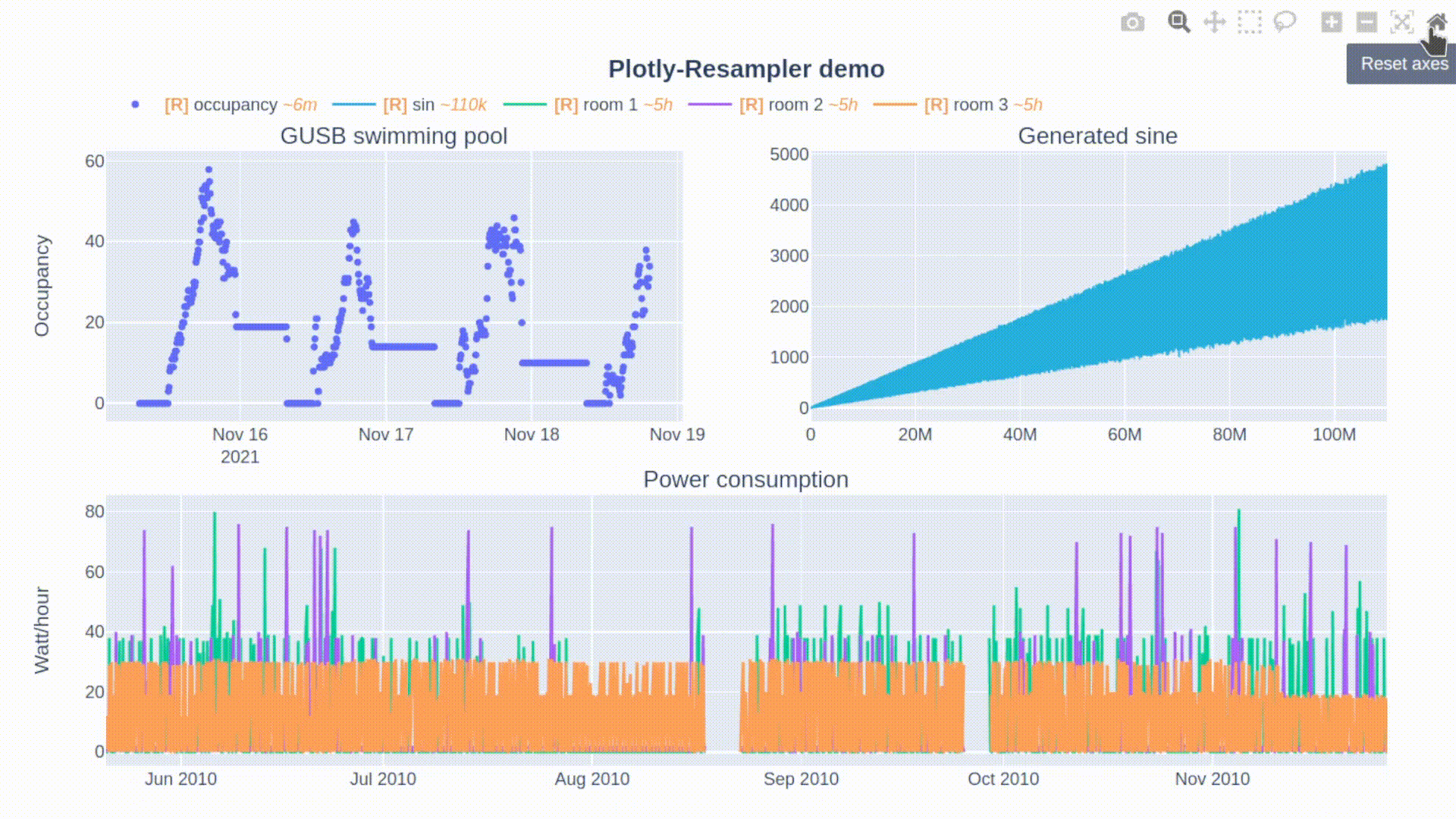
论文:Plotly-Resampler: Effective Visual Analytics for Large Time Series
论文标题:Plotly-Resampler: Effective Visual Analytics for Large Time Series
论文时间:17 Jun 2022
所属领域:时间序列
对应任务:Data Visualization,Time Series,Time Series Analysis,数据可视化,时间序列,时间序列分析
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08703
代码实现:https://github.com/predict-idlab/plotly-resampler
论文作者:Jonas Van Der Donckt, Jeroen Van Der Donckt, Emiel Deprost, Sofie Van Hoecke
论文简介:We observe that open source Python visualization toolkits empower data scientists in most visual analytics tasks, but lack the combination of scalability and interactivity to realize effective time series visualization./我们观察到,开源的Python可视化工具包使数据科学家能够完成大多数可视化分析任务,但缺乏实现有效时间序列可视化的可扩展性和互动性的组合工具。
论文摘要:Visual analytics is arguably the most important step in getting acquainted with your data. This is especially the case for time series, as this data type is hard to describe and cannot be fully understood when using for example summary statistics. To realize effective time series visualization, four requirements have to be met; a tool should be (1) interactive, (2) scalable to millions of data points, (3) integrable in conventional data science environments, and (4) highly configurable. We observe that open source Python visualization toolkits empower data scientists in most visual analytics tasks, but lack the combination of scalability and interactivity to realize effective time series visualization. As a means to facilitate these requirements, we created Plotly-Resampler, an open source Python library. Plotly-Resampler is an add-on for Plotly’s Python bindings, enhancing line chart scalability on top of an interactive toolkit by aggregating the underlying data depending on the current graph view. Plotly-Resampler is built to be snappy, as the reactivity of a tool qualitatively affects how analysts visually explore and analyze data. A benchmark task highlights how our toolkit scales better than alternatives in terms of number of samples and time series. Additionally, Plotly-Resampler’s flexible data aggregation functionality paves the path towards researching novel aggregation techniques. Plotly-Resampler’s integrability, together with its configurability, convenience, and high scalability, allows to effectively analyze high-frequency data in your day-to-day Python environment.
可视化分析可以说是熟悉数据的最重要步骤。这对于时间序列来说尤其如此,因为这种数据类型很难描述,在使用例如汇总统计时无法完全理解。为了实现有效的时间序列可视化,必须满足四个要求;一个工具应该是(1)互动的,(2)可扩展到数百万的数据点,(3)可集成到传统的数据科学环境中,以及(4)高度可配置。我们观察到,开源的Python可视化工具包使数据科学家能够完成大多数可视化分析任务,但缺乏可扩展性和互动性的结合,无法实现有效的时间序列可视化。作为促进这些要求的一种手段,我们创建了Plotly-Resampler,一个开源的Python库。Plotly-Resampler是Plotly的Python绑定的一个插件,通过根据当前的图形视图聚合底层数据,在交互式工具包的基础上增强线图的可扩展性。Plotly-Resampler的建立是为了让它更敏捷,因为一个工具的反应性从质量上影响了分析师对数据的视觉探索和分析。一个基准任务强调了我们的工具包在样本数和时间序列方面的扩展性优于其他方案。此外,Plotly-Resampler灵活的数据聚合功能为研究新型聚合技术铺平了道路。Plotly-Resampler的可整合性,加上它的可配置性、便利性和高可扩展性,可以在日常的Python环境中有效地分析高频数据。
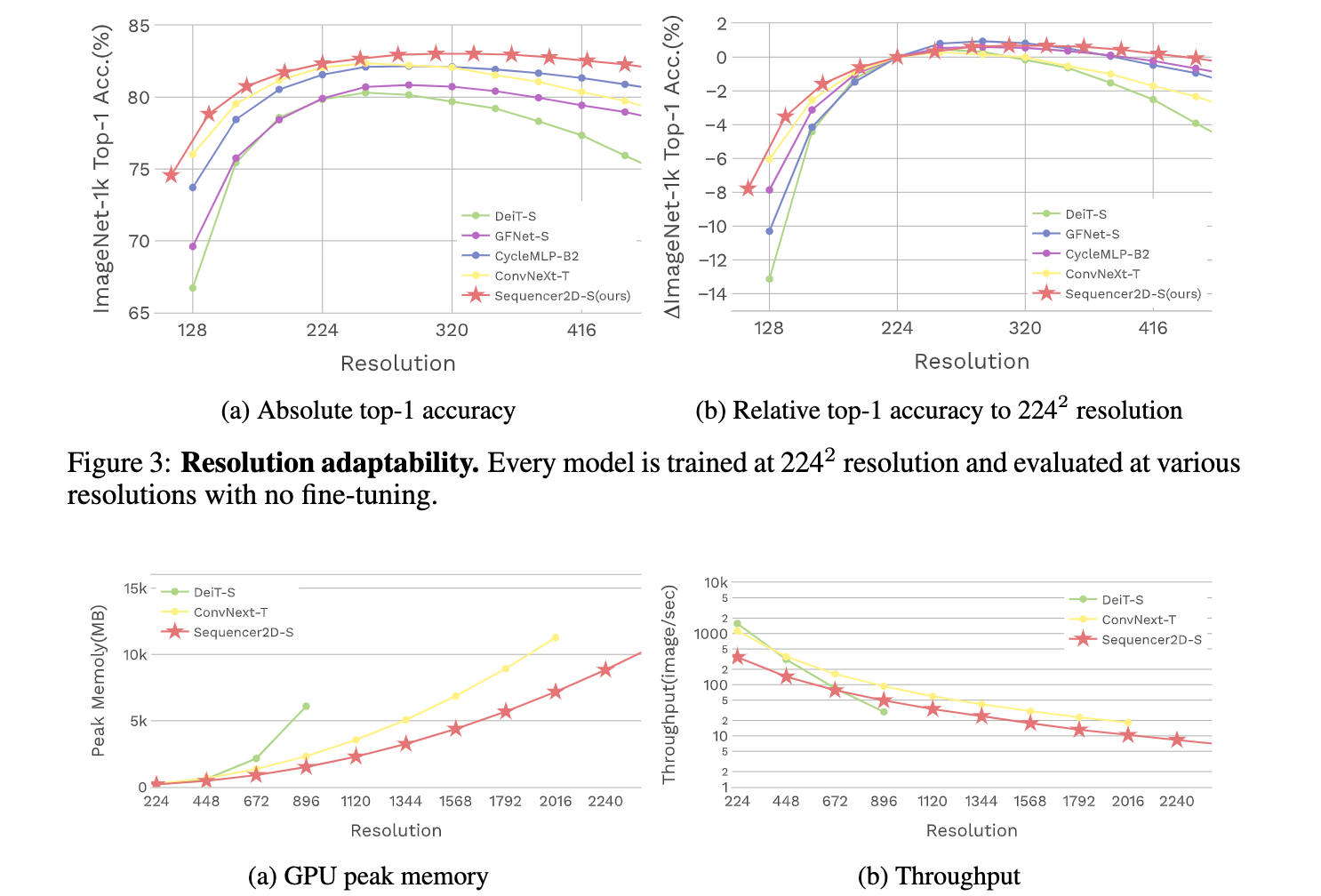
论文:Sequencer: Deep LSTM for Image Classification
论文标题:Sequencer: Deep LSTM for Image Classification
论文时间:4 May 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Classification,Domain Generalization,Image Classification,Inductive Bias,Natural Language Processing,图像分类,域泛化,图像分类,归纳偏置,自然语言处理
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01972
代码实现:https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models , https://github.com/okojoalg/sequencer , https://github.com/timeseriesAI/tsai , https://github.com/liuruiyang98/Jittor-MLP
论文作者:Yuki Tatsunami, Masato Taki
论文简介:Here we propose Sequencer, a novel and competitive architecture alternative to ViT that provides a new perspective on these issues./在这里,我们提出了Sequencer,一个新颖的、有竞争力的架构,可以替代ViT,为这些问题提供一个新的视角。
论文摘要:In recent computer vision research, the advent of the Vision Transformer (ViT) has rapidly revolutionized various architectural design efforts: ViT achieved state-of-the-art image classification performance using self-attention found in natural language processing, and MLP-Mixer achieved competitive performance using simple multi-layer perceptrons. In contrast, several studies have also suggested that carefully redesigned convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can achieve advanced performance comparable to ViT without resorting to these new ideas. Against this background, there is growing interest in what inductive bias is suitable for computer vision. Here we propose Sequencer, a novel and competitive architecture alternative to ViT that provides a new perspective on these issues. Unlike ViTs, Sequencer models long-range dependencies using LSTMs rather than self-attention layers. We also propose a two-dimensional version of Sequencer module, where an LSTM is decomposed into vertical and horizontal LSTMs to enhance performance. Despite its simplicity, several experiments demonstrate that Sequencer performs impressively well: Sequencer2D-L, with 54M parameters, realizes 84.6% top-1 accuracy on only ImageNet-1K. Not only that, we show that it has good transferability and the robust resolution adaptability on double resolution-band.
在最近的计算机视觉研究中,视觉Transformer(ViT)的出现迅速革新了各种架构设计工作。ViT利用自然语言处理中发现的自我注意实现了最先进的图像分类性能,而MLP-Mixer利用简单的多层感知器实现了具有竞争力的性能。相比之下,一些研究也表明,精心重新设计的卷积神经网络(CNN)可以实现与ViT相媲美的先进性能,而无需借助这些新的想法。在此背景下,人们对什么样的归纳偏向适合于计算机视觉的兴趣越来越大。在这里,我们提出了Sequencer,一个新颖的、有竞争力的架构,可以替代ViT,为这些问题提供一个新的视角。与ViTs不同,Sequencer使用LSTMs而不是自我注意层来模拟长距离的依赖关系。我们还提出了一个二维版本的Sequencer模块,其中一个LSTM被分解成垂直和水平LSTM以提高性能。尽管它很简单,但一些实验证明Sequencer的表现令人惊讶。Sequencer2D-L,有54M个参数,仅在ImageNet-1K上就实现了84.6%的最高精度。不仅如此,我们还表明它具有良好的可转移性和对双分辨率段的强大的分辨率适应性。
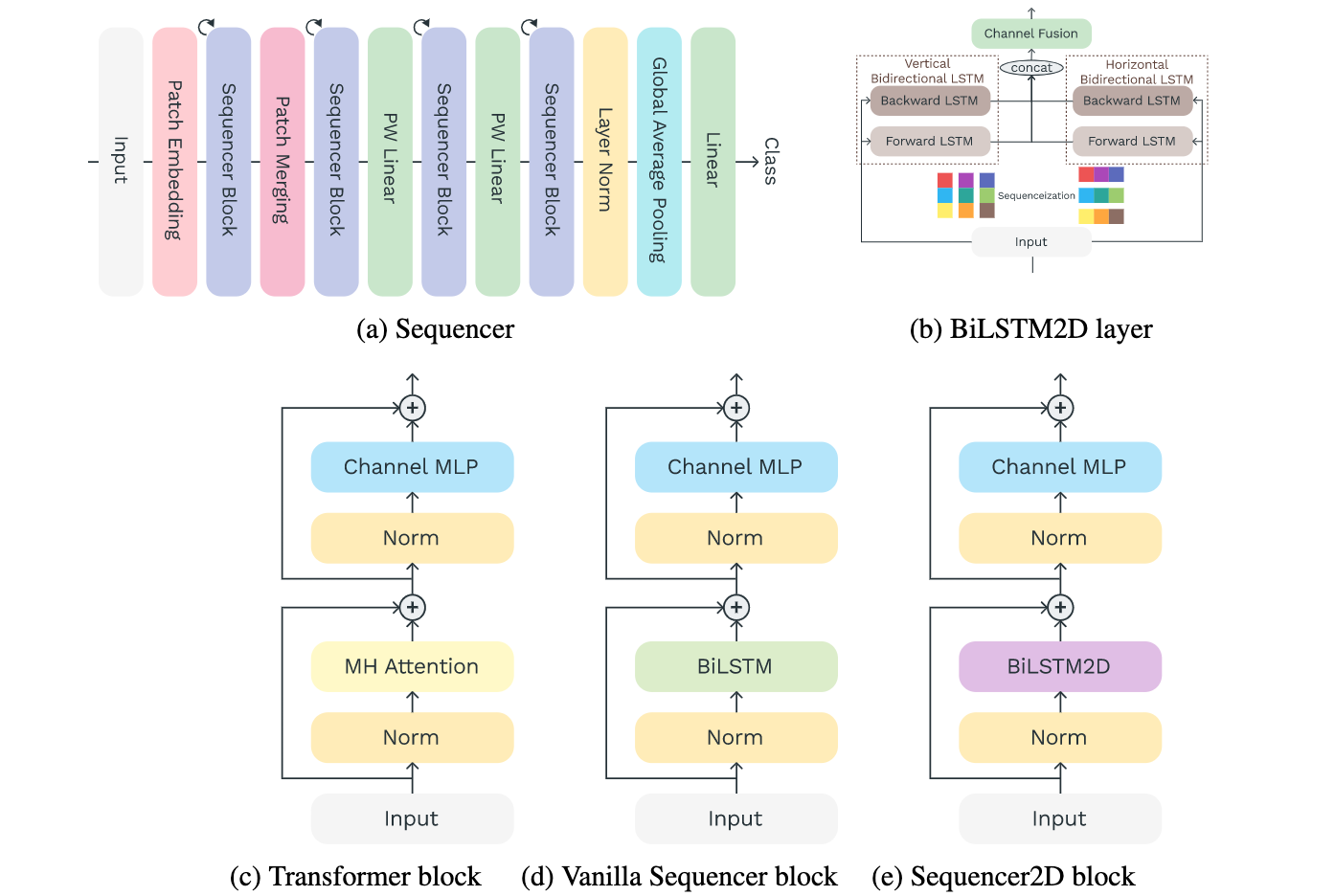
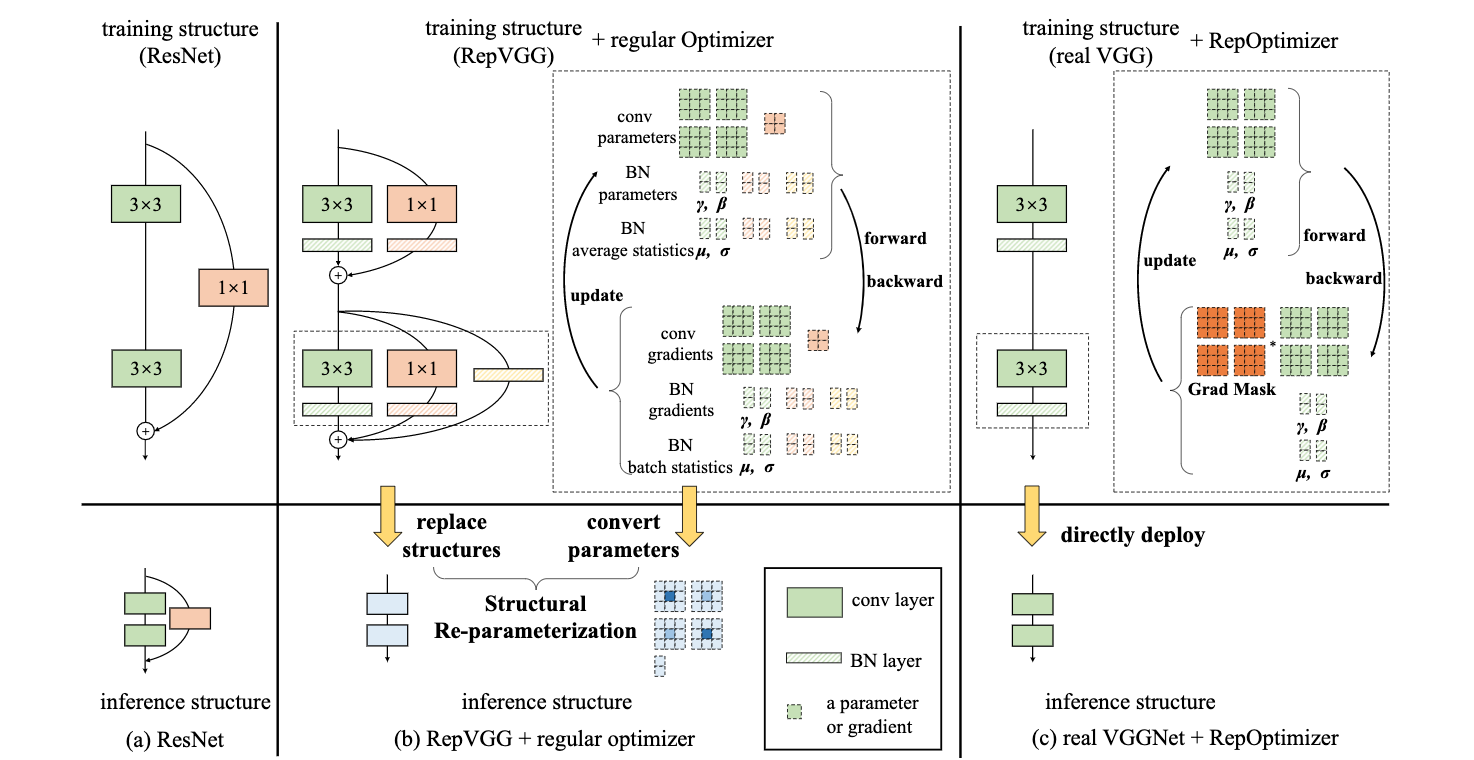
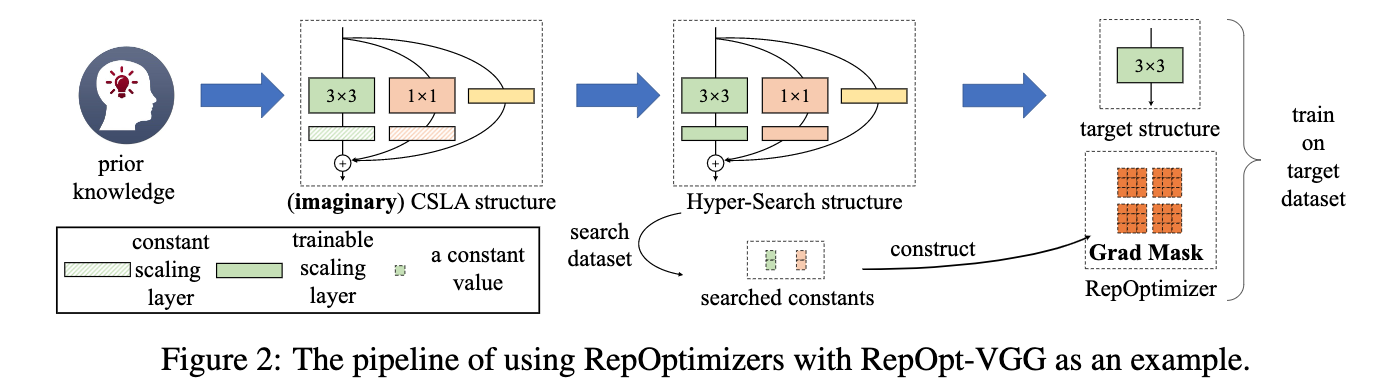
论文:Re-parameterizing Your Optimizers rather than Architectures
论文标题:Re-parameterizing Your Optimizers rather than Architectures
论文时间:30 May 2022
所属领域:机器学习
对应任务:优化算法
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15242
代码实现:https://github.com/dingxiaoh/repoptimizers
论文作者:Xiaohan Ding, Honghao Chen, Xiangyu Zhang, Kaiqi Huang, Jungong Han, Guiguang Ding
论文简介:In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm of incorporating model-specific prior knowledge into optimizers and using them to train generic (simple) models./在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的范式,即把特定模型的先验知识纳入优化器,并利用它们来训练通用(简单)模型。
论文摘要:The well-designed structures in neural networks reflect the prior knowledge incorporated into the models. However, though different models have various priors, we are used to training them with model-agnostic optimizers (e.g., SGD). In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm of incorporating model-specific prior knowledge into optimizers and using them to train generic (simple) models. As an implementation, we propose a novel methodology to add prior knowledge by modifying the gradients according to a set of model-specific hyper-parameters, which is referred to as Gradient Re-parameterization, and the optimizers are named RepOptimizers. For the extreme simplicity of model structure, we focus on a VGG-style plain model and showcase that such a simple model trained with a RepOptimizer, which is referred to as RepOpt-VGG, performs on par with the recent well-designed models. From a practical perspective, RepOpt-VGG is a favorable base model because of its simple structure, high inference speed and training efficiency. Compared to Structural Re-parameterization, which adds priors into models via constructing extra training-time structures, RepOptimizers require no extra forward/backward computations and solve the problem of quantization. The code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/dingxiaoh/repoptimizers
神经网络中精心设计的结构反映了纳入模型中的先验知识。然而,虽然不同的模型有不同的先验知识,但我们习惯于用与模型无关的优化器(如SGD)来训练它们。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的范式,将特定模型的先验知识纳入优化器,并使用它们来训练通用(简单)模型。作为一种实现方式,我们提出了一种新的方法,通过根据一组特定模型的超参数修改梯度来增加先验知识,这被称为梯度再参数化,优化器被称为RepOptimizers。为了使模型结构极其简单,我们把重点放在一个VGG风格的普通模型上,并展示了这样一个用RepOptimizer训练的简单模型,我们称之为RepOpt-VGG,其性能与最近设计好的模型相当。从实用的角度来看,RepOpt-VGG是一个有利的基础模型,因为它结构简单,推理速度快,训练效率高。与结构性重新参数化相比,结构性重新参数化是通过构建额外的训练时结构将先验因素加入到模型中,RepOptimizers不需要额外的前向/后向计算,并解决了量化问题。代码和模型可在 https://github.com/dingxiaoh/repoptimizers 公开。
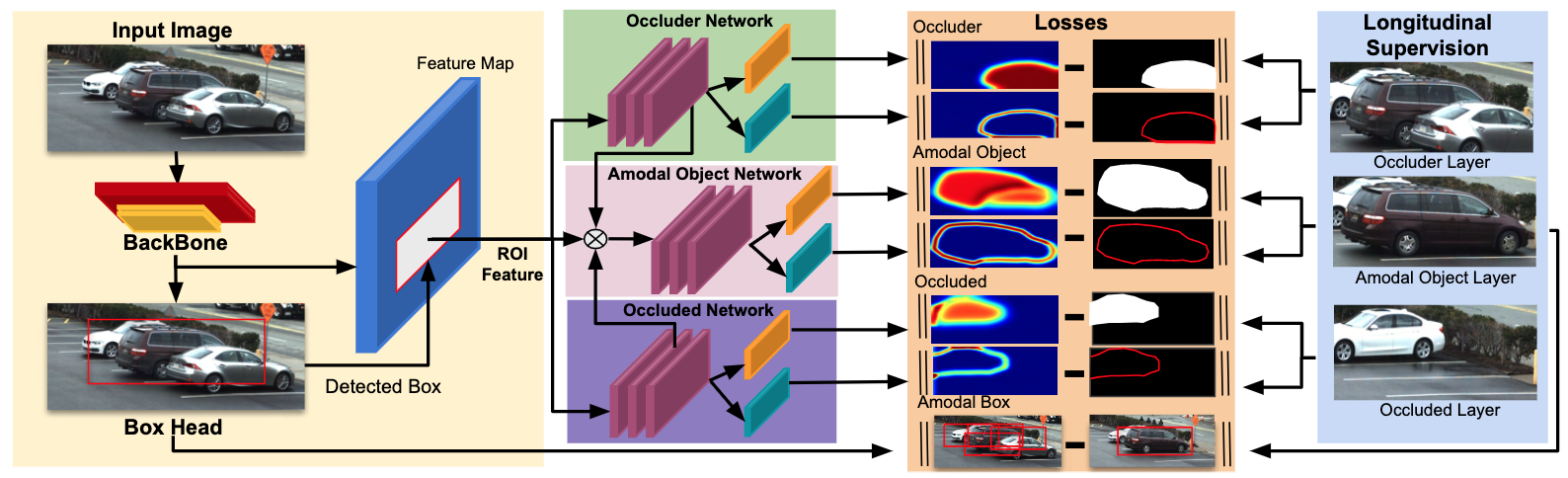
论文:WALT: Watch and Learn 2D Amodal Representation From Time-Lapse Imagery
论文标题:WALT: Watch and Learn 2D Amodal Representation From Time-Lapse Imagery
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Amodal Instance Segmentation,object-detection,Object Detection,实例分割,物体检测,目标检测
论文地址:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2022/papers/Reddy_WALT_Watch_and_Learn_2D_Amodal_Representation_From_Time-Lapse_Imagery_CVPR_2022_paper.pdf
代码实现:https://github.com/dineshreddy91/WALT
论文作者:N. Dinesh Reddy, Robert Tamburo, Srinivasa G. Narasimhan
论文简介:Labeled real data of occlusions is scarce (even in large datasets) and synthetic data leaves a domain gap, making it hard to explicitly model and learn occlusions./标记的闭塞物真实数据很少(即使在大型数据集中),而合成数据留下了领域空白,因此很难明确地对闭塞物进行建模和学习。
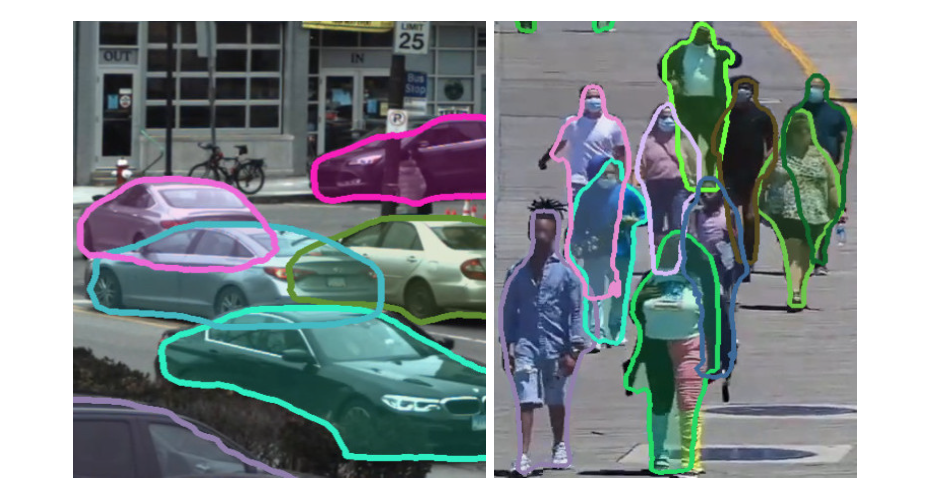
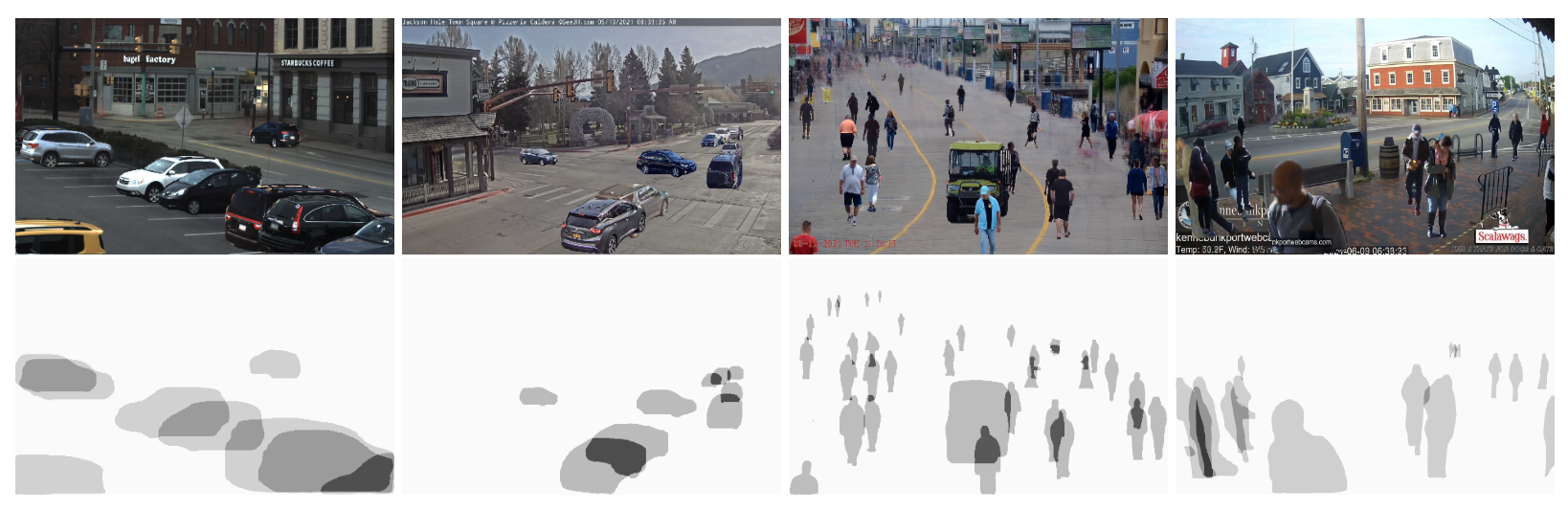
论文摘要:Current methods for object detection, segmentation, and tracking fail in the presence of severe occlusions in busy urban environments. Labeled real data of occlusions is scarce (even in large datasets) and synthetic data leaves a domain gap, making it hard to explicitly model and learn occlusions. In this work, we present the best of both the real and synthetic worlds for automatic occlusion supervision using a large readily available source of data: time-lapse imagery from stationary webcams observing street intersections over weeks, months, or even years. We introduce a new dataset, Watch and Learn Time-lapse (WALT), consisting of 12 (4K and 1080p) cameras capturing urban environments over a year. We exploit this real data in a novel way to automatically mine a large set of unoccluded objects and then composite them in the same views to generate occlusions. This longitudinal self-supervision is strong enough for an amodal network to learn object-occluder-occluded layer representations. We show how to speed up the discovery of unoccluded objects and relate the confidence in this discovery to the rate and accuracy of training occluded objects. After watching and automatically learning for several days, this approach shows significant performance improvement in detecting and segmenting occluded people and vehicles, over human-supervised amodal approaches.
目前用于物体检测、分割和跟踪的方法在繁忙的城市环境中存在严重的遮挡现象时失败了。标记的闭塞物的真实数据很少(甚至在大型数据集中),而合成数据则留下了一个领域的空白,因此很难对闭塞物进行明确的建模和学习。在这项工作中,我们提出了真实世界和合成世界中最好的自动闭塞监督,使用了大量现成的数据源:来自固定网络摄像机的延时图像,在几周、几个月甚至几年内观察街道交叉口。我们引入了一个新的数据集–观察和学习延时(WALT),由12个(4K和1080p)摄像头组成,在一年内捕捉城市环境。我们以一种新颖的方式利用这些真实的数据,自动挖掘出一大批未被遮挡的物体,然后在同一视图中对它们进行合成,生成遮挡物。这种纵向的自我监督足以让一个模态网络学习物体-闭塞物-闭塞层的表征。我们展示了如何加快发现未被遮挡的物体,并将这种发现的信心与训练被遮挡物体的速度和准确性联系起来。经过几天的观察和自动学习,这种方法在检测和分割被遮挡的人和车辆方面显示出明显的性能改进,超过了人类监督的模数方法。



论文:AiTLAS: Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation
论文标题:AiTLAS: Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation
论文时间:21 Jan 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Semantic Segmentation,Type prediction,语义分割,类型预估
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.08789
代码实现:https://github.com/biasvariancelabs/aitlas
论文作者:Ivica Dimitrovski, Ivan Kitanovski, Panče Panov, Nikola Simidjievski, Dragi Kocev
论文简介:The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets./AiTLAS工具箱(地球观测人工智能工具箱)包括最先进的机器学习方法,用于卫星图像的探索和预测分析,以及可用于人工智能的地球观测(EO)数据集的储存库。
论文摘要:The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets. It can be easily applied for a variety of Earth Observation tasks, such as land use and cover classification, crop type prediction, localization of specific objects (semantic segmentation), etc. The main goal of AiTLAS is to facilitate better usability and adoption of novel AI methods (and models) by EO experts, while offering easy access and standardized format of EO datasets to AI experts which further allows benchmarking of various existing and novel AI methods tailored for EO data.
AiTLAS工具箱(地球观测人工智能工具箱)包括最先进的机器学习方法,用于对卫星图像进行探索性和预测性分析,以及可用于人工智能的地球观测(EO)数据集库。它可以很容易地应用于各种地球观测任务,如土地利用和覆盖分类、作物类型预测、特定物体的定位(语义分割)等。AiTLAS的主要目标是促进EO专家更好地使用和采用新的人工智能方法(和模型),同时为人工智能专家提供方便的EO数据集和标准化的格式,这进一步允许为EO数据定制的各种现有和新的人工智能方法进行基准测试。

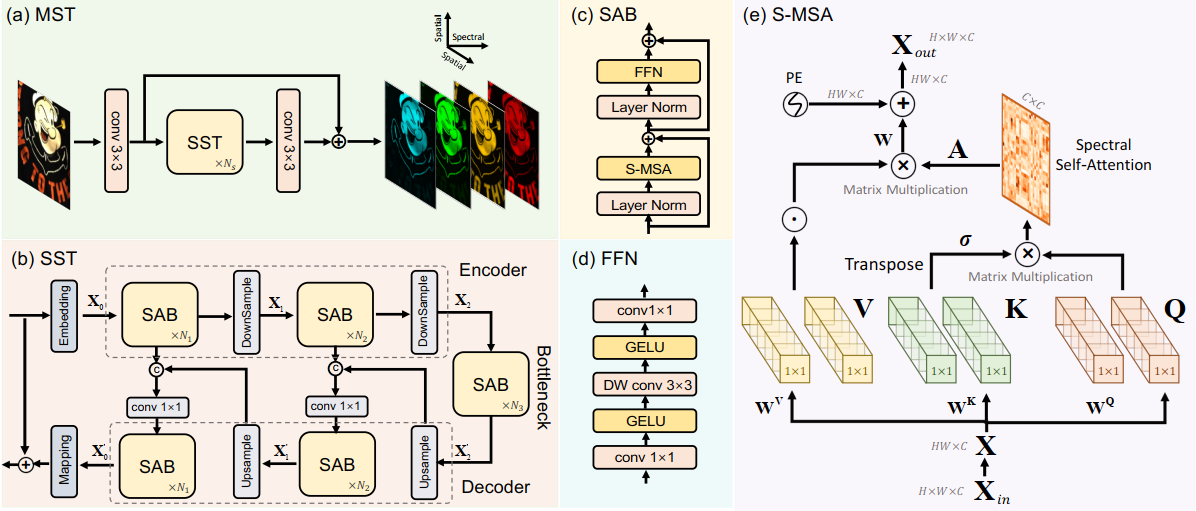
论文:MST++: Multi-stage Spectral-wise Transformer for Efficient Spectral Reconstruction
论文标题:MST++: Multi-stage Spectral-wise Transformer for Efficient Spectral Reconstruction
论文时间:17 Apr 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Restoration,Spectral Reconstruction,Spectral Super-Resolution,图像修复,光谱重建,光谱超分辨率
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.07908
代码实现:https://github.com/caiyuanhao1998/MST-plus-plus
论文作者:Yuanhao Cai, Jing Lin, Zudi Lin, Haoqian Wang, Yulun Zhang, Hanspeter Pfister, Radu Timofte, Luc van Gool
论文简介:Existing leading methods for spectral reconstruction (SR) focus on designing deeper or wider convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to learn the end-to-end mapping from the RGB image to its hyperspectral image (HSI)./现有的光谱重建(SR)的领先方法侧重于设计更深或更广的卷积神经网络(CNN)来学习从RGB图像到其高光谱图像(HSI)的端到端映射。
论文摘要:Existing leading methods for spectral reconstruction (SR) focus on designing deeper or wider convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to learn the end-to-end mapping from the RGB image to its hyperspectral image (HSI). These CNN-based methods achieve impressive restoration performance while showing limitations in capturing the long-range dependencies and self-similarity prior. To cope with this problem, we propose a novel Transformer-based method, Multi-stage Spectral-wise Transformer (MST++), for efficient spectral reconstruction. In particular, we employ Spectral-wise Multi-head Self-attention (S-MSA) that is based on the HSI spatially sparse while spectrally self-similar nature to compose the basic unit, Spectral-wise Attention Block (SAB). Then SABs build up Single-stage Spectral-wise Transformer (SST) that exploits a U-shaped structure to extract multi-resolution contextual information. Finally, our MST++, cascaded by several SSTs, progressively improves the reconstruction quality from coarse to fine. Comprehensive experiments show that our MST++ significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art methods. In the NTIRE 2022 Spectral Reconstruction Challenge, our approach won the First place. Code and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/caiyuanhao1998/MST-plus-plus
现有的光谱重建(SR)的领先方法侧重于设计更深或更广的卷积神经网络(CNN)来学习从RGB图像到其高光谱图像(HSI)的端对端映射。这些基于CNN的方法取得了令人印象深刻的修复性能,但在捕捉长距离依赖性和自相似性的先验方面显示出局限性。为了应对这一问题,我们提出了一种新的基于Transformer的方法,即多级逐光谱Transformer(MST++),用于高效的光谱重建。特别是,我们采用了基于HSI空间稀疏而光谱自相似性质的逐光谱多头自注意(S-MSA)来组成基本单元,即逐光谱注意块(SAB)。然后,SABs建立了单级逐频谱Transformer(SST),利用U形结构来提取多分辨率的上下文信息。最后,我们的MST++,通过几个SST的级联,逐步提高重建质量,从粗到细。综合实验表明,我们的MST++明显优于其他最先进的方法。在NTIRE 2022年的光谱重建挑战赛中,我们的方法赢得了第一名。代码和预训练的模型在 https://github.com/caiyuanhao1998/MST-plus-plus 公开。

论文:Ensembling Off-the-shelf Models for GAN Training
论文标题:Ensembling Off-the-shelf Models for GAN Training
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Generation,图像生成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.09130
代码实现:https://github.com/nupurkmr9/vision-aided-gan
论文作者:Nupur Kumari, Richard Zhang, Eli Shechtman, Jun-Yan Zhu
论文简介:Can the collective “knowledge” from a large bank of pretrained vision models be leveraged to improve GAN training?/大型预训练视觉模型库的集体 "知识 "能否被用来改善GAN训练?
论文摘要:The advent of large-scale training has produced a cornucopia of powerful visual recognition models. However, generative models, such as GANs, have traditionally been trained from scratch in an unsupervised manner. Can the collective “knowledge” from a large bank of pretrained vision models be leveraged to improve GAN training? If so, with so many models to choose from, which one(s) should be selected, and in what manner are they most effective? We find that pretrained computer vision models can significantly improve performance when used in an ensemble of discriminators. Notably, the particular subset of selected models greatly affects performance. We propose an effective selection mechanism, by probing the linear separability between real and fake samples in pretrained model embeddings, choosing the most accurate model, and progressively adding it to the discriminator ensemble. Interestingly, our method can improve GAN training in both limited data and large-scale settings. Given only 10k training samples, our FID on LSUN Cat matches the StyleGAN2 trained on 1.6M images. On the full dataset, our method improves FID by 1.5x to 2x on cat, church, and horse categories of LSUN.
大规模训练的出现产生了一个强大的视觉识别模型的宝库。然而,生成模型,如GANs,传统上是以无监督的方式从头开始训练。能否利用来自大型预训练视觉模型库的集体 "知识 "来改善GAN训练?如果可以的话,有这么多模型可供选择,应该选择哪一个(几个),以及它们以何种方式最有效?我们发现,预训练的计算机视觉模型在用于判别器的集合时可以显著提高性能。值得注意的是,所选模型的特定子集对性能影响很大。我们提出了一个有效的选择机制,通过探测预训练模型嵌入中真假样本之间的线性可分离性,选择最准确的模型,并逐步将其加入到判别器集合中。有趣的是,我们的方法在有限的数据和大规模的环境中都能改善GAN的训练。鉴于只有1万个训练样本,我们在LSUN Cat上的FID与在1.6M图像上训练的StyleGAN2匹配。在完整的数据集上,我们的方法在LSUN的猫、教堂和马的类别上提高了1.5倍到2倍的FID。




我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。

- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~