Title:
Differentiation of intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn’s disease through explainable machine learning method
用可解释机器学习方法鉴别肠结核和克罗恩病
Keywords:
Intestinal tuberculosis; Crohn’s disease; Shapley Value; Machine learning
肠结核,克罗恩病,沙普利值,机器学习
沙普利值法( Shapley Value Method)由2009年诺贝尔经济学奖得主、著名经济学家劳埃德·沙普利(Lloyd Shapley,1923-2016)提出,主要用于解决在合作博弈中各方的利益分配问题,防止“有难能够同当,有福不知如何分配”的尴尬情况。(From: 经管下午茶:沙普利值法( Shapley Value Method)https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/165051523)
Abstract:
This study set out to develop an effective framework to distinguish Crohn’s disease from intestinal tuberculosis through an explainable machine learning (ML) model. A cohort consisting of 200 patient data (CD = 160, ITB = 40) is used in training and validating models. After feature selection, a total of nine variables are extracted, including intestinal surgery, abdominal, bloody stool, PPD, knot, ESAT-6, CFP-10, intestinal dilatation and comb sign. Besides, we compared the predictive performance of the ML models with traditional statistical methods. This work also provides insights into the ML model’s outcome through the SHAP method. Results illustrate that the XGBoost algorithm outperforms other classifiers in terms of area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, precision and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC), yielding values of 0.891, 0.813, 0.969, 0.867 and 0.801 respectively. More importantly, the prediction outcomes of XGBoost can be effectively explained through the SHAP method. The proposed framework proves that the effectiveness of distinguishing CD from ITB through interpretable machine learning, which has potential value in clinical application.
本研究旨在建立一个有效的框架,通过可解释机器学习(ML)模型来区分克罗恩病和肠结核。一个由200个病人数据(克罗恩病160,肠结核40)组成的队列用于训练和验证模型。经过特征选择,共提取9个变量,包括肠道外科、腹部、血便、结核菌素试验、结节、ESAT-6、CFP-10、肠道扩张和梳状征。此外,我们还比较了ML模型与传统统计方法的预测性能。这项工作还通过SHAP方法(黑盒模型事后归因解析)提供了对ML模型结果的见解。结果表明,XGBoost算法在接收者工作特性曲线下面积(AUC)、灵敏度、特异性、精度和马修斯相关系数(MCC)等方面均优于其他分类器,分别得到0.891、0.813、0.969、0.867和0.801。更重要的是,通过SHAP方法可以有效地解释XGBoost的预测结果。该框架证明了通过可解释机器学习区分克罗恩病和肠结核的有效性,具有潜在的临床应用价值。
马修斯相关系数:
马修斯相关系数是在使用机器学习作为二进制(2类)的质量的度量的分类,通过布赖恩W.马修斯在1975年由生物化学引入。它返回介于-1和+1之间的值。系数+1表示完美预测,0表示不比随机预测好,-1表示预测和观察之间的完全不一致。统计数据也称为phi系数。可以使用以下公式直接从混淆矩阵计算MCC :
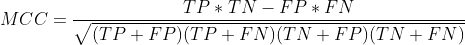
(From:【机器学习】马修斯相关系数(Matthews correlation coefficient)https://blog.csdn.net/ARPOSPF/article/details/84997220)
The proposed framework consists of three components. The first level performs the imbalanced treatment of the dataset using a SMOTE algorithm (Chawla et al., 2002). In the second level, a tree-based model is applied to detect CD from ITB. At the last level, the interpretation and visualization of the model are demonstrated through Shapley values (Lundberg and Lee, 2017b). To validate the superiority of the proposed method, we compare the performance of six different classical algorithms, including Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), Logistic Regression (LOG), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Radom Forest (RF) and Adaptive Boosting (Adaboost) (Fisher, 1936; Kleinbaum et al., 2002; Noble, 2006;Wang, 2003; Breiman, 2001; Hastie et al., 2009). The main contribution of this research addresses a real-world problem, differentiating CD fromITB based on explainablemachine learning. Thismethod can provide local interpretation and direct results of visualization without losing the classification accuracy.
本研究提出的框架包括三个部分。首先使用SMOTE算法对数据集进行不平衡处理(Chawla et al., 2002); 其次采用基于树的模型检测肠结核和克罗恩病;最后通过Shapley值演示了模型的解释和可视化 (Lundberg and Lee, 2017b)。为了验证该方法的优越性,我们比较了六种经典算法的性能,包括LDA、逻辑回归、支持向量机、人工神经网络、随机森林和自适应提升(Fisher, 1936; Kleinbaum et al., 2002; Noble, 2006;Wang, 2003; Breiman, 2001; Hastie et al., 2009)。本研究的主要贡献在于解决了一个现实问题,即基于可解释机器学习将克罗恩病与肠结核区分开来。该方法能在不损失分类精度的前提下,提供局部解释和直观的可视化结果。
SMOTE算法的介绍:
为了解决数据的非平衡问题,2002年Chawla提出了SMOTE算法,即合成少数过采样技术,它是基于随机过采样算法的一种改进方案。该技术是目前处理非平衡数据的常用手段,并受到学术界和工业界的一致认同,接下来简单描述一下该算法的理论思想。SMOTE算法的基本思想就是对少数类别样本进行分析和模拟,并将人工模拟的新样本添加到数据集中,进而使原始数据中的类别不再严重失衡。该算法的模拟过程采用了KNN技术,模拟生成新样本的步骤如下:
(1)采样最邻近算法,计算出每个少数类样本的K个近邻;
(2)从K个近邻中随机挑选N个样本进行随机线性插值;
(3)构造新的少数类样本;
(4)将新样本与原数据合成,产生新的训练集;
(版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「MXuDong」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33472765/article/details/87891320)