代码
learn_kalman.py
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import time
from kinematic_model import freedrop
from controller import kalman_filterimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 支持中文
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.family']='SimHei'
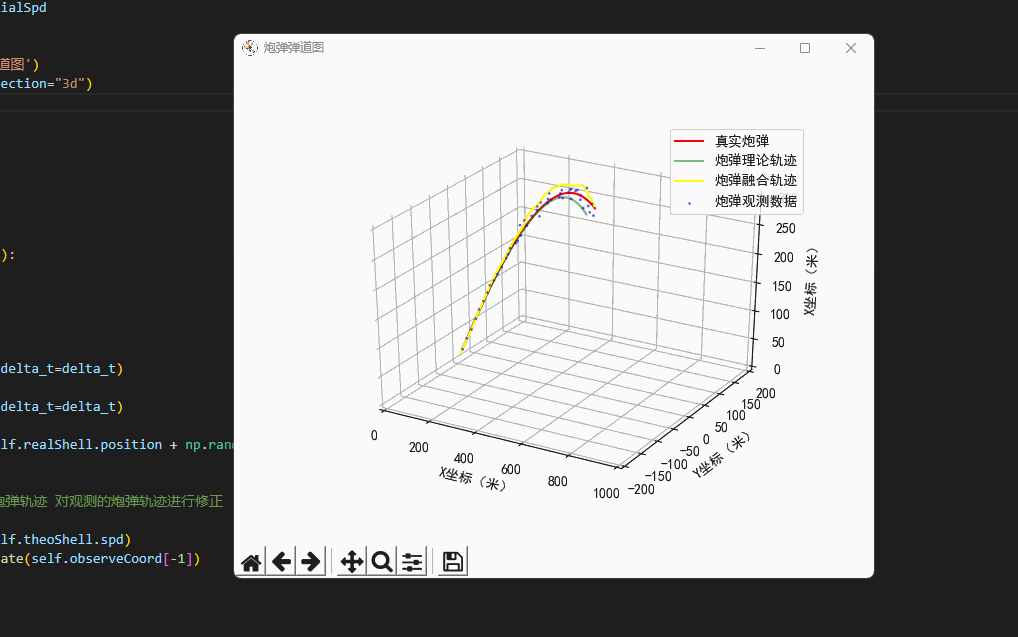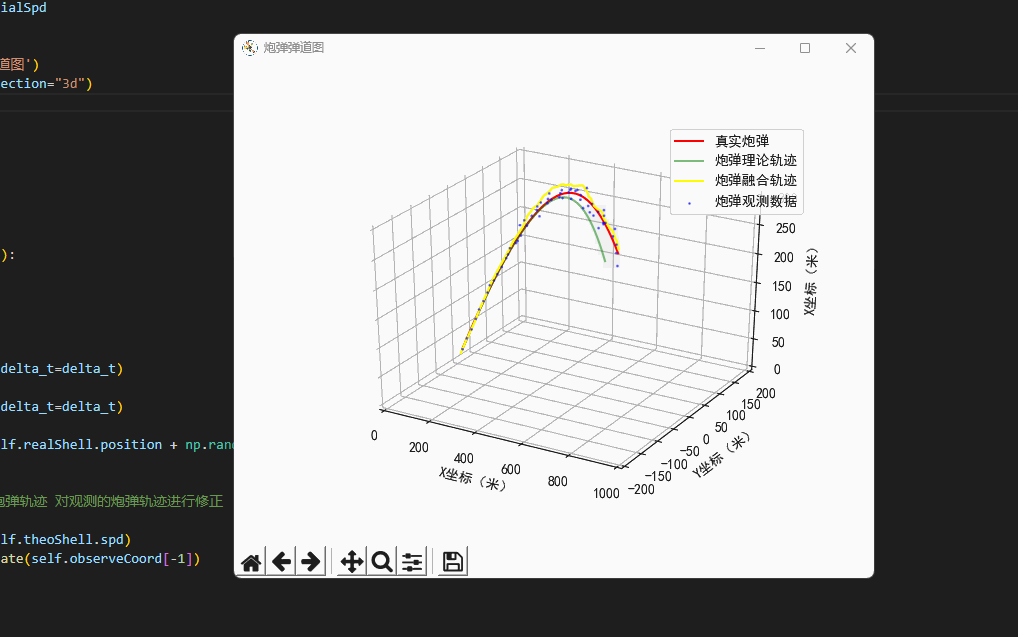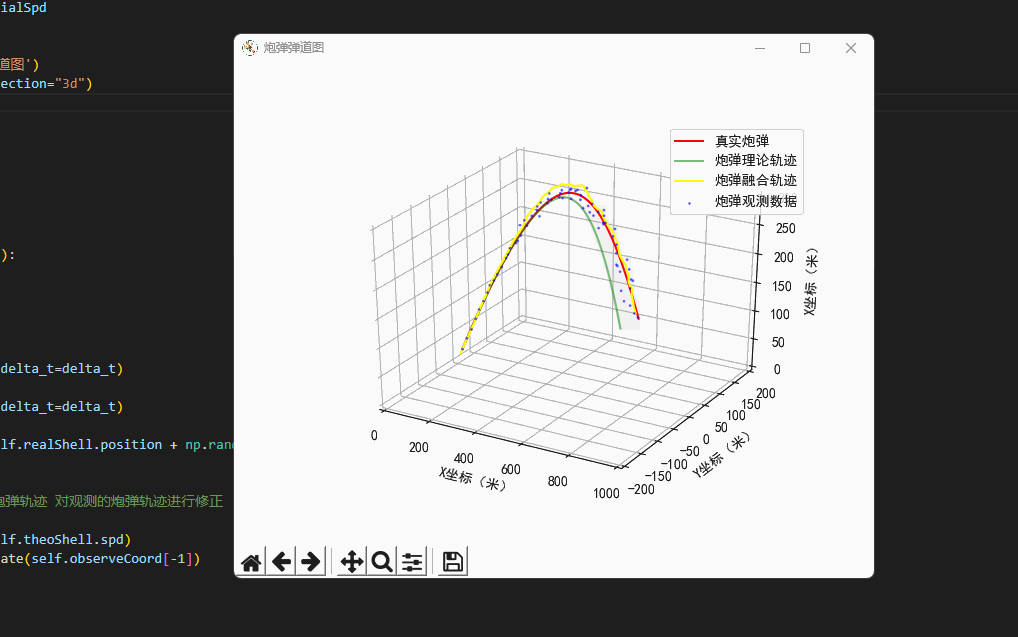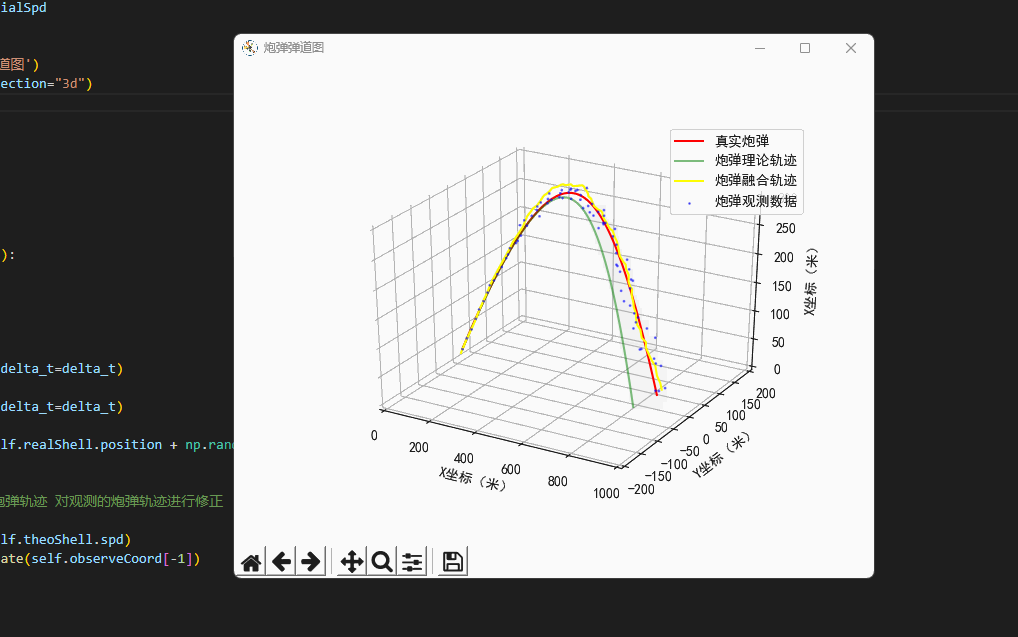
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False #用来正常显示负号class Scene:'''场景'''def __init__(self,windSpd=np.array([0.7,0.3,0.0]),\initialSpd=np.array([120.0,0.0,120.0])):'''我现在是一个防空兵防空炮打出一枚炮弹,真实的炮弹轨迹,它可能会受风的影响,可能会有随机因素导致偏离目标导致打不中飞机...我们可以使用指挥所观测到的炮弹轨迹,因为炮弹距离很远,所以这个观测不是很靠谱...所以我们所使用了卡尔曼滤波算法,得到了一条真实的炮弹轨迹...'''# 真实的炮弹self.realShell=freedrop.FreeDropBinder(windSpd=windSpd,initialSpd=initialSpd)# 理论上炮弹的落点self.theoShell=freedrop.FreeDropBinder(windSpd=np.array([0.0,0.0,0.0]),initialSpd=initialSpd,randRatio=0.0)# 卡卡尔曼滤波器self.kf=kalman_filter.KF_Onmi3D()self.kf.initState[3:6]=initialSpd# 绘图区self.fig=plt.figure('炮弹弹道图')self.ax = self.fig.gca(projection="3d")# 数据缓存self.realCoord=[]self.theoCoord=[]self.kalmanCoord=[]self.observeCoord=[]def UpdateData(self,delta_t=0.2):'''更新虚拟环境的数据:return:'''# 真实炮弹轨迹self.realShell.StateUpdate(delta_t=delta_t)# 理论炮弹轨迹self.theoShell.StateUpdate(delta_t=delta_t)# 观测到的炮弹轨迹self.observeCoord.append(self.realShell.position + np.random.random(3) * self.realShell.position[0]/20.0 - self.realShell.position[0]/40.0)# 卡尔曼滤波'''基于卡尔曼滤波,结合理论炮弹轨迹 对观测的炮弹轨迹进行修正'''self.kf.Predict(velocity=self.theoShell.spd)Hybrid_Position=self.kf.Update(self.observeCoord[-1])# 绘图(真实的弹道)plt.cla()self.ax.set_xlim(0, 1000)self.ax.set_ylim(-200, 200)self.ax.set_zlim(0, 300)self.ax.set_xlabel("X坐标(米)")self.ax.set_ylabel("Y坐标(米)")self.ax.set_zlabel("X坐标(米)")# 计算三个类型的炮弹self.realCoord.append(np.copy(self.realShell.position)) # 真实炮弹self.theoCoord.append(np.copy(self.theoShell.position)) # 理论模型self.kalmanCoord.append(np.copy(Hybrid_Position))self.curve2Draw=np.array(self.realCoord)self.curve2 = np.array(self.observeCoord)self.curve3 = np.array(self.theoCoord)self.curve4 = np.array(self.kalmanCoord)self.ax.plot(self.curve2Draw[:,0],self.curve2Draw[:,1],self.curve2Draw[:,2],label='真实炮弹',color='red')self.ax.scatter(self.curve2[:, 0], self.curve2[:, 1], self.curve2[:, 2],'rv+', label='炮弹观测数据', color='blue',alpha=0.5,s=1)self.ax.plot(self.curve3[:, 0], self.curve3[:, 1], self.curve3[:, 2], label='炮弹理论轨迹', color='green', alpha=0.5)self.ax.plot(self.curve4[:, 0], self.curve4[:, 1], self.curve4[:, 2], label='炮弹融合轨迹', color='yellow', alpha=1.0)self.ax.legend()plt.pause(0.05)# 开始模拟环境
#plt.ion()s=Scene()for i in range(1000):if s.realShell.position[2]<0: breaks.UpdateData()
plt.ioff()
plt.show()freerop.py
#coding=utf-8
import timeimport numpy as np
'''3D自由落体模型(含有风阻)
'''class FreeDropBinder:'''为实体绑定自由落体属性'''def __init__(self,windSpd=np.array([0.0,0.0,0.0]),resRatio=0.0004,G=9.8,initialPos=np.array([0.0,0.0,0.0]),initialSpd=np.array([0.0,0.0,0.0]),randRatio=0.1):''':param windSpd: 风速(三维):param resRatio: 风阻比例(全向):param G: 重力加速度:param initialPos: 物体初始位置:param initialSpd: 物体初始速度'''self.position=initialPosself.spd=initialSpdself.windSpd=windSpdself.resRatio=resRatioself.G=Gself.randRatio=randRatiodef StateUpdate(self,delta_t=0.05,driveForce=np.array([0.0,0.0,0.0])):'''更新实体位置信息:param delta_t::return:'''# 重力因素self.spd+=np.array([0,0,-self.G*delta_t])# 风阻因素self.spd=np.where(self.spd>0,self.spd-self.resRatio*self.spd*self.spd,self.spd)self.spd = np.where(self.spd <= 0, self.spd + self.resRatio * self.spd * self.spd, self.spd)# 风力因素# 驱动因素self.spd+=(driveForce+self.windSpd)*delta_t# 随机因素self.spd+=(np.random.rand(3)-0.5)*2*self.randRatio*delta_t# 更新坐标self.position=self.position+self.spd*delta_tif __name__=='__main__':box=FreeDropBinder(initialSpd=np.array([10.0,0.0,100.0]))for i in range(30):print(box.Update())
kalman_filter.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltclass KF_Onmi3D:'''三维,无方向场景下的卡尔曼滤波算法模组'''def __init__(self):# 初始状态 x y z vx vy vzself.initState=np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],dtype=np.float)# 初始协方差,可以看出是每个维度都是一一对应的关系'''[ 1 0 0 0 0 0 ][ 0 1 0 0 0 0 ][ 0 0 1 0 0 0 ][ 0 0 0 1 0 0 ][ 0 0 0 0 1 0 ][ 0 0 0 0 0 1 ]'''self.initCov=np.eye(6)# 状态转移矩阵self.stateTransMatrix=np.array([[1,0,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0,0,1],[0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0,0,1]],dtype=np.float)# 观测矩阵 X Y Z Vx Vy Vzself.observeMatrix=np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]],dtype=np.float)# 过程噪声(先设定一个初始值,这个需要跟据你系统的评估来确定)self.procNoise=np.eye(6)*0.001# 观测噪声的协方差矩阵self.observeNoiseCov=np.eye(3)*1self.InitParams()def InitParams(self):'''初始化状态变量:return:'''self.currentState=self.initState.copy()self.predictState=self.initState.copy()self.currentCov=self.initCovself.predictedCov=self.currentCovdef Predict(self,velocity=np.array([0,0,0],dtype=np.float)):'''预测过程:param v::return:'''# 基于当前的速度,预测机器人下一个状态的状态数值self.predictState=self.stateTransMatrix.dot(self.currentState)# 预测三维环境下的协方差矩阵self.predictedCov=self.stateTransMatrix.dot(self.currentCov).dot(self.stateTransMatrix.T)+self.procNoise# 把速度赋值给状态中的“速度”属性self.currentState[3:6] = velocitydef Update(self,observed_Pos=np.array([0,0,0],dtype=np.float)):'''更新数据:param observed_Pos: 带有误差的位置观测值:return:'''# 卡尔曼增益(Kalman Gain)计算'''K=\frac{估计的误差}{估计的误差+测量的误差}=\frac{\hat{P_k}C}{C\hat{P_k}C^T+Error}'''self.Kalman_Gain = self.predictedCov.dot(self.observeMatrix.T) \.dot(np.linalg.inv( \self.observeMatrix.dot(self.predictedCov).dot(self.observeMatrix.T) + self.observeNoiseCov))'''基于Kalman Gain估算当前状态'''self.currentState = self.predictState + self.Kalman_Gain.dot(observed_Pos-self.observeMatrix.dot(self.predictState))'''当前协方差估计'''self.currentCov = (np.eye(6) - self.Kalman_Gain.dot(self.observeMatrix)).dot(self.predictedCov)return self.currentState[0:3]
参考
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1gF411f78t/?spm_id_from=333.337.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=667c3d14dbb51ec849c0bc7c38329d10