文章目录
- Fastjson 使用指南
- 0 简要说明
- 为什么要用JSON?用JSON的好处是什么?
- 为什么要用JSON?
- JSON好处
- 1 常用数据类型的JSON格式
- 值的范围
- 2 快速上手
- 2.1 依赖
- 2.2 实体类
- 2.3 测试类
- 3 常见用法
- 3.1 序列化操作
- 核心操作
- 对象转换为JSON串
- list转换JSON串
- map转换为JSON串
- 3.2 反序列化操作
- JSON串转换为对象
- JSON串转换为map
- JSON串转换为list
- 4 常见问题
- 4.1 如何处理日期毫秒值问题
- 4.2 定制化序列化字段
- 4.3 指定某些字段不序列化
- 4.4 自定义序列化器
- 4.5 使用ordinal指定字段的顺序
- 4.6 序列化起别名
- 4.7 空值序列化操作处理
w3school
JSON格式化
序列化操作
Fastjson 使用指南
0 简要说明
Fastjson是一个Java语言编写的高性能功能完善的SON库。它采用一种"假定有序快速匹配”的算法,把JSON Parse的性能提升到极致,是目前)ava语言中最快的)SON库。Fastjson接口简单易用,已经被广泛使用在缓存序列化、协议交互、Web输出、Android客户端等多种应用场景。
主要特点:
快速FAST(比其它任何基于Java的解析器和生成器更快,包括jackson)
强大(支持普通DK类包括任意Java Bean Class、Collection、Map、Date或enum)
零依赖(除了DK没有依赖其它任何类库)
为什么要用JSON?用JSON的好处是什么?
1.首先JSON是一种数据格式,我们HTTP请求交互/内容存储到JSON,我们可以替代的方案就是XML,或者直接文本,当然首先是是使用JSON或者XML,其次才是文本,因为您考虑到存储方便也要考虑解析方便。
2.JSON是一个轻量级的数据格式,轻量级是相比较XML等其他复杂的存储格式而言,各个语言都兼容,都有各自解析JSON的组件。
为什么要用JSON?
1.其实用JSON主要是因为它轻量,各个平台语言都支持JSON交互、JSON解析和存储。
2.JSON常用于我们接口交互,前后端交互中,有解析速度快,方便的特点。
3.JSON常用于我们一些配置文件也是因为解析方便,JSON存储数据体积小等特征,而不像XML、PList(也是xml的一种)等格式,定义各种Dom节点(当然复杂的格式还是建议XML)。
JSON好处
1.JSON是大家公认的传输格式,所以学习成本低,程序员之间交流经常会问,您接口返回什么格式?答曰:“JSON”,其实就没啥问题了。
2.各个语言、各个框架(第三方组件)都支持JSON,所以使用上来讲,复用率更高,不用格式转来转去。
3.上面也讲了,体积小、解析速度快。
1 常用数据类型的JSON格式
值的范围
- Number:数字(整数或浮点数)
- String:字符串(在双引号中),一定是英文双引号(“”),个别弱语言可以支持单引号。
- Boolean:逻辑值(true 或 false)
- Array:数组(在方括号中),一般是在Value位置上。
- Object:对象(在花括号中),一般是在Value位置上。
- null:没什么好说的。
{"key":"value"},最简单的JSON 格式。
{"key1":"value1","key2":"value2"},一个JSON中有多个键值对的表达方式。
{"key":["a","b","sojson.com"]},value是一个Array 的JSON格式。
{"sojson":["5年","JSON在线解析","sojson.com",true,1,null]},value是一个Array 的JSON格式,并且这个数组中有多重类型的元素,有String,Boolean,Number,null。
{"key":{"json":"json for javascript"}},value 是JSONObject的JSON格式。
2 快速上手
2.1 依赖
仓库地址
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>1.2.51</version></dependency>
https://www.sojson.com/
2.2 实体类
package com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.domain;import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.annotation.Excel;
import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.annotation.ExcelIgnore;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserDomain implements Serializable {/*** 用户名*/private String userName;/*** 生日*/private Date birthday;/*** 性别*/private String sex;/*** 地址*/private String address;}
2.3 测试类
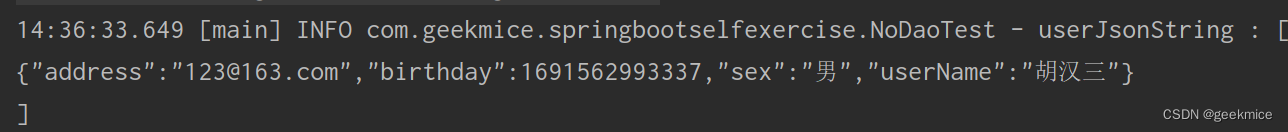
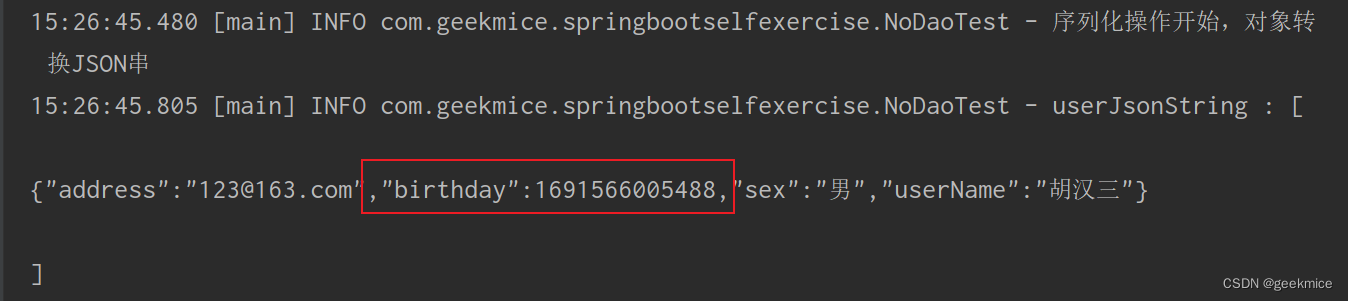
/*** 处理fastjson*/@Testpublic void validateFastJson() {UserDomain user = UserDomain.builder().userName("胡汉三").sex("男").birthday(new Date()).address("123@163.com").build();String userJsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);log.info("userJsonString : [\n{}\n]", userJsonString);}
14:36:33.649 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - userJsonString : [
{“address”:“123@163.com”,“birthday”:1691562993337,“sex”:“男”,“userName”:“胡汉三”}
]
3 常见用法
3.1 序列化操作
序列化:将一个对象编码成一个字节流(I/O),序列化的目的是为了方便数据的传递以及存储到磁盘上(把一个Java对象写入到硬盘或者传输到网路上面的其它计算机,这时我们就需要将对象转换成字节流才能进行网络传输。对于这种通用的操作,就出现了序列化来统一这些格式)。
核心操作
/*** This method serializes the specified object into its equivalent Json representation. Note that this method works fine if the any of the object fields are of generic type,* just the object itself should not be of a generic type. If you want to write out the object to a* {@link Writer}, use {@link #writeJSONString(Writer, Object, SerializerFeature[])} instead.** @param object the object for which json representation is to be created setting for fastjson* @return Json representation of {@code object}.*/
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(obj);对象转换为JSON串
/*** 处理fastjson*/@Testpublic void validateFastJson() {log.info("序列化操作开始,对象转换JSON串");UserDomain user = UserDomain.builder().userName("胡汉三").sex("男").birthday(new Date()).address("123@163.com").build();String userJsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);log.info("userJsonString : [\n\n{}\n\n]", userJsonString);}
14:59:16.377 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - userJsonString : [
{“address”:“123@163.com”,“birthday”:1691564356144,“sex”:“男”,“userName”:“胡汉三”}
]
list转换JSON串
/*** 处理fastjson*/@Testpublic void validateFastJson() {log.info("序列化操作开始,list转换JSON串");List<UserDomain> result = Arrays.asList(UserDomain.builder().userName("胡汉三").sex("男").birthday(new Date()).address("123@163.com").build(),UserDomain.builder().userName("笑笑").sex("女").birthday(new Date()).address("345@163.com").build());String listStr = JSON.toJSONString(result);log.info("listStr : [\n\n{}\n\n]" , listStr);}
14:59:16.381 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - listStr : [
[{“address”:“123@163.com”,“birthday”:1691564356380,“sex”:“男”,“userName”:“胡汉三”},{“address”:“345@163.com”,“birthday”:1691564356380,“sex”:“女”,“userName”:“笑笑”}]
]
map转换为JSON串
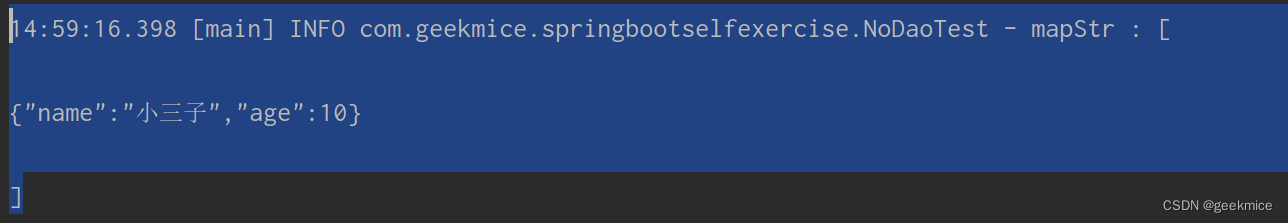
/*** 处理fastjson*/@Testpublic void validateFastJson() {log.info("序列化操作开始,map转换JSON串");HashMap<Object, Object> map = Maps.newHashMap();map.put("name","小三子");map.put("age",10);final String mapStr = JSON.toJSONString(map);log.info("mapStr : [\n\n{}\n\n]" , mapStr);}
14:59:16.398 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - mapStr : [
{“name”:“小三子”,“age”:10}
]
3.2 反序列化操作
JSON串转换为对象
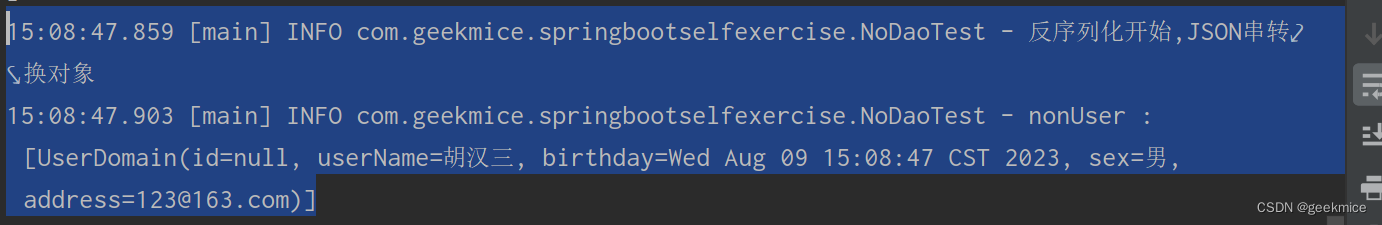
String userJsonString="{\"address\":\"123@163.com\",\"birthday\":1691564927544,\"sex\":\"男\",\"userName\":\"胡汉三\"}";log.info("反序列化开始,JSON串转换对象");UserDomain nonUser = JSON.parseObject(userJsonString, UserDomain.class);log.info("nonUser : [{}]" , nonUser);
15:08:47.859 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - 反序列化开始,JSON串转换对象
15:08:47.903 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - nonUser : [UserDomain(id=null, userName=胡汉三, birthday=Wed Aug 09 15:08:47 CST 2023, sex=男, address=123@163.com)]
JSON串转换为map
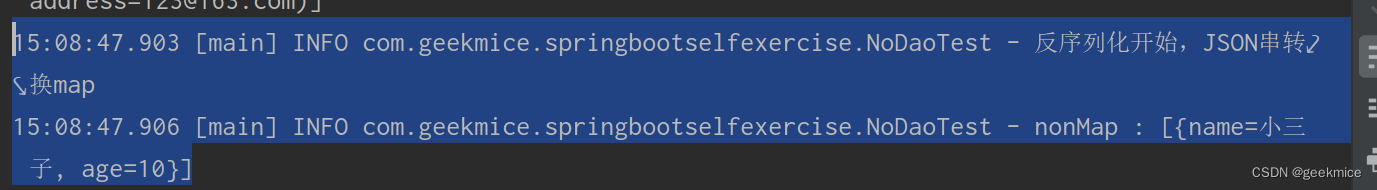
String mapStr="{\"name\":\"小三子\",\"age\":10}";log.info("反序列化开始,JSON串转换map");Map<Object, Object> nonMap = JSON.parseObject(mapStr, new TypeReference<Map<Object, Object>>() {});log.info("nonMap : [{}]" , nonMap);
15:08:47.903 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - 反序列化开始,JSON串转换map
15:08:47.906 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - nonMap : [{name=小三子, age=10}]
JSON串转换为list
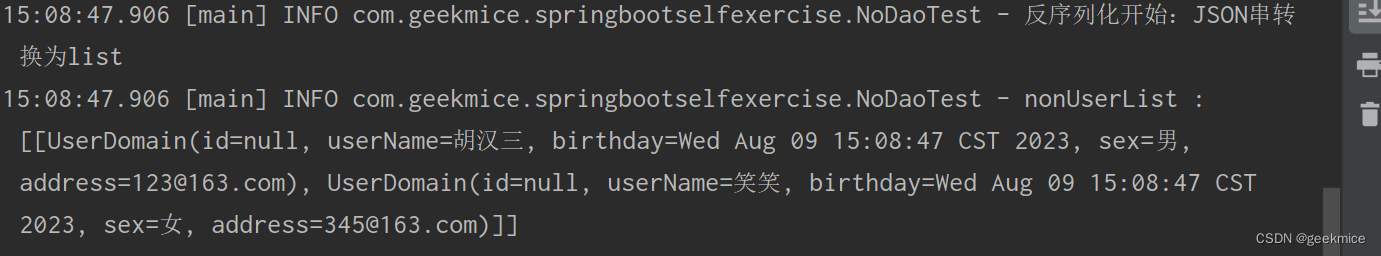
String listStr ="{\"address\":\"123@163.com\",\"birthday\":1691564927840,\"sex\":\"男\",\"userName\":\"胡汉三\"},{\"address\":\"345@163.com\",\"birthday\":1691564927840,\"sex\":\"女\",\"userName\":\"笑笑\"}"log.info("反序列化开始:JSON串转换为list");List<UserDomain> nonUserList = JSON.parseArray(listStr, UserDomain.class);log.info("nonUserList : [{}]" , nonUserList);
15:08:47.906 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - 反序列化开始:JSON串转换为list
15:08:47.906 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - nonUserList : [[UserDomain(id=null, userName=胡汉三, birthday=Wed Aug 09 15:08:47 CST 2023, sex=男, address=123@163.com), UserDomain(id=null, userName=笑笑, birthday=Wed Aug 09 15:08:47 CST 2023, sex=女, address=345@163.com)]]
4 常见问题
4.1 如何处理日期毫秒值问题
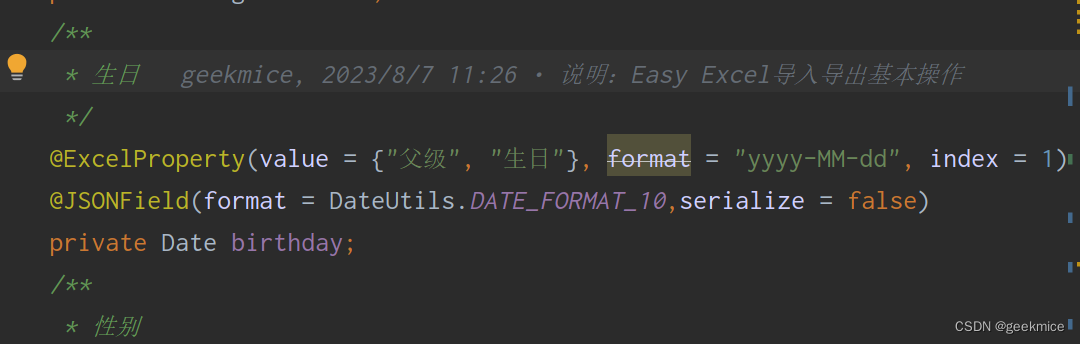
方案一:使用 @JSONField(format = DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_10)
format属性指定时间日期格式,只是针对于某几个字段,使用了这个注解有效
方案二:通过代码实现,这种形式所有date类型都是指定时间格式 yyyy-MM-dd
String result = JSON.toJSONStringWithDateFormat(user, com.alibaba.excel.util.DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_10);
4.2 定制化序列化字段
4.3 指定某些字段不序列化
@JSONField(serialize= false)
4.4 自定义序列化器
1 定义
package com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.serializer;import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.DefaultJSONParser;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer.ObjectDeserializer;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.JSONSerializer;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.ObjectSerializer;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializeWriter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateUtils;import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Objects;/*** @BelongsProject: spring-boot-self-exercise* @BelongsPackage: com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.serializer* @Author: pingmingbo* @CreateTime: 2023-08-09 15:59* @Description: TODO* @Version: 1.0*/
@Slf4j
public class MyDateSerializer implements ObjectSerializer, ObjectDeserializer {@Overridepublic void write(JSONSerializer serializer, Object object, Object fieldName, Type fieldType, int features) throws IOException {// 序列化,// log.info("serializer : [{}]" , serializer); // 数据源// log.info("object : [{}]" , object); // 字段值// log.info("fieldName : [{}]" , fieldName); // 字段名称// log.info("fieldType : [{}]" , fieldType);// 类型if (Objects.isNull(object)) {return;}String dateStr = object.toString();Date date = null;if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(dateStr)) {try {date = DateUtils.parseDate(dateStr, com.alibaba.excel.util.DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_19);} catch (ParseException e) {log.error("error msg:【{}】", e);throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);}}long time = date.getTime();SerializeWriter writer = serializer.getWriter();writer.writeLong(time);}@Overridepublic <T> T deserialze(DefaultJSONParser parser, Type type, Object fieldName) {return null;}@Overridepublic int getFastMatchToken() {return 0;}
}
2.实体类添加
// @JSONField(ordinal = 7,format = DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_10)@JSONField(ordinal = 7,serializeUsing = MyDateSerializer.class)private String testStrDate;
3.测试类使用
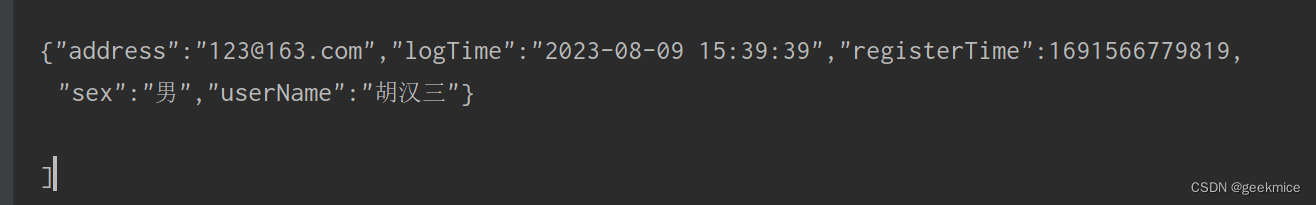
log.info("序列化操作开始,对象转换JSON串");TempData user = TempData.builder().userName(null).sex("男").birthday(new Date()).address("123@163.com").logTime(new Date()).registerTime(new Date()).testStrDate("2023-08-09 23:22:21").score(new BigDecimal("2384.23")).build();// 字符串类型字段为null,不进行序列化String userJsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user, SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty,SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty,SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero,SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse);log.info("userJsonString : [\n\n{}\n\n]", userJsonString);
21:18:42.724 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - userJsonString : [
{“id”:0,“username”:“”,“sex”:“男”,“address”:“123@163.com”,“logTime”:“2023-08-09 21:18:42”,“registerTime”:1691587122488,“testStrDate”:1691594541000,“score”:2384.23}
]
4.5 使用ordinal指定字段的顺序
package com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.domain;import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.annotation.Excel;
import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.annotation.ExcelIgnore;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.util.DateUtils;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFilter;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;/*** @BelongsProject: spring-boot-self-exercise* @BelongsPackage: com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.domain* @Author: pingmingbo* @CreateTime: 2023-08-07 09:53* @Description: Easy Excel 导入导出对应的实体类* @Version: 1.0*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class TempData implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 611155229642304781L;/*** 忽略这个字段*/private Long id;/*** 用户名*/@JSONField(name = "username",ordinal = 1)private String userName;/*** 生日*/@JSONField(format = DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_10,serialize = false,ordinal = 2)private Date birthday;/*** 性别*/@JSONField(ordinal = 3)private String sex;/*** 地址*/@JSONField(ordinal = 4)private String address;@JSONField(ordinal = 5)private Date registerTime;
}
4.6 序列化起别名
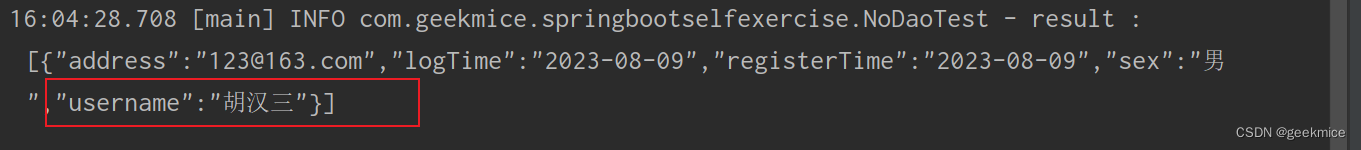
@JSONField(name = "username", ordinal = 3)
@ExcelProperty(value = {"父级", "用户名"}, index = 0)
@JSONField(name = "username")
private String userName;
16:04:28.708 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - result : [{“address”:“123@163.com”,“logTime”:“2023-08-09”,“registerTime”:“2023-08-09”,“sex”:“男”,“username”:“胡汉三”}]
4.7 空值序列化操作处理
| SerializerFeature | 描述 |
|---|---|
| WriteNullListAsEmpty | 将Collection类型字段的字段空值输出为[] |
| WriteNullStringAsEmpty | 将字符串类型字段的空值输出为空字符串 “” |
| WriteNullNumberAsZero | 将数值类型字段的空值输出为0 |
| WriteNullNumberAsZero | 将Boolean类型字段的空值输出为false |
log.info("序列化操作开始,对象转换JSON串");TempData user = TempData.builder().userName(null).sex("男").birthday(new Date()).address("123@163.com").logTime(new Date()).registerTime(new Date()).testStrDate("2023-07-18 23:22:21").build();// 字符串类型字段为null,不进行序列化String userJsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user, SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty,SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty,SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero,SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse);
20:42:40.253 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - 序列化操作开始,对象转换JSON串
20:42:40.664 [main] INFO com.geekmice.springbootselfexercise.NoDaoTest - userJsonString : [{“id”:0,“username”:“”,“sex”:“男”,“address”:“123@163.com”,“logTime”:“2023-08-09 20:42:40”,“registerTime”:1691584960267,“testStrDate”:1689693741000,“score”:0}
]