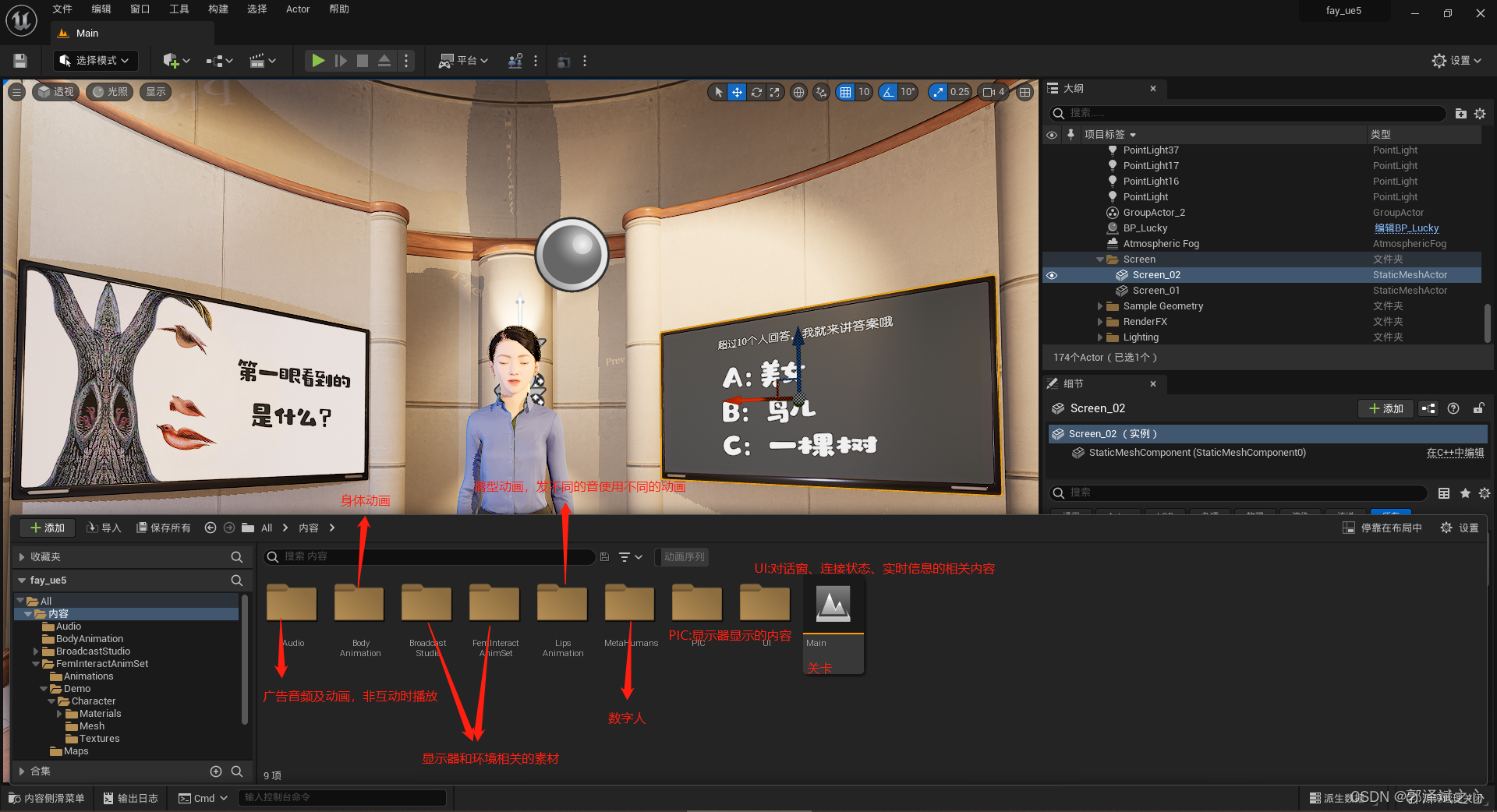
HTTP的认证方式之DIGEST
- 1.是什么
- 2.认值流程
- 2.1 客户端发送请求
- 2.2 服务器返回质询信息
- 2.2.1 质询参数
- 2.2.2 质询举例
- 2.3 客户端生成响应
- 2.4 服务器验证响应
- 2.5 服务器返回响应
- 3.算法
- 3.1 SHA-256
- 3.1.1 Response
- 3.1.2 A1
- 3.1.3 A2
- 3.2 MD5
- 3.2.1 Request-Digest
- 3.2.2 A1
- 3.2.3 A2
- 4.举例
详细的说明文档:WWW-Authenticate - HTTP | MDN (mozilla.org)
1.是什么
摘要认证(Digest Authentication)是一种用于在网络通信中验证用户身份的认证方法。它主要应用于HTTP和其他应用层协议中。
Digest认证相对于基本认证更加安全,因为它不直接传输明文密码。但它也不是完全的安全解决方案,因为在中间人攻击等情况下,仍然可能受到攻击。在现代网络中,更安全的认证方法通常是基于令牌(Token)的认证机制。
2.认值流程
类似与Basic认证流程:

Digest认证的整体流程如下:
-
客户端发送请求: 客户端向服务器发送请求,请求中包含需要访问的资源路径。
-
服务器返回挑战信息: 服务器接收到客户端请求后,返回一个“质询”信息(Challenge)给客户端。这个挑战信息是一个包含随机数、领域名(realm)以及其他一些参数的字符串。
-
客户端生成响应: 客户端使用用户名、密码和挑战信息来生成一个响应字符串。这个响应字符串的生成过程包括以下几个步骤:
- 拼接:将用户名、领域名和密码用冒号分隔,并将它们拼接成一个字符串。
- 对字符串进行哈希:对上述拼接后的字符串进行哈希运算,通常使用MD5或SHA-1等哈希算法。
-
客户端发送响应: 客户端将生成的响应字符串发送给服务器,放在请求的"Authorization"头部中。
-
服务器验证响应: 服务器收到客户端的响应后,使用相同的方式在服务器端重现生成响应字符串。然后将客户端发送的响应字符串和服务器端生成的响应字符串进行比较。如果两者相等,说明客户端拥有正确的用户名和密码。
-
服务器返回响应: 如果服务器验证成功,它会返回请求的资源内容给客户端,同时在响应的头部中包含认证成功的标识。
2.1 客户端发送请求
客户端的第一次请求。
2.2 服务器返回质询信息
2.2.1 质询参数
-
qop:带引号的字符串,表示服务器支持的保护程度。这必须提供,并且必须忽略无法识别的选项。
-
"auth":身份验证"auth-int":有完整保护的身份验证
-
nonce:一个服务器指定的带引号的字符串,在每次的 401 响应期间,服务器可以使用它去验证指定的凭据。这必须是在每次 401 响应时唯一的生成,并且可以更频繁地重新生成(例如,允许一个摘要仅使用一次)。该规范包含有关生成此值算法的建议。nonce 值对客户端是不透明的。
-
opaque:一个服务器指定的带引号的字符串,应在
Authorization中原封不动的返回。这对客户端是不透明的。建议服务器包含 Base64 或十六进制数据。 -
<realm>(可选)一个指示要使用的用户名/密码的字符串。至少应该包括主机名,但是可能指示具有访问权限的用户或组。 -
domain(可选)一个带引号,以空格分隔的 URI 前缀列表,定义了可以使用身份验证信息的所有位置。如果未指定此关键字,则可以在 web 根目录的任意位置使用身份验证信息。 -
stale(可选)一个不区分大小写的标志,指示客户端之前的请求因nonce太旧了(过期)而被拒绝。如果为true,则可以使用新的nonce加密相同用户名/密码重试请求。如果它是任意其他的值,那么用户名/密码无效,并且必须向用户重新请求。 -
algorithm(可选)algorithm 被用于产生一个摘要。有效的非会话值是:"MD5"(如果未指定,则是默认)、"SHA-256"、"SHA-512"。有效的会话值是:"MD5-sess"、"SHA-256-sess"、"SHA-512-sess"。 -
charset="UTF-8"(可选)当提交用户名和密码时,告诉客户端服务器的首选编码方案。仅允许的值是不区分大小写的“UTF-8”字符串。 -
userhash(可选)服务器可能指定为"true",以指示它支持用户名哈希(默认是"false")。
2.2.2 质询举例
客户端试图访问http://www.example.org/dir/index.html处的文档,该文档受到 digest 身份验证的保护。这个文档的用户名是“Mufsas”,并且它的密码是“Circle of Life”。客户端第一次请求该文档时,不会发送 Authorization 标头字段。在这里,服务器使用 HTTP 401 消息响应,其中包括对它支持的每个摘要算法的质询,按照其优先顺序(SHA256,然后是 MD5)。
服务器将质询信息放在WWW-Authenticate响应头发送给客户端,如下例子:
HTTP/1.1 401 UnauthorizedWWW-Authenticate: Digestrealm="http-auth@example.org",qop="auth, auth-int",algorithm=SHA-256,nonce="7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v",opaque="FQhe/qaU925kfnzjCev0ciny7QMkPqMAFRtzCUYo5tdS"WWW-Authenticate: Digestrealm="http-auth@example.org",qop="auth, auth-int",algorithm=MD5,nonce="7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v",opaque="FQhe/qaU925kfnzjCev0ciny7QMkPqMAFRtzCUYo5tdS"
2.3 客户端生成响应
客户端接收到401响应,表示需要进行认证,客户端提示用户输入他们的用户名和密码,然后响应一个新的请求,该请求在 Authorization 标头字段中对凭据进行加密。如果客户端选择 MD5 摘要,则 Authorization 标头字段看起来可能像如下这样:
Authorization: Digest username="Mufasa",realm="http-auth@example.org",uri="/dir/index.html",algorithm=MD5,nonce="7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v",nc=00000001,cnonce="f2/wE4q74E6zIJEtWaHKaf5wv/H5QzzpXusqGemxURZJ",qop=auth,response="8ca523f5e9506fed4657c9700eebdbec",opaque="FQhe/qaU925kfnzjCev0ciny7QMkPqMAFRtzCUYo5tdS"
如果客户端选择 SHA-256 摘要,则 Authorization 标头看起来可能像以下这样:
Authorization: Digest username="Mufasa",realm="http-auth@example.org",uri="/dir/index.html",algorithm=SHA-256,nonce="7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v",nc=00000001,cnonce="f2/wE4q74E6zIJEtWaHKaf5wv/H5QzzpXusqGemxURZJ",qop=auth,response="753927fa0e85d155564e2e272a28d1802ca10daf4496794697cf8db5856cb6c1",opaque="FQhe/qaU925kfnzjCev0ciny7QMkPqMAFRtzCUYo5tdS"
2.4 服务器验证响应
服务器收到客户端的响应后,使用相同的方式在服务器端重现生成响应字符串。然后将客户端发送的响应字符串和服务器端生成的响应字符串进行比较。如果两者相等,说明客户端拥有正确的用户名和密码。
2.5 服务器返回响应
如果服务器验证成功,它会返回请求的资源内容给客户端,同时在响应的头部中包含认证成功的标识。
3.算法
根据请求体里的algorithm的值:
HTTP/1.1 401 UnauthorizedWWW-Authenticate: Digestrealm="http-auth@example.org",qop="auth, auth-int",algorithm=SHA-256,nonce="7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v",opaque="FQhe/qaU925kfnzjCev0ciny7QMkPqMAFRtzCUYo5tdS"
一下是标准文档里的说明,来自RFC 7616: HTTP Digest Access Authentication (rfc-editor.org):
A string indicating an algorithm used to produce the digest and an unkeyed digest. If this is not present, it is assumed to be “MD5”. If the algorithm is not understood, the challenge SHOULD be ignored (and a different one used, if there is more than one). When used with the Digest mechanism, each one of the algorithms has two variants: Session variant and non-Session variant. The non-Session variant is denoted by “”, e.g., “SHA-256”, and the Session variant is denoted by “-sess”, e.g., “SHA-256-sess”.
In this document, the string obtained by applying the digest algorithm to the data “data” with secret “secret” will be denoted by KD(secret, data), and the string obtained by applying theunkeyed digest algorithm to the data “data” will be denoted H(data). KD stands for Keyed Digest, and the notation unq(X) means the value of the quoted-string X without the surrounding quotes and with quoting slashes removed.
For "<algorithm>" and "<algorithm>-sess"H(data) = <algorithm>(data)
andKD(secret, data) = H(concat(secret, ":", data))For example:For the "SHA-256" and "SHA-256-sess" algorithmsH(data) = SHA-256(data)For the "MD5" and "MD5-sess" algorithms H(data) = MD5(data)
i.e., the digest is the “” of the secret concatenated with a colon concatenated with the data. The “-sess” is intended to allow efficient third-party authentication servers; for the difference in usage, see the description in Section 3.4.2.
简单进行一下解释:
- KD(secret,data)是将
secret和data用冒号:拼接之后secret:data进行算法加密 - H(data)是直接对数据进行算法加密
- unq(username)是不带引号的字符串
3.1 SHA-256
我们可以参考RFC 7616: HTTP Digest Access Authentication (rfc-editor.org)
3.1.1 Response
If the qop value is “auth” or “auth-int”:
response = KD(H(A1),unq(nonce):nc:unq(cnonce):unq(qop):H(A2))
See below for the definitions for A1 and A2.
3.1.2 A1
If the algorithm parameter’s value is “”, e.g., “SHA-256”,then A1 is:
A1 = unq(username):unq(realm):passwd
where passwd = < user's password >
If the algorithm parameter’s value is “-sess”, e.g., “SHA-256-sess”, then A1 is calculated using the nonce value provided in the challenge from the server, and cnonce value from the request by the client following receipt of a WWW-Authenticate challenge from the server. It uses the server nonce from that challenge, herein called nonce-prime, and the client nonce value from the response, herein called cnonce-prime, to construct A1 as follows:
A1 = H(unq(username):unq(realm):passwd):unq(nonce-prime):unq(cnonce-prime)
This creates a “session key” for the authentication of subsequent requests and responses that is different for each “authentication session”, thus limiting the amount of material hashed with any one key. (Note: see further discussion of the authentication session in Section 3.6.) Because the server needs only use the hash of the user credentials in order to create the A1 value, this construction could be used in conjunction with a third-party authentication service so that the web server would not need the actual password value. The specification of such a protocol is beyond the scope of this specification.
3.1.3 A2
If the qop parameter’s value is “auth” or is unspecified, then A2 is:
A2 = Method:request-uri
If the qop value is “auth-int”, then A2 is:
A2 = Method:request-uri:H(entity-body)
3.2 MD5
我们可以参考RFC 2617 - HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication (ietf.org)
3.2.1 Request-Digest
If the “qop” value is “auth” or “auth-int”:
request-digest = KD(H(A1), unq(nonce-value):nc-value:unq(cnonce-value):unq(qop-value):H(A2))
If the “qop” directive is not present (this construction is for compatibility with RFC 2069):
request-digest = KD(H(A1), unq(nonce-value):H(A2))
See below for the definitions for A1 and A2.
3.2.2 A1
If the “algorithm” directive’s value is “MD5” or is unspecified, then A1 is:
A1 = unq(username-value):unq(realm-value):passwd
where passwd = < user's password >
If the “algorithm” directive’s value is “MD5-sess”, then A1 is calculated only once - on the first request by the client following receipt of a WWW-Authenticate challenge from the server. It uses the server nonce from that challenge, and the first client nonce value to construct A1 as follows:
A1 = H(unq(username-value):unq(realm-value):passwd):unq(nonce-value):unq(cnonce-value)
This creates a ‘session key’ for the authentication of subsequent requests and responses which is different for each “authentication session”, thus limiting the amount of material hashed with any one key. (Note: see further discussion of the authentication session in section 3.3.) Because the server need only use the hash of the user credentials in order to create the A1 value, this construction could be used in conjunction with a third party authentication service so that the web server would not need the actual password value. The specification of such a protocol is beyond the scope of this specification.
3.2.3 A2
If the “qop” directive’s value is “auth” or is unspecified, then A2 is:
A2 = Method:digest-uri-value
If the “qop” value is “auth-int”, then A2 is:
A2 = Method:digest-uri-value:H(entity-body)
4.举例
我们还拿上边的例子进行一下算法处理,algorithm没有赋值就是默认MD5,用户名还是使用Mufasa,密码使用123456:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
WWW-Authenticate: Digestrealm="http-auth@example.org",qop="auth",nonce="7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v",opaque="FQhe/qaU925kfnzjCev0ciny7QMkPqMAFRtzCUYo5tdS"
响应:
Authorization: Digest username="Mufasa", realm="http-auth@example.org", uri="/dir/index.html", algorithm=MD5, nonce="7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v", nc=00000001, cnonce="nvlfh1ra", qop=auth, response="7bddc3c7fceb317dc002c524187fa170", opaque="FQhe/qaU925kfnzjCev0ciny7QMkPqMAFRtzCUYo5tdS"
完整算法,这里我们要非常注意带不带双引号:
// A1 = unq(username-value):unq(realm-value):passwd
String A1 = StrUtil.format("{}:{}:\"{}\"", "Mufasa", "http-auth@example.org", "123456");
// A2 = Method:digest-uri-value
String A2 = StrUtil.format("\"{}\":\"{}\"", "POST", "/dir/index.html");
// request-digest = KD(H(A1), unq(nonce-value):nc-value:unq(cnonce-value):unq(qop-value):H(A2))
String HA1 = SecureUtil.md5(A1);
String HA2 = SecureUtil.md5(A2);
String responseStr = StrUtil.format("\"{}\":{}:\"{}\":{}:{}:\"{}\"", HA1, "7ypf/xlj9XXwfDPEoM4URrv/xwf94BcCAzFZH4GiTo0v","00000001", "nvlfh1ra", "auth", HA2);
String response = SecureUtil.md5(responseStr);


![Vue [Day7] 综合案例](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b8ad82c8592c4d16bc9494c6be105c93.png)