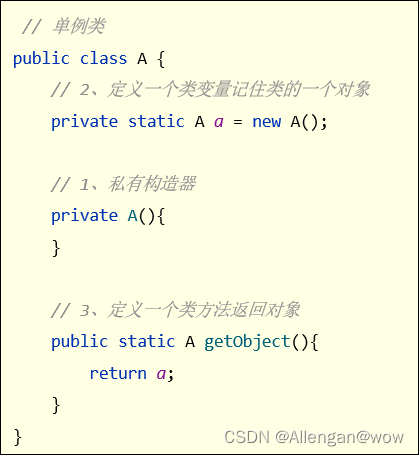
定义
将一个请求(行为)封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤销的操作。
应用场景
- 在软件构建过程中,“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”通常呈现一种“紧耦合”。但在某些场合——比如需要对行为进行“记录、撤销/重(undo/redo)、事务等处理,这种无法抵御变化的紧耦合是不合适的。
- 在这种情况下,如何将“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”解耦?将一组行为抽象为对象,可以实现二者之间的松耦合。
结构
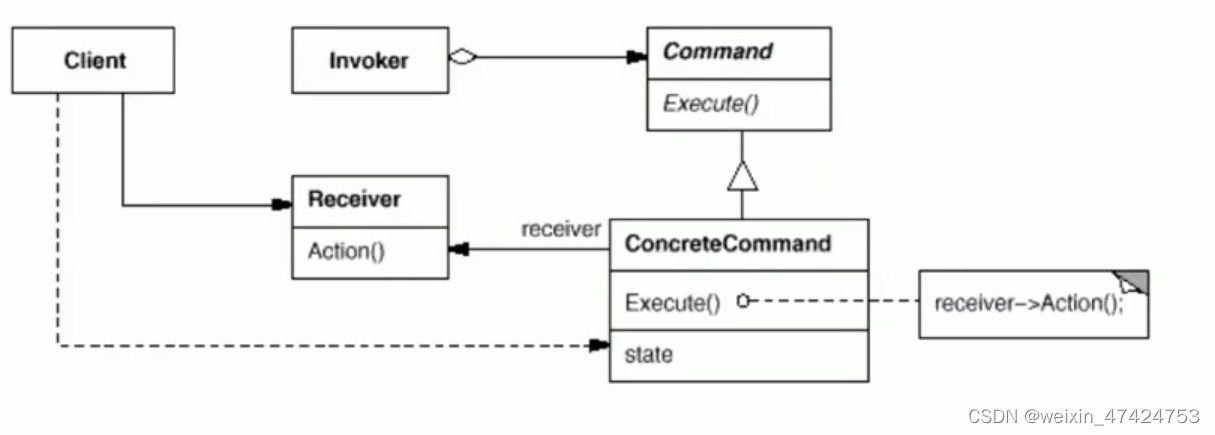
代码示例
//Command.h
/****************************************************/
#ifndef COMMAND_H
#define COMMAND_H
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>using namespace std;//人的基类=-= 子类实现这些基操
class IPerson{
public:virtual void Run() = 0;virtual void Eating() = 0;virtual void Sleeping() = 0;virtual void Bash() = 0;
};//执行人
class CRunPerson:public IPerson{
public:virtual void Run(){cout << "执行跑步命令,很快" << endl;}virtual void Bash(){cout << "执行洗澡命令" << endl;}virtual void Sleeping(){cout << "执行睡觉命令" << endl;}virtual void Eating(){cout << "执行吃饭命令" << endl;}
};//执行人
class CEatPerson:public IPerson{
public:virtual void Run(){cout << "执行跑步命令,很快" << endl;}virtual void Bash(){cout << "执行洗澡命令" << endl;}virtual void Sleeping(){cout << "执行睡觉命令" << endl;}virtual void Eating(){cout << "执行吃饭汉堡命令" << endl;}
};class ICommand{
protected:IPerson * m_pPerson;
public:ICommand(IPerson *p){m_pPerson = p;}virtual void ExcuteCommand()=0;
};class CommandRun:public ICommand{
public:CommandRun(IPerson*p):ICommand(p){};void ExcuteCommand(){m_pPerson->Run();}};class CommandEat:public ICommand{
public:CommandEat(IPerson*p):ICommand(p){};void ExcuteCommand(){m_pPerson->Eating();}};class CommandBash:public ICommand{
public:CommandBash(IPerson*p):ICommand(p){};void ExcuteCommand(){m_pPerson->Bash();}
};class CommandSleep:public ICommand{
public:CommandSleep(IPerson*p):ICommand(p){};void ExcuteCommand(){m_pPerson->Sleeping();}
};//调用者
class CCaller{
private:vector<ICommand*> m_vecCommand;
public:void AddCommand(ICommand* iCommand){m_vecCommand.push_back(iCommand);}void RunCommand(){for (auto it = m_vecCommand.begin();it != m_vecCommand.end();it++){(*it)->ExcuteCommand();}}void ReleaseCommand(){for (auto it = m_vecCommand.begin();it != m_vecCommand.end();it++){delete *it;*it = nullptr;}}};#endif
//test.cpp
/****************************************************/
#include "Command.h"int main()
{CEatPerson * eat_ = new CEatPerson();CRunPerson * rp = new CRunPerson();CCaller mp;mp.AddCommand(new CommandEat(eat_));mp.AddCommand(new CommandRun(rp));mp.AddCommand(new CommandBash(eat_));mp.RunCommand();mp.ReleaseCommand();return 0;
}
运行结果

要点总结
- Command模式的根本目的在于将“行为请求者”与”行为实现者”解耦,在面向对象语言中,常见的实现手段是“将行为抽象为对象”。
- 实现Command接口的具体命令对象ConcreteCommand有时候根据需要可能会保存一些额外的状态信息。通过使用Composite模式,可以将多个“命令”封装为一个“复合命令”MacroCommand。
- Command模式与C++中的函数对象有些类似。但两者定义行为接口的规范有所区别: Command以面向对象中的‘接口-实现"来定义行为接口规范,更严格,但有性能损失; C++函数对象以函数签名来定义行为接口规范,更灵活,性能更高。