目录
- 前言
- 1. Tensor封装
- 总结
前言
杜老师推出的 tensorRT从零起步高性能部署 课程,之前有看过一遍,但是没有做笔记,很多东西也忘了。这次重新撸一遍,顺便记记笔记。
本次课程学习 tensorRT 高级-tensor封装,索引计算,内存标记及自动复制
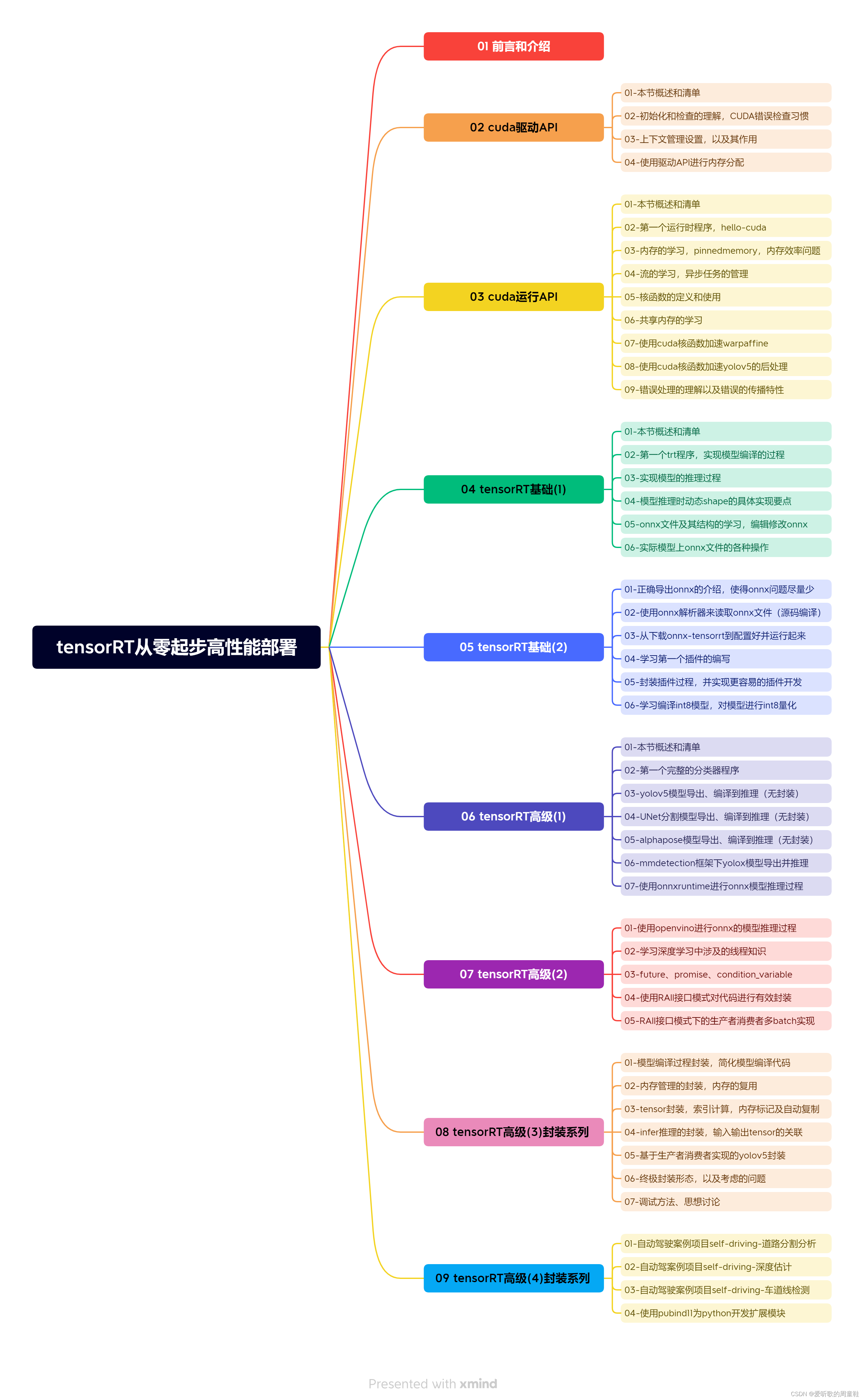
课程大纲可看下面的思维导图
1. Tensor封装
这节我们学习 tensor 的封装,张量是 CNN 中常见的基本单元,尤其是计算偏移量的工作需要封装,其次是内存的复制、分配需要引用 memory 进行封装,避免使用时面对指针不好管控
Tensor 封装主要考虑以下几点:
1. Tensor 的封装是针对输入与输出的,使得对输入或输出的操作更加的便捷
2. Tensor 内部的内存管理则是对 MixMemory 进行了包装
3. Tensor 封装所考虑的,是便于访问,因此有 offset 函数,实现索引的计算
在看代码之前,我们先把握下 tensor 封装的四个重点:
1. 内存的管理,可以使用 MixMemory 解决
2. 内存的复用,依然可以用 MixMemory 解决
3. 内存的 copy,比如说 cpu → \rightarrow → gpu,gpu → \rightarrow → cpu
- 解决方案(从 caffe 上学到的思路)
- a. 定义内存的状态,表示内存当前最新的内容在哪里(GPU/CPU/Init)
- b. 懒分配原则,当你需要使用时,才会考虑分配内存
- c. 获取内存地址,即表示:想拿到最新的数据,比如说 tensor.cpu 表示我想拿到最新的数据,并且把它放到 cpu 上
4. 索引的计算,比如说,我有 5d tensor(B,D,C,H,W),此时我要获取 B = 1,D = 3,C = 0,H = 5,W = 9 的位置元素属于非常基础且非常频繁的一个能力
了解完重点之后,我们再来看代码:
trt-tensor.hpp
#ifndef TRT_TENSOR_HPP
#define TRT_TENSOR_HPP#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "mix-memory.hpp"struct CUstream_st;
typedef CUstream_st CUStreamRaw;
typedef CUStreamRaw* CUStream;namespace TRT{enum class DataHead : int{Init = 0,Device = 1,Host = 2};enum class DataType : int {Float = 0,Float16 = 1,Int32 = 2,UInt8 = 3};int data_type_size(DataType dt);const char* data_head_string(DataHead dh);const char* data_type_string(DataType dt);class Tensor {public:Tensor(const Tensor& other) = delete;Tensor& operator = (const Tensor& other) = delete;explicit Tensor(DataType dtype = DataType::Float, std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> data = nullptr, int device_id = CURRENT_DEVICE_ID);explicit Tensor(int n, int c, int h, int w, DataType dtype = DataType::Float, std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> data = nullptr, int device_id = CURRENT_DEVICE_ID);explicit Tensor(int ndims, const int* dims, DataType dtype = DataType::Float, std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> data = nullptr, int device_id = CURRENT_DEVICE_ID);explicit Tensor(const std::vector<int>& dims, DataType dtype = DataType::Float, std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> data = nullptr, int device_id = CURRENT_DEVICE_ID);virtual ~Tensor();int numel() const;inline int ndims() const{return shape_.size();}inline int size(int index) const{return shape_[index];}inline int shape(int index) const{return shape_[index];}inline int batch() const{return shape_[0];}inline int channel() const{return shape_[1];}inline int height() const{return shape_[2];}inline int width() const{return shape_[3];}inline DataType type() const { return dtype_; }inline const std::vector<int>& dims() const { return shape_; }inline const std::vector<size_t>& strides() const {return strides_;}inline int bytes() const { return bytes_; }inline int bytes(int start_axis) const { return count(start_axis) * element_size(); }inline int element_size() const { return data_type_size(dtype_); }inline DataHead head() const { return head_; }std::shared_ptr<Tensor> clone() const;Tensor& release();Tensor& set_to(float value);bool empty() const;template<typename ... _Args>int offset(int index, _Args ... index_args) const{const int index_array[] = {index, index_args...};return offset_array(sizeof...(index_args) + 1, index_array);}int offset_array(const std::vector<int>& index) const;int offset_array(size_t size, const int* index_array) const;template<typename ... _Args>Tensor& resize(int dim_size, _Args ... dim_size_args){const int dim_size_array[] = {dim_size, dim_size_args...};return resize(sizeof...(dim_size_args) + 1, dim_size_array);}Tensor& resize(int ndims, const int* dims);Tensor& resize(const std::vector<int>& dims);Tensor& resize_single_dim(int idim, int size);int count(int start_axis = 0) const;int device() const{return device_id_;}Tensor& to_gpu(bool copy=true);Tensor& to_cpu(bool copy=true);inline void* cpu() const { ((Tensor*)this)->to_cpu(); return data_->cpu(); }inline void* gpu() const { ((Tensor*)this)->to_gpu(); return data_->gpu(); }template<typename DType> inline const DType* cpu() const { return (DType*)cpu(); }template<typename DType> inline DType* cpu() { return (DType*)cpu(); }template<typename DType, typename ... _Args> inline DType* cpu(int i, _Args&& ... args) { return cpu<DType>() + offset(i, args...); }template<typename DType> inline const DType* gpu() const { return (DType*)gpu(); }template<typename DType> inline DType* gpu() { return (DType*)gpu(); }template<typename DType, typename ... _Args> inline DType* gpu(int i, _Args&& ... args) { return gpu<DType>() + offset(i, args...); }template<typename DType, typename ... _Args> inline DType& at(int i, _Args&& ... args) { return *(cpu<DType>() + offset(i, args...)); }std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> get_data() const {return data_;}std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> get_workspace() const {return workspace_;}Tensor& set_workspace(std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> workspace) {workspace_ = workspace; return *this;}bool is_stream_owner() const {return stream_owner_;}CUStream get_stream() const{return stream_;}Tensor& set_stream(CUStream stream, bool owner=false){stream_ = stream; stream_owner_ = owner; return *this;}Tensor& set_mat (int n, const cv::Mat& image);Tensor& set_norm_mat(int n, const cv::Mat& image, float mean[3], float std[3]);cv::Mat at_mat(int n = 0, int c = 0) { return cv::Mat(height(), width(), CV_32F, cpu<float>(n, c)); }Tensor& synchronize();const char* shape_string() const{return shape_string_;}const char* descriptor() const;Tensor& copy_from_gpu(size_t offset, const void* src, size_t num_element, int device_id = CURRENT_DEVICE_ID);Tensor& copy_from_cpu(size_t offset, const void* src, size_t num_element);void reference_data(const std::vector<int>& shape, void* cpu_data, size_t cpu_size, void* gpu_data, size_t gpu_size, DataType dtype);/**# 以下代码是python中加载Tensorimport numpy as npdef load_tensor(file):with open(file, "rb") as f:binary_data = f.read()magic_number, ndims, dtype = np.frombuffer(binary_data, np.uint32, count=3, offset=0)assert magic_number == 0xFCCFE2E2, f"{file} not a tensor file."dims = np.frombuffer(binary_data, np.uint32, count=ndims, offset=3 * 4)if dtype == 0:np_dtype = np.float32elif dtype == 1:np_dtype = np.float16else:assert False, f"Unsupport dtype = {dtype}, can not convert to numpy dtype"return np.frombuffer(binary_data, np_dtype, offset=(ndims + 3) * 4).reshape(*dims)**/bool save_to_file(const std::string& file) const;bool load_from_file(const std::string& file);private:Tensor& compute_shape_string();Tensor& adajust_memory_by_update_dims_or_type();void setup_data(std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> data);private:std::vector<int> shape_;std::vector<size_t> strides_;size_t bytes_ = 0;DataHead head_ = DataHead::Init;DataType dtype_ = DataType::Float;CUStream stream_ = nullptr;bool stream_owner_ = false;int device_id_ = 0;char shape_string_[100];char descriptor_string_[100];std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> data_;std::shared_ptr<MixMemory> workspace_;};
}; // namespace TRT#endif // TRT_TENSOR_HPP
trt-tensor.cpp
#include "trt-tensor.hpp"
#include <algorithm>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "cuda-tools.hpp"
#include "simple-logger.hpp"using namespace cv;
using namespace std;namespace TRT{int data_type_size(DataType dt){switch (dt) {case DataType::Float: return sizeof(float);case DataType::Int32: return sizeof(int);case DataType::UInt8: return sizeof(uint8_t);default: {INFOE("Not support dtype: %d", dt);return -1;}}}inline static int get_device(int device_id){if(device_id != CURRENT_DEVICE_ID){CUDATools::check_device_id(device_id);return device_id;}checkRuntime(cudaGetDevice(&device_id));return device_id;}const char* data_head_string(DataHead dh){switch(dh){case DataHead::Init: return "Init";case DataHead::Device: return "Device";case DataHead::Host: return "Host";default: return "Unknow";}}const char* data_type_string(DataType dt){switch(dt){case DataType::Float: return "Float32";case DataType::Float16: return "Float16";case DataType::Int32: return "Int32";case DataType::UInt8: return "UInt8";default: return "Unknow";}}Tensor::Tensor(int n, int c, int h, int w, DataType dtype, shared_ptr<MixMemory> data, int device_id) {this->dtype_ = dtype;this->device_id_ = get_device(device_id);descriptor_string_[0] = 0;setup_data(data);resize(n, c, h, w);}Tensor::Tensor(const std::vector<int>& dims, DataType dtype, shared_ptr<MixMemory> data, int device_id){this->dtype_ = dtype;this->device_id_ = get_device(device_id);descriptor_string_[0] = 0;setup_data(data);resize(dims);}Tensor::Tensor(int ndims, const int* dims, DataType dtype, shared_ptr<MixMemory> data, int device_id) {this->dtype_ = dtype;this->device_id_ = get_device(device_id);descriptor_string_[0] = 0;setup_data(data);resize(ndims, dims);}Tensor::Tensor(DataType dtype, shared_ptr<MixMemory> data, int device_id){shape_string_[0] = 0;descriptor_string_[0] = 0;this->device_id_ = get_device(device_id);dtype_ = dtype;setup_data(data);}Tensor::~Tensor() {release();}const char* Tensor::descriptor() const{char* descriptor_ptr = (char*)descriptor_string_;int device_id = device();snprintf(descriptor_ptr, sizeof(descriptor_string_), "Tensor:%p, %s, %s, CUDA:%d", data_.get(),data_type_string(dtype_), shape_string_, device_id);return descriptor_ptr;}Tensor& Tensor::compute_shape_string(){// clean stringshape_string_[0] = 0;char* buffer = shape_string_;size_t buffer_size = sizeof(shape_string_);for(int i = 0; i < shape_.size(); ++i){int size = 0;if(i < shape_.size() - 1)size = snprintf(buffer, buffer_size, "%d x ", shape_[i]);elsesize = snprintf(buffer, buffer_size, "%d", shape_[i]);buffer += size;buffer_size -= size;}return *this;}void Tensor::reference_data(const vector<int>& shape, void* cpu_data, size_t cpu_size, void* gpu_data, size_t gpu_size, DataType dtype){dtype_ = dtype;data_->reference_data(cpu_data, cpu_size, gpu_data, gpu_size);setup_data(data_);resize(shape);}void Tensor::setup_data(shared_ptr<MixMemory> data){data_ = data;if(data_ == nullptr){data_ = make_shared<MixMemory>(device_id_);}else{device_id_ = data_->device_id();}head_ = DataHead::Init;if(data_->cpu()){head_ = DataHead::Host;}if(data_->gpu()){head_ = DataHead::Device;}}shared_ptr<Tensor> Tensor::clone() const{auto new_tensor = make_shared<Tensor>(shape_, dtype_);if(head_ == DataHead::Init)return new_tensor;if(head_ == DataHead::Host){memcpy(new_tensor->cpu(), this->cpu(), this->bytes_);}else if(head_ == DataHead::Device){CUDATools::AutoDevice auto_device_exchange(device());checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync(new_tensor->gpu(), this->gpu(), bytes_, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice, stream_));}return new_tensor;}Tensor& Tensor::copy_from_gpu(size_t offset, const void* src, size_t num_element, int device_id){if(head_ == DataHead::Init)to_gpu(false);size_t offset_location = offset * element_size();if(offset_location >= bytes_){INFOE("Offset location[%lld] >= bytes_[%lld], out of range", offset_location, bytes_);return *this;}size_t copyed_bytes = num_element * element_size();size_t remain_bytes = bytes_ - offset_location;if(copyed_bytes > remain_bytes){INFOE("Copyed bytes[%lld] > remain bytes[%lld], out of range", copyed_bytes, remain_bytes);return *this;}if(head_ == DataHead::Device){int current_device_id = get_device(device_id);int gpu_device_id = device();if(current_device_id != gpu_device_id){checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyPeerAsync(gpu<unsigned char>() + offset_location, gpu_device_id, src, current_device_id, copyed_bytes, stream_));//checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync(gpu<unsigned char>() + offset_location, src, copyed_bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice, stream_));}else{checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync(gpu<unsigned char>() + offset_location, src, copyed_bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice, stream_));}}else if(head_ == DataHead::Host){CUDATools::AutoDevice auto_device_exchange(this->device());checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync(cpu<unsigned char>() + offset_location, src, copyed_bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream_));}else{INFOE("Unsupport head type %d", head_);}return *this;}Tensor& Tensor::copy_from_cpu(size_t offset, const void* src, size_t num_element){if(head_ == DataHead::Init)to_cpu(false);size_t offset_location = offset * element_size();if(offset_location >= bytes_){INFOE("Offset location[%lld] >= bytes_[%lld], out of range", offset_location, bytes_);return *this;}size_t copyed_bytes = num_element * element_size();size_t remain_bytes = bytes_ - offset_location;if(copyed_bytes > remain_bytes){INFOE("Copyed bytes[%lld] > remain bytes[%lld], out of range", copyed_bytes, remain_bytes);return *this;}if(head_ == DataHead::Device){CUDATools::AutoDevice auto_device_exchange(this->device());checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync((char*)data_->gpu() + offset_location, src, copyed_bytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream_));}else if(head_ == DataHead::Host){//checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync((char*)data_->cpu() + offset_location, src, copyed_bytes, cudaMemcpyHostToHost, stream_));memcpy((char*)data_->cpu() + offset_location, src, copyed_bytes);}else{INFOE("Unsupport head type %d", head_);}return *this;}Tensor& Tensor::release() {data_->release_all();shape_.clear();bytes_ = 0;head_ = DataHead::Init;if(stream_owner_ && stream_ != nullptr){CUDATools::AutoDevice auto_device_exchange(this->device());checkRuntime(cudaStreamDestroy(stream_));}stream_owner_ = false;stream_ = nullptr;return *this;}bool Tensor::empty() const{return data_->cpu() == nullptr && data_->gpu() == nullptr;}int Tensor::count(int start_axis) const {if(start_axis >= 0 && start_axis < shape_.size()){int size = 1;for (int i = start_axis; i < shape_.size(); ++i) size *= shape_[i];return size;}else{return 0;}}Tensor& Tensor::resize(const std::vector<int>& dims) {return resize(dims.size(), dims.data());}int Tensor::numel() const{int value = shape_.empty() ? 0 : 1;for(int i = 0; i < shape_.size(); ++i){value *= shape_[i];}return value;}Tensor& Tensor::resize_single_dim(int idim, int size){assert(idim >= 0 && idim < shape_.size());auto new_shape = shape_;new_shape[idim] = size;return resize(new_shape);}Tensor& Tensor::resize(int ndims, const int* dims) {vector<int> setup_dims(ndims);for(int i = 0; i < ndims; ++i){int dim = dims[i];if(dim == -1){assert(ndims == shape_.size());dim = shape_[i];}setup_dims[i] = dim;}this->shape_ = setup_dims;// strides = element_sizethis->strides_.resize(setup_dims.size());size_t prev_size = element_size();size_t prev_shape = 1;for(int i = (int)strides_.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i){if(i + 1 < strides_.size()){prev_size = strides_[i+1];prev_shape = shape_[i+1];}strides_[i] = prev_size * prev_shape;}this->adajust_memory_by_update_dims_or_type();this->compute_shape_string();return *this;}Tensor& Tensor::adajust_memory_by_update_dims_or_type(){int needed_size = this->numel() * element_size();if(needed_size > this->bytes_){head_ = DataHead::Init;}this->bytes_ = needed_size;return *this;}Tensor& Tensor::synchronize(){ CUDATools::AutoDevice auto_device_exchange(this->device());checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream_));return *this;}Tensor& Tensor::to_gpu(bool copy) {if (head_ == DataHead::Device)return *this;head_ = DataHead::Device;data_->gpu(bytes_);if (copy && data_->cpu() != nullptr) {CUDATools::AutoDevice auto_device_exchange(this->device());checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync(data_->gpu(), data_->cpu(), bytes_, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream_));}return *this;}Tensor& Tensor::to_cpu(bool copy) {if (head_ == DataHead::Host)return *this;head_ = DataHead::Host;data_->cpu(bytes_);if (copy && data_->gpu() != nullptr) {CUDATools::AutoDevice auto_device_exchange(this->device());checkRuntime(cudaMemcpyAsync(data_->cpu(), data_->gpu(), bytes_, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream_));checkRuntime(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream_));}return *this;}template<typename _T>static inline void memset_any_type(_T* ptr, size_t count, _T value){for (size_t i = 0; i < count; ++i)*ptr++ = value;}Tensor& Tensor::set_to(float value) {int c = count();if (dtype_ == DataType::Float) {memset_any_type(cpu<float>(), c, value);}else if(dtype_ == DataType::Int32) {memset_any_type(cpu<int>(), c, (int)value);}else if(dtype_ == DataType::UInt8) {memset_any_type(cpu<uint8_t>(), c, (uint8_t)value);}else{INFOE("Unsupport type: %d", dtype_);}return *this;}int Tensor::offset_array(size_t size, const int* index_array) const{assert(size <= shape_.size());int value = 0;for(int i = 0; i < shape_.size(); ++i){if(i < size)value += index_array[i];if(i + 1 < shape_.size())value *= shape_[i+1];}return value;}int Tensor::offset_array(const std::vector<int>& index_array) const{return offset_array(index_array.size(), index_array.data());}Tensor& Tensor::set_norm_mat(int n, const cv::Mat& image, float mean[3], float std[3]) {assert(image.channels() == 3 && !image.empty() && type() == DataType::Float);assert(ndims() == 4 && n < shape_[0]);to_cpu(false);int width = shape_[3];int height = shape_[2];float scale = 1 / 255.0;cv::Mat inputframe = image;if(inputframe.size() != cv::Size(width, height))cv::resize(inputframe, inputframe, cv::Size(width, height));if(CV_MAT_DEPTH(inputframe.type()) != CV_32F){inputframe.convertTo(inputframe, CV_32F, scale);}cv::Mat ms[3];for (int c = 0; c < 3; ++c)ms[c] = cv::Mat(height, width, CV_32F, cpu<float>(n, c));split(inputframe, ms);assert((void*)ms[0].data == (void*)cpu<float>(n));for (int c = 0; c < 3; ++c)ms[c] = (ms[c] - mean[c]) / std[c];return *this;}Tensor& Tensor::set_mat(int n, const cv::Mat& _image) {cv::Mat image = _image;assert(!image.empty() && CV_MAT_DEPTH(image.type()) == CV_32F && type() == DataType::Float);assert(shape_.size() == 4 && n < shape_[0] && image.channels() == shape_[1]);to_cpu(false);int width = shape_[3];int height = shape_[2];if (image.size() != cv::Size(width, height))cv::resize(image, image, cv::Size(width, height));if (image.channels() == 1) {memcpy(cpu<float>(n), image.data, width * height * sizeof(float));return *this;}vector<cv::Mat> ms(image.channels());for (int i = 0; i < ms.size(); ++i) ms[i] = cv::Mat(height, width, CV_32F, cpu<float>(n, i));cv::split(image, &ms[0]);assert((void*)ms[0].data == (void*)cpu<float>(n));return *this;}bool Tensor::save_to_file(const std::string& file) const{if(empty()) return false;FILE* f = fopen(file.c_str(), "wb");if(f == nullptr) return false;int ndims = this->ndims();unsigned int head[3] = {0xFCCFE2E2, ndims, static_cast<unsigned int>(dtype_)};fwrite(head, 1, sizeof(head), f);fwrite(shape_.data(), 1, sizeof(shape_[0]) * shape_.size(), f);fwrite(cpu(), 1, bytes_, f);fclose(f);return true;}bool Tensor::load_from_file(const std::string& file){FILE* f = fopen(file.c_str(), "rb");if(f == nullptr){INFOE("Open %s failed.", file.c_str());return false;}unsigned int head[3] = {0};fread(head, 1, sizeof(head), f);if(head[0] != 0xFCCFE2E2){fclose(f);INFOE("Invalid tensor file %s, magic number mismatch", file.c_str());return false;}int ndims = head[1];auto dtype = (TRT::DataType)head[2];vector<int> dims(ndims);fread(dims.data(), 1, ndims * sizeof(dims[0]), f);this->dtype_ = dtype;this->resize(dims);fread(this->cpu(), 1, bytes_, f);fclose(f);return true;}
};
头文件中首先定义了两个枚举类,分别是 DataHead 和 DataType,用于表示数据目前的状态(初始化、CPU、GPU)和数据类型,然后定义了一个 Tensor 类,用于获取和设置张量的属性,如维度、形状、类型等
Tensor 存在多个构造函数,比如接受 n,c,h,w 作为 shape,MixMemory 作为 data,关于 tensor 内存的管理和复用我们是通过上节课封装的 MixMemory 来实现的,因此我们重点来看 tensor 内存的拷贝和索引的计算
tensor 内存的拷贝是通过 to_cpu 和 to_gpu 函数实现的,在 to_cpu 函数中,它首先会检查当前内存数据的状态,如果当前的数据已经在 CPU 上了,它会立即返回,避免再次拷贝;如果数据不在 CPU 上,那就说明在 GPU 上,此时我们会将 head_ 设置为 CPU,通过调用 data_->cpu(byes_) 分配一块 CPU 内存,调用的是 MixMemory 的 cpu 方法,像之前说的一样,如果当前分配的 cpu 内存大小已经满足了要求,则它会直接拿之前的内存,实现内存的复用。最后通过 CUDA 的 cudaMemcpyAsync 函数从 GPU 异步复制数据到 CPU,同时还引入了流同步,确保复制完成
tensor 索引的计算是通过 offset 函数来完成的,该函数接收一个变参,然后将它转换成一个数组送到 offset_array 中进行索引计算,遵循我们之前讲解的左乘右加原则,它直接返回的是偏移量,代表 tensor 中的某个元素在内存中的位置
我们接下来看下 main.cpp 中的不同
// tensor的建立并不会立即分配内存,而是在第一次需要使用的时候进行分配
TRT::Tensor input_data({input_batch, input_channel, input_height, input_width}, TRT::DataType::Float);// 为input关联stream,使得在同一个pipeline中执行复制操作
input_data.set_stream(stream);首先是 input_data 的构建,我们可以利用封装好的 Tensor 来实现
// 利用opencv mat的内存地址引用,实现input与mat的关联,然后利用split函数一次性完成mat到input的复制
cv::Mat channel_based[3];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)// 注意这里 2 - i是实现bgr -> rgb的方式// 这里cpu提供的参数0是表示batch的索引是0,第二个参数表示通道的索引,因此获取的是0, 2-i通道的地址// 而tensor最大的好处就是帮忙计算索引,否则手动计算就得写很多代码channel_based[i] = cv::Mat(input_height, input_width, CV_32F, input_data.cpu<float>(0, 2-i));cv::split(image, channel_based);
其次是预处理部分,我们采用了 opencv 中的 split 方法将三个通道分割开,这样的性能更好,这也是从 caffe 中学习到了
// 如果不写,input_data.gpu获取gpu地址时会自动进行复制
// 目的就是把内存复制变为隐式进行
input_data.to_gpu();...float* bindings[] = {input_data.gpu<float>(), output_data.gpu<float>()};
还有一点要注意的是,我们不需要显性的去做内存复制,在需要的时候会隐式的完成,比如 input_data.gpu 获取 gpu 的数据时,会将 cpu 的数据自动复制到 gpu 上
以上就是 tensor 封装的分析,封装好的 tensor 不用显性的去调用 cuda 的 API,接口更加高级,性能更好。更多细节还是需要多去看
这是一个相对复杂的版本的 tensor 封装,其实也可以只考虑之前提过的四条来封装 tensor,也能解决绝大部分问题
总结
本次课程学习了 tensor 的封装,对 tensor 的封装重点考虑四个方面:内存的管理、内存的复用、内存的拷贝以及索引的计算,其中前面两个可以用 MixMemory 来解决,内存的拷贝通过定义内存的状态,懒分配原则实现的,而索引的计算则是通过之前说的左乘右加完成的。tensor 的封装使得输入和输出的操作更加的便捷,索引的计算也更加的方便。






![[.NET/WPF] CommunityToolkit.Mvvm 异步指令](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ca07eac8f7284e51a4607ec072cadafe.gif)