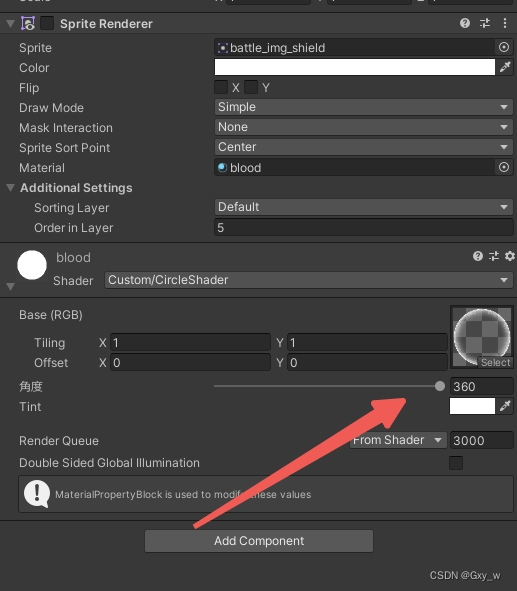
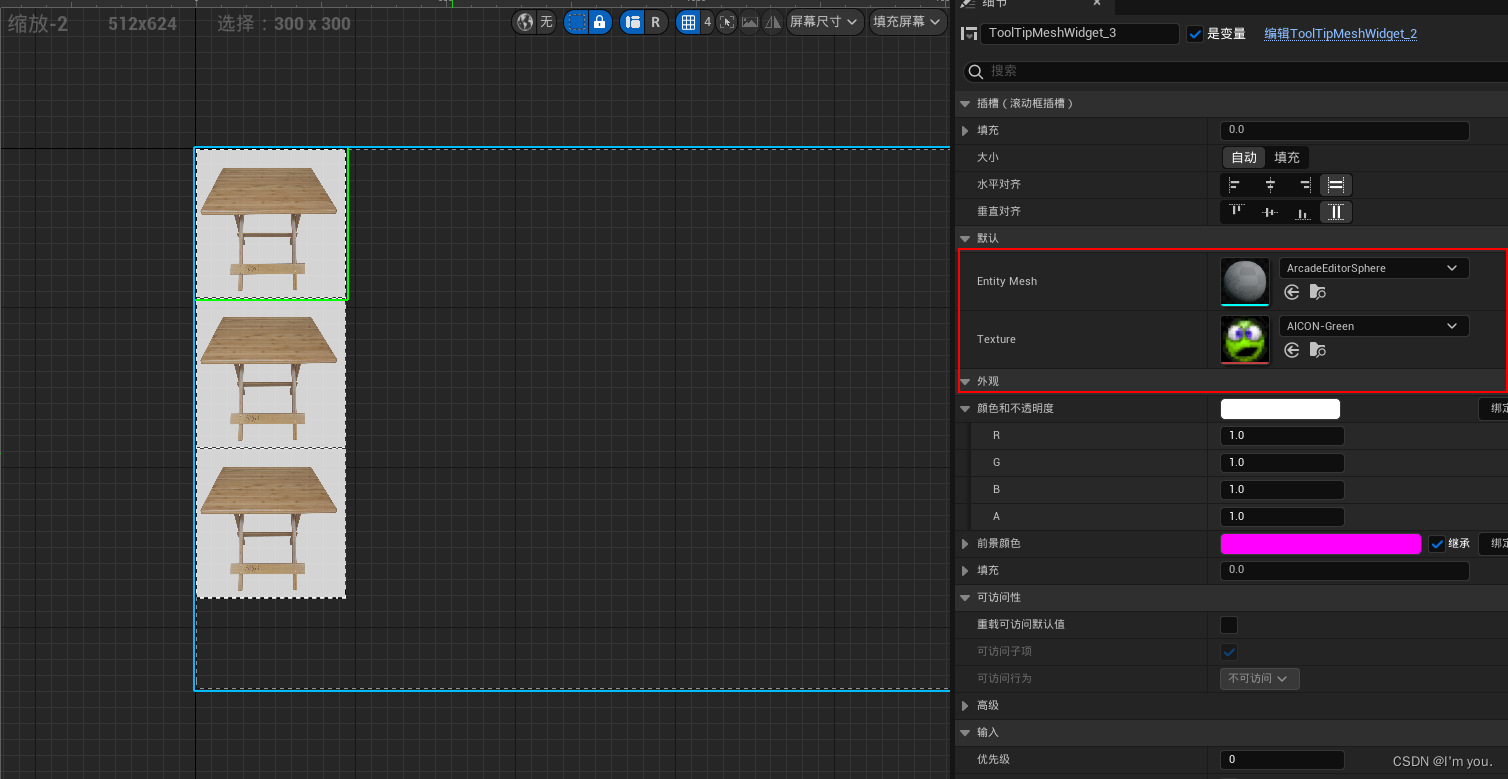
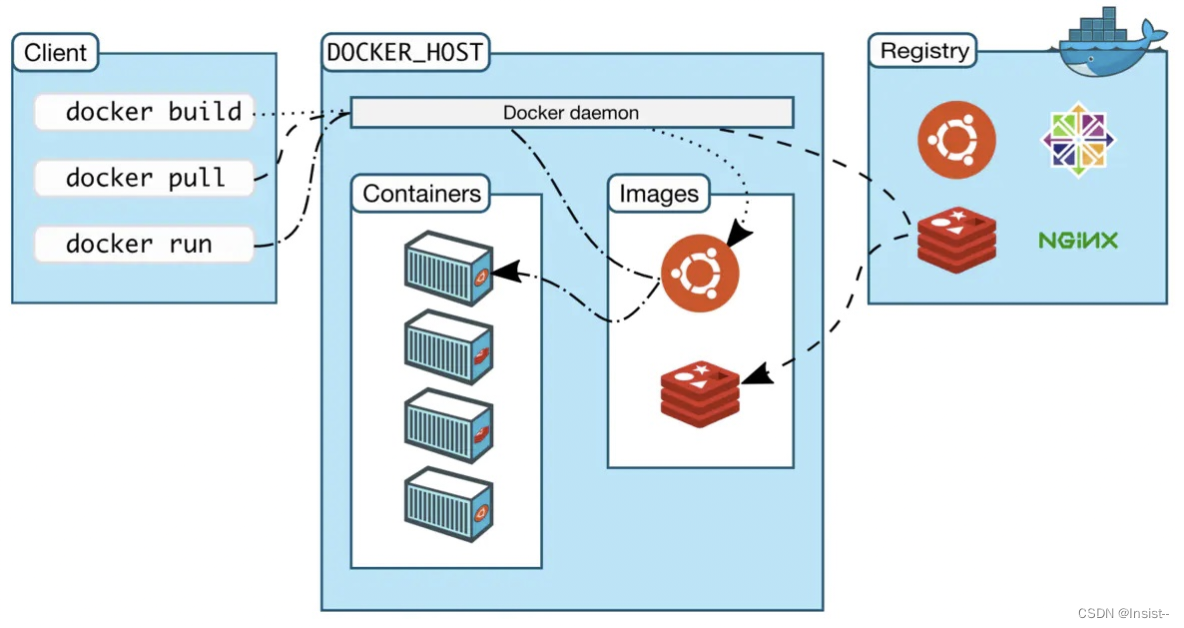
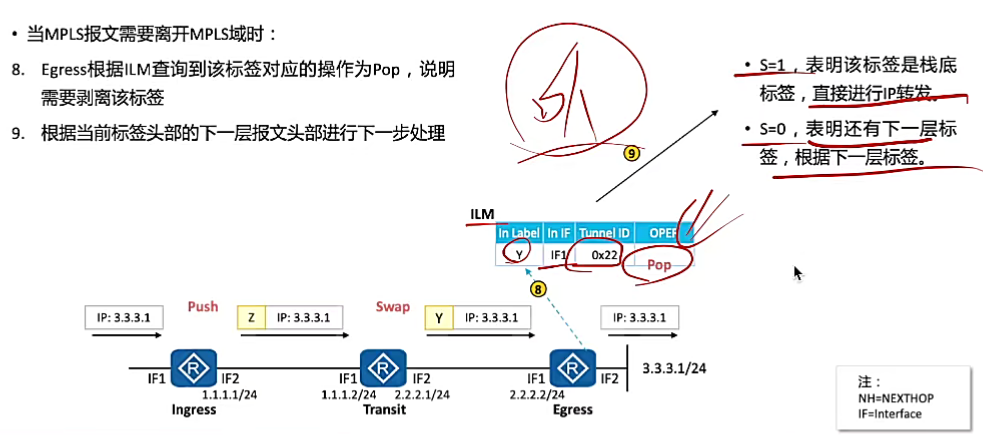
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sqlite3.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
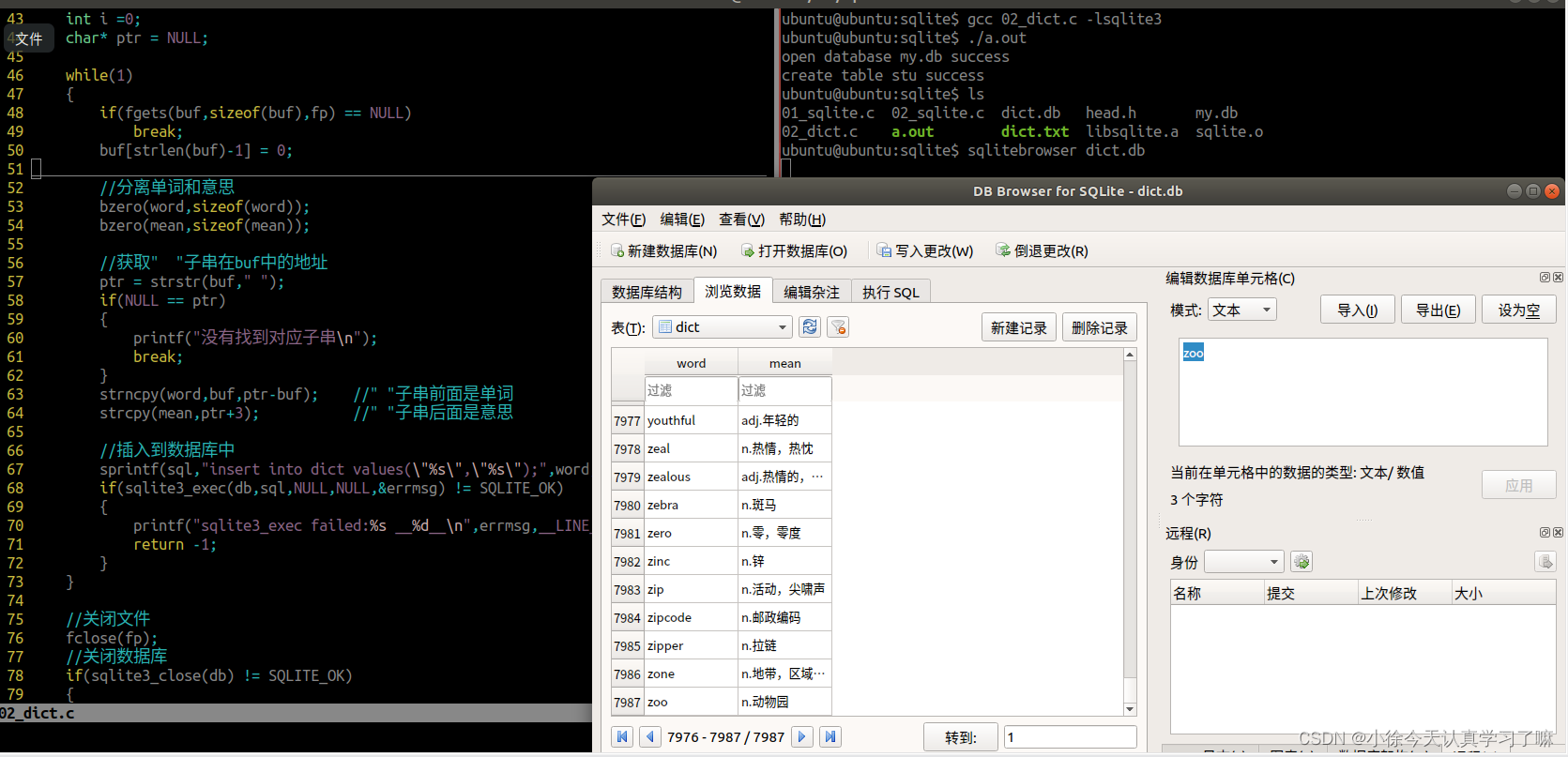
{//创建并打开一个数据库sqlite3 *db = NULL;if(sqlite3_open("./dict.db",&db) != SQLITE_OK){printf("sqlite3_open:%s %d __%d__\n",\sqlite3_errmsg(db),sqlite3_errcode(db),__LINE__);return -1;}printf("open database my.db success\n");//创建一个表格 create table stu (id int,name char,score float);//数据库中sql语句怎么写,这里就怎么写char sql[128] = "create table if not exists dict (word char,mean char);";char* errmsg = NULL;if(sqlite3_exec(db,sql,NULL,NULL,&errmsg) != SQLITE_OK){fprintf(stderr,"sqlite3_open:%s %d __%d__\n",\errmsg,sqlite3_errcode(db),__LINE__);return -1;}printf("create table stu success\n");//打开文件FILE* fp = fopen("./dict.txt","r");if(NULL == fp){perror("fopen");return -1;}//循环读取文件中的数据,一行一行的读取char buf[256] = "";char word[32] = "";char mean[200] = "";int count = 1;int i =0;char* ptr = NULL;while(1){if(fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),fp) == NULL)break;buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;//分离单词和意思bzero(word,sizeof(word));bzero(mean,sizeof(mean));//获取" "子串在buf中的地址ptr = strstr(buf," ");if(NULL == ptr){printf("没有找到对应子串\n");break;}strncpy(word,buf,ptr-buf); //" "子串前面是单词strcpy(mean,ptr+3); //" "子串后面是意思//插入到数据库中sprintf(sql,"insert into dict values(\"%s\",\"%s\");",word,mean);if(sqlite3_exec(db,sql,NULL,NULL,&errmsg) != SQLITE_OK){printf("sqlite3_exec failed:%s __%d__\n",errmsg,__LINE__);return -1;}}//关闭文件fclose(fp);//关闭数据库if(sqlite3_close(db) != SQLITE_OK){fprintf(stderr,"sqlite3_close:%s %d __%d__\n",\sqlite3_errmsg(db),sqlite3_errcode(db),__LINE__);return -1;}return 0;
}