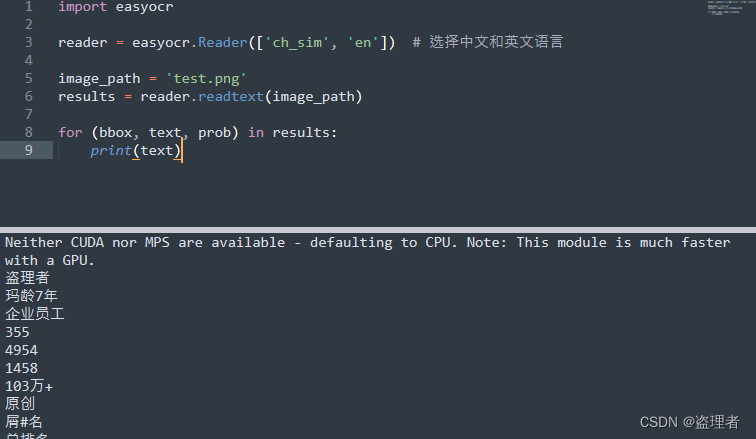
Kalman滤波算法的原理可以参考: 卡尔曼滤波理解
python中filterpy库中实现了各种滤波算法, 其中就包括了kalman滤波算法。
具体实现代码: https://github.com/rlabbe/filterpy/blob/master/filterpy/kalman/kalman_filter.py
本文针对该代码进行详细解读分析。
1 初始化及参数设置
需要设定的几个参数可参考: 详解多目标跟踪(MOT)算法中的Kalman滤波
- 状态变量的维度: dim_x
- 观测变量的维度:dim_z
- 状态变量:x, 初始化为大小为dim_x, 全0的列向量
- 观测变量:z, 初始化为大小为dim_z, 全0的列向量
- 状态转移矩阵: F, 初始化为维度为dim_x, 值为1的对角阵
- 状态变量协方差矩阵: P, 初始化为维度为dim_x, 值为1的对角阵
- 处理噪声写房产矩阵: Q, 初始化为维度为dim_x, 值为1的对角阵
- 测量矩阵:H,初始化为维度为(dim_z, dim_x)的全0矩阵
- 测量误差协方差矩阵: R, 初始化为维度为dim_z, 值为1的对角阵
def __init__(self, dim_x, dim_z, dim_u=0):if dim_x < 1:raise ValueError('dim_x must be 1 or greater')if dim_z < 1:raise ValueError('dim_z must be 1 or greater')if dim_u < 0:raise ValueError('dim_u must be 0 or greater')self.dim_x = dim_xself.dim_z = dim_zself.dim_u = dim_uself.x = zeros((dim_x, 1)) # stateself.P = eye(dim_x) # uncertainty covarianceself.Q = eye(dim_x) # process uncertaintyself.B = None # control transition matrixself.F = eye(dim_x) # state transition matrixself.H = zeros((dim_z, dim_x)) # measurement functionself.R = eye(dim_z) # measurement uncertaintyself._alpha_sq = 1. # fading memory controlself.M = np.zeros((dim_x, dim_z)) # process-measurement cross correlationself.z = np.array([[None]*self.dim_z]).T
2 predict
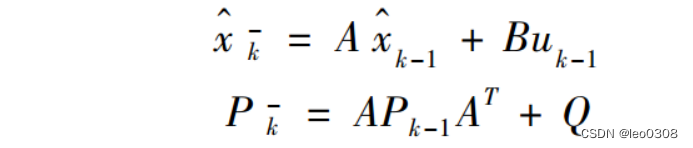
def predict(self, u=None, B=None, F=None, Q=None):"""Predict next state (prior) using the Kalman filter state propagationequations.Parameters----------u : np.array, default 0Optional control vector.B : np.array(dim_x, dim_u), or NoneOptional control transition matrix; a value of Nonewill cause the filter to use `self.B`.F : np.array(dim_x, dim_x), or NoneOptional state transition matrix; a value of Nonewill cause the filter to use `self.F`.Q : np.array(dim_x, dim_x), scalar, or NoneOptional process noise matrix; a value of None will cause thefilter to use `self.Q`."""if B is None:B = self.Bif F is None:F = self.Fif Q is None:Q = self.Qelif isscalar(Q):Q = eye(self.dim_x) * Q# x = Fx + Buif B is not None and u is not None:self.x = dot(F, self.x) + dot(B, u)else:self.x = dot(F, self.x)# P = FPF' + Qself.P = self._alpha_sq * dot(dot(F, self.P), F.T) + Q# save priorself.x_prior = self.x.copy()self.P_prior = self.P.copy()predict的过程比较简单, 就是根据上一次的状态变量, 估计当前的状态变量值, 同时更新状态变量的协方差。
3 update
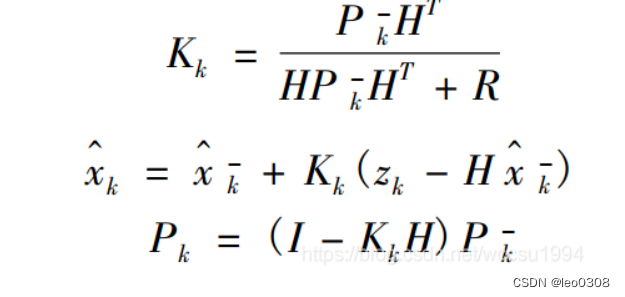
def update(self, z, R=None, H=None):"""Add a new measurement (z) to the Kalman filter.If z is None, nothing is computed. However, x_post and P_post areupdated with the prior (x_prior, P_prior), and self.z is set to None.Parameters----------z : (dim_z, 1): array_likemeasurement for this update. z can be a scalar if dim_z is 1,otherwise it must be convertible to a column vector.If you pass in a value of H, z must be a column vector theof the correct size.R : np.array, scalar, or NoneOptionally provide R to override the measurement noise for thisone call, otherwise self.R will be used.H : np.array, or NoneOptionally provide H to override the measurement function for thisone call, otherwise self.H will be used."""# set to None to force recomputeself._log_likelihood = Noneself._likelihood = Noneself._mahalanobis = Noneif z is None:self.z = np.array([[None]*self.dim_z]).Tself.x_post = self.x.copy()self.P_post = self.P.copy()self.y = zeros((self.dim_z, 1))returnif R is None:R = self.Relif isscalar(R):R = eye(self.dim_z) * Rif H is None:z = reshape_z(z, self.dim_z, self.x.ndim)H = self.H# y = z - Hx# error (residual) between measurement and predictionself.y = z - dot(H, self.x)# common subexpression for speedPHT = dot(self.P, H.T)# S = HPH' + R# project system uncertainty into measurement spaceself.S = dot(H, PHT) + Rself.SI = self.inv(self.S)# K = PH'inv(S)# map system uncertainty into kalman gainself.K = dot(PHT, self.SI)# x = x + Ky# predict new x with residual scaled by the kalman gainself.x = self.x + dot(self.K, self.y)# P = (I-KH)P(I-KH)' + KRK'# This is more numerically stable# and works for non-optimal K vs the equation# P = (I-KH)P usually seen in the literature.I_KH = self._I - dot(self.K, H)self.P = dot(dot(I_KH, self.P), I_KH.T) + dot(dot(self.K, R), self.K.T)# save measurement and posterior stateself.z = deepcopy(z)self.x_post = self.x.copy()self.P_post = self.P.copy()
update的过程需要提供观测变量z。
1 首先计算卡尔曼增益。
2 计算当前观测值与通过观测矩阵得到的值之间的误差, 这个误差值乘上卡尔曼增益, 再加上predict过程得到的先验状态估计结果, 得到当前的卡尔曼滤波估计结果。
3 更新状态变量协方差矩阵。