二叉搜索树
- 1. 二叉搜索树概念
- 2. 二叉搜索树的实现
- 3. 二叉树的应用
- 4. 练习
1. 二叉搜索树概念
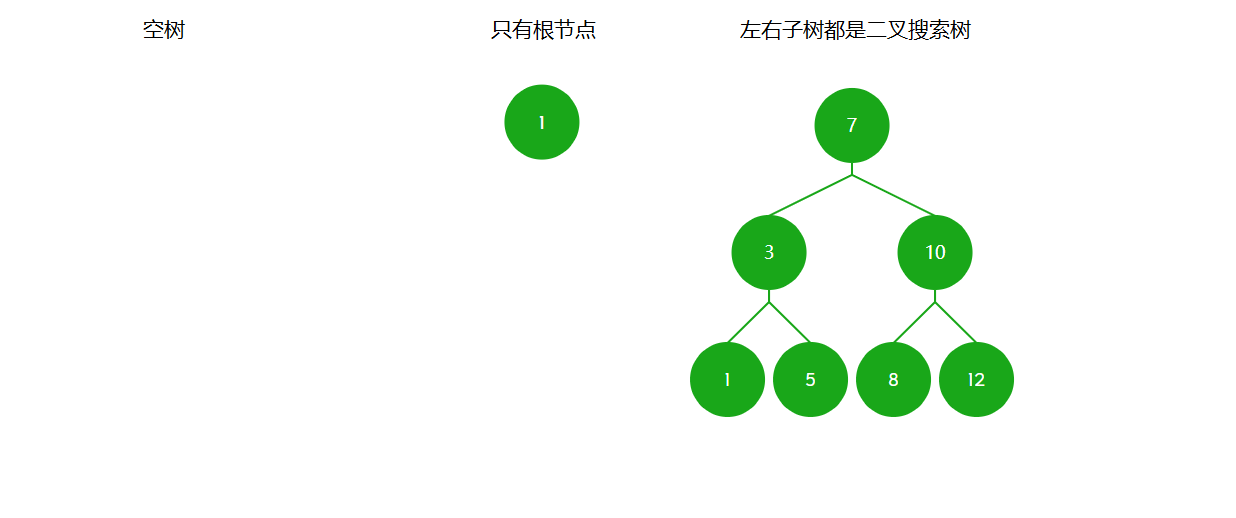
二叉搜索树要么是棵空树,要么满足以下性质:(1)若左子树不为空,左子树上所有节点的键值小于根节点的键值;(2)若右子树不为空,右子树上所有节点的键值大于根节点的键值;(3)左右子树都是二叉搜索树。
通过中序遍历可以得到升序序列,因此二叉搜索树又叫二叉排序树。因其方便查找,又叫做二叉查找树。
2. 二叉搜索树的实现
非递归版本
//节点
template<class K>
struct TreeNode
{TreeNode(const K&key):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_key(key){}TreeNode<K>* _left;TreeNode<K>* _right;K _key;
};
//二叉搜索树
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
public:typedef TreeNode<K> Node;//查找//key大于根节点的键值就往右边找,小于根节点的键值就往左边找//找到了返回节点地址,找不到返回nullptrNode* Find(const T& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (key > cur->_key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (key < cur->_key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}//插入//若为空树,直接申请根节点;若不为空,查找合适的位置插入//插入成功,返回true;当已有相同的key值,插入失败,返回falsebool Insert(const K& key){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(key);//new = operator new + 自定义类型调用构造函数return true;}Node* parent = _root;Node* cur = _root;//找到合适的位置while (cur){if (key > cur->_key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (key < cur->_key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}//插入if (key < parent->_key){parent->_left = new Node(key);}else if (key > parent->_key){parent->_right = new Node(key);}return true;}//删除//删除共有三种情况:(1)当要删除节点的左孩子不为空(2)当要删除节点的右孩子不为空,//(3)当要删除节点的左右孩子都不为空bool Erase(const K& key){//先找到要删除的节点Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (key > cur->_key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (key < cur->_key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{//找到了考虑三种情况//右孩子为空if (cur->_right == nullptr){//考虑到要删除的节点是根节点if (cur == _root){_root = cur->_left;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){parent->_left = cur->_left;}else{parent->_right = cur->_left;}}}//左孩子为空else if (cur->_left == nullptr){if (cur == _root){_root = cur->_right;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){parent->_left = cur->_right;}else{parent->_right = cur->_right;}}}//左右孩子都不为空//用替换法,找到左子树的最大节点(最右节点),或者找到右子树的最小节点(最左节点),//然后替换要删除的节点的键值。最后再删除节点else{Node* LeftMax = cur->_left;Node* parentMax;while (LeftMax->_right){parentMax = LeftMax;LeftMax = LeftMax->_right;}swap(LeftMax->_key, cur->_key);if (parentMax->_left == LeftMax){parentMax->_left = LeftMax->_left;}else{parentMax->_right = LeftMax->_left;}cur = LeftMax;}delete cur;return true;}}return false;}//交换void swap(K& k1, K& k2){std::swap(k1, k2);}//中序遍历//_root是private成员,在类外无法访问void _Inorder(Node* _root){if (_root == nullptr){return;}Inorder(_root->_left);cout << _root->_key << " ";Inorder(_root->_right);}void Inorder(){_Inorder(_root);}
private:Node* _root;
};
递归版本补充
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
public:typedef TreeNode<K> Node;//查找//key大于根节点的键值就往右边找,小于根节点的键值就往左边找//找到了返回节点地址,找不到返回nullptrNode* Find(const T& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (key > cur->_key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (key < cur->_key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}//查找Node* FindR(const K& key){return _FindR(_root, key);}//插入bool InsertR(const K& key){return _InsertR(_root, key);}//删除bool EraseR(const K& key){return _EraseR(_root, key);}//拷贝构造//就是复制一个相同的二叉搜索树BSTree(const BSTree<K>& b){_root = _Copy(b._root);}//=重载BSTree<T>& operator=(BSTree<K> b){//_root指向b的空间,b指向_root原来的旧空间,函数结束后销毁swap(_root, b._root);return *this;}//析构~BSTree(){Destroy(_root);}
private:Node* _root;//查找Node* _FindR(Node* root ,const K& key){if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}if ( key == root->_key ){return root;}else if (key > root->_key){return _FindR(root->_right,key);}else{return _FindR(root->_left,key);}}//插入bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){//传引用的好处,不用记住其父节点,返回之后自动链接到二叉搜索树root = new Node(key);return true;}if (key == root->_key){return false;}else if (key > root->_key){return _InsertR(root->_right, key);}else{return _InsertR(root->_left, key);}}//删除bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){return false;}if (key == root->_key){//左孩子为空if (root->_left == nullptr){delete root;root = root->_right;}//右孩子为空else if (root->_right == nullptr){delete root;root = root->_left;}//都不为空else{Node* LeftMax = root->_left;while (LeftMax->_right){LeftMax = LeftMax->_right;}swap(LeftMax->_key, root->_key);//此时将左右孩子都不为空的问题,转换成右孩子为空的问题return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}}else if (key > root->_key){return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}else{return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}}//拷贝Node* Copy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return root;}_root = new Node(b->_key);_root->_left = Copy(_root->_left);_root->_right = Copy(root->_right);}//销毁void Destroy(Node*& root){if (root == nullptr){return;}Destroy(root->_left);Destroy(root->_right);delete root;root = nullptr;}
};
3. 二叉树的应用
- K模型:节点只有key一个键值。KV模型:节点中有<key,value>键值对,每个key都对应一个value。
template<class K,class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;K _key;V _value;
};
template<class K, class V>class BSTree{typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;public:BSTree() : _root(nullptr) {}Node* Find(const K& key){return _FindR(_root,key);}bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value){return _InsertR(_root, key, value);}bool Erase(const K& key){return _EraseR(_root, key);}private:Node* _root;//查找Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}if (key == root->_key){return root;}else if (key > root->_key){return _FindR(root->_right, key);}else{return _FindR(root->_left, key);}}//插入bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value){if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key,value);return true;}if (key == root->_key){return false;}else if (key > root->_key){return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);}else{return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);}}//删除bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){return false;}if (key == root->_key){//左孩子为空if (root->_left == nullptr){delete root;root = root->_right;}//右孩子为空else if (root->_right == nullptr){delete root;root = root->_left;}//都不为空else{Node* LeftMax = root->_left;while (LeftMax->_right){LeftMax = LeftMax->_right;}swap(LeftMax->_key, root->_key);swap(LeftMax->_value, LeftMax->_value);return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}}else if (key > root->_key){return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}else{return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}}};
- K模型可以用来判断在不在的场景。例如检查一篇英文文章的单词是否拼写正确,将词库的单词以及单词的各种变化读取到二叉树中,从文章读取单词,能够在二叉树找到,说明拼写正确,不在说明拼写错误。
- KV模型可以通过key找到value。例如从词库中读取英文单词以及对应的中文放到二叉树中,输入单词,查找对应的中文。
void test()
{BSTree<string, string> dict;//词典dict.Insert("string", "字符串");dict.Insert("tree", "树");dict.Insert("left", "左边、剩余");dict.Insert("right", "右边");dict.Insert("sort", "排序");// 插入词库中所有单词string str;while (cin>>str){BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.Find(str);if (ret == nullptr){cout << "单词拼写错误,词库中没有这个单词:" <<str <<endl;}else{cout << str << "中文翻译:" << ret->_value << endl;}}
}
4. 练习
- 根据二叉树创建字符串
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}};
//本题的重点在于括号的省略
//1. 左边为空,右不为空。左边括号保留。
//2. 左边为空,右边为空。括号不保留。
//3. 左边不为空,右边为空。右边括号不保留。
class Solution {
public:string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {if(root==nullptr){return "";}string str = to_string(root->val);if(root->left!=nullptr || root->right!=nullptr){str+="(";str+=tree2str(root->left);str+=")";}if(root->right!=nullptr){str+="(";str+=tree2str(root->right);str+=")";} return str;}
};
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先
法1
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}};
class Solution {
public:bool FindTreeNode(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*x){if(root==nullptr){return false;}if(root->val==x->val){return true;} return FindTreeNode(root->left,x)||FindTreeNode(root->right,x);}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {//思路:如果root是p和q的公共节点,那么p和q一定在root的左右子树,如果在同一棵树,判断在哪棵树,进行递归,直到找到为止。if(root==p||root==q){return root;}if(root == nullptr){return nullptr;}//判断p在哪棵树int pInLeft = FindTreeNode(root->left,p);int pInRight = FindTreeNode(root->right,p);//判断q在哪棵树int qInLeft = FindTreeNode(root->left,q);int qInRight = FindTreeNode(root->right,q);//if(pInLeft==1 && pInLeft == qInLeft){return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);}else if(pInRight ==1 && pInRight == qInRight){return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);}else{return root;}}
};
//这种方法适用于普通二叉树,时间复杂度是O(N)。
//若是二叉搜索树,则只需比较大小,就能判断两个节点是在左树还是右树,
//不用遍历找节点,时间复杂度是O(N)。
法2
//思路:将问题转换成链表的相交问题,用两个栈来存储p和q的路径,再找出第一个相交的节点。
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {//创建两个栈,用来存放p和q的两条路径stack<TreeNode*> pPath;stack<TreeNode*> qPath;//找到p和q的节点前,将路径上的节点入栈FindPath(pPath,root,p);FindPath(qPath,root,q);//将两条路径变得一样长while(pPath.size()>qPath.size()){pPath.pop();}while(pPath.size()<qPath.size()){qPath.pop();}//一直弹出栈顶节点,直到栈顶节点相同while(pPath.top()!=qPath.top()){pPath.pop();qPath.pop();}//此时相同的栈顶节点就是它们的最近公共祖先return pPath.top();}bool FindPath(stack<TreeNode*>& Path,TreeNode*& root,TreeNode* x){if(root==nullptr){return false;}//先进栈,再判断//因为root可能是路径上的节点Path.push(root);if(root == x){return true;}//往左子树找if(FindPath(Path,root->left,x)){return true;}//往右子树找if(FindPath(Path,root->right,x)){return true;}//找不到就将节点弹出Path.pop();return false;}
};
- 二叉搜索树转换成双向循环链表
struct TreeNode
{int val;struct TreeNode *left;struct TreeNode *right;TreeNode(int x) :val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public://prev记得引用接收,因为prev要发生变化void inorder(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*&prev){if(root==nullptr){return;}inorder(root->left,prev);root->left = prev;//将上一个与现在链接起来,如果是null就不用if(prev){prev->right = root;}prev = root;inorder(root->right,prev);}TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {//有序->中序遍历//在双向链表中,left表示prev,right表示next//在中序遍历中,顺便链接双向链表//来一个prev记录前一个节点TreeNode*prev = nullptr;inorder(pRootOfTree,prev);TreeNode*head = pRootOfTree;//还要防止pRootOfTree为null的情况while(head&&head->left){head = head->left;}return head;}
};
- 从前序和中序列构造二叉树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode*build(vector<int>&preorder,vector<int>&inorder,int& previ,int inbegin, int inend){if(inbegin>inend){return nullptr;}TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[previ]);int rooti = 0;while(inorder[rooti]!=preorder[previ]){++rooti;}++previ;root->left = build(preorder,inorder,previ,inbegin,rooti-1);root->right = build(preorder,inorder,previ,rooti+1,inend);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {//思路:前序遍历确定根结点,用来构建二叉树//中序遍历用来分割区间//用递归来实现//细节:(1)需要一个下标来实时记录在前序列表中的位置,//方便遍历//(2)需要一个区间来分割中序列表int index = 0;int begin = 0;int end = inorder.size()-1;return build(preorder,inorder,index,begin,end);}
};
- 从中序和后序序列构造二叉树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* build(vector<int>&inorder,vector<int>postorder,int& posti,int inbegin,int inend){if(inbegin>inend){return nullptr;}TreeNode*root = new TreeNode(postorder[posti]);int rooti = 0;while(inorder[rooti]!=postorder[posti]){++rooti;}--posti;root->right = build(inorder,postorder,posti,rooti+1,inend);root->left = build(inorder,postorder,posti,inbegin,rooti-1);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {//思路:后序遍历:从后往前,可以确定根结点//中序可以用来分割//构造二叉树时,用一个从后往前的下标,且先构造右子树int begin = 0;int end = inorder.size()-1;int index = postorder.size()-1;return build(inorder,postorder,index,begin,end);}
};
- 二叉树的前序遍历(非递归)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {//思路:将这棵树分为左路节点和右子树,再创建一个栈,//将左路节点入栈,同时节点的键值加到vector,直到左路节点为空,//再出栈,从出栈节点开始,分为左路节点和右子树,继续入栈,//一直循环,直到栈为空vector<int> vt;stack<TreeNode*> st;TreeNode*cur = root;while(cur||!st.empty()){while(cur){vt.push_back(cur->val);st.push(cur);cur = cur->left;}TreeNode* tmp = st.top();st.pop();cur = tmp->right;}return vt;}
};
- 二叉树的中序遍历(非递归)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {//思路:依次将左路节点全部入栈后,再出栈将数据入vector,相当于先访问左子树,再访问右子树,一直循环,直到栈为空。vector<int> vt;stack<TreeNode*> st;TreeNode*cur = root;while(cur||!st.empty()){while(cur){//入栈st.push(cur);cur = cur->left;}TreeNode*tmp = st.top();vt.push_back(tmp->val);st.pop();cur = tmp->right;}return vt;}
};
- 二叉树的后序遍历(非递归)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {//该节点已经访问右子树,那么就将入vector//如果没有访问右子树就访问右子树。//用一个指针来表示有没有访问vector<int> vt;stack<TreeNode*> st;TreeNode* cur = root;TreeNode* prev = nullptr;while(cur||!st.empty()){while(cur){st.push(cur);cur = cur->left;}TreeNode*tmp = st.top();//如果右子树为空,或者右子树已经访问,就直接入vectorif(tmp->right==nullptr||prev==tmp->right){vt.push_back(tmp->val);st.pop();prev = tmp;}else{cur = tmp->right;prev = tmp;}}return vt;}
};