目录
- 1.枚举指定路径下的文件目录
- 2.获取文件属性stat
- 其他方式:Linux获取文件属性stat()、fstat()、lstat()函数实现
- stat属性
- 代码
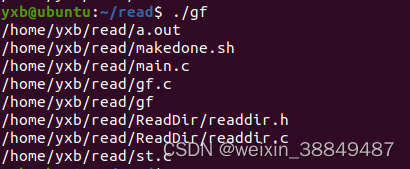
1.枚举指定路径下的文件目录
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>void list_files_recursive(const char* path) {DIR* dir;struct dirent* entry;struct stat file_stat;// 打开目录dir = opendir(path);if (dir == NULL) {printf("Failed to open directory: %s\n", path);return;}// 逐个读取目录项while ((entry = readdir(dir)) != NULL) {char file_path[256];// 构建文件路径snprintf(file_path, sizeof(file_path), "%s/%s", path, entry->d_name);// 获取文件信息if (stat(file_path, &file_stat) == -1) {printf("Failed to get file stat: %s\n", file_path);continue;}// 判断是否为目录if (S_ISDIR(file_stat.st_mode)) {// 忽略 "." 和 ".." 目录if (strcmp(entry->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(entry->d_name, "..") == 0) {continue;}// 递归调用自身处理子目录list_files_recursive(file_path);} else {// 输出文件路径printf("%s\n", file_path);}}// 关闭目录closedir(dir);
}int main() {const char* folder_path = "/home/yxb/read"; // 替换为你的文件夹路径list_files_recursive(folder_path);return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{DIR * dir;struct dirent * ptr;int i;dir = opendir("/home/yxb/sense");while((ptr = readdir(dir)) != NULL){printf("d_name : %s\n", ptr->d_name);}closedir(dir);
}
2.获取文件属性stat
其他方式:Linux获取文件属性stat()、fstat()、lstat()函数实现
函数原型 #include <sys/stat.h>int stat(const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf);
提供文件名字,获取文件对应属性。int fstat(int filedes, struct stat *buf);
通过文件描述符获取文件对应的属性。int lstat(const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf);
类似于stat.但是当命名的文件是一个符号链接时,lstat返回该符号链接的有关信息,而不是由该符号链接引用文件
函数说明: 通过文件名filename获取文件信息,并保存在buf所指的结构体stat中返回值: 执行成功则返回0,失败返回-1,错误代码存于errno第二个参数是个指针,它指向一个我们应提供的结构。这些函数填写由buf指向的结构。
该结构的实际定义可能所实施而有所不同,但其基本形式是:stat属性
stat结构体
struct stat {dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ // 文件所在设备的IDino_t st_ino; /* inode number */ // inode节点号mode_t st_mode; /* protection */ // 文件对应的模式,文件、目录等nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */ // 链向此文件的连接数(硬连接)uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ // 所有者用户IDgid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ // 所有者组IDdev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */ // 设备号,针对设备文件off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */ // 文件大小,单位为字节blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */ // 系统块的大小(文件内容对应的块大小)blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */ // 文件所占块数time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ // 最近存取时间(最近一次访问的时间)time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ // 最近修改时间time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ // 文件状态改变时间(文件创建时间)
};结构体 struct stat 中的 st_mode 属性可以用来判断指定文件为目录、普通文件、链接文件等,可以通过使用相应的宏进行判断,以下列出部分常用文件的宏,以及其使用方法。
S_ISDIR(st_mode):是否为目录
S_ISREG(st_mode):是否为常规文件
S_ISLNK(st_mode):是否为链接文件
S_ISCHR(st_mode):是否为字符设备
S_ISBLK(st_mode):是否为块设备
S_ISFIFO(st_mode):是否为FIFO文件
S_ISSOCK(st_mode):是否为SOCKET文件代码
/* file stat example */ #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h> #include <stdlib.h>
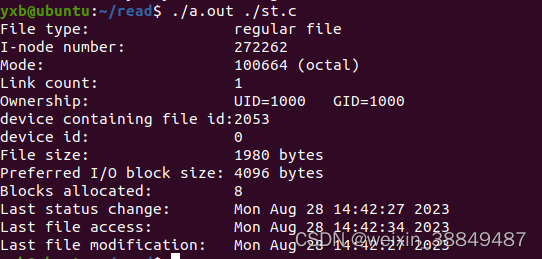
#include <time.h> int main(int argc, char **argv){ struct stat st; if(argc != 2){ fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <file_pathname> \n", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if(stat(argv[1], &st) == -1){ perror("stat"); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } printf("File type: "); switch(st.st_mode & S_IFMT){ case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n"); break; case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n"); break; case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n"); break; case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO/pipe\n"); break; case S_IFLNK: printf("symlink\n"); break; case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n"); break; case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n"); break; default: printf("unknown?\n"); break; } printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) st.st_ino); printf("Mode: %lo (octal)\n", (unsigned long) st.st_mode); printf("Link count: %ld\n", (long) st.st_nlink); printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n", (long) st.st_uid, (long) st.st_gid); printf("device containing file id:%ld \n", (long) st.st_dev); printf("device id: %ld \n", (long) st.st_rdev); printf("File size: %lld bytes\n", (long long) st.st_size); printf("Preferred I/O block size: %ld bytes\n", (long) st.st_blksize); printf("Blocks allocated: %lld\n", (long long) st.st_blocks); printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&st.st_ctime)); printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&st.st_atime)); printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&st.st_mtime)); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
![[ES]mac安装es、kibana、ik分词器](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/367d53f3587a4ca38300808d2ed38685.png)