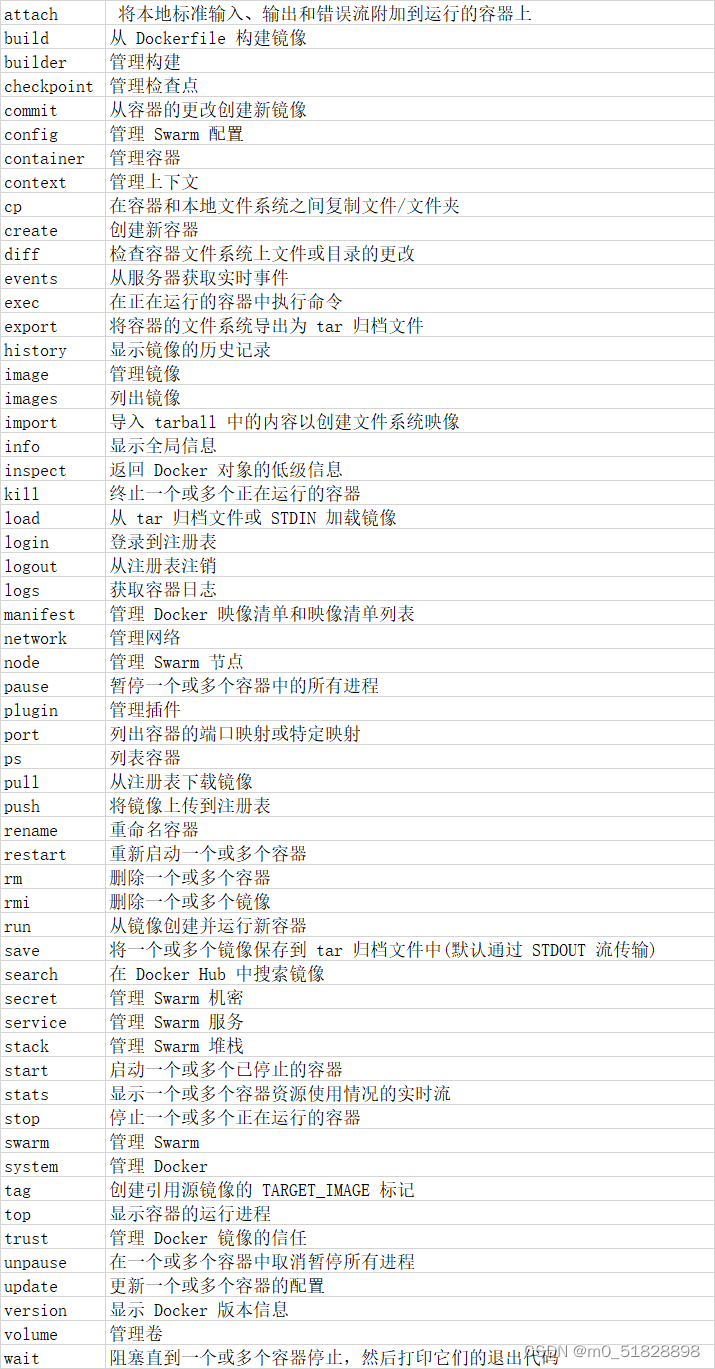
目录
- 课程一、C#基础
- 1.C#编译环境、基础语法
- 2.Winform-后续未学完
- 课程二、Timothy C#底层讲解
- 一、类成员
- 0常量
- 1字段
- 2属性
- 3索引器
- 5方法
- 5.1值参数(创建副本,方法内对值的操作,不会影响原来变量的值)
- 5.2引用参数(传的是地址,方法内对值的操作,出了方法后原来的值也被修改)
- 5.3 输出参数(普通方法一次调用只产出一个返回值,但希望一次调用返回多个输出值,所以用输出参数)
- 5.4 数组参数 parmas(可供函数输出多个值)
- 5.5 具名参数(调用方法时,参数带有名字,位置随意)
- 5.6 可选参数(方法定义声明时,有默认值)
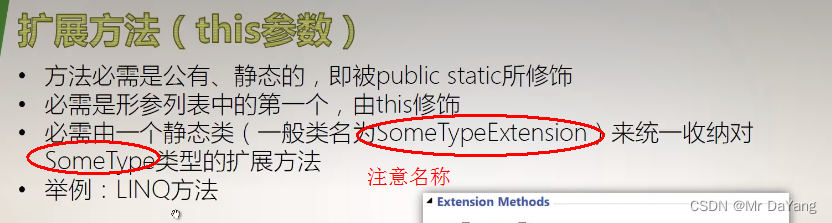
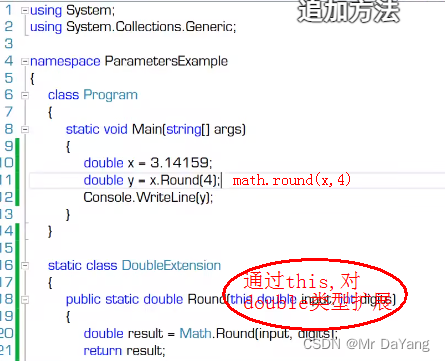
- 5.7 扩展方法(this参数)
- 二、委托
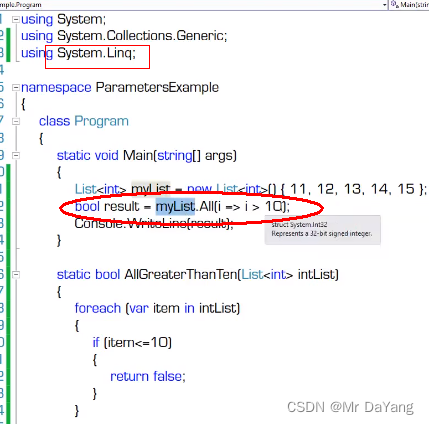
- 1委托(c# Action,Func常规委托)
- 2委托声明 (delegate自定义委托)
- 3委托使用(把方法当做参数会给另一个方法:模板法,回调法)
- 4委托高级使用(多播委托\异步委托调用)
- 三、事件
- 1事件定义
- 2事件应用(5要素)
- 3事件自定义
- 四、类
- 1构造器、析构器
- 2.类修饰符(public\internal\abstract)
- 3类的继承
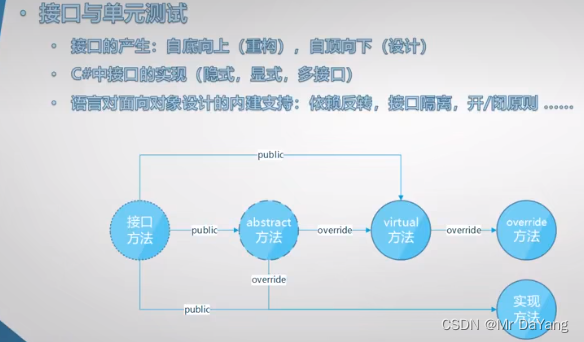
- 五、接口、抽象类
- 六、反射、依赖注入
- 七、泛型(这里代码多练习)
- 八、核心代码汇总
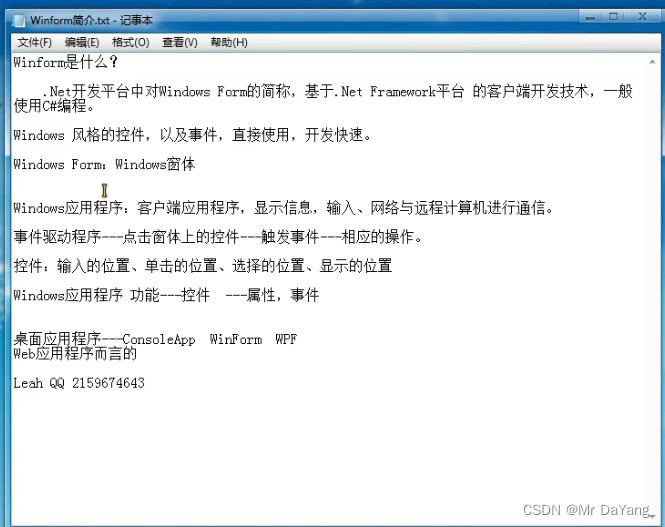
课程一、C#基础
视频
1.C#编译环境、基础语法

F12查看函数被引用的地方,ctrl +减号 返回
F10,debug时的一步步调试
alt+s左键 选几行中的某些字段calculator.repoort() 加括号表示调用方法 calculator.repoort 表示方法名
1.查看变量类型
Debug.WriteLine(array3.GetType().ToString())
2.抛出异常
try
{可能会出现异常的代码块;
}
//try和catch之间不能有其它的代码
catch
{出现异常后要执行的代码块;
}
3.查看两变量或对象是否是一个值?
Console.WriteLine{"{0}",stu.GetHashCode()};
4.将文件中一个变量名统一修改成另外一个
对一个修改完后,按 ctrl+点 实现
5.类是典型的引用类型
6.Action action1 = new Action(stu1.dohomework); stu1.dohomework 是函数名
7.1.类中定义方法时,后面不用加; 只有执行的语句要加;2.stu1.dohomework()是方法的调用 stu1.dohomework 是函数名 public double Price { get; set; } Action action1 = new Action(stu1.dohomework); stu1.dohomework 是函数名
8.registerMonitor.get_Reg = get_reg_values; get_reg_values没有变量类型,没有括号表示方法,那么是委托
9.使用alt+enter对写的代码进行补充
10.//委托类型创建 为 order事件创建 public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;//委托字段,用来存储事件处理器
11.一个类可以继承单个类,一个类可以有多个接口,一个接口也可以继承多个接口
12. new 创建的是静态类型,typeof 拿到的是动态描述
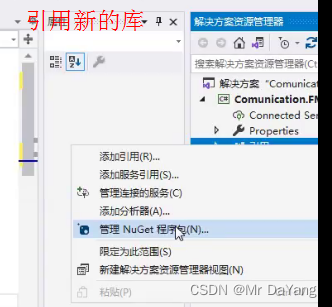
c# 了解
1.net 运行平台上,运行vb,c#,c++语言(.net环境为vb,c#,c++封装了各种工具包) .net core跨平台开发(可运行win linux) 相当于java开发工具包jdk上,包含java运行环境(jre,jvm+java系统类库)和java工具
2.c#工具 visual studio 2019

关键字声明 class类 namespace int(申明整数变量)
//单行注释
/* */多选注释
// 放到类、方法前按下///进行注释
变量为小数1.123,系统将其认为是double 型, float a=1.123报错 double a=1.123正确
string s='“” 与s=null 区别:“”“”的字符串为空, null直接就是空,存字符串的地方都没有,只有string才可以=null,其他类型变量不可以
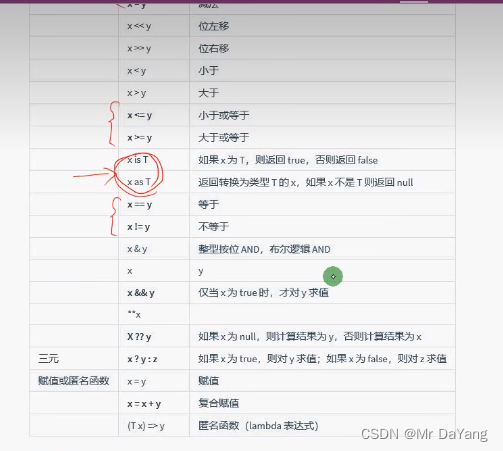
int x=2;
show(++x) ; x=3 前++先执行
show(x); x=3
string a=5;
show(a++); a=5 后++ 后执行
show(a); a=6
IF要一个个判断才能选择某个分支,switch直接进入那个分支
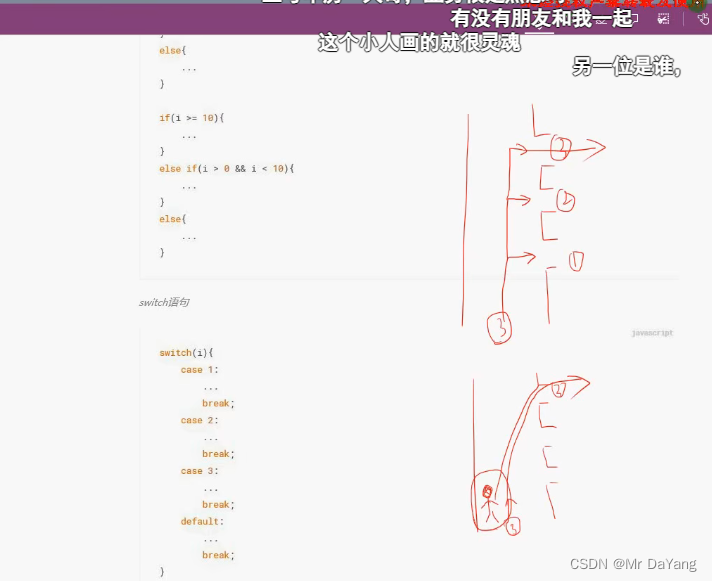
private void InitializeComponent(){MessageBox.Show("linyang");int a = 2; switch (a) //a可以为数字也可为string{case 1:MessageBox.Show("1");break;case 2:MessageBox.Show("2");break;//必须要break}
//for 循环直接循环 while 预设一个条件,当条件满足时进入循环, do {}while 先执行,达到条件退出for (int a =2; a<4; a++){MessageBox.Show(a.ToString());};int i = 1;
while (i <=3) {MessageBox.Show((i++).ToString());
}int b = 1;
do {MessageBox.Show((b).ToString()); b++;
}
while (b < 4);
每次new就会开辟一个新地址,尽管内容一次,但不是同一个
//关键字 int,int[] 声明变量类型,new 创建数组int q = 2;int[] a = new int[6];int[] b = new int[3] { 1,2,3};int[] c = new int[] { 'a',2,3};MessageBox.Show(c[0].ToString()); //输出97

/*无修饰时函数内部处理的是副本不影响原来的值string want = "2222"; //want = "2222"Sellhouse(want); //box显示1111MessageBox.Show(want.ToString()); //box显示2222*//*out修饰时,引用传递, 函数内部处理的是原地址,影响原来的值string want = "2222"; //want = "2222"Sellhouse1(out want); //box显示1111MessageBox.Show(want.ToString()); //box显示1111*//*ref修饰时,引用传递, 函数内部处理的是原地址,影响原来的值,与out不同,out使用函数中(Sellhouse1)必须要赋值否则报错string want = "2222"; //want = "2222"Sellhouse2(ref want); //box显示1111MessageBox.Show(want.ToString()); //box显示1111*/}public void Sellhouse(string want){want = "1111";MessageBox.Show(want.ToString());}public void Sellhouse1(out string want) {want = "1111"; //有out时必须要赋值,否则报错MessageBox.Show(want.ToString());}public void Sellhouse2(ref string want){want = "1111"; //有ref时,谁调用它必须赋初值,否则报错MessageBox.Show(want.ToString());}
类与方法
{get,set}参考1,参考2,参考3


数组是连续的不能add,delete(new int[3])
集合(arraylist支持add,delete但是装箱拆箱耗时-由于存储变量类型不一致情况导致,
list泛型 list约束了只支持一种类型)
int[] a=new int[5]
Arraylist a=new Arraylist()


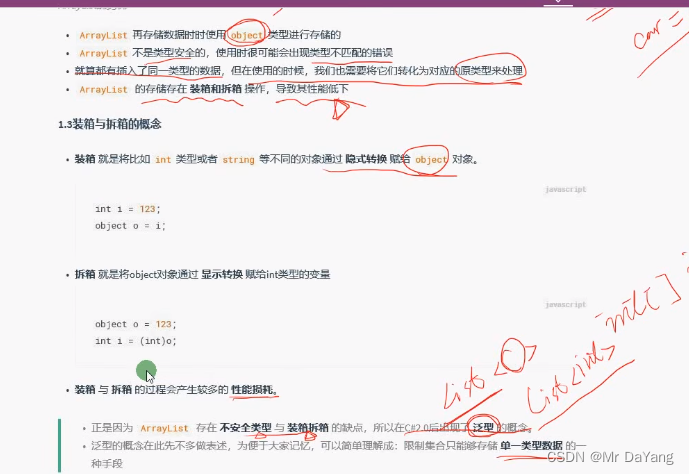
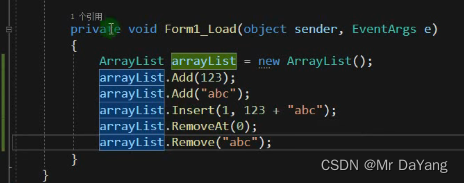

List<int> a = new List<int>( );List<int> b = new List<int> { 1,2,2};List<Person> p = new List<Person>();a.Add(112);a[0] = 4;a.Insert(0, 3);a.RemoveAt(0);a.Remove(4);a.Clear();p.Add(new Person() { });Dictionary<int, string> c = new Dictionary<int, string>();Dictionary<int, string> d = new Dictionary<int, string> { //对象初始化器{ 2,"333"},{4,"555"}};c.Add(1, "111");c.Add(2, "222");c.Add(3, "333");string value = c[2];//通过键索引到值; “222”bool f=c.Remove(1);//通过键删除那个值


int[] a = new int[] { 3,4,5};foreach (int i in a){MessageBox.Show(i.ToString());}List<int> b = new List<int> { 2,3,4};foreach(int i in b){MessageBox.Show(i.ToString());}Dictionary<string, string> c = new Dictionary<string, string>() { {"aa","aaaaa" },{"bb","bbbb" } };foreach (KeyValuePair<string,string> i in c){string key = i.Key;string value = i.Value;}
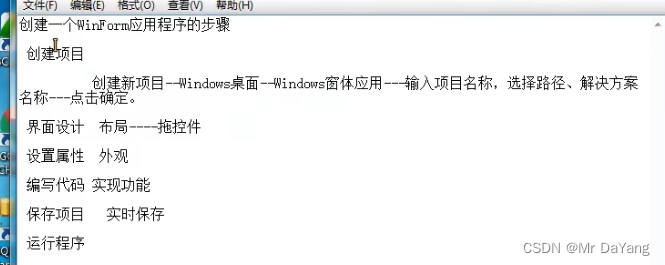
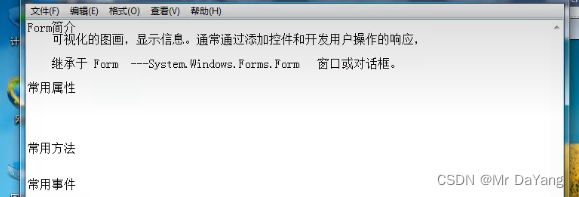
2.Winform-后续未学完
视频
课程二、Timothy C#底层讲解
C#语法介绍–介绍底层全面深刻-Timothy
一、类成员
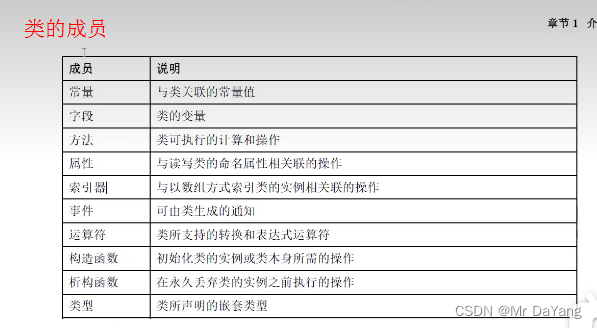
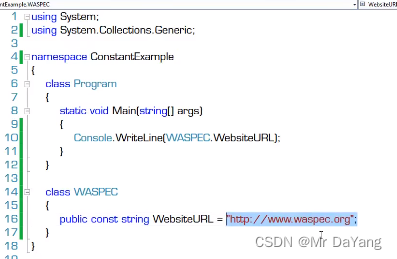
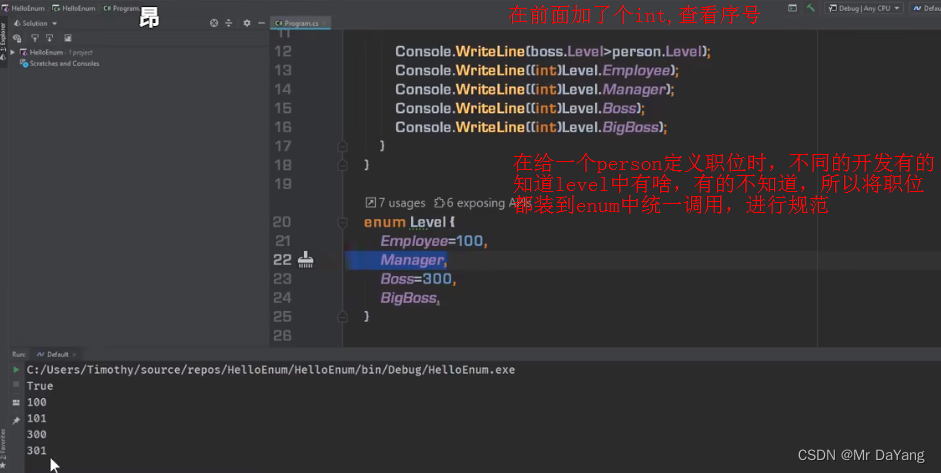
0常量
math.PI 就是常量 运算效率高,不用从内存中读

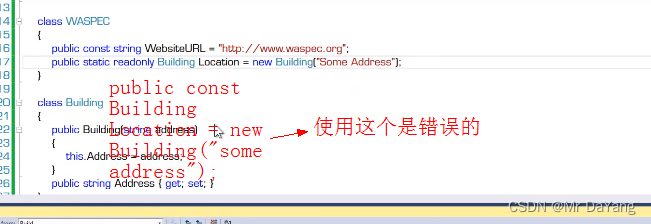
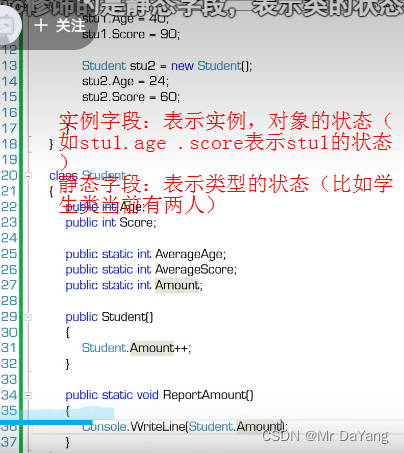
1字段

实例字段初始化时机:创建一个类时
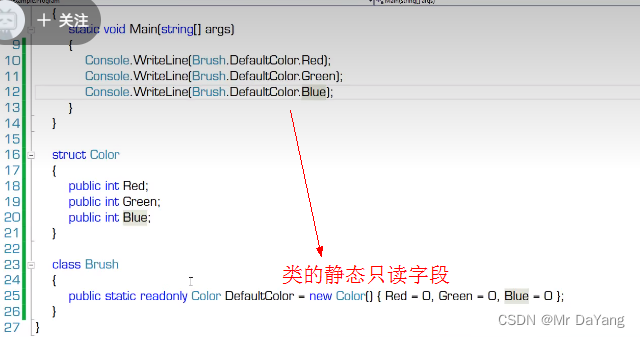
静态字段初始化时机:这个程序被加载时,字段在声明时就初始化了,只初始化一次
2属性
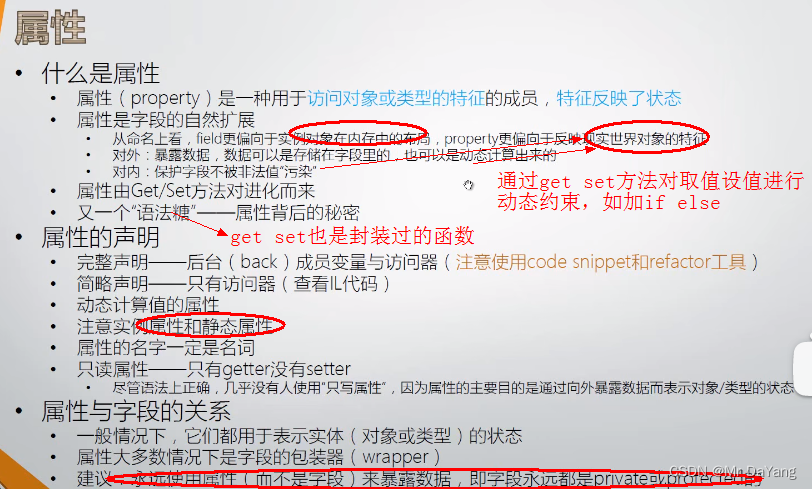
1属性完整申明
// 在类中输入 propfull按两下tab自动生成class person{private int age; public int Age{get { return age; }set { if (value >= 0 && value <= 120)//这个value是微软特定设置在set下的,不用申明{age = value;}else{throw new Exception("age value has error11111");}}}}
//使用,使用private后person p1 = new person();p1.Age=100;
2属性简易申明,对字段没有保护措施
// 在类中输入 prop按两下tab自动生成class person{public int MyProperty { get; set; }}
3字段int age->方法对 get() ->属性Age{get;set}的推演
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){try{Student stu1 = new Student();stu1.Age = 20;//使用private后,类调用属性只能get set方法//stu1.Setage(20);Student stu2 = new Student();//stu2.Setage(20);stu2.Age = 20;Student stu3 = new Student();//stu3.Setage(810);stu3.Age = 210;int avgage = (stu1.Age + stu2.Age + stu3.Age) / 3;Console.WriteLine(avgage);Console.Read();}catch(Exception ee){Console.WriteLine(ee.Message);//"age value has error"打印到前台Console.Read();}}}class Student{private int age;public int Getage (){ return this.age;}public void Setage(int value)//属性可以对变量防护{if (value >= 0 && value <= 120) { this.age = value;}else{throw new Exception("age value has error");}}private int age;public int Age{get { return this.age; }set{if (value >= 0 && value <= 120)//这个value是微软特定设置在set下的,不用申明{this.age = value;}else{throw new Exception("age value has error11111");}}}}
}3索引器
索引器用在集合中
//输入index 按两下TAB生成
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){try{Student stu = new Student();var mathscore = stu["Math"];Console.WriteLine(mathscore==null);Console.Read();}catch(Exception ee){Console.WriteLine(ee.Message);//"age value has error"打印到前台Console.Read();}}}class Student{private Dictionary<string, int> score = new Dictionary<string, int>();public int? this[string subject] //int?可空int型号 subject自己定义的成绩科目名为subject{get {if (this.score.ContainsKey(subject)){return this.score[subject];}else{return null;}}set { /* set the specified index to value here */if (value.HasValue == false){throw new Exception("score cannot be null");}if (this.score.ContainsKey(subject)){this.score[subject]=value.Value;//int?可空int型号}else{this.score.Add(subject, value.Value);}}}}}
5方法

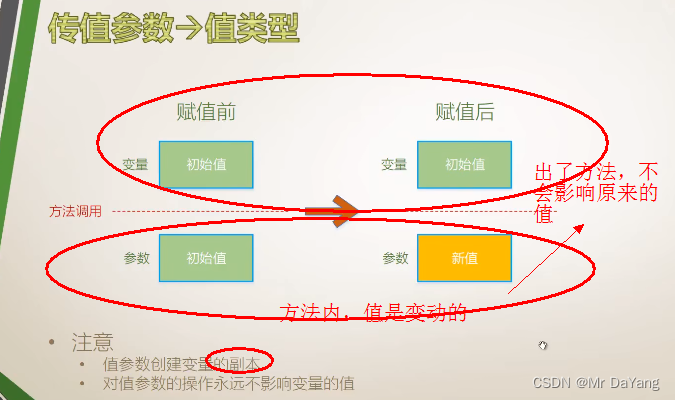
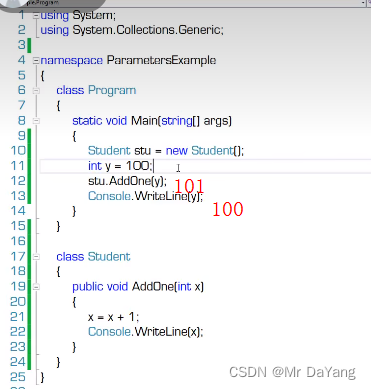
5.1值参数(创建副本,方法内对值的操作,不会影响原来变量的值)
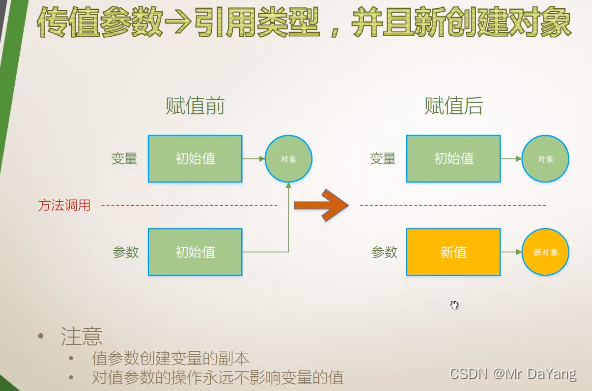
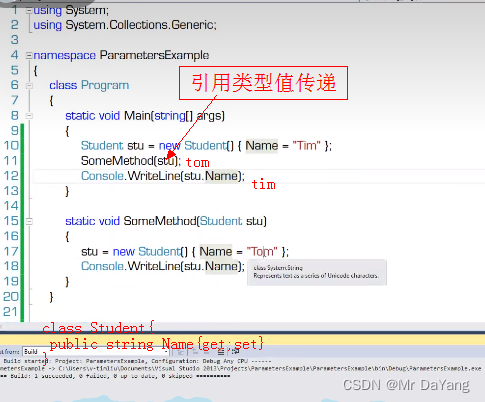
引用类型,不创建新对象
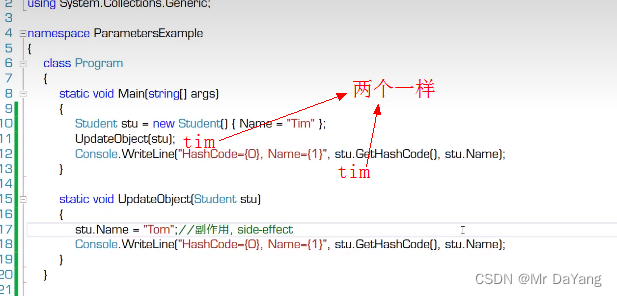
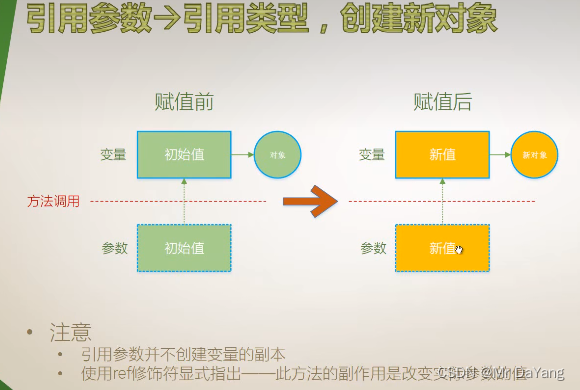
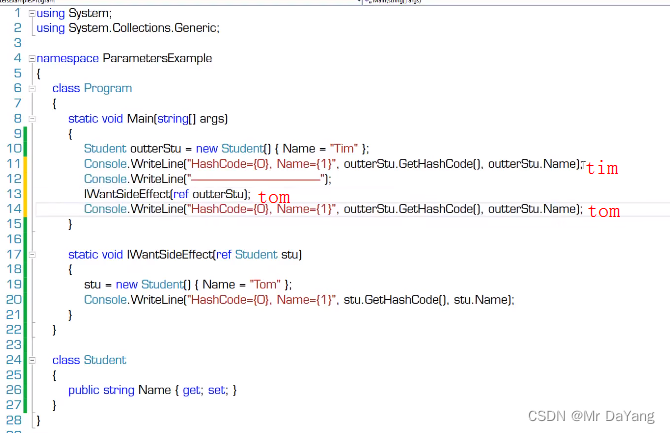
5.2引用参数(传的是地址,方法内对值的操作,出了方法后原来的值也被修改)
引用参数在传入方法前必须有个明确的赋值,然后在方法中修改

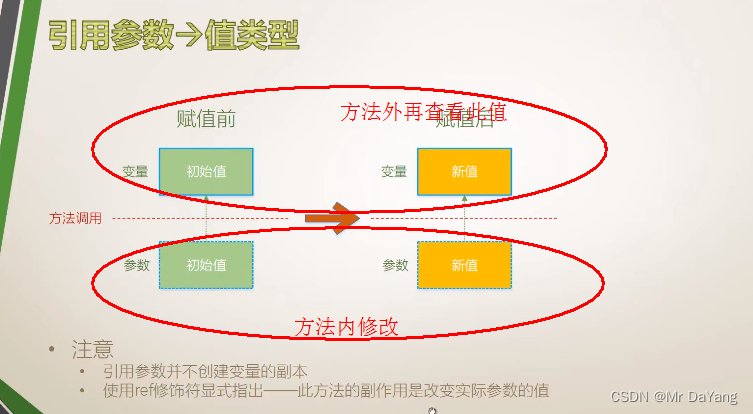
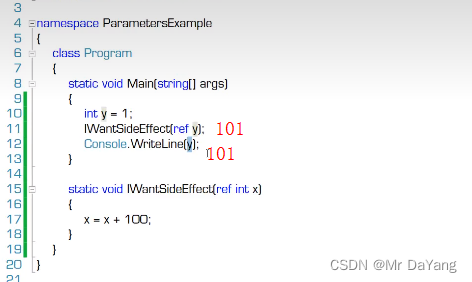
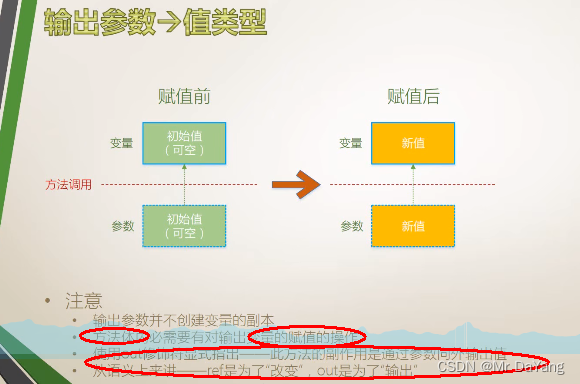
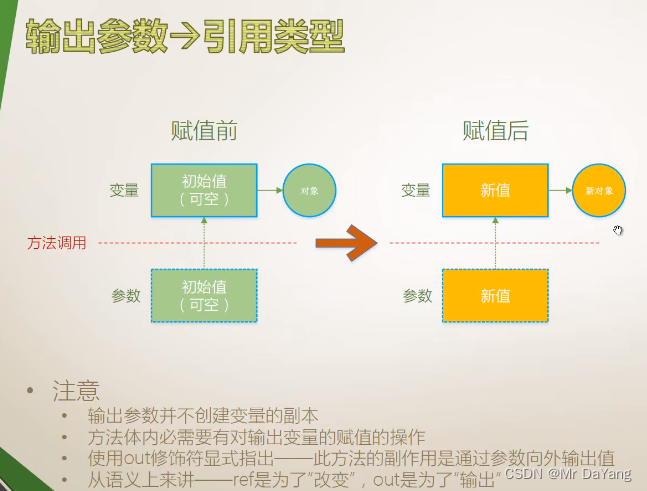
5.3 输出参数(普通方法一次调用只产出一个返回值,但希望一次调用返回多个输出值,所以用输出参数)
讲解的时值先讲值 引用变化,再讲类引用变化



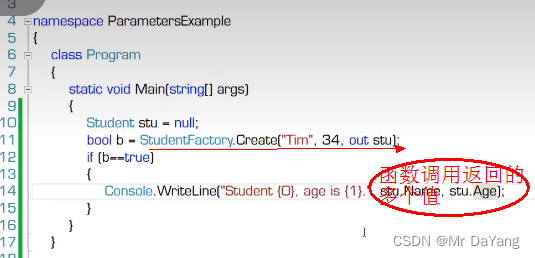

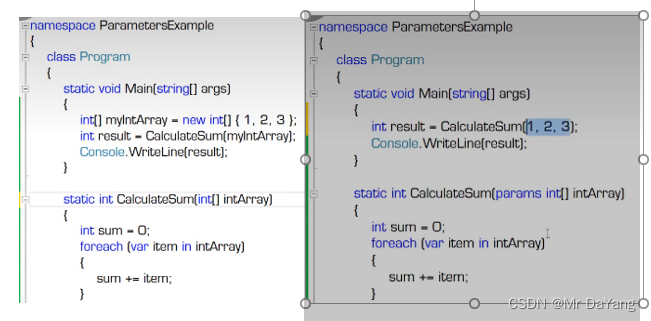
5.4 数组参数 parmas(可供函数输出多个值)


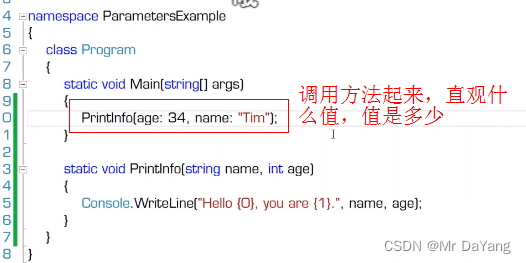
5.5 具名参数(调用方法时,参数带有名字,位置随意)
5.6 可选参数(方法定义声明时,有默认值)


5.7 扩展方法(this参数)
二、委托
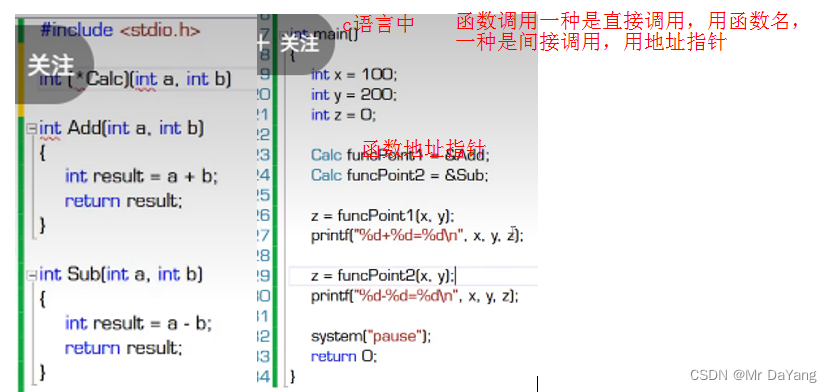
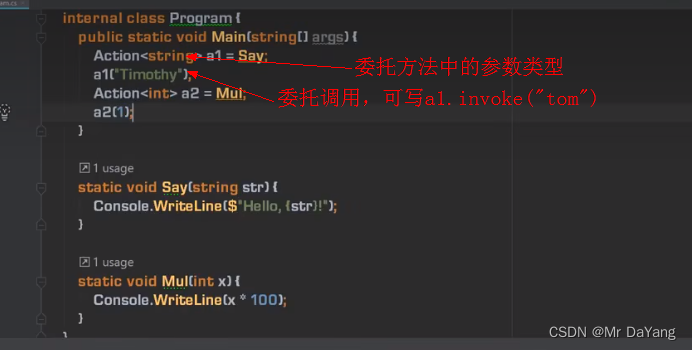
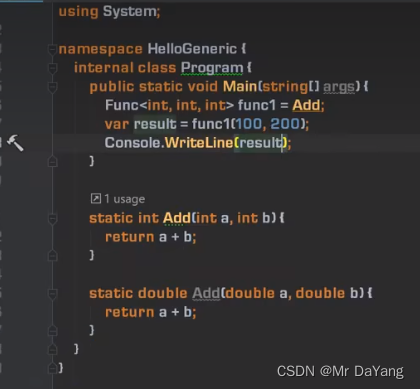
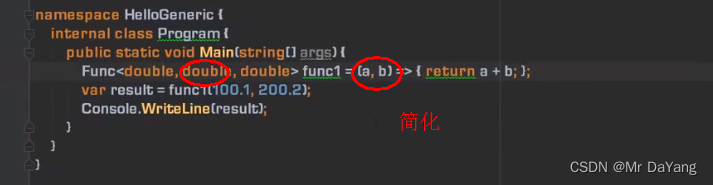
1委托(c# Action,Func常规委托)


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculator calculator = new Calculator();Action action = new Action(calculator.Report);//Action: 方法是void,并且无参数action.Invoke();//委托调用action();//模仿c中函数指针的书写格式calculator.Report();//直接调用方法名//<第一个int为返回值, 第二三个int为函数输入>Func<int, int, int> func1 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Add);//Func :方法是有返回,有参数Func<int, int, int> func2 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Sub);int x = 100;int y = 200;int z = 0;z = func1.Invoke(x, y);//委托调用Console.WriteLine(z);z = func2.Invoke(x, y);Console.WriteLine(z);func1(x, y);//模仿c中函数指针的书写格式}}class Calculator{public void Report() {Console.WriteLine("i have 3 methods");}public int Add(int a,int b){int result = a + b;return result;}public int Sub(int a, int b){int result = a - b;return result;}} }
2委托声明 (delegate自定义委托)

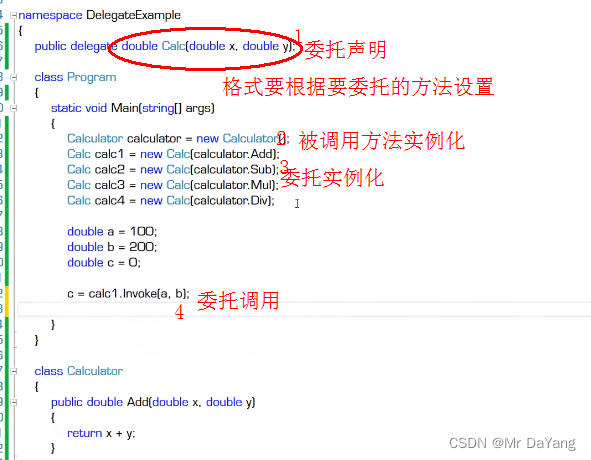
3委托使用(把方法当做参数会给另一个方法:模板法,回调法)

实现目的:方法中调用方法
现实中是无法操作的,所以采用模板方法+用委托类型参数封装的方法的方式来实现,委托相当于一个指针,可以指定任意方法,就可以实现方法调方法。
模板方法:方法中 输入 用委托类型参数封装的方法
回调方法:方法中 在调用 用委托类型参数封装的方法 时,有条件判断
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ProdectFactory prodectFactory = new ProdectFactory();WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();//<第一个int为返回值, 第二三个int为函数输入>// Func<int, int, int> func1 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Add);//Func :方法是有返回,有参数//1委托封装方法 //Product为委托的返回类型 ,func1为委托名 =new委托的返回值类型是Product,委托的函数名称=prodectFactory.MakePizaFunc<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(prodectFactory.MakePiza);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(prodectFactory.Makecar);Logger logger = new Logger();Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);//2调用模板方法,返回值为box1Box box1=wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1,log);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2,log);Console.WriteLine(box1.product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.product.Name);Console.Read();}class Logger{public void Log(Product product){Console.WriteLine("Product '{0}' created at {1},price is {2}", product.Name, DateTime.UtcNow, product.Price);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; } //类属性是stringpublic double Price { get; set; }}class Box{public Product product { get; set; }//类属性是一个类}class WrapFactory{//WrapProduct 委托的模板方法,Box方法的返回值//委托模板方法的输入是委托函数 Func<Product> getProductpublic Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct, Action<Product> logCallback){Box box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();if (product.Price > 50){logCallback(product);}box.product=product;return box;}}class ProdectFactory{public Product MakePiza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";product.Price = 12;return product;}public Product Makecar(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "car";product.Price = 100;return product;}}} }
4委托高级使用(多播委托\异步委托调用)
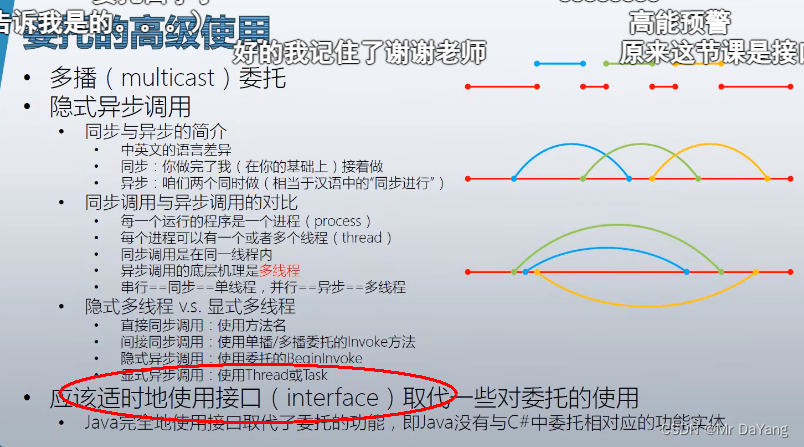
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student() { id = 1, pencolor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu2 = new Student() { id = 2, pencolor = ConsoleColor.Green };Student stu3 = new Student() { id = 3, pencolor = ConsoleColor.Red };/* 1.同步间接调用-使用委托Action action1 = new Action(stu1.dohomework);Action action2 = new Action(stu2.dohomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.dohomework);//action1.Invoke();//单播委托// action2.Invoke();//action3.Invoke();//多播委托action1 += action2;action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();*///------------------------------------------------------------/*// 2同步直接调用 stu1.dohomework();stu2.dohomework();stu3.dohomework();//------------------------------------------------------------// 3隐式异步调用 Action action1 = new Action(stu1.dohomework);Action action2 = new Action(stu2.dohomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.dohomework);action1.BeginInvoke(null, null);//第一个null为执行完线程后的回调函数action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);//------------------------------------------------------------// 4显式异步调用 Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.dohomework));Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu2.dohomework));Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu3.dohomework));thread1.Start();thread2.Start();thread3.Start();*/// 4显式异步调用 Task task1 = new Task(new Action(stu1.dohomework));Task task2 = new Task(new Action(stu2.dohomework));Task task3 = new Task(new Action(stu3.dohomework));task1.Start();task1.Start();task1.Start();for (int i=0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("main thread{0}", i);Thread.Sleep(1000);Console.Read();}}class Student{public int id { get; set; }public ConsoleColor pencolor { get; set; }public void dohomework(){for (int i =0; i <5;i++) {Console.ForegroundColor = this.pencolor;Console.WriteLine("student{0} doing homework {1} hours", this.id, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}}
}三、事件
1事件定义

一个对象有事件,对象通过事件的发生来通知其他对象
程序员自己写的代码 订阅一个按钮,当按钮点击事件由客户触发时,那么代码就会对其进行响应。
用户操作下鼠标,就会执行一块程序,鼠标不用,那么这块程序就不执行。称这块程序为事件驱动程序。


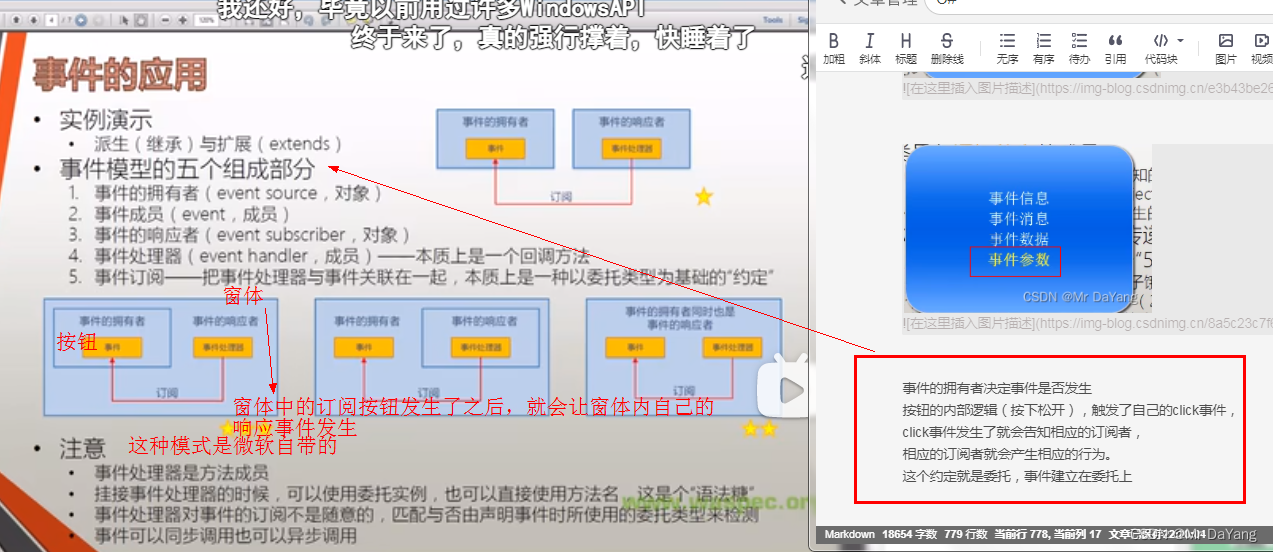
2事件应用(5要素)
事件的拥有者决定事件是否发生
按钮的内部逻辑(按下松开),触发了自己的click事件,
click事件发生了就会告知相应的订阅者,
相应的订阅者就会产生相应的行为。
这个约定就是委托,事件建立在委托上
事件与响应方法是可以1对多,多对1
订阅的挂接方式
this.button.click+=this.buttoonclicked;
this.button.click+=new EventHandler(this.buttoonclicked);
this.button.click+=(object sender, EventArgs e)=>{ this.textBox.text='hah';}; //流行
this.button.click+=delegate(object sender, EventArgs e){ this.textBox.text='hah';}//匿名方法过时
事件与响应方法是可以1对多,多对1
//一星展示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;
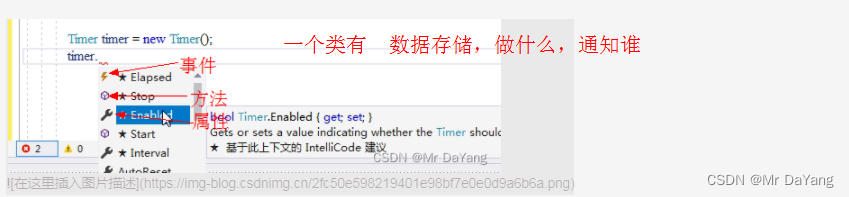
using System.Timers;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Timer timer = new Timer(); // timer.Elapsed事件的拥有者Timertimer.Interval = 1000;Boy boy = new Boy(); //事件的订阅者 Girl girl = new Girl();// 订阅者的处理器 +=表示订阅 拿方法订阅一个事件时,它们要遵守约定:约定就是委托类型// timer.Elapsed的类型就是 public delegate void ElapsedEventHandler(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e);// 所以使用alt+enter自动按照委托形式对boy.Action进行方法创建timer.Elapsed += boy.Action; //timer.Elapsed 为事件,boy.Action为事件处理器timer.Elapsed += girl.Action; //一个事件两个订阅者timer.Start();Console.ReadLine();}class Boy{internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e){Console.WriteLine("Jump");}}class Girl{internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e){Console.WriteLine("sing");}}}}//三星展示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Form form=new Form();//事件的拥有者Controller controller = new Controller(form);//事件的响应者form.ShowDialog();}class Controller{private Form form;public Controller(Form form){if (form != null){this.form = form;this.form.Click += this.Formclicked;//约定}}private void Formclicked(object sender, EventArgs e){this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();}}}
}//自己调自己,两星事件
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Myform myform = new Myform();myform.Click += myform.Formclicked;myform.ShowDialog();}class Myform : Form{internal void Formclicked(object sender, EventArgs e){this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();}}}
}//三星:事件的拥有者是响应者的成员
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace ConsoleApp1
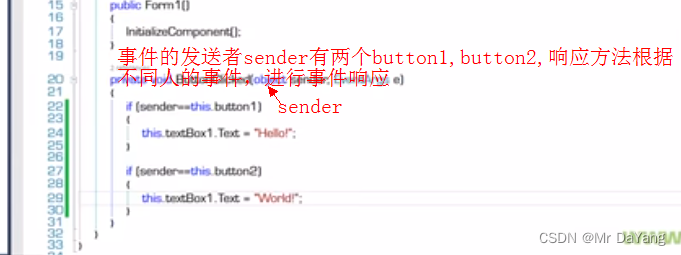
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Myform myform = new Myform();myform.ShowDialog();}}class Myform : Form {private TextBox textBox;private Button button;//form的字段成员,拥有者public Myform(){this.textBox = new TextBox();this.button = new Button();this.Controls.Add(this.button);this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);this.button.Click += this.buttonCllicked; //form =响应者this.button.Text = "sss";}private void buttonCllicked(object sender, EventArgs e){this.textBox.Text = "hello world```````````````````````````";}}
}
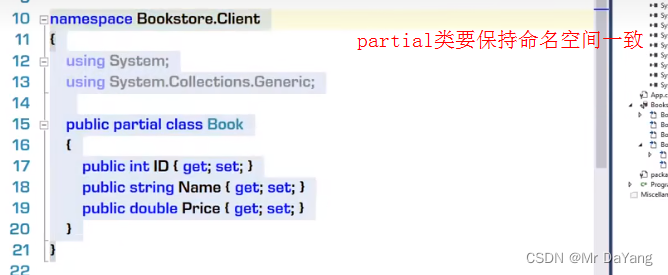
3事件自定义
委托是事件的底层基础,事件是委托的上层建筑
//第三种
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace ConsoleApp1
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Customer customer = new Customer(); //1事件拥有者Waiter waiter = new Waiter();//2事件的响应者customer.Order += waiter.Action;//事件 , 事件处理器 事件拥有者的内部逻辑触发了事件customer.Action();//事件触发customer.Paybill();} }//事件的信息public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs{public string Dishname { get; set; }public string Size { get; set; }}//委托类型创建 为 order事件创建 public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);public class Customer //1事件拥有者{private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;//委托字段,用来存储事件处理器public event OrderEventHandler Order //2事件{add{this.orderEventHandler += value;}remove{this.orderEventHandler -= value;}}public double Bill { get; set; }public void Paybill (){Console.WriteLine("i will pay ¥{0}", this.Bill);}public void Walk(){Console.WriteLine("walk into restaurant");}public void Sitdown(){Console.WriteLine("Sitdown");}public void Think()//事件触发{for (int i=0; i < 5; i++){Console.WriteLine("let me thikn''''");Thread.Sleep(1000);}if (this.orderEventHandler != null)//如果没人订阅这个事件,事件发生时会报错{OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();e.Dishname = "KONGBAO JIDING"; e.Size = "large";this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);}}public void Action(){Console.ReadLine();this.Walk();this.Sitdown();this.Think();}}public class Waiter{public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e){Console.WriteLine("i will serve you dish {0}", e.Dishname);double price = 10;switch (e.Size){case "small":price = price * 0.5;break;case "large":price = price * 2;break;default:break;}customer.Bill += price;}}
}四、类
1构造器、析构器

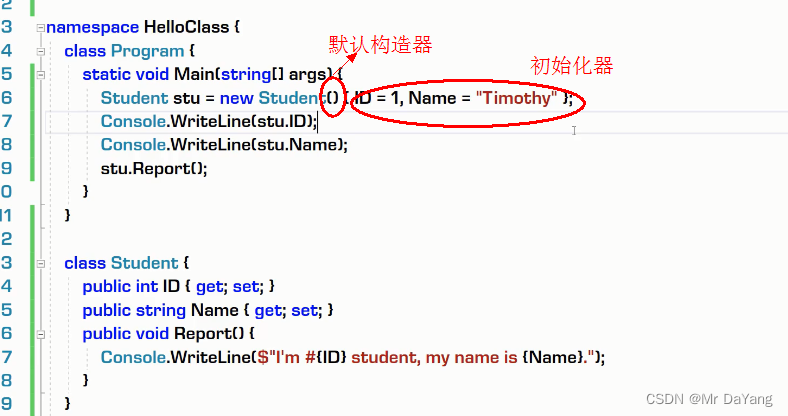
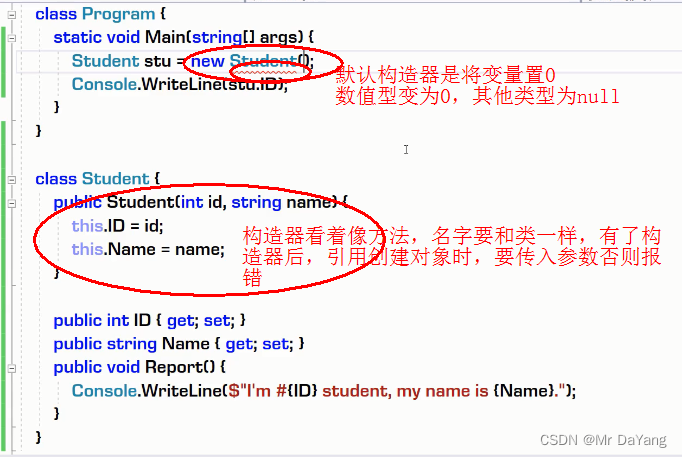
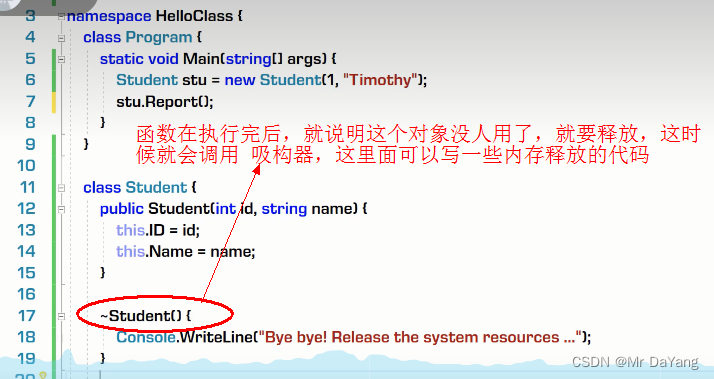
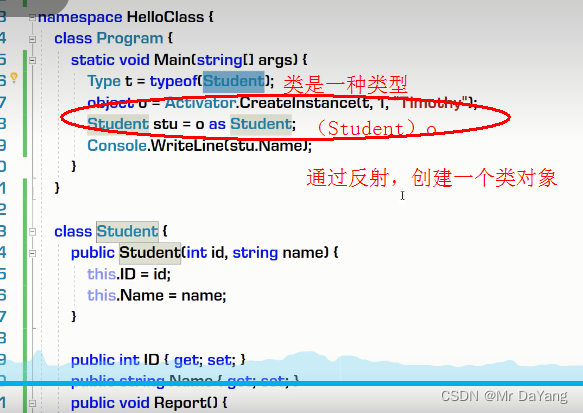
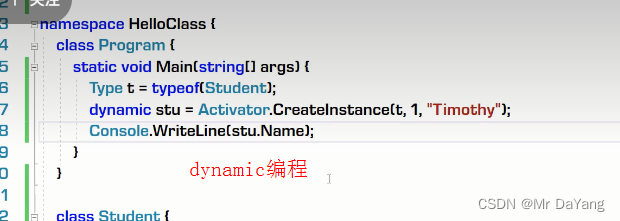
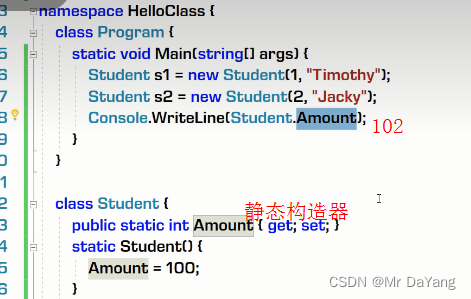

2.类修饰符(public\internal\abstract)

类的继承


sealed修饰类后,这个类不能被当成基类使用
一个类只能有一个基类
子类的类访问级别不能超越基类
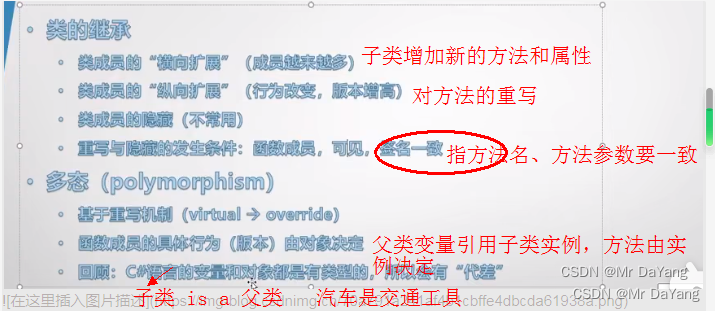
横向扩展对类成员的扩充,纵向扩展对类成员的重写
子类是对父类的全盘继承



类成员的访问级别 低于类的访问级别
类定义默认是public ;类是属性默认为private
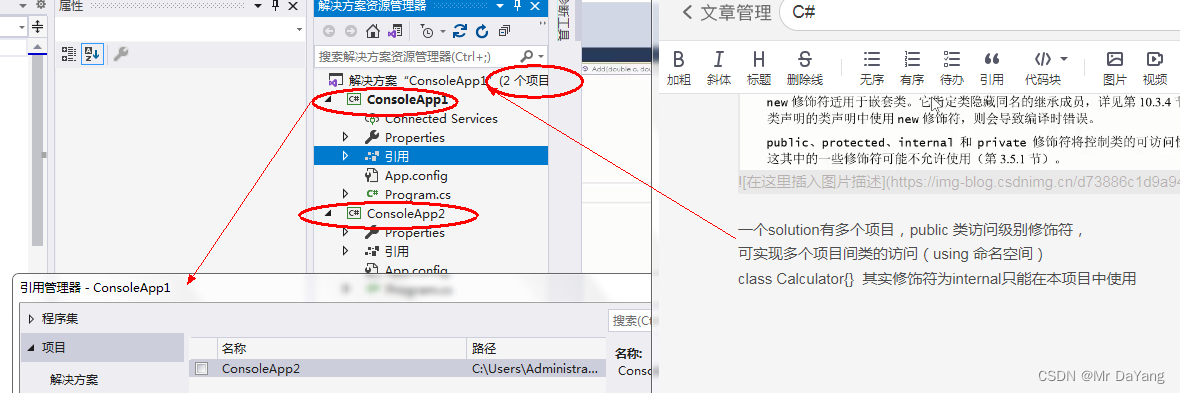
public 一个solution的多个项目都可访问
internal 在一个项目中的多个类中访问
private 只在当前类中使用,就算继承也不能访问
protected 修饰的类成员,此类成员只能被继承的类所调用

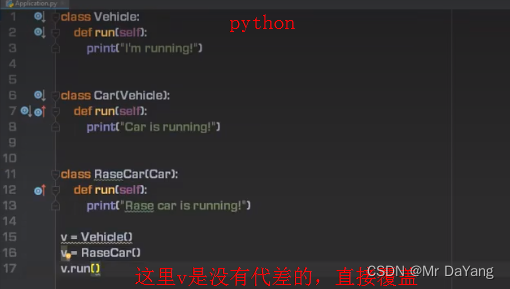
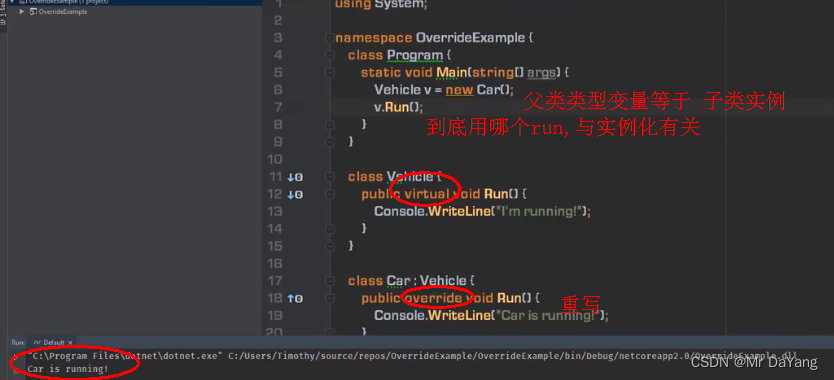
3类的继承

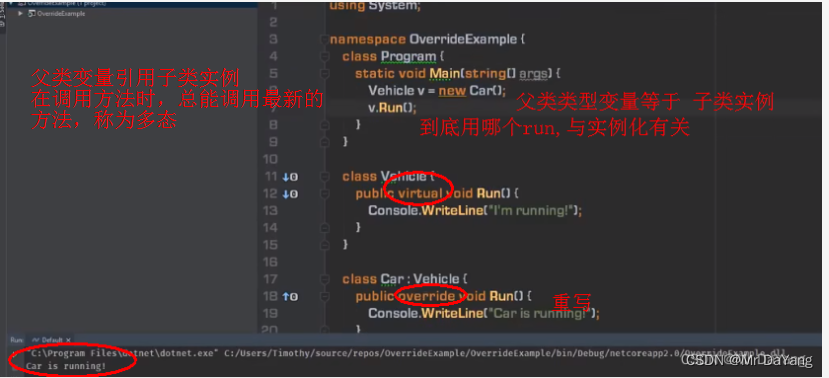

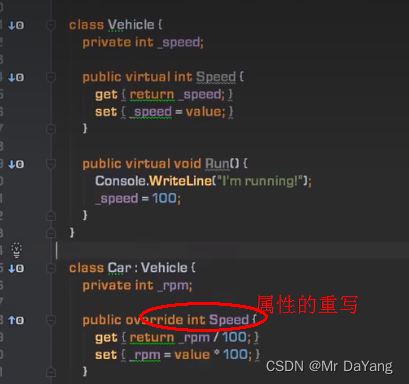
五、接口、抽象类

(人–接口–手机)多个人可分别使用不同款式手机

面向对象设计基本原则,通过设计的规则,让代码更为规范
abstract抽象类:函数成员未被完全实现的类(无方法体),不能实例化,抽象类只能作为基类,为子类服务,子类进行重写
abstract抽象类 一方面是用于子类继承,第二方法抽象类父类变量引用子类实例,代查
concrete具体类
开闭原则:在设计类的时候,把那些固定不变的方法,属性进行封装,把来回变动的采用抽象类,抽象方法供子类使用
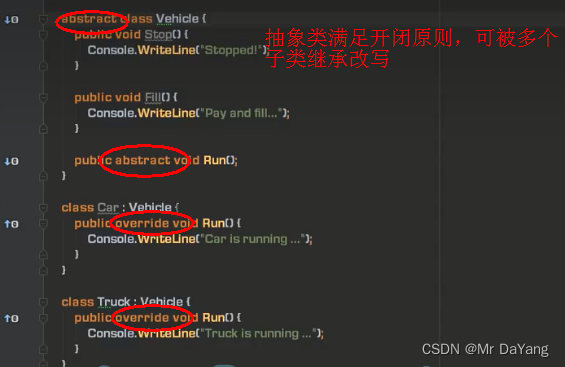
接口,抽象类,具体类
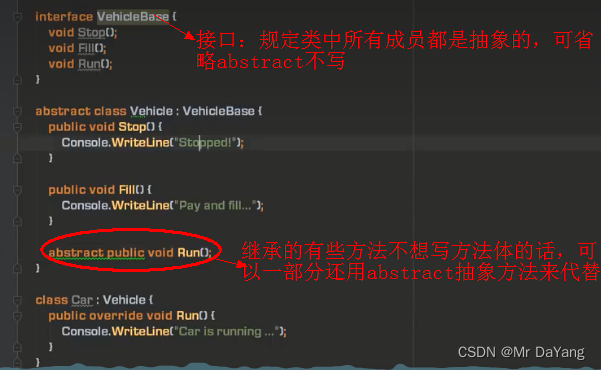
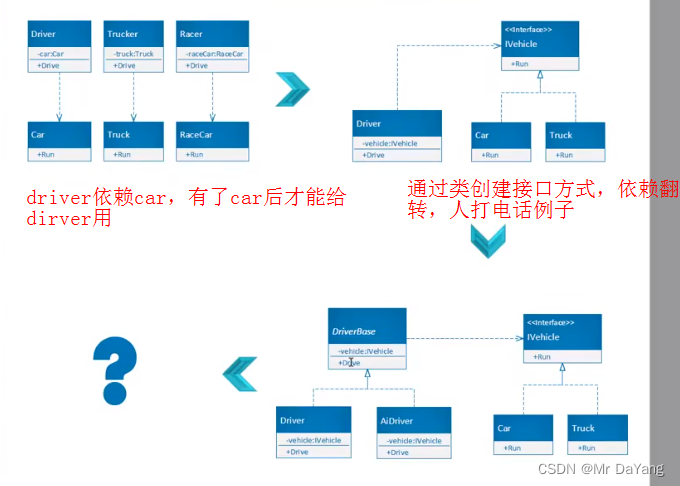
//耦合过多,car依赖于engine,engine出了问题 car也出问题,所以使用接口来解耦合
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var engine = new Engine();var car = new Car(engine);car.Run(3);Console.WriteLine(car.Speed);Console.ReadKey();}}class Engine{public int RPM { get; private set; }public void Work(int gas){this.RPM = 1000 * gas;}}class Car{private Engine _engine;public Car(Engine engine){_engine = engine;}public int Speed { get; private set; }public void Run(int gas){_engine.Work(gas);this.Speed = _engine.RPM / 100;}}
}//用接口来解耦合
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var user = new phoneuser(new nokia());var user1 = new phoneuser(new erision());user.usephone();Console.Read();}}class phoneuser{private iphone _phone;public phoneuser( iphone phone){_phone = phone;}public void usephone(){_phone.dail();_phone.pickup();_phone.send();_phone.receive();}}interface iphone{void dail();void pickup();void send();void receive();}class nokia : iphone{public void dail(){Console.WriteLine("dailing........");}public void pickup(){Console.WriteLine("pickup......");}public void receive(){Console.WriteLine("receiving.......");}public void send(){Console.WriteLine("sending......");}}class erision : iphone{public void dail(){Console.WriteLine("dailing-------");}public void pickup(){Console.WriteLine("pickup---------");}public void receive(){Console.WriteLine("receiving-------");}public void send(){Console.WriteLine("sending--------");}}}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var fan = new deskfan(new powersupply());Console.WriteLine(fan.work());Console.Read();}interface ipowersupply{int getpower();//定义一个返回值为int 的方法,无方法体}class powersupply:ipowersupply{public int getpower(){return 100;}} class deskfan{private ipowersupply _powersupply;//由耦合函数powersupply换成接口函数 ipowersupplypublic deskfan(ipowersupply powersupply)//由耦合函数powersupply换成接口函数 ipowersupply{_powersupply = powersupply;}public string work(){int power = _powersupply.getpower();if (power < 0) { return "wont work"; }else if (power < 100) { return "slow"; }else if (power < 200) { return "work fine"; }else { return "warning"; }}}}}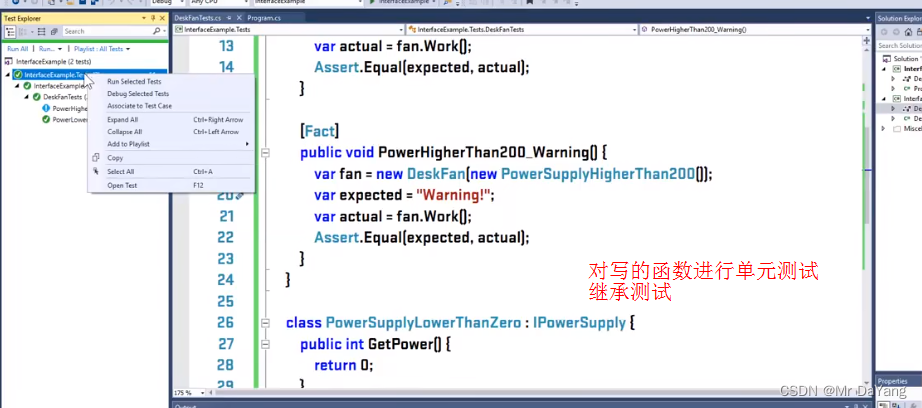

六、反射、依赖注入

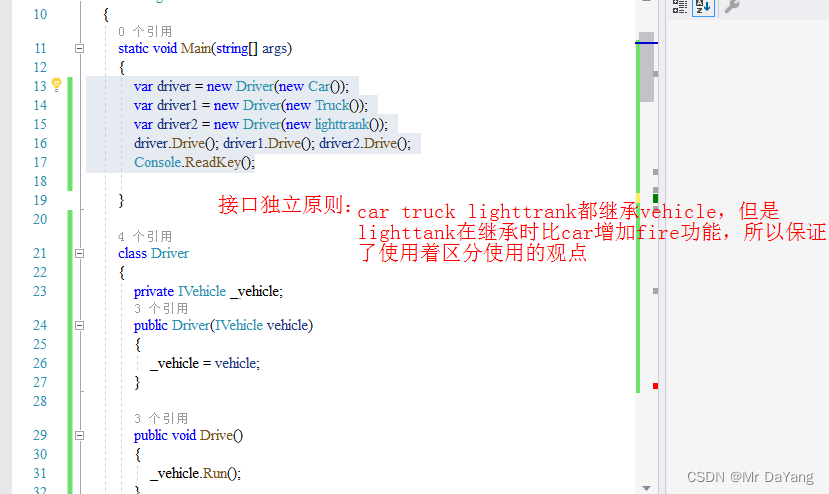
## 一个类多个可以多个接口,接口也可继承多个接口interface Itrank: IVehicle, Iweaponclass Program{static void Main(string[] args){var driver = new Driver(new Car());var driver1 = new Driver(new Truck());var driver2 = new Driver(new lighttrank());driver.Drive(); driver1.Drive(); driver2.Drive();Console.ReadKey();}class Driver{private IVehicle _vehicle;public Driver(IVehicle vehicle){_vehicle = vehicle;}public void Drive(){_vehicle.Run();}}interface IVehicle{void Run();}class Car : IVehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("car is running");}}class Truck : IVehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Truck is running");}}interface Iweapon{void Fire();}interface Itrank: IVehicle, Iweapon{void Run();void Fire();}
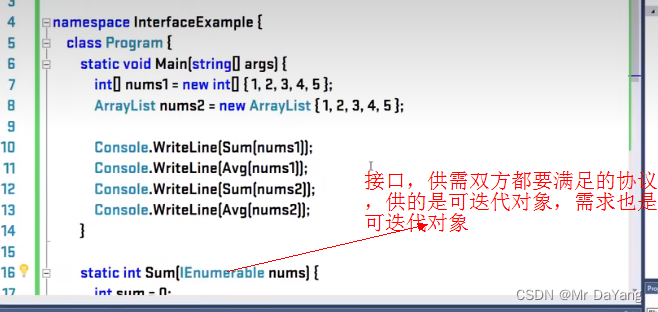
## int[],ArrayList都继承了ICollection类,所以都可用于foreach的迭代
namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int[] num1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };ArrayList num2 = new ArrayList { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };Console.WriteLine(Sum(num1));Console.WriteLine(Sum(num2));Console.ReadKey();}static int Sum(ICollection nums){int sum = 0;foreach(var n in nums){sum += (int)n;}return sum;}}
}
//接口的显示实现,c#独有
//void Ikill.Kill()//显示实现所有成员时, wk.Kill()是调不到此方法的
//Ikill ikill = wk; ikill.Kill(); 只有Ikill变量时,才能调用Kill()方法
namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var wk = new Warmkill();wk.Kill();Ikill ikill = wk;ikill.Kill();Console.ReadKey();}interface Igentleman{void Love();}interface Ikill{void Kill();}class Warmkill : Igentleman, Ikill{public void Love(){Console.WriteLine("love you");}void Ikill.Kill()//显示实现所有成员{throw new NotImplementedException();}}}
}

开发在编译代码的时候相当于静态代码,软件给用户使用时,处于dynamic状态,需要交互。开发可以枚举1000种方法来处理用户可能的操作,但太臃肿,也有可能覆盖不到,所以需要自己程序可以以不变应万变的能力,这个能力就是反射
反射可以不用new的情况,创建与类一个的类型,而且可访问其内部方法,相当于解耦合(用new创建时,后面要接类型,一有类型就有依赖)
普通反射

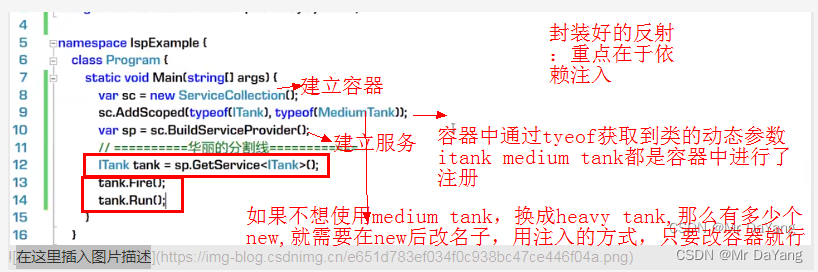
反射的用途1-依赖注入:用注册的动态类型,创建的实例,注入到Driver构造器中

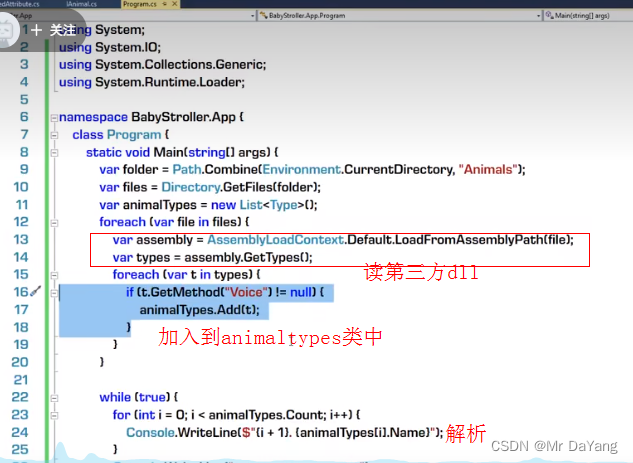
反射的用途2-利用反射追求更松的耦合
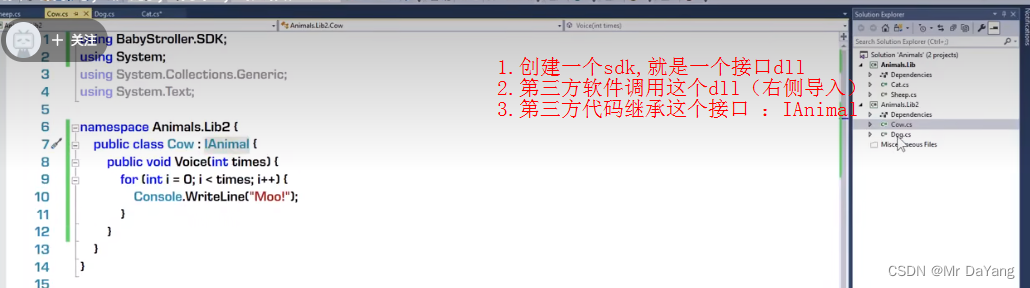
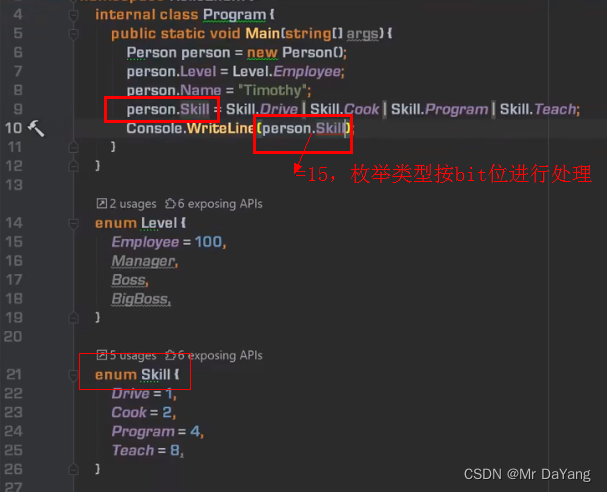
七、泛型(这里代码多练习)

1.类型膨胀,1000种产品就会有1000种box,不好维护
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Apple apple = new Apple() { Color="red"};AppleBox applebox = new AppleBox() { cargo = apple };Console.WriteLine(applebox.cargo.Color);Book book = new Book() { Name = "shuji" };BookBox bookbox = new BookBox() { cargo = book };Console.WriteLine(bookbox.cargo.Name);Console.ReadKey();}class Apple{public string Color { get; set; }//Color属性}class AppleBox { public Apple cargo { get; set; } }//cargo属性class Book{public string Name { get; set; }}class BookBox { public Book cargo { get; set; } }//cargo属性}
}2.成员膨胀:一个box类有多个属性,给不同的商品
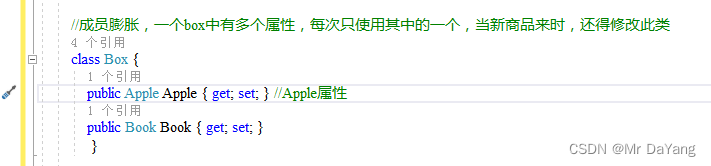

3.通过向box中传objecet对象,可以快速装箱,但读取箱中内容时,不好操作

namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Apple apple = new Apple() { Color="red"};Book book = new Book() { Name = "shuji" };Box box1 = new Box() { cargo = apple };Box box2 = new Box() { cargo = book };Console.WriteLine(box1.cargo.Color);//此处已经将book对象转换成object对象,无法再获得book对象中属性Console.WriteLine((box1.cargo as Apple)?.Color);//可类型转换Console.ReadKey();}class Apple{public string Color { get; set; }//Color属性}class Book{public string Name { get; set; }}//成员膨胀,一个box中有多个属性,每次只使用其中的一个,当新商品来时,还得修改此类class Box {public Object cargo { get; set; }}}
}
4.使用泛型不会产生类型膨胀、成员膨胀
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApp2
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Apple apple = new Apple() { Color="red"};Book book = new Book() { Name = "shuji" };//用泛型将box特化Box<Apple> box1 = new Box<Apple>() { cargo = apple };Box<Book> box2 = new Box<Book>() { cargo = book };Console.WriteLine(box1.cargo.Color);Console.WriteLine(box2.cargo.Name);Console.ReadKey();}class Apple{public string Color { get; set; }//Color属性}class Book{public string Name { get; set; }}class Box<Tcargo> {public Tcargo cargo{ get; set; }}}
}
5.泛型接口
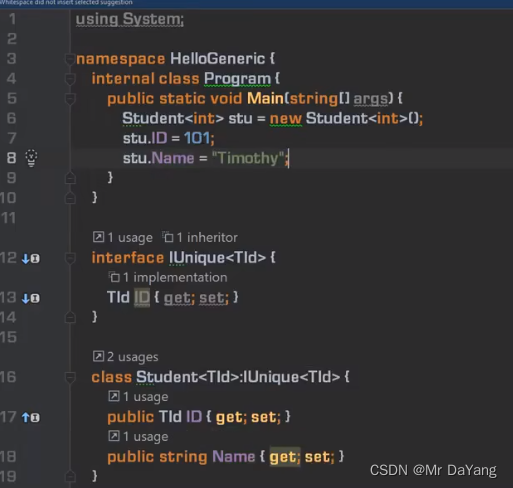
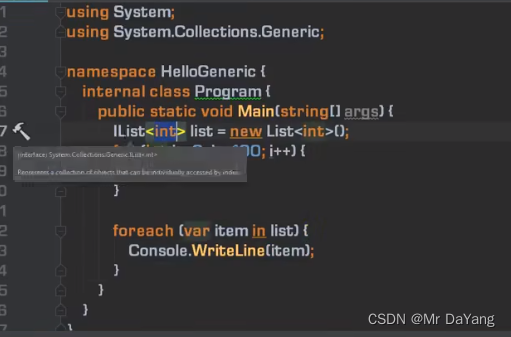
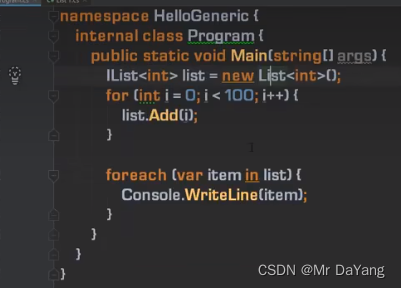
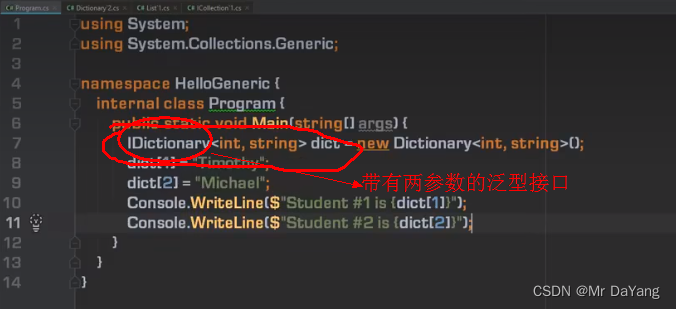
泛型方法
成员膨胀
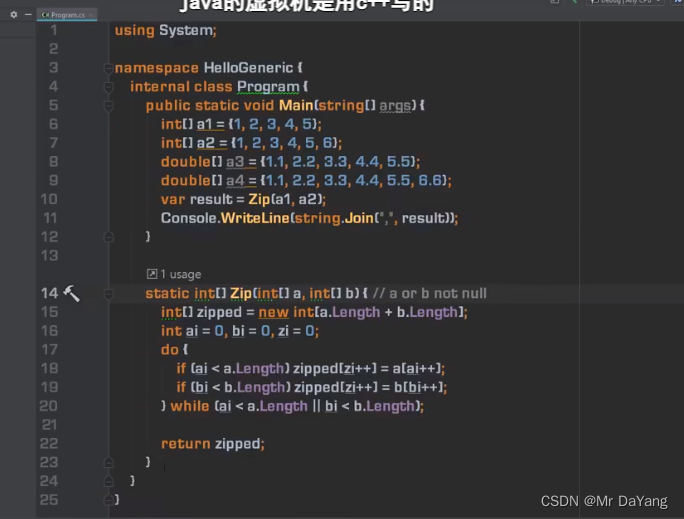
泛型方法(类型参数 加到zip方法后)
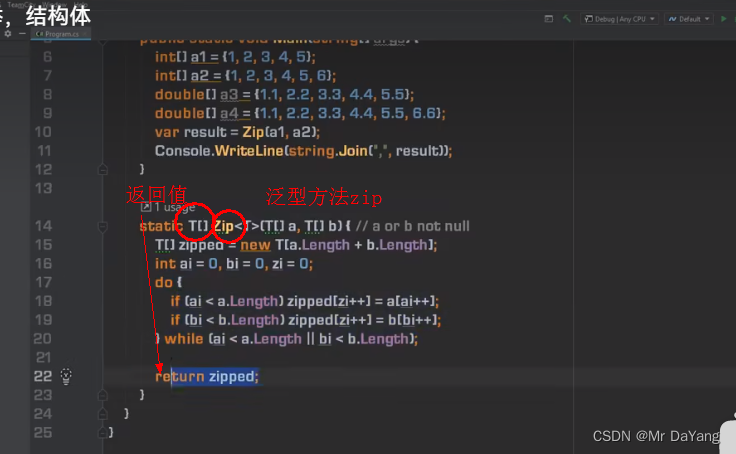
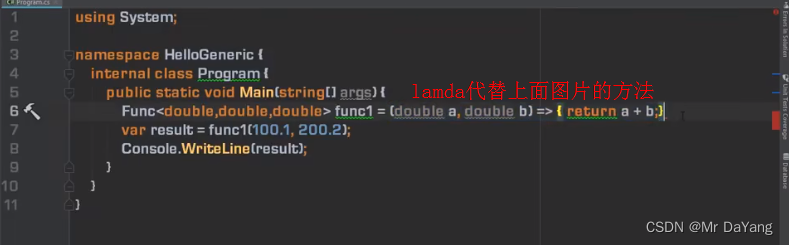
泛型委托


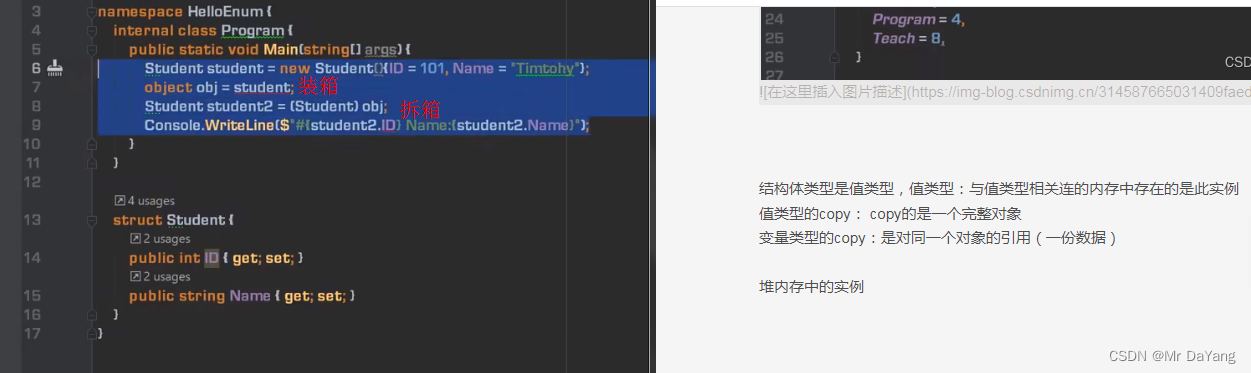
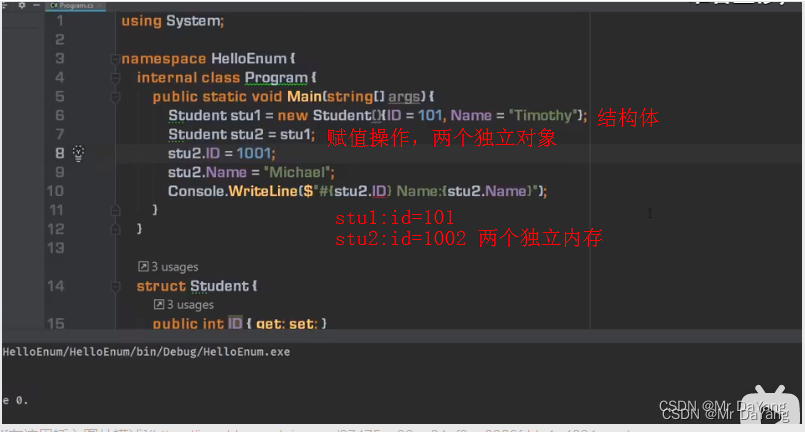
结构体类型是值类型,值类型:与值类型相关连的内存中存在的是此实例
值类型的copy: copy的是一个完整对象
变量类型的copy:是对同一个对象的引用(一份数据)
堆内存中的实例
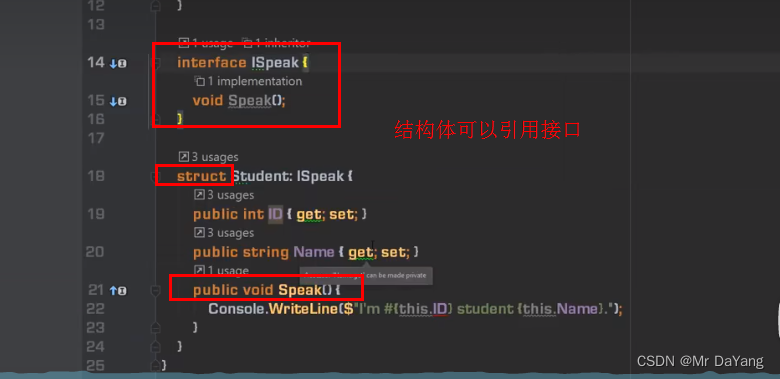
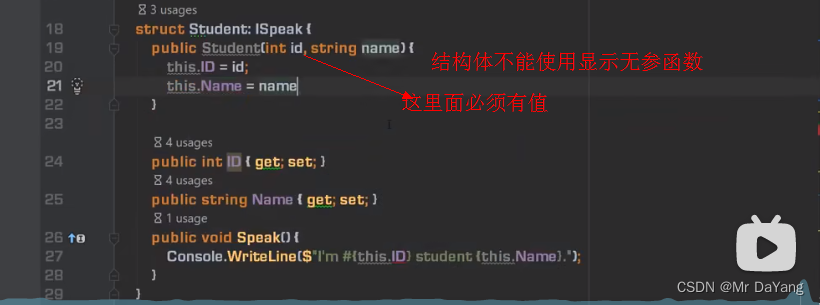
结构体不能由其他结构体类型、类类型派生而来,只能由interface来
八、核心代码汇总
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace Core_knowledge
{public partial class Form1 : Form{//1类//1.1属性方法定义int a01 = 3;public double Price { get; set; }private void dosomething(string name){Console.WriteLine($"[****Dosomething {name} start: 线程号:({Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")})---{System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff")}*******]");long result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++){result += i;}Thread.Sleep(2000);Console.WriteLine($"[****Dosomething {name} end: 线程号:({Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")})---{System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff")}{result}*******]");}//1.2默认构造器 Student()是将数值型变成0,其他类型设置为null Student stu = new Student();//1.3构造器看着像方法,名子和类一样,有构造器后,引用创建对象时要传参否则报错-见class StudentStudent stu2 = new Student(5, "timo");//1.4初始化器{id=1,name="timothy" }Student stu1 = new Student() { id = 1, name = "timothy" };//1.5 析构器 ~Student() 函数在执行完后,说明这个对象没人用了就要释放,这里就会调用析构器,这里面可以写内存释放的代码//1.6反射/*Type tt = typeof(Student);object o = Activator.CreateInstance(tt, 15, "sss");Student stu5 = o as Student;Console.WriteLine(stu5.Name);*///1.7横向扩展对类成员的扩充,纵向扩展对类成员的重写//1.8父类类型变量引用 子类类型实例 子类 is a 父类 汽车是车public void s(){Vehicle v = new Car();//到底是哪个run,与实例化有关,谁被new,谁的被执行,这里是car runningv.run();}//1.9枚举-在定义一个person职位时,有人知道person有多少个level,有人不知道,所以放到enum中统一管理public void meiju(){Console.WriteLine((int)Level.employee);}//1.10.见struct Student1 : ISpeak -结构体类型是值类型,值类型:与值类型相关连的内存中存在的是此实例/*值类型的copy: copy的是一个完整对象变量类型的copy:是对同一个对象的引用(一份数据) 堆内存中的实例结构体不能由其他结构体类型、类类型派生而来,只能由interface来*///2 IF_FOR_SWITCHpublic void IF_FOR_SWITCH_foreach(){for (int c = 0; c < 5; c++){int k = c;Task.Run(() =>{Thread.Sleep(100);Console.WriteLine($"k={k}, i={c}");});}int i = 0;if (i > 10){Console.WriteLine(1);}else if (i > 0 && i < 10){Console.WriteLine(2);}else{Console.WriteLine(3);}switch (i){case 1:Console.WriteLine(1);break;case 2:Console.WriteLine(1);break;default:Console.WriteLine(1);break;}int[] p = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };foreach (int p1 in p){}}//3常用代码public void Commoncode(){//数据类型int q = 2;int[] a = new int[6];int[] b = new int[3] { 1, 2, 3 };Console.WriteLine(a[1].ToString());int[] c = new int[] { 'a', 2, 3 };List<string> a1 = new List<string>() { "a", "b" };Console.WriteLine(a1[1].ToString());//List<Person> p = new List<Person>();//p.Add(new Person() { });a1.Add("112");a[0] = 4;a1.Insert(0, "3");a1.RemoveAt(0);a1.Remove("a");a1.Clear();Dictionary<int, string> d = new Dictionary<int, string> { //对象初始化器{ 2,"333"},{4,"555"}};MessageBox.Show(c[0].ToString());MessageBox.Show("1");Console.WriteLine($"[------------主线程start: 线程号:({Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")})---{System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff")}-----]");}//4Trycatch()public void Trycatch(){try{if (2 > 1){throw new Exception(string.Format($"执行失败"));}}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);}try{float a = 3;double b = 3.2;}catch (AggregateException aex){foreach (var item in aex.InnerExceptions){Console.WriteLine(item.Message);}}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);}}//5委托使用-委托相当于一个指针,可以指定任意方法,就可以实现方法调方法。public void action(){//5.1.无返回值委托-Action委托Calculator calculator = new Calculator();Action action = new Action(calculator.Report);//Action: 方法是void,并且无参数action.Invoke();//委托调用Action<string> action = this.dosomething;//委托带参数Action action1 = () => this.dosomething("CC");//委托不带参数Logger logger = new Logger();Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);//5.2.有返回值委托-Func委托//<第一个int为返回值, 第二三个int为函数输入>Func<int, int, int> func1 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Add);//Func :方法是有返回,有参数int x = 100;int y = 200;int z = 0;int c = 0;z = func1.Invoke(x, y);//委托调用func1(x, y);//模仿c中函数指针的书写格式//Product为委托的返回类型 ,func1为委托名 委托的返回值类型是Product,委托的函数名称=prodectFactory.MakePiza//Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(prodectFactory.MakePiza);//5.3.委托简单使用-delegate自定义委托//public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);//自定义委托是个类,格式要与委托函数一致Calc calc1 = new Calc(calculator.Add);//委托实例化c = calc1.Invoke(x, y);//5.4.实现目的:方法中调用方法//模板方法:方法中 输入 用委托类型参数封装的方法-具体看WrapProduct方法//回调方法:方法中 在调用 用委托类型参数封装的方法 时,有条件判断-具体看WrapProduct方法WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();ProdectFactory prodectFactory = new ProdectFactory();Action<Product> log1 = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(prodectFactory.MakePiza);//用委托将方法进行封装,然后将这个委托传到B方法中,在B方法中对委托进行调用,实现了方法中调用方的目的//同时委托相当于一个指针,可以封装各式各样的方法,那么B方法也就可以调用任意方法Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2, log1);//5.5.多播委托\异步委托调用//直接同步调用:使用方法名Student stu1 = new Student() { id = 1, pencolor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu2 = new Student() { id = 1, pencolor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu3 = new Student() { id = 1, pencolor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };stu1.dohomework();//5.6.间接同步调用:使用单播、多播委托invokeAction action1 = new Action(stu1.dohomework);Action action2 = new Action(stu2.dohomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.dohomework);action1.Invoke();//单播委托action1 += action2;//多播委托action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();//5.7.隐式异步调用:使用委托的begininvokeAction action4 = new Action(stu1.dohomework);action4.BeginInvoke(null, null);//第一个null为执行完线程后的回调函数//5.8. 显示异步调用:使用thread或taskThread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.dohomework));thread1.Start();}//6.事件public void shijian(){System.Timers.Timer timer = new System.Timers.Timer(); // timer.Elapsed事件的拥有者Timertimer.Interval = 3000;Boy boy = new Boy(); //事件的订阅者 Girl girl = new Girl();// 订阅者的处理器 +=表示订阅 拿方法订阅一个事件时,它们要遵守约定:约定就是委托类型// timer.Elapsed的类型就是 public delegate void ElapsedEventHandler(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e);// 所以使用alt+enter自动按照委托形式对boy.Action进行方法创建timer.Elapsed += boy.Action; //timer.Elapsed 为事件,boy.Action为事件处理器timer.Elapsed += girl.Action; //一个事件两个订阅者timer.Start();Console.ReadLine();//三星:事件的拥有者是响应者的成员,见class Myform : Form//事件自定义-可再找之间代码学习,学习过}//7.抽象类//abstract抽象类-不能实例化:函数成员未被完全实现的类(无方法体),抽象类只能作为基类,为子类服务,子类进行重写 见-abstract class vehicle1//abstract抽象类 一方面是用于子类继承,第二方法抽象类父类变量引用子类实例,代查//concrete具体类//8.接口-纯虚类-不能实例化 见class phoneuser、interface vehiclebasepublic void jiekou() //(人–接口–(苹果手机,华为手机))多个人可分别使用不同款式手机{var user = new phoneuser(new nokia());var user1 = new phoneuser(new erision());user.usephone();Console.Read();//一个类多个可以多个接口,接口也可继承多个接口interface Itrank: IVehicle, Iweaponvar driver = new Driver(new Car1());var driver1 = new Driver(new Truck());driver.Drive(); driver1.Drive();}//9.反射的用途//9.1.反射的用途-依赖注入: 用注册的动态类型,创建的实例,注入到Driver构造器中//开发在编译代码的时候相当于静态代码,软件给用户使用时,处于dynamic状态,需要交互。开发可以枚举1000种方法来处理用户可能的操作,但太臃肿,也有可能覆盖不到,所以需要自己程序可以以不变应万变的能力,这个能力就是反射//反射可以不用new的情况,创建与类一个的类型,而且可访问其内部方法,相当于解耦合(用new创建时,后面要接类型,一有类型就有依赖)/*public void fanshe(){Tank tank = new Tank();var t = tank.GetType();object o=Activator.CreateInstance(t);MethodInfo fire= t.GetMethod("fire");fire.Invoke(o, null);}public void zhuru(){var sc = new ServiceCollection();//建立容器sc.AddScoped(typeof(ITank), typeof(MdediumTank));//typeof()获取类的动态参数,在容器中进行注册var sp = sc.BuildServiceProvider();//建立服务ITank tank=sp.GetService<ITank>();//使用tank.fire();tank.run();}//9.2反射的用途-利用反射追求更松的耦合--读第三方dllEnvironmentVariableTarget assembly = AssemblyLoadContext.Defalut.Load....*///10泛型/*1.类型膨胀,1000种产品就会有1000种box,不好维护 2.成员膨胀:一个box类有多个属性,给不同的商品*/List<int> list = new List<int>();//参考泛型写法:前面List类型中只能存放int类的变量public void fanxing(){Apple apple = new Apple() { Color = "red" };Book book = new Book() { Name = "shuji" };//用泛型将box特化Box<Apple> box1 = new Box<Apple> { cargo = apple };Box<Book> box2 = new Box<Book>() { cargo = book };Console.WriteLine(box1.cargo.Color);Console.WriteLine(box2.cargo.Name);//泛型接口Student<int> stu = new Student<int>();stu.ID = 101;stu.Name = "asd";}//11.partial类 相当于一个类被切分成多个部分进行存放-要保持命名空间一致(namespace)public Form1(){InitializeComponent();}private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){//Trycatch();//Commoncode();//shijian();//Myform myform = new Myform();//myform.ShowDialog();fanxing();}}class Calculator{public void Report(){Console.WriteLine("i have 3 methods");}public int Add(int a, int b){int result = a + b;return result;}public int Sub(int a, int b){int result = a - b;return result;}}public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);//自定义委托是个类,格式要与委托函数一致class Logger{public void Log(Product product){Console.WriteLine("Product '{0}' created at {1},price is {2}", product.Name, DateTime.UtcNow, product.Price);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; } //类属性是stringpublic double Price { get; set; }}class Box{public Product product { get; set; }//类属性是一个类}class WrapFactory{//WrapProduct 委托的模板方法,Box方法的返回值//委托模板方法的输入是委托函数 Func<Product> getProductpublic Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct, Action<Product> logCallback){Box box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();if (product.Price > 50){logCallback(product);}box.product = product;return box;}}class ProdectFactory{public Product MakePiza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";product.Price = 12;return product;}public Product Makecar(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "car";product.Price = 100;return product;}}class Student{public Student()//创建一个空的,给不传参使用,否则会报错{}public Student(int Id, string Name)//构造器看着像方法,名子和类一样,有构造器后,引用创建对象时要传参否则报错{this.id = Id;this.name = Name;}public static int Amount { get; set; }static Student() { Amount = 100; }~Student(){Console.WriteLine("bye bye");}public int id { get; set; }public string name { get; set; }public ConsoleColor pencolor { get; set; }public void dohomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.pencolor;Console.WriteLine("student{0} doing homework {1} hours", this.id, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}class Boy{internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e){Console.WriteLine("Jump");}}class Girl{internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e){Console.WriteLine("sing");}}//三星:事件的拥有者是响应者的成员class Myform : Form{private TextBox textBox;private Button button;//form的字段成员,拥有者public Myform(){this.button = new Button();this.button.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(276, 176);this.button.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23);this.button.Text = "sss";this.textBox = new TextBox();this.textBox.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(176, 176);this.textBox.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(120, 23);this.Controls.Add(this.button);this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);this.button.Click += this.buttonCllicked; //form =响应者}private void buttonCllicked(object sender, EventArgs e){this.textBox.Text = "hello world```````````````````````````";}}class Vehicle{public Vehicle(){this.Owner = "NA";}public Vehicle(string owner){this.Owner = owner;}public virtual void run(){Console.WriteLine("vehicle is running");}public string Owner { get; set; }}class Car : Vehicle{public Car(){this.Owner = "car";}//public Car() :base("NA")//基类构造器中有参数,子类构造器也要声明//{// this.Owner ="car owner";//}public void doing(){Console.WriteLine("222");}public override void run(){Console.WriteLine("car is running");}}abstract class vehicle1{public void fill()//{Console.WriteLine("111");}public abstract void run1();//抽象方法}class car1 : vehicle1{public override void run1(){Console.WriteLine("111");}}interface vehiclebase{void stop();void fill();}class phoneuser{private iphone _phone;public phoneuser(iphone phone){_phone = phone;}public void usephone(){_phone.dail();_phone.pickup();_phone.send();_phone.receive();}}interface iphone{void dail();void pickup();void send();void receive();}class nokia : iphone{public void dail(){Console.WriteLine("dailing........");}public void pickup(){Console.WriteLine("pickup......");}public void receive(){Console.WriteLine("receiving.......");}public void send(){Console.WriteLine("sending......");}}class erision : iphone{public void dail(){Console.WriteLine("dailing-------");}public void pickup(){Console.WriteLine("pickup---------");}public void receive(){Console.WriteLine("receiving-------");}public void send(){Console.WriteLine("sending--------");}}class Driver{private IVehicle _vehicle;public Driver(IVehicle vehicle){_vehicle = vehicle;}public void Drive(){_vehicle.Run();}}interface IVehicle{void Run();}class Car1 : IVehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("car is running");}}class Truck : IVehicle{public void Run(){Console.WriteLine("Truck is running");}}interface Iweapon{void Fire();}interface Itrank : IVehicle, Iweapon{void Run();void Fire();}class Tank{void run(){} void fire() { }}class Book{public string Name { get; set; }}class Apple{public string Color { get; set; }}class Box<Tcargo>{public Tcargo cargo { get; set; }}interface IUnique<TId>{TId ID { get; set; }}class Student<TId>: IUnique<TId>{public TId ID { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}enum Level{employee=100,manager,boss=300,}interface ISpeak{void speak();}struct Student1 : ISpeak{public Student1(int id )//结构体不能使用显示无参函数,这里面必须有值{this.ID = id;}public int ID { get; set; }public void speak(){Console.WriteLine("234");}}}



![2、[春秋云镜]CVE-2022-30887](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a281e80d062547c98c80eb394c90919e.png#pic_center)