链表节点定义
public class ListNode {// 结点的值int val;// 下一个结点ListNode next;// 节点的构造函数(无参)public ListNode() {}// 节点的构造函数(有一个参数)public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}// 节点的构造函数(有两个参数)public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {this.val = val;this.next = next;}
}
*移除链表节点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
【思路】
有时候增加一个虚拟节点,可以让后面的操作都一致
public static ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {if (head == null) {return null;}// 增加一个虚拟节点ListNode virtualNode = new ListNode();virtualNode.next = head;ListNode cur = virtualNode;ListNode next = cur.next;while (next != null) {if (next.val == val) {cur.next = next.next;} else {cur = next;}next = cur.next;}return virtualNode.next;
}
*反转链表
双指针法
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)

public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode cur = head;ListNode pre = null;ListNode temp = null;while (cur != null) {temp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = temp;}return pre;
}
递归法
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
这里的逻辑和双指针法的逻辑是一样的,只是实现方式是递归,那为什么空间复杂度更高呢?
答:因为递归本质上是一种函数调用,在每一次递归调用时,都会在函数栈中分配一段内存空间来保存函数的局部变量、返回地址以及参数等信息。因此,递归实现相对于循环实现的空间复杂度更高,会占用更多的内存空间。尤其是在递归深度较大的情况下,可能会导致栈溢出等问题。而使用循环实现通常不需要使用额外的栈空间,因此循环实现的空间复杂度比递归实现要低
public static ListNode reverseList1(ListNode head) {return reverse(null, head);
}public static ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur) {if (cur != null) {ListNode temp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = reverse(cur, temp);}return pre;
}
*两两交换链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
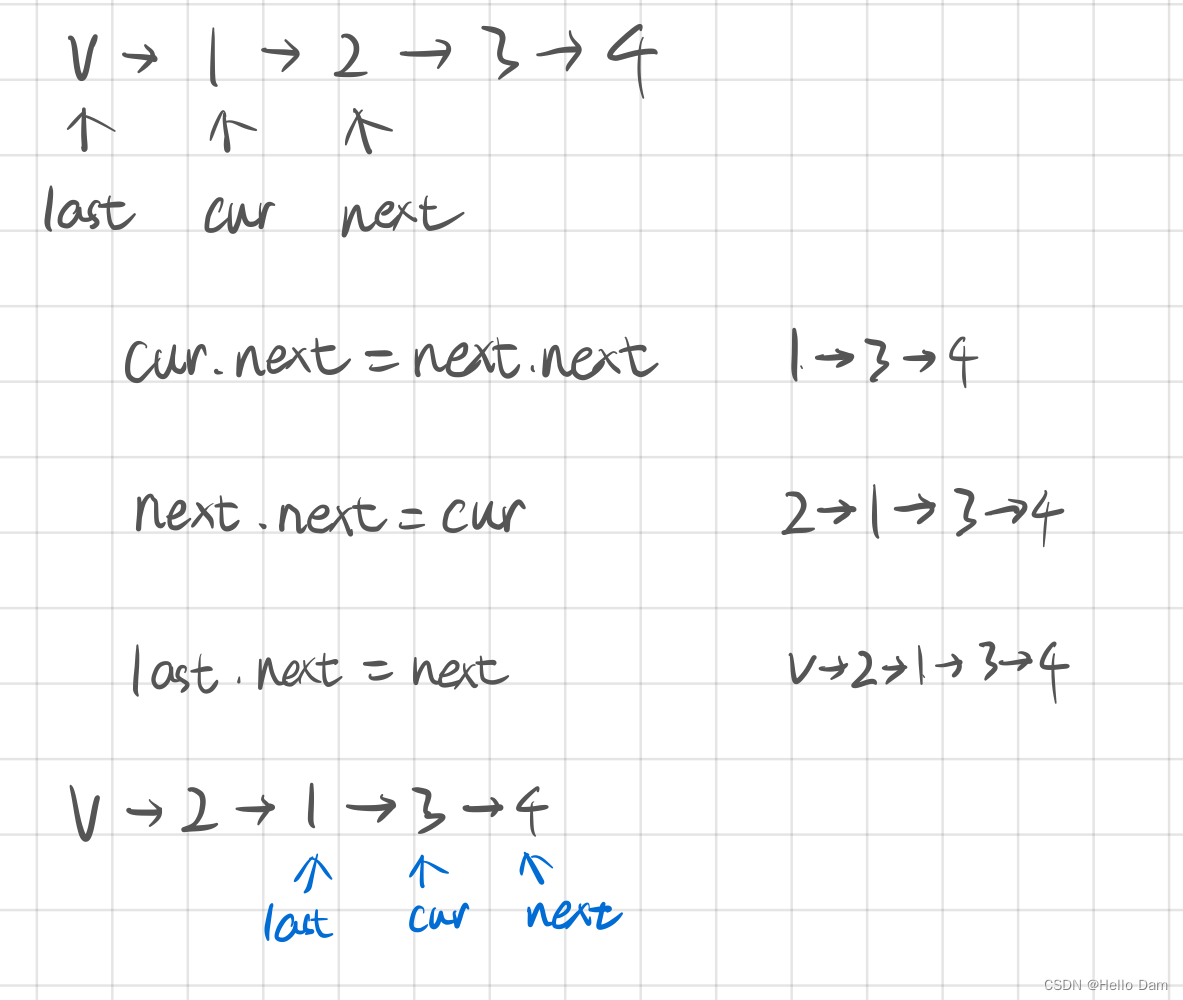
public static ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {// 如果链表中没有元素 或者 只有一个元素,直接返回就行if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}// 增加一个虚拟头节点ListNode virtualNode = new ListNode();virtualNode.next = head;ListNode last = virtualNode;ListNode cur = head;ListNode next = cur.next;ListNode temp = null;while (next != null) {// 交换temp = next.next;cur.next = next.next;next.next = cur;last.next = next;// 指针移动到新的位置last = cur;cur = temp;if (cur != null) {next = cur.next;} else {break;}}return virtualNode.next;
}
*删除链表的倒数第N个节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/submissions/
快慢指针法

/*** 让快指针比慢指针先移动 n 步** @param head* @param n* @return*/
public static ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode virtual = new ListNode();virtual.next = head;// 让快指针先移动到n个节点ListNode fast = virtual;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next;}}// slow和fast一起移动,等fast到达最后一个节点的时候,slow也就到达了要删除的节点前面的节点ListNode slow = virtual;while (fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}// 执行删除操作slow.next = slow.next.next;return virtual.next;
}
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
*链表相交
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/
注意点
并不是判断val相等,而是hashcode相等
暴力求解
直接两重循环,循环两个链表
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
进阶解法
利用题目中的信息,已经是链表的尾部才有可能相交,可以先让一条链表前进 两条链表长度差值 的位置,最后再两条链表一起前进
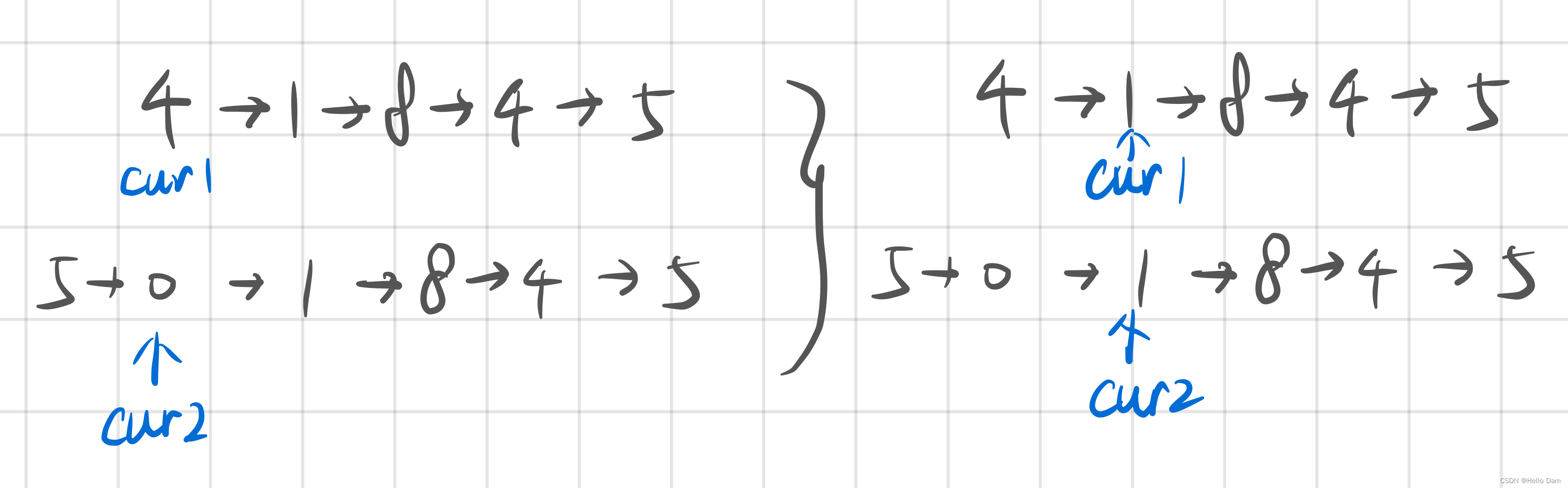
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode cur1 = headA;ListNode cur2 = headB;int sizeA = 0;int sizeB = 0;// 统计链表A的长度while (cur1 != null) {sizeA += 1;cur1 = cur1.next;}// 统计链表B的长度while (cur2 != null) {sizeB += 1;cur2 = cur2.next;}// 回到初始位置cur1 = headA;cur2 = headB;// 先让元素较多的链表的指针移动一段距离if (sizeA > sizeB) {// 链表A的元素较多,先走一段距离for (int i = 0; i < (sizeA - sizeB); i++) {cur1 = cur1.next;}} else if (sizeA < sizeB) {for (int i = 0; i < (sizeB - sizeA); i++) {cur2 = cur2.next;}}// 两个链表同时走动while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {// 注意,需要的是hash值if (cur1.hashCode() == cur2.hashCode()) {return cur1;}cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}return null;
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n + m)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
*环形链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
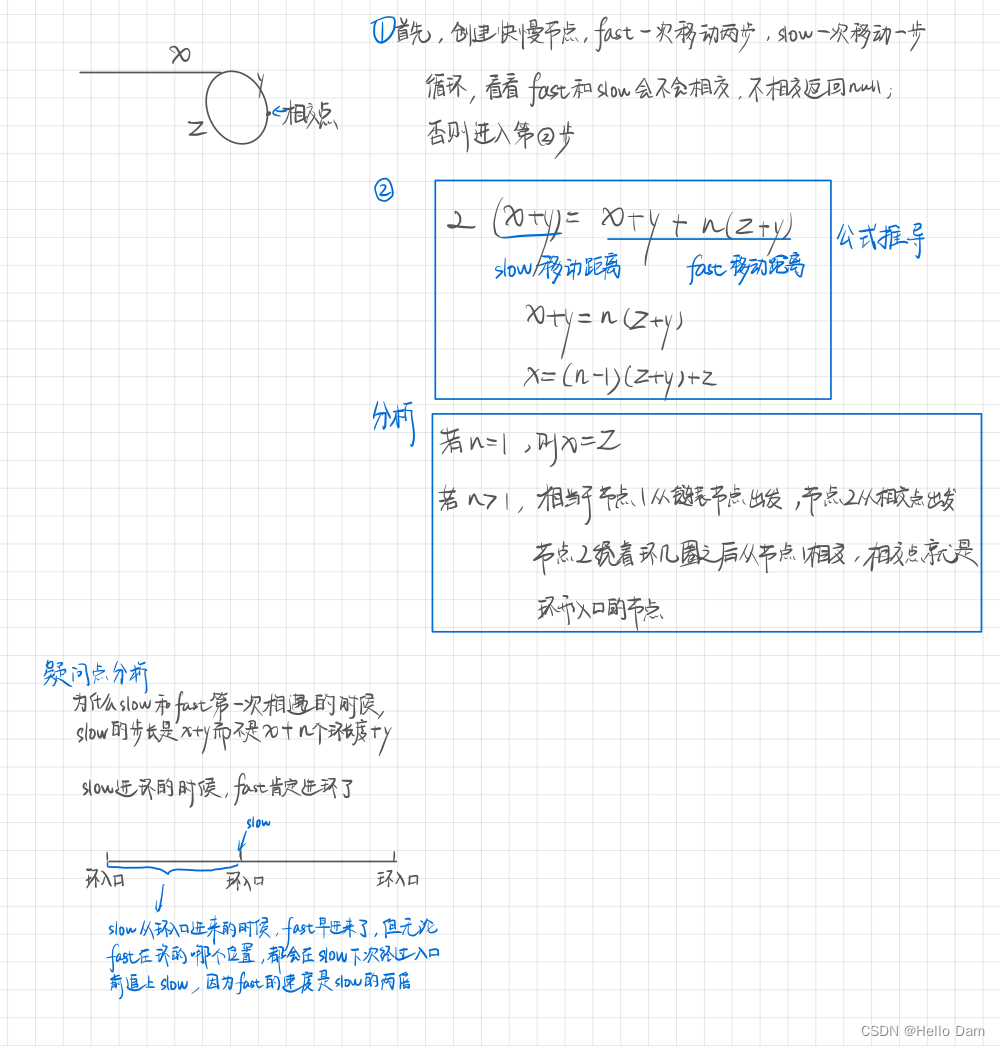
public static ListNode detectCycle1(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;ListNode node2 = null;// 先找到相交点while (slow != null && fast.next != null) {// slow移动一步slow = slow.next;// fast移动两步fast = fast.next.next;if (slow.hashCode() == fast.hashCode()) {// slow 和 fast相交node2 = slow;// 让node1从起点出发,node2从相交点出发,当node1和node2相交的时候,相交时的节点即环的入口ListNode node1 = head;while (true) {if (node1.hashCode() == node2.hashCode()) {return node1;} else {node1 = node1.next;node2 = node2.next;}}}}return null;
}
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。因为快慢指针相遇前,指针走的次数小于链表长度;快慢指针相遇后,两个node指针走的次数也小于链表长度,因此走的总次数小于 2n
- 空间复杂度: O(1)