前言:
参考:
5G Mobile Communications:《Carrier Aggregation in 5G》
目录:
1: carrier Allocation Schemes
2: 网络结构
3: LTE CA
4: 5G CA
一 Carrier Allocation Schemes
CA 主要作用是增加BandWidth,跟子载波分配方式,主要分为以下三种
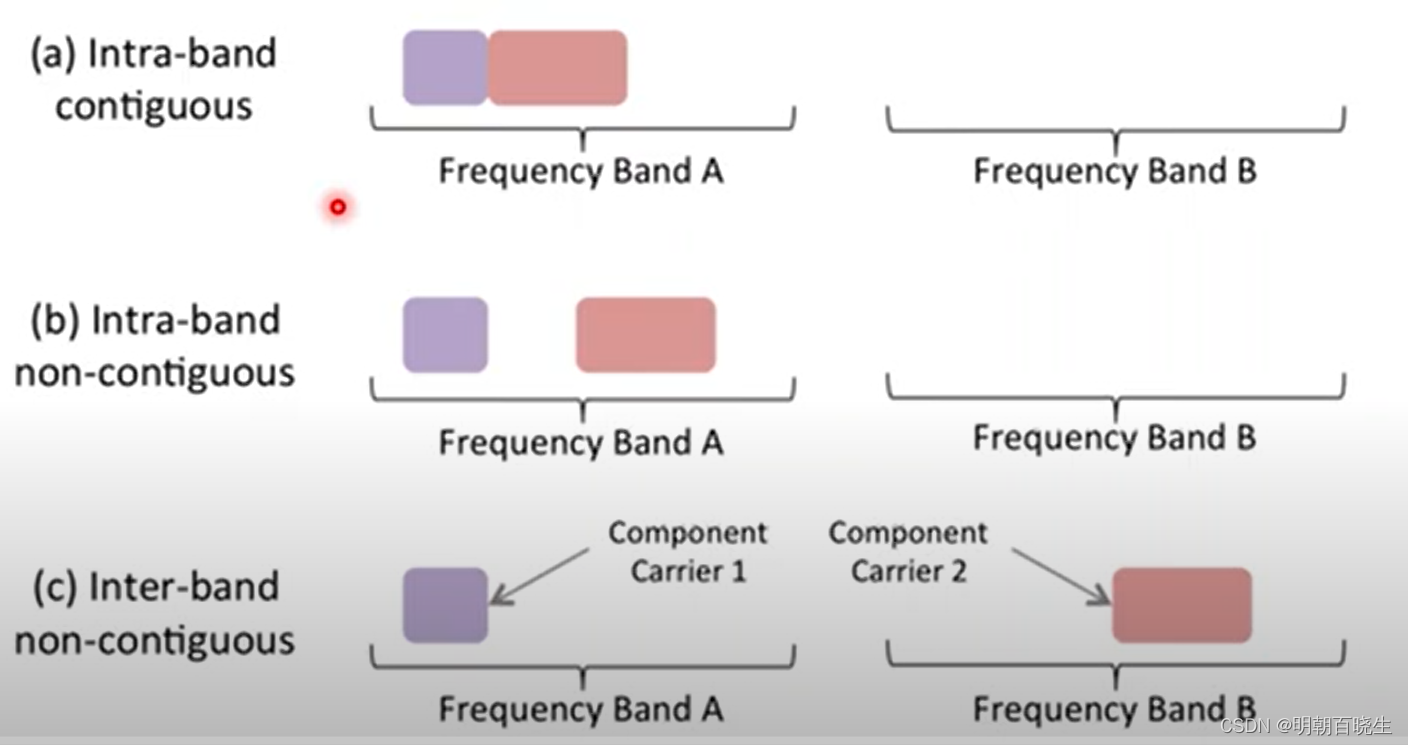
比如 Intra-band contiguous:
Component carrier is contiguous in BandA
二 网络结构
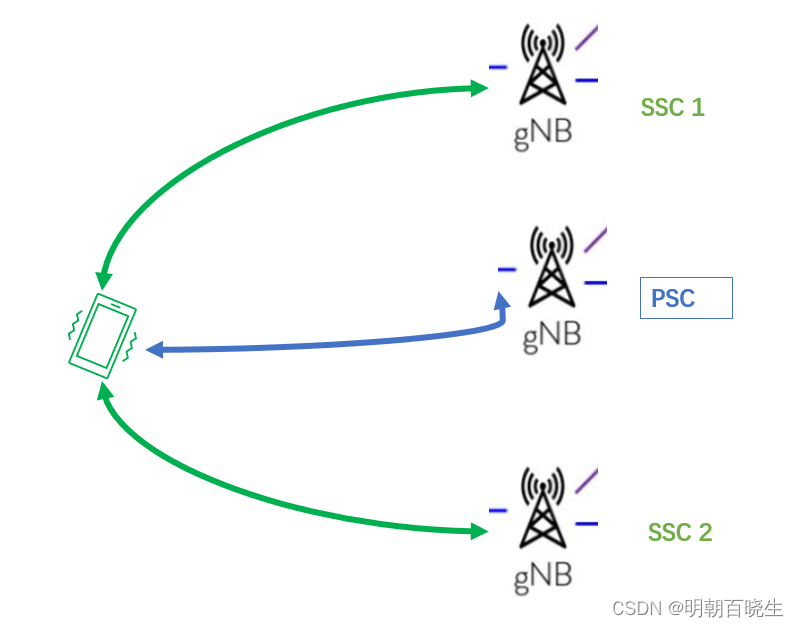
| PSC | Primary Serving Cell |
| PCC | Primary Component Carrier: RRC & data |
| SSC | Secondary Serving cell |
| SCC | Secondary Component carrier: user data |
三 LTE CA
LTE Rel-10 支持5个CA:100M
LTE Rel-13 支持32 CA: 640M
接入层支持的版本在前面讲过,在上行OTA UE Capbaility Information 可以看到

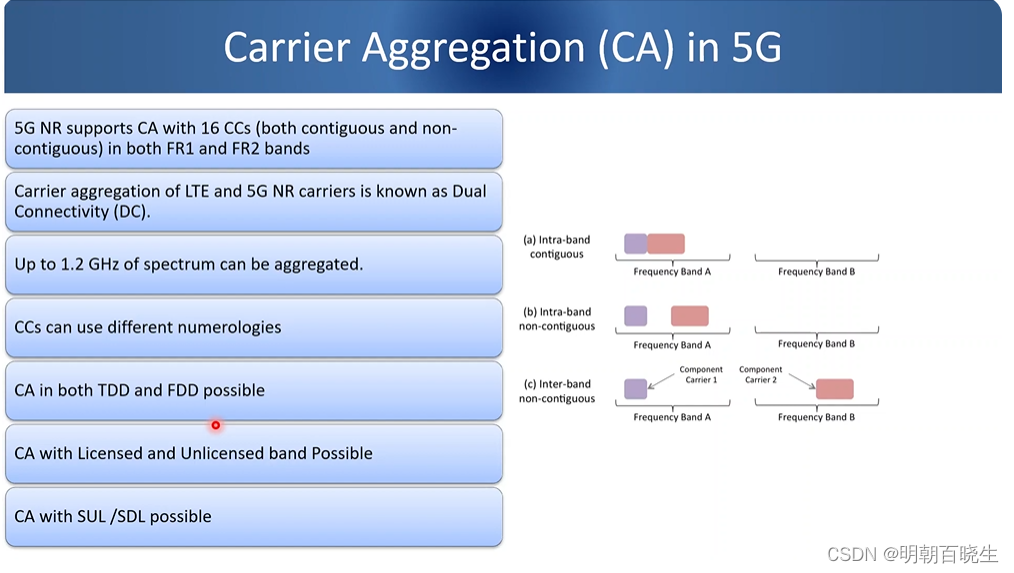
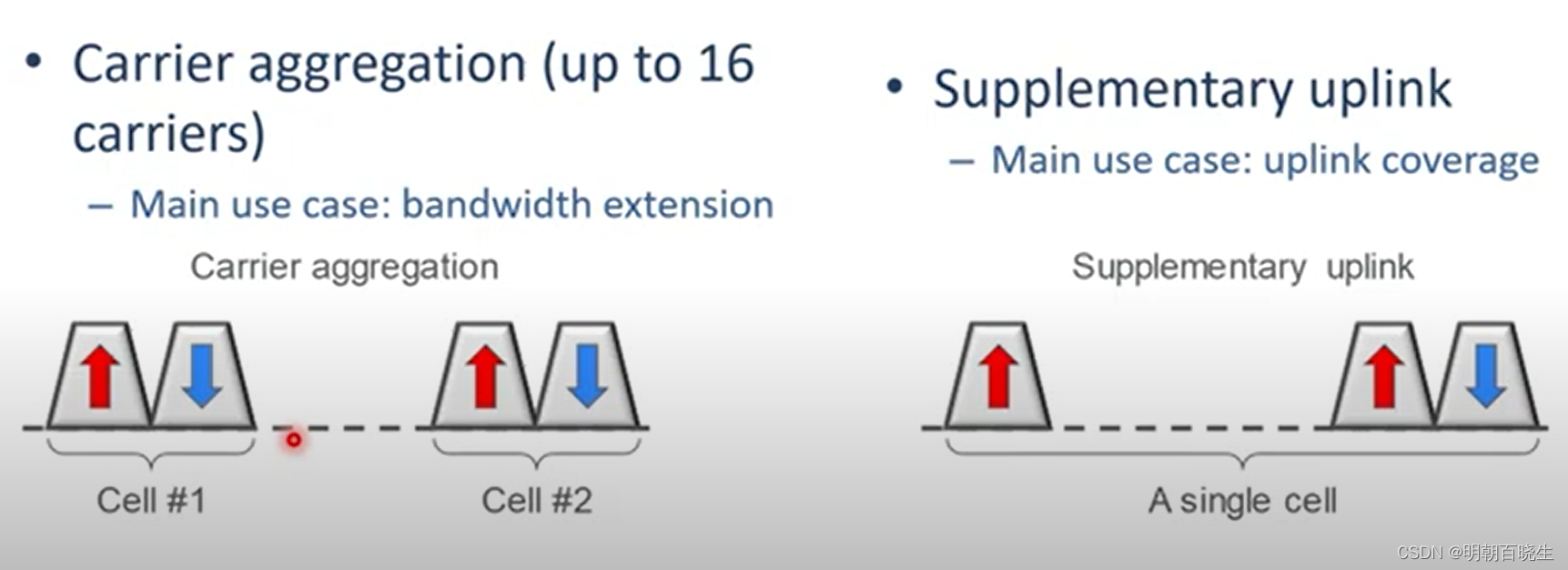
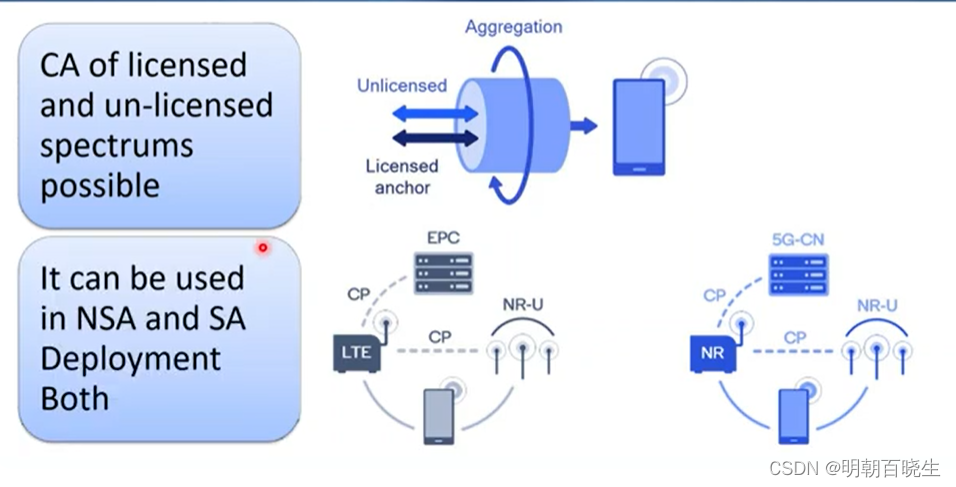
四 5G CA
Carrier aggregation (CA) [1] is one of the key features of LTE-Advanced (LTE-A) systems. According to the CA approach, the user equipments (UEs) can access a wider transmission bandwidth by using CA to aggregate a number of individual component carriers (CCs) shaping heterogeneous contiguous and non-contiguous frequency bands.
These bands can be also unlicensed to the system and therefore a transmission scheme should include sophisticated interference management techniques, according to 3GPP standards [2]. Several new challenging issues arise in radio resource management (RRM) framework for LTE-A systems supporting multipleCC operation, including the selection of the optimal subset of carriers and or the optimal power allocation that maximize the rate of a UE etc.
The performance of CA over deploying independent carriers is investigated from different aspects in [3]-[6]. Resource allocation schemes are also important for the efficient implementation of a CA scheme. A cross layer approach for carrier selection and power control for the uplink of a CA system is examined in [7]. A greedy algorithm for efficient resource allocation for the downlink case is proposed in [8]. The theoretical analysis and the experimental results in these works show that CA can significantly enhance the system capabilities in user accommodation and throughput.