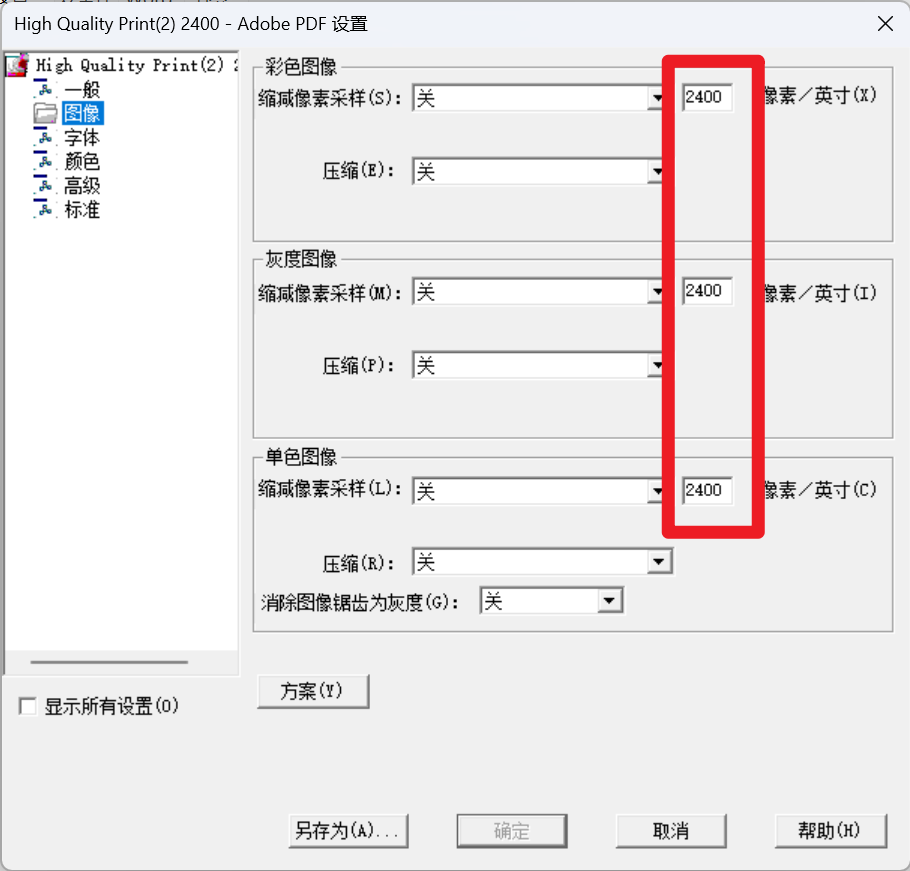
一、M-K 趋势检验
Mann-Kendall 突变检验是一种非参数的假设检验方法,用于检验时间序列数据中的趋势性变化。该检验方法通过比较每个数据点与其之前数据点的大小,来检测时间序列数据中的单调趋势(上升、下降或没有趋势)。具体来说,Mann-Kendall测试将时间序列中的每个数据点与所有之前的数据点进行比较,计算出每个数据点之前比它小的数据点数目和比它大的数据点数目,然后比较这两个数量的大小关系,以确定是否存在单调趋势。
Mann-Kendall检验的优点是不需要对数据进行任何假设,可以用于各种类型的时间序列数据,包括非正态数据。但是它的缺点是无法检测出具体的趋势形式,如线性、非线性等。此外,它对时间序列数据中的周期性变化不敏感。

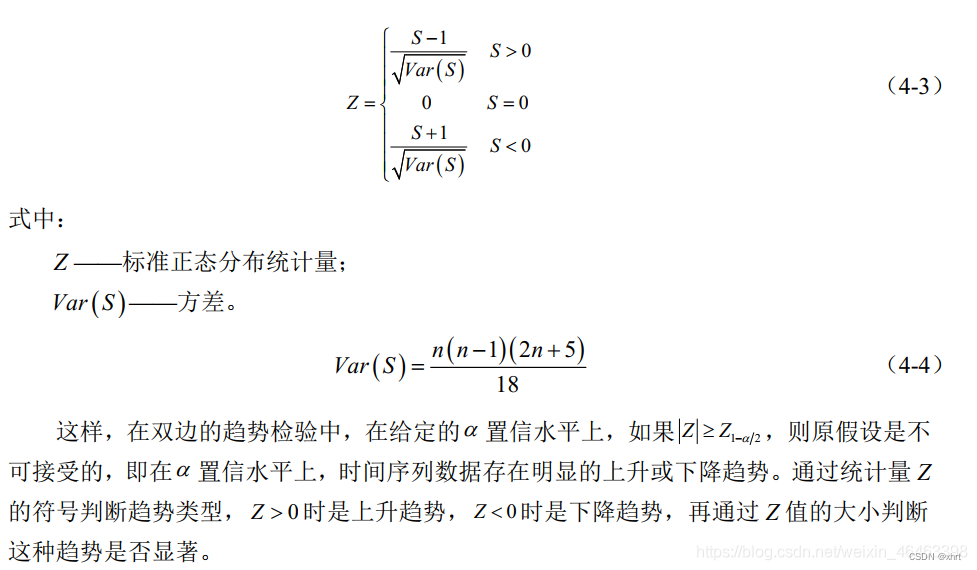
当Z的绝对值大于等于1.64、 1.96、 2.58时则说明该时间序列分别通过了置信水平90%、95%、99%的显著性检验。
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import normdef mann_kendall_test(x):"""Mann-Kendall trend test for a given data sequence x.Args:x: A list or numpy array of data sequence.Returns:trend: The calculated trend (positive, negative or no trend).p_value: The p-value of the test."""n = len(x)s = 0for i in range(n - 1):for j in range(i + 1, n):s += np.sign(x[j] - x[i])# Calculate the variance of the test statistic.var_s = (n * (n - 1) * (2 * n + 5)) / 18# Calculate the standardized test statistic.if s > 0:z = (s - 1) / np.sqrt(var_s)elif s < 0:z = (s + 1) / np.sqrt(var_s)else:z = 0# Calculate the p-value of the test.p_value = 2 * (1 - norm.cdf(abs(z)))# Determine the trend based on the sign of the test statistic.if z > 0:trend = 'increasing'elif z < 0:trend = 'decreasing'else:trend = 'no trend'return trend, p_value


参考链接:
M-K趋势检验以及突变检验_m-k检验_@二十五的博客-CSDN博客