FastThreadLocal 快在哪里 ?
- 引言
- FastThreadLocal
- set
- 如何获取当前线程私有的InternalThreadLocalMap ?
- 如何知道当前线程使用到了哪些FastThreadLocal实例 ?
- get
- 垃圾回收
- 小结
引言
FastThreadLocal 是 Netty 中造的一个轮子,那么为什么放着好端端的ThreadLocal不用,却要重复造轮子呢?下面是Netty官方在源码注释中给出的解释:
- FastThreadLocal是ThreadLocal的一种特殊变体,当从FastThreadLocalThread访问时可以获得更高的访问性能。
- 内部FastThreadLocal使用数组中的常量索引来查找变量,而不是使用哈希码和哈希表来查找。尽管看似非常微小,但与使用哈希表相比,它在性能上略有优势,特别是在频繁访问时。
本文我们就来简单看看FastThreadLocal的具体实现。
在正式进入实现解析之前,下面先给出FastThreadLocal使用示例:
private static void fastThreadLocal() {final int MAX = 100000;long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// DefaultThreadFactory是Netty提供的实现,用于创建类型为FastThreadLocalThread的线程DefaultThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory = new DefaultThreadFactory(FastThreadLocalTest.class);FastThreadLocal<String>[] fastThreadLocal = new FastThreadLocal[MAX];for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {fastThreadLocal[i] = new FastThreadLocal<>();}// 测试单线程读写FastThreadLocal的耗时Thread thread = defaultThreadFactory.newThread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {fastThreadLocal[i].set("java: " + i);}System.out.println("fastThreadLocal set: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++) {fastThreadLocal[i].get();}}});thread.start();try {thread.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("fastThreadLocal total: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}FastThreadLocal
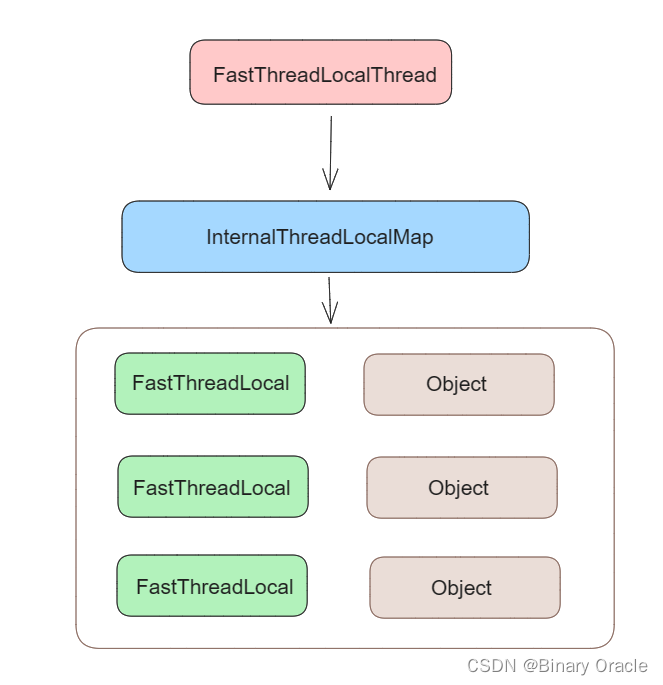
整体来看,FastThreadLocal的整体结构和ThreadLocal是一致的,唯一的区别在于InternalThreadLocalMap 内部存储上,ThreadLocalMap 采用哈希定位实现,而InternalThreadLocalMap 采用数组常量索引实现,即:
- 每个FastThreadLocal与一个固定的数字常量相关联。
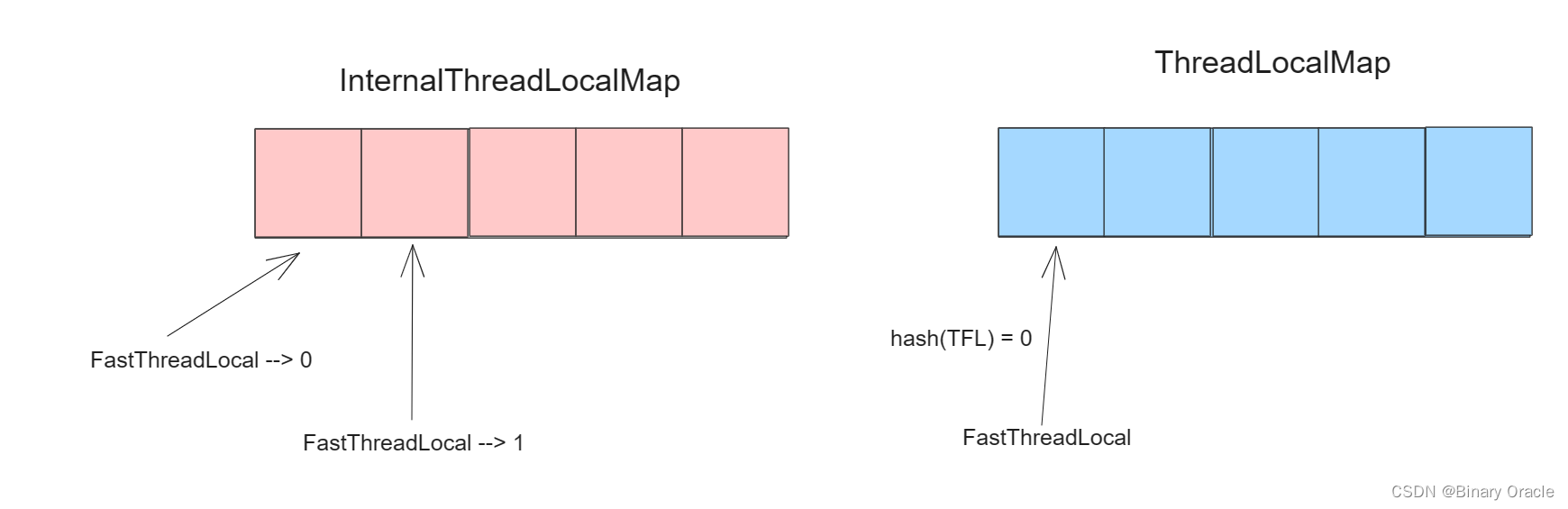
FastThreadLocal内部都会保存一个index下标,该下标在FastThreadLocal实例初始化的时候被赋值:
public class FastThreadLocal<V> {// index 被final修饰,确保FastThreadLocal在InternalThreadLocalMap数组中的下标是固定不变的private final int index;public FastThreadLocal() {// 计数器不断递增index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();}...
}
还有一点也很重要,InternalThreadLocalMap内部使用的桶数组没有采用弱引用实现,而是普通的强引用:
// 1. InternalThreadLocalMap中桶数组的实现private Object[] indexedVariables;// 2. ThreadLocalMap中桶数组的实现static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}}private Entry[] table;
大家可以思考,InternalThreadLocalMap此处不使用弱引用实现,是否存在内存泄漏问题 ? 即当用户程序本身失去了对FastThreadLocal实例的强引用后,仍然被InternalThreadLocalMap强引用的FastThreadLocal如何被回收掉呢?
这里需要注意一点: InternalThreadLocalMap与ThreadLocalMap没有继承关系
set
当我们通过FastThreadLocal的set方法设置值时,其实和ThreadLocal一样,还是向InternalThreadLocalMap中设置值:
public final void set(V value) {// 1. UNSET 是空桶标记-->等价于ThreadLocal中被垃圾回收后key为null的空Entry if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {// 2. 获取与当前线程关联的InternalThreadLocalMap// 以FastThreadLocal为key,value为val设置到InternalThreadLocalMap中 InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value);} else {// 3. 当设置的值为UNSET时,表明需要清空当前FastThreadLocalremove();}}
关于Set的整个流程,有两点值得我们思考:
如何获取当前线程私有的InternalThreadLocalMap ?
如果我们当前使用的线程类型为FastThreadLocalThread,那么可以直接获取FastThreadLocalThread内部持有的InternalThreadLocalMap:
public class FastThreadLocalThread extends Thread {...// 这一点和Thread内部保存ThreadLocalMap实现一致private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap;...
}
如果我们当前使用的线程类型是原始类型Thread,那么Netty这里会将InternalThreadLocalMap保存于当前线程私有的ThreadLocal内部:
public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {private static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap =new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();...
}
上面两种获取方式,前一种被称为fastGet,而后一种被称为slowGet :
public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);} else {return slowGet();}}// 1. 当前线程类型为FastThreadLocalThread,则直接从获取其内部持有的InternalThreadLocalMap实例private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();if (threadLocalMap == null) {thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());}return threadLocalMap;}// 2. 当前线程类型为传统的Thread类型,则从当前线程私有的ThreadLocal中获取InternalThreadLocalMap实例 private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();if (ret == null) {ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);}return ret;} ...
}
如何知道当前线程使用到了哪些FastThreadLocal实例 ?
为什么FastThreadLocal需要获取到当前线程使用到的所有FastThreadLocal实例呢?
上面说过,InternalThreadLocalMap本身没有采用弱引用实现,那么Netty就需要另想办法回收掉失去了用户程序强引用的FastThreadLocal,防止产生内存泄漏。Netty此处采用的方式就是在FastThreadLocalRunnable包装的Runnable对象任务执行完毕后,清理掉当前线程使用到的所有FastThreadLocal实现的:
final class FastThreadLocalRunnable implements Runnable {private final Runnable runnable;private FastThreadLocalRunnable(Runnable runnable) {this.runnable = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(runnable, "runnable");}@Overridepublic void run() {try {runnable.run();} finally {FastThreadLocal.removeAll();}}static Runnable wrap(Runnable runnable) {return runnable instanceof FastThreadLocalRunnable ? runnable : new FastThreadLocalRunnable(runnable);}
}
那这里还是回归第二个问题本身,即如何获取当前线程使用到的所有FastThreadLocal实例呢?
public class FastThreadLocal<V> {private void setKnownNotUnset(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, V value) {// 1. 尝试向threadLocalMap中设置值,如果是第一次设置,则记录当前线程使用到了当前ThreadLocal// (直接常量值定位FastThreadLocal在ThreadLocalMap的哪个槽中) if (threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, value)) {// 2. 记录当前线程使用到了当前FastThreadLocaladdToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);}}private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) {// 1. variablesToRemoveIndex固定为0,threadLocalMap数组第一个槽位存放当前线程使用到的FastThreadLocal集合Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove;// 2. 说明当前FastThreadLocal是当前线程第一个使用到的FastThreadLocal实例if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) {// 3. 准备一个Set集合variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<FastThreadLocal<?>, Boolean>());// 4. threadLocalMap中的0号槽位固定存放当前线程使用到的FastThreadLocal实例threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove);} else {variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;}// 5. 记录当前FastThreadLocal到集合中去variablesToRemove.add(variable);}...
}public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;// 1. 判断InternalThreadLocalMap是否装满if (index < lookup.length) {Object oldValue = lookup[index];lookup[index] = value;// 2. 如果当前槽位先前为空,说明是第一次使用到当前FastThreadLocalreturn oldValue == UNSET;} else {// 3. 执行扩容,扩容完毕后,在设置进去 --> 说明当前FastThreadLocal是第一次被使用expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);return true;}}....
}
当前线程会在第一次使用到某个FastThreadLocal时进行记录,使用到的FastThreadLocal集合保存在InternalThreadLocalMap数组的0号槽位中:
public class FastThreadLocal<V> {// 当FastThreadLocal类本身执行初始化时,该下标就被初始化了,值默认为0private static final int variablesToRemoveIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();...
}public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {// 这里的计数器也是全局共享的private static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();...public static int nextVariableIndex() { // 每次获取下标时,计数器累加一位int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();...return index;}
}
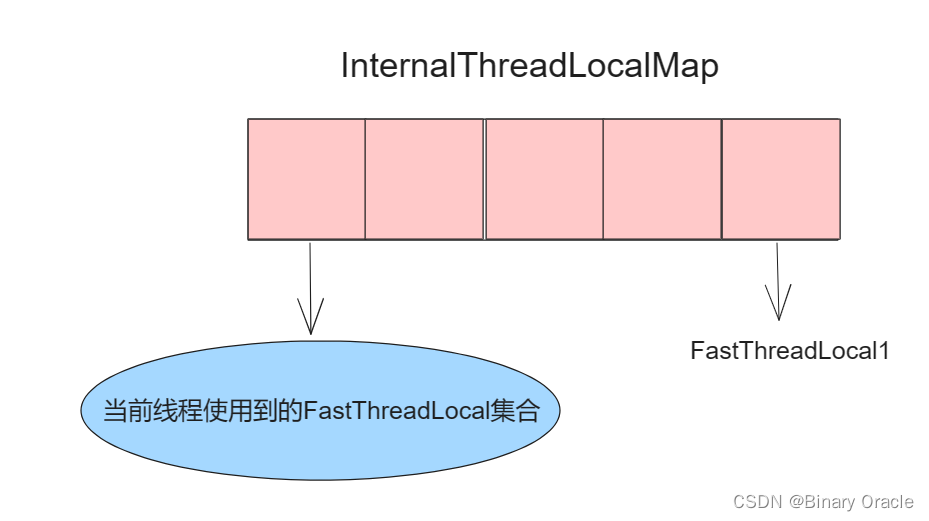
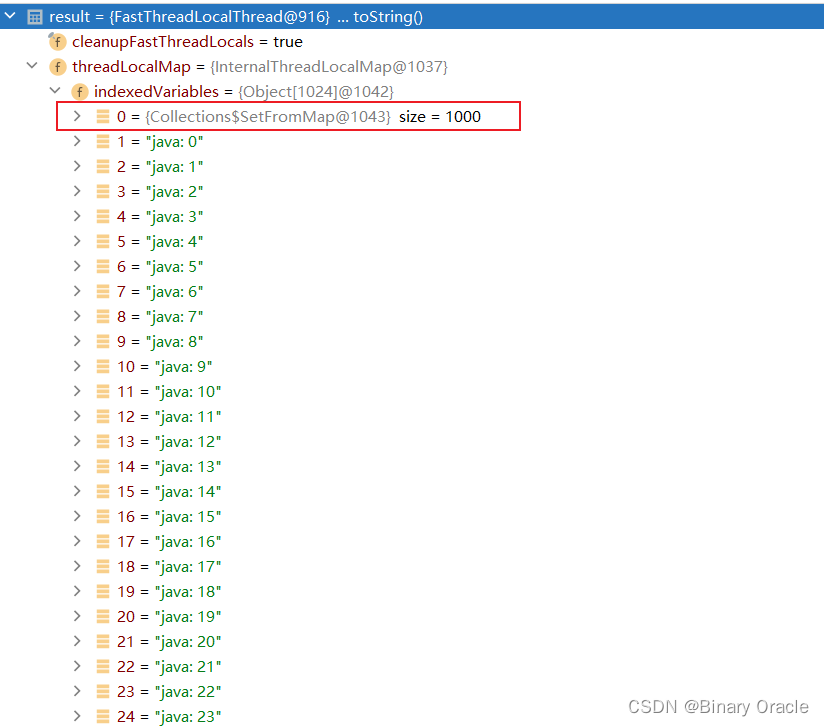
set的整个流程中,我们也可以看出FastThreadLocal快就快在,可以根据当前FastThreadLocal实例关联的常量值直接定位其在InternalThreadLocalMap中的位置。
get
FastThreadLocal get的流程很简单,如下所示:
public class FastThreadLocal<V> {public final V get(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {// 1. 直接常量定位所在槽位Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);// 2. 如果当前FastThreadLocal并非首次访问,则直接对应的值if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {return (V) v;}// 3. 初始化FastThreadLocalreturn initialize(threadLocalMap);}private V initialize(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {V v = null;try {// 1. 调用回调进行初始化v = initialValue();} catch (Exception e) {PlatformDependent.throwException(e);}// 2. 设置初始化的值threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, v);// 3. 注册当前FastThreadLocal,即记录当前线程使用了当前FastThreadLocal实例addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);return v;}...
}
垃圾回收
上面说过,InternalThreadLocalMap本身没有采用弱引用实现,那么Netty就需要另想办法回收掉失去了用户程序强引用的FastThreadLocal,防止产生内存泄漏。Netty此处采用的方式就是在FastThreadLocalRunnable包装的Runnable对象任务执行完毕后,清理掉当前线程使用到的所有FastThreadLocal实现的,这一点上面已经提到过了,下面我们看看具体实现。
final class FastThreadLocalRunnable implements Runnable {private final Runnable runnable;private FastThreadLocalRunnable(Runnable runnable) {this.runnable = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(runnable, "runnable");}@Overridepublic void run() {try {runnable.run();} finally {FastThreadLocal.removeAll();}}static Runnable wrap(Runnable runnable) {return runnable instanceof FastThreadLocalRunnable ? runnable : new FastThreadLocalRunnable(runnable);}
}
FastThreadLocal提供了一个静态的removeAll方法,用于清除当前线程使用到的所有FastThreadLocal实例:
public class FastThreadLocal<V> {... public static void removeAll() {// 1. 如果当前线程没有使用到FastThreadLocal,这里直接返回InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet();if (threadLocalMap == null) {return;}try {// 2. 获取固定的0号槽位保存的Set集合,该集合内保存了当前线程使用到的所有FastThreadLocal实例集合 Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);if (v != null && v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;// 3. 遍历该集合内每个FastThreadLocal实例,依次调用remove方法 FastThreadLocal<?>[] variablesToRemoveArray =variablesToRemove.toArray(new FastThreadLocal[0]);for (FastThreadLocal<?> tlv: variablesToRemoveArray) {tlv.remove(threadLocalMap);}}} finally {// 4. 置空threadlocalmapInternalThreadLocalMap.remove();}}
- 清空单个FastThreadLocal
public class FastThreadLocal<V> {public final void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {if (threadLocalMap == null) {return;}// 1. 清除当前FastThreadLocal占用的槽位Object v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index);// 2. 取消当前FastThreadLocal的注册removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);// 3. 执行回调通知 if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {try {onRemoval((V) v);} catch (Exception e) {PlatformDependent.throwException(e);}}}private static void removeFromVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) {// 1. 获取threadlocalmap的0号槽位保存的set集合 Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);...// 2. 从set集合中移除当前fastThreadLocalSet<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;variablesToRemove.remove(variable);}...
}public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {public Object removeIndexedVariable(int index) {Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;if (index < lookup.length) {Object v = lookup[index];// 将对应槽位设置为UNSETlookup[index] = UNSET;return v;} else {return UNSET;}}...
}
- 置空ThreadLocalMap
public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {public static void remove() {Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();// 1. 如果threadLocalMap保存在FastThreadLocalThread内部,则直接设置为nullif (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).setThreadLocalMap(null);} else {// 2. 如果保存在当前线程threadlocal中,则调用threadlocal的remove方法移除 slowThreadLocalMap.remove();}}...
}
小结
FastThreadLocal为什么那么快,这个问题比较好回答:
- FastThreadLocal 内部维护了一个索引常量 index,该常量在每次创建 FastThreadLocal 中都会自动+1,从而保证了下标的不重复性。
- 这要做虽然会产生大量的 index,但避免了在 ThreadLocal 中计算索引下标位置以及处理 hash 冲突带来的损耗,所以在操作数组时使用固定下标要比使用计算哈希下标有一定的性能优势,特别是在频繁使用时会非常显著,用空间换时间,这就是高性能 Netty 的巧妙之处。
- 要利用 FastThreadLocal 带来的性能优势,就必须结合使用 FastThreadLocalThread 线程类或其子类,因为 FastThreadLocalThread 线程类会存储必要的状态,如果使用了非 FastThreadLocalThread 线程类则会回到常规 ThreadLocal。
下面给出一个测试用例,来看看FastThreadLocal和ThreadLocal在性能上的差异:
public class FastThreadLocalTest {public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(FastThreadLocalTest::threadLocal).start();new Thread(FastThreadLocalTest::fastThreadLocal).start();}private static void fastThreadLocal() {final int MAX = 100000;long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// DefaultThreadFactory是Netty提供的实现,用于创建类型为FastThreadLocalThread的线程DefaultThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory = new DefaultThreadFactory(FastThreadLocalTest.class);FastThreadLocal<String>[] fastThreadLocal = new FastThreadLocal[MAX];for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {fastThreadLocal[i] = new FastThreadLocal<>();}// 测试单线程读写FastThreadLocal的耗时Thread thread = defaultThreadFactory.newThread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {fastThreadLocal[i].set("java: " + i);}System.out.println("fastThreadLocal set: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++) {fastThreadLocal[i].get();}}});thread.start();try {thread.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("fastThreadLocal total: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}private static void threadLocal() {final int MAX = 100000;long start = System.currentTimeMillis();ThreadLocal<String>[] threadLocals = new ThreadLocal[MAX];for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {threadLocals[i] = new ThreadLocal<>();}Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {threadLocals[i].set("java: " + i);}System.out.println("threadLocal set: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++) {threadLocals[i].get();}}});thread.start();try {thread.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("threadLocal total: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}}
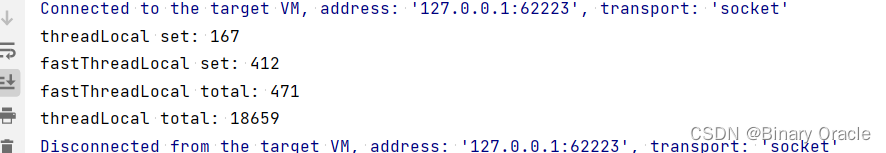
在大量读写面前,写操作的效率差不多,但读操作 FastThreadLocal 比 ThreadLocal 快的不是一个数量级,简直是秒杀 ThreadLocal 的存在。
当我们把max的值缩小为1000时,此时读写操作不多时,ThreadLocal 明显更胜一筹!

Netty 中的 FastThreadLocal 在大量频繁读写操作时效率要高于 ThreadLocal,但要注意结合 Netty 自带的线程类使用。
如果没有大量频繁读写操作的场景,JDK 自带的 ThreadLocal 足矣,并且性能还要优于 FastThreadLocal。



![[NewStarCTF 2023 公开赛道] week1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b0f1e58f85c44a90a94e95d36bd2945c.png)

![【QT5-程序控制电源-[GPIB-USB-HS]-SCPI协议-上位机-基础样例【2】】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b8cbae930c5e4fa3aa611470c05809d8.png)