目录
(反)序列化二叉树(str<->tree):前序
前序遍历(迭代)/路径
stack.length
入栈:中右左
出栈:中左右
中序遍历(迭代)
cur||stack.length
后序遍历(迭代)
和前序遍历不同:
入栈:中左右
出栈:中右左
reverse出栈:左右中
层序遍历(BFS):可求树的深/高度
找树左下角的值:最后一行的最左边的值
判断完全二叉树
queue.length
flag = false; //是否遇到空节点
判断平衡二叉树
递归Math.max(getMaxDepth(root.left)+1,getMaxDepth(root.right)+1)
判断对称二叉树
递归deep(left.left, right.right) && deep(left.right, right.left)
翻转/生成镜像二叉树
递归交换左右
两节点的最近公共祖先
递归后序遍历
构造二叉树
从中序与前/后序遍历序列构造二叉树
最大二叉树:二叉树的根是数组中的最大元素(递归定义)
二叉搜索树:左<根<右(按中序遍历有序的树)
删除二叉搜索树中的节点
修剪二叉搜索树
有序数组转换为平衡二叉搜索树
left, right比arr.slice高效
Math.floor(left + (right - left) / 2)
最值、差值->有序数组的差值、最值
二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
二叉搜索树转换为累加树
(反)序列化二叉树(str<->tree):前序
function TreeNode(x) {this.val = x;this.left = null;this.right = null;
}
//反序列化二叉树:tree->str 把一棵二叉树按照某种遍历方式的结果以某种格式保存为字符串
function Serialize(pRoot, arr = []) {if (!pRoot) {arr.push("#");return arr;} else {arr.push(pRoot.val);//注意是val。而不是rootSerialize(pRoot.left, arr);Serialize(pRoot.right, arr);}return arr;
}
//序列化二叉树:str->tree 根据字符串结果str,重构二叉树
function Deserialize(s) {//转换为数组let arr = Array.isArray(s) ? s : s.split("");//取出vallet a = arr.shift();//构建二叉树结点let node = null;if (typeof a === "number") {//还有可能等于#node = new TreeNode(a);node.left = Deserialize(arr);node.right = Deserialize(arr);}return node;
}
module.exports = {Serialize: Serialize,Deserialize: Deserialize,
};
前序遍历(迭代)/路径
stack.length
入栈:中右左
出栈:中左右
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }*/
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {let stack=[]let res = []let cur = null;if(!root) return res;root&&stack.push(root)while(stack.length){cur = stack.pop()res.push(cur.val)cur.right&&stack.push(cur.right)cur.left&&stack.push(cur.left)}return res
};
中序遍历(迭代)
cur||stack.length
指针的遍历来帮助访问节点,栈则用来处理节点上的元素
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }*/
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {let stack = []let res = []let cur = rootwhile(cur||stack.length){if(cur){stack.push(cur)cur = cur.left} else {cur = stack.pop()res.push(cur.val)cur = cur.right}}return res
};
后序遍历(迭代)
和前序遍历不同:
入栈:中左右
出栈:中右左
reverse出栈:左右中
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }*/
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {let stack = []let res = []let cur = rootif(!root) return resstack.push(root)while(stack.length){cur = stack.pop()res.push(cur.val)cur.left&&stack.push(cur.left)cur.right&&stack.push(cur.right)}return res.reverse()};
层序遍历(BFS):可求树的深/高度
树的层序遍历,相似 图的广度优先搜索
- 初始设置一个空队,根结点入队
- 队首结点出队,其左右孩子 依次 入队
- 若队空,说明 所有结点 已处理完,结束遍历;否则(2)
/** function TreeNode(x) {* this.val = x;* this.left = null;* this.right = null;* }*//**** @param root TreeNode类* @return int整型二维数组*/
function levelOrder(root) {// write code hereif (root == null) {return [];}const arr = [];const queue = [];queue.push(root);while (queue.length) {const preSize = queue.length;const floor = [];//当前层for (let i = 0; i < preSize; ++i) {const v = queue.shift();floor.push(v.val);v.left&&queue.push(v.left);v.right&&queue.push(v.right);}arr.push(floor);}return arr;//[[1],[2,3]]
}
module.exports = {levelOrder: levelOrder,
};
找树左下角的值:最后一行的最左边的值
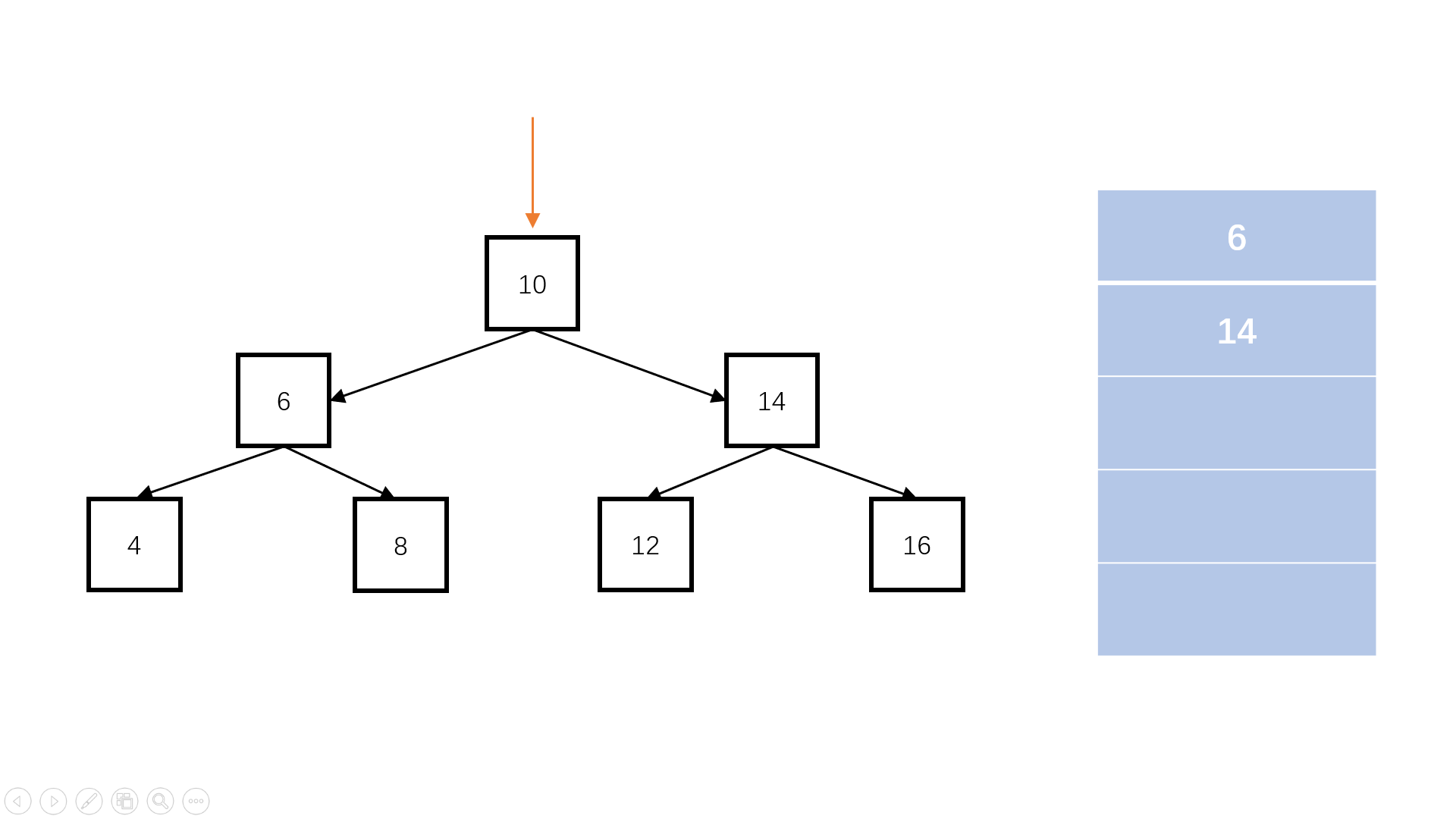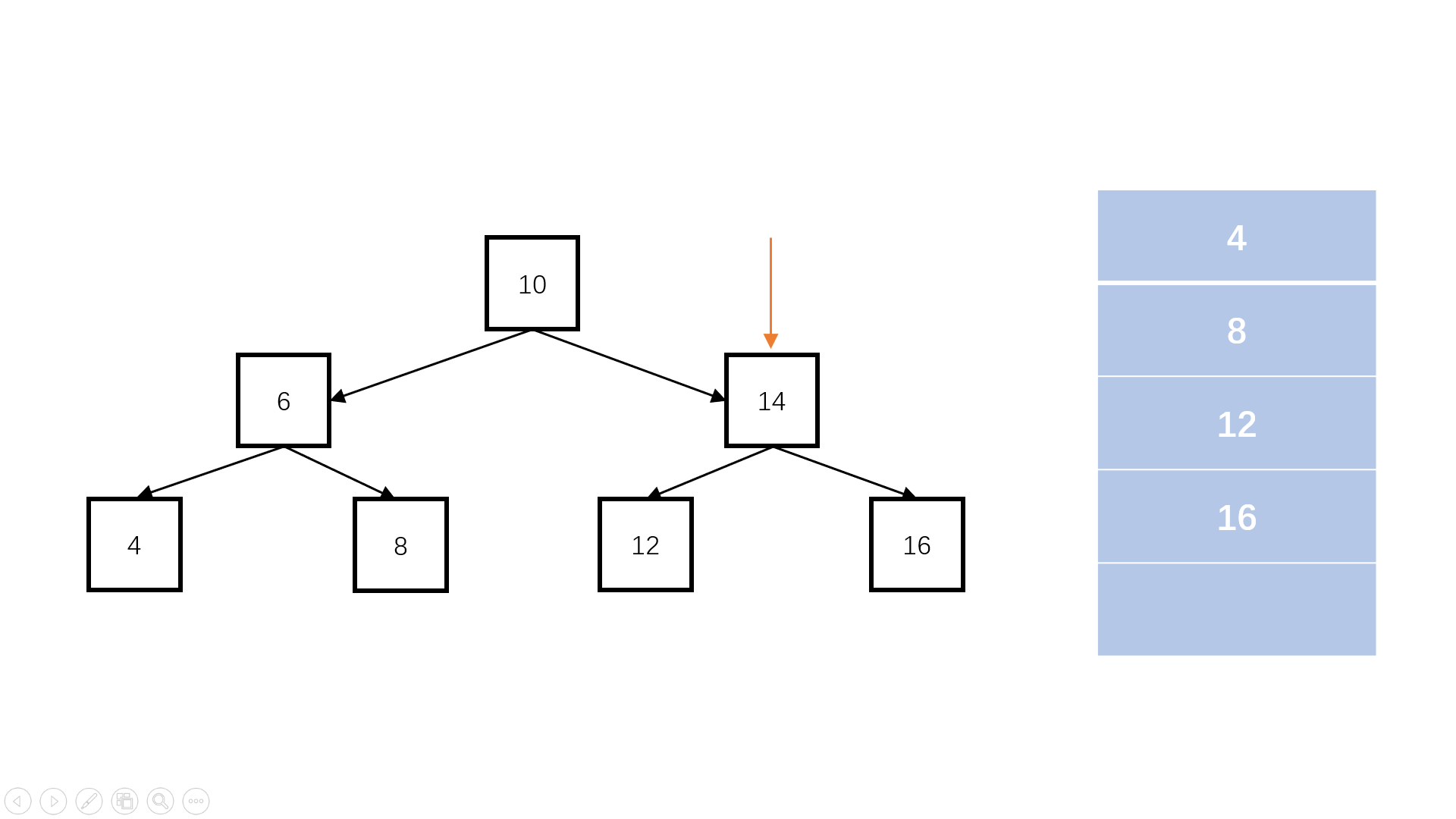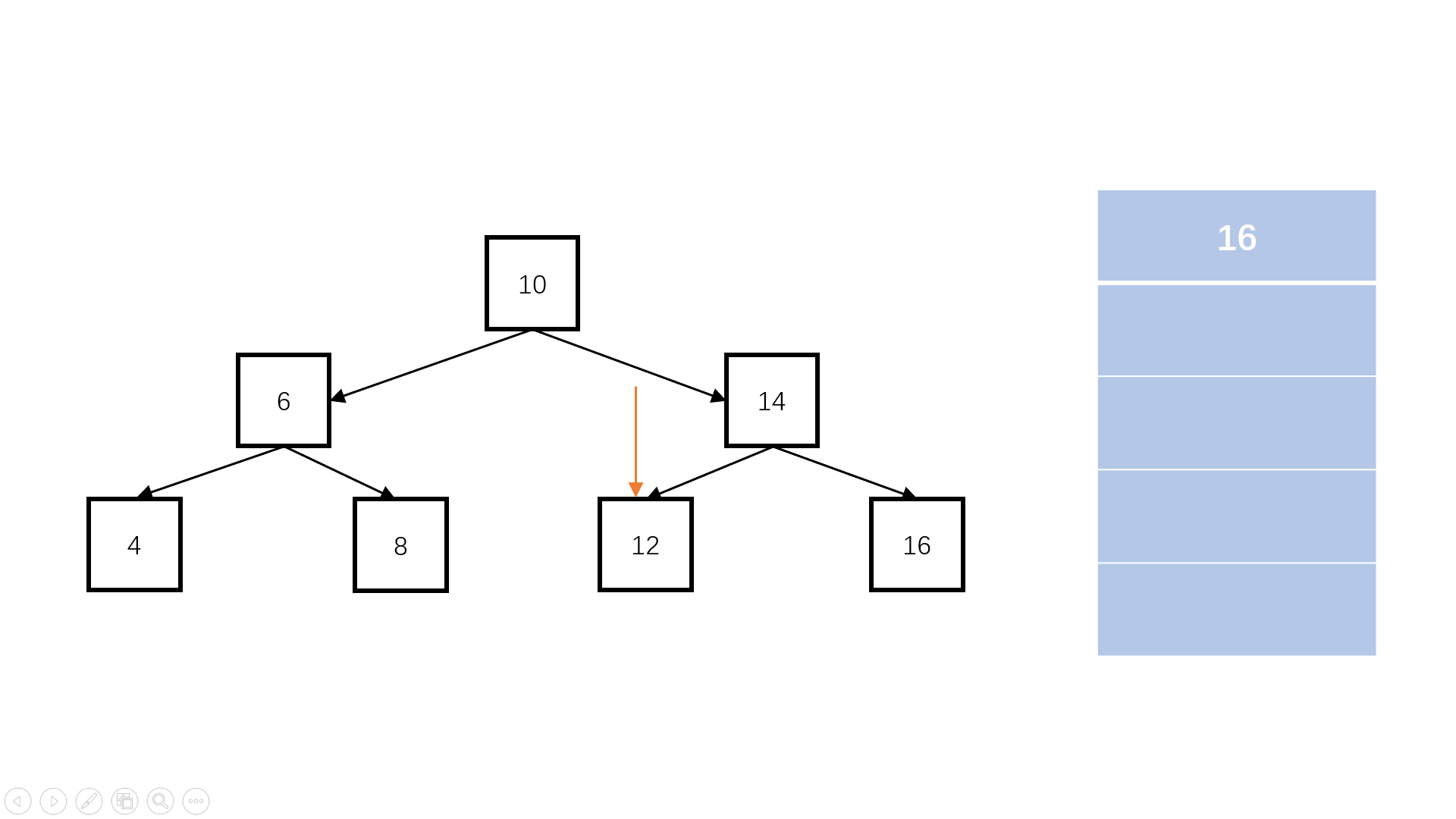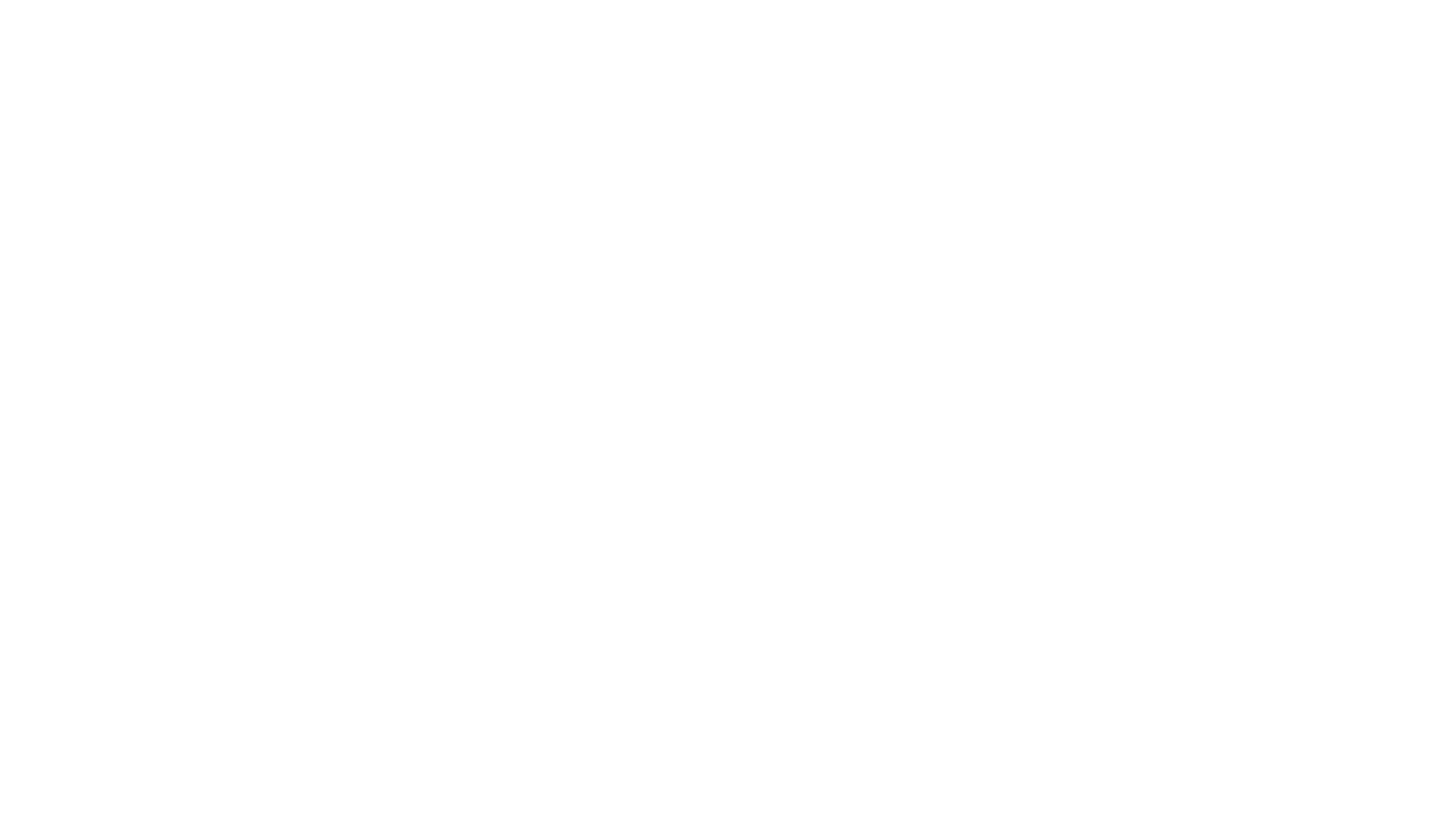
判断完全二叉树
queue.length
flag = false; //是否遇到空节点
完全二叉树:叶子节点只能出现在最下层和次下层,且最下层的叶子节点集中在树的左部。
/** function TreeNode(x) {* this.val = x;* this.left = null;* this.right = null;* }*/
/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可*** @param root TreeNode类* @return bool布尔型*/
function isCompleteTree(root) {// write code hereif (root == null) return true;const queue = [];queue.push(root);let flag = false; //是否遇到空节点while (queue.length) {const node = queue.shift();if (node == null) {//如果遇到某个节点为空,进行标记,代表到了完全二叉树的最下层flag = true;continue;}if (flag == true) {//若是后续还有访问,则说明提前出现了叶子节点,不符合完全二叉树的性质。return false;}queue.push(node.left);queue.push(node.right);}return true;
}
module.exports = {isCompleteTree: isCompleteTree,
};
判断平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树是左子树的高度与右子树的高度差的绝对值小于等于1,同样左子树是平衡二叉树,右子树为平衡二叉树。
递归Math.max(getMaxDepth(root.left)+1,getMaxDepth(root.right)+1)
/* function TreeNode(x) {this.val = x;this.left = null;this.right = null;
} */
function IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot)
{if(!pRoot) return true;// write code herereturn (Math.abs(getMaxDepth(pRoot.left) - getMaxDepth(pRoot.right)) <=1) && IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot.left) && IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot.right)
}function getMaxDepth(root) {if(!root) return 0;return Math.max(getMaxDepth(root.left)+1,getMaxDepth(root.right)+1)
}
module.exports = {IsBalanced_Solution : IsBalanced_Solution
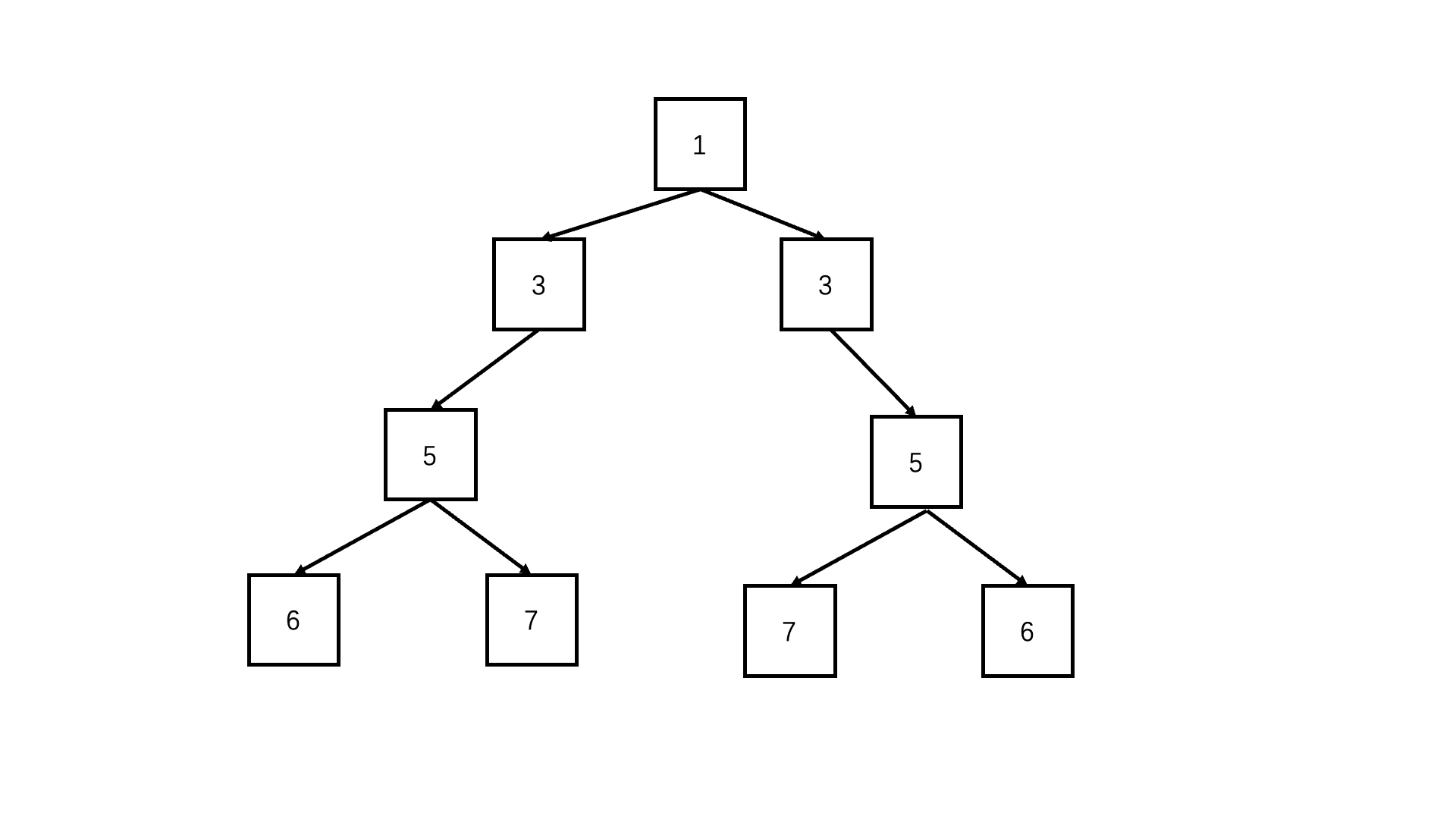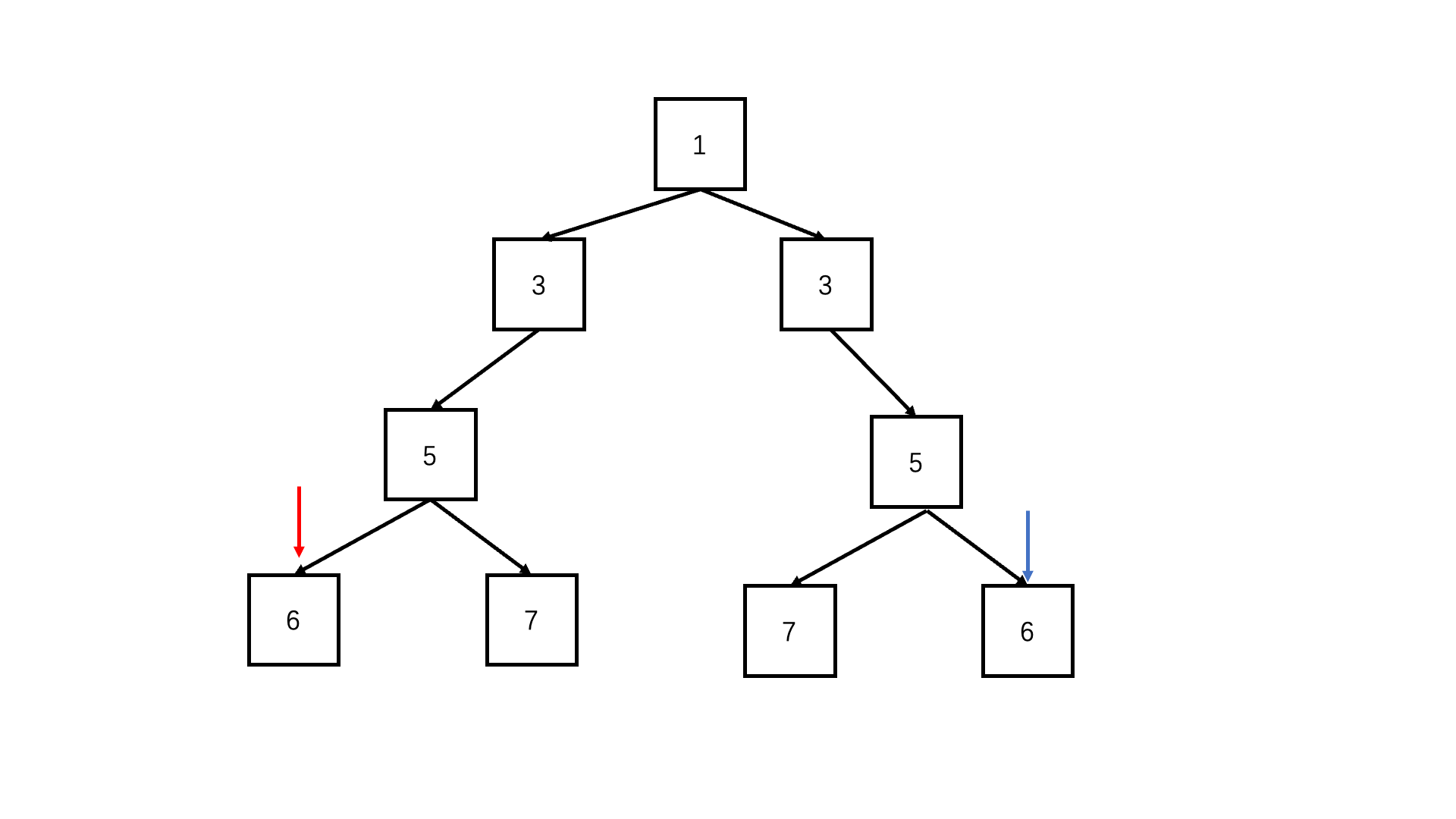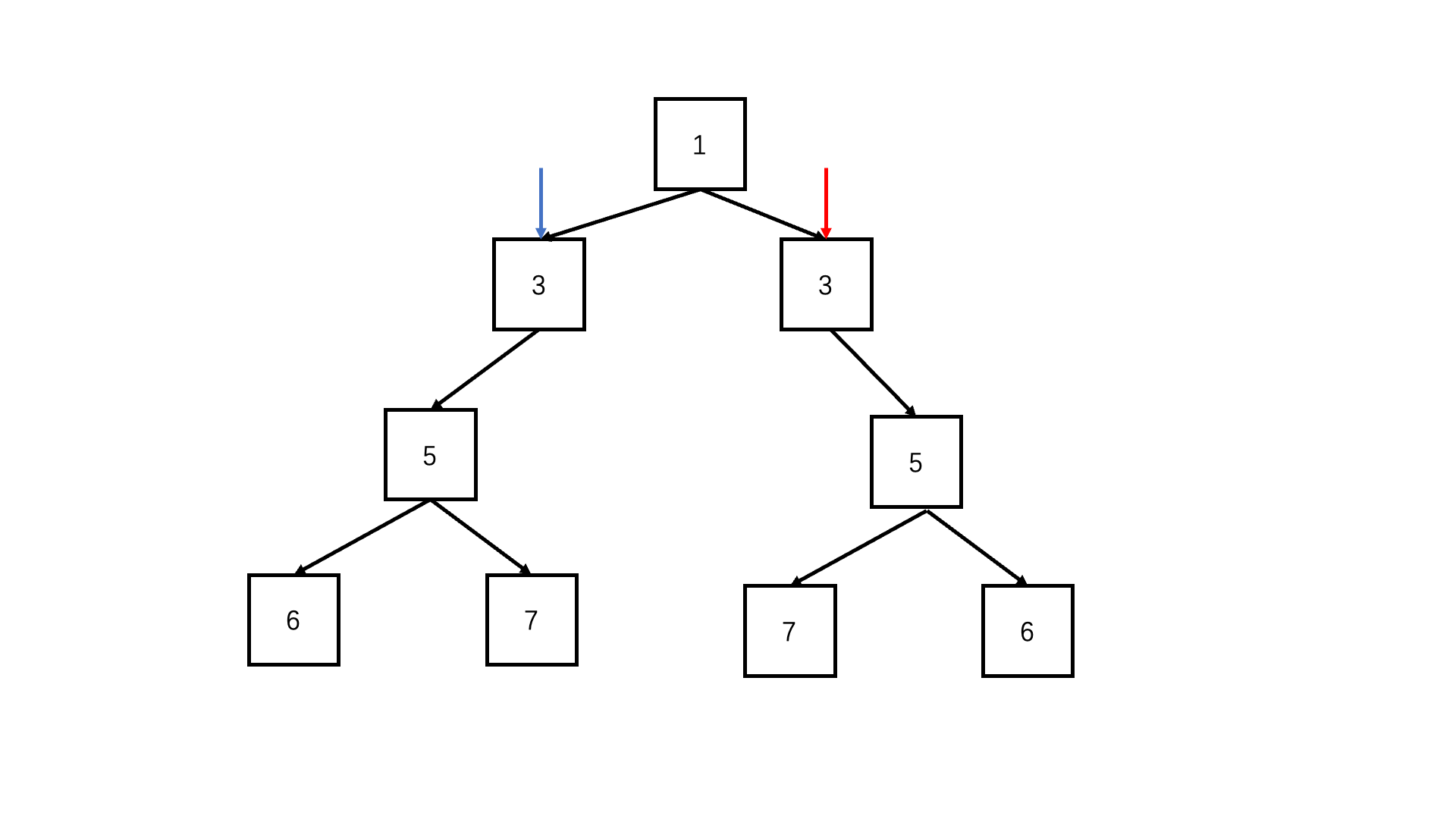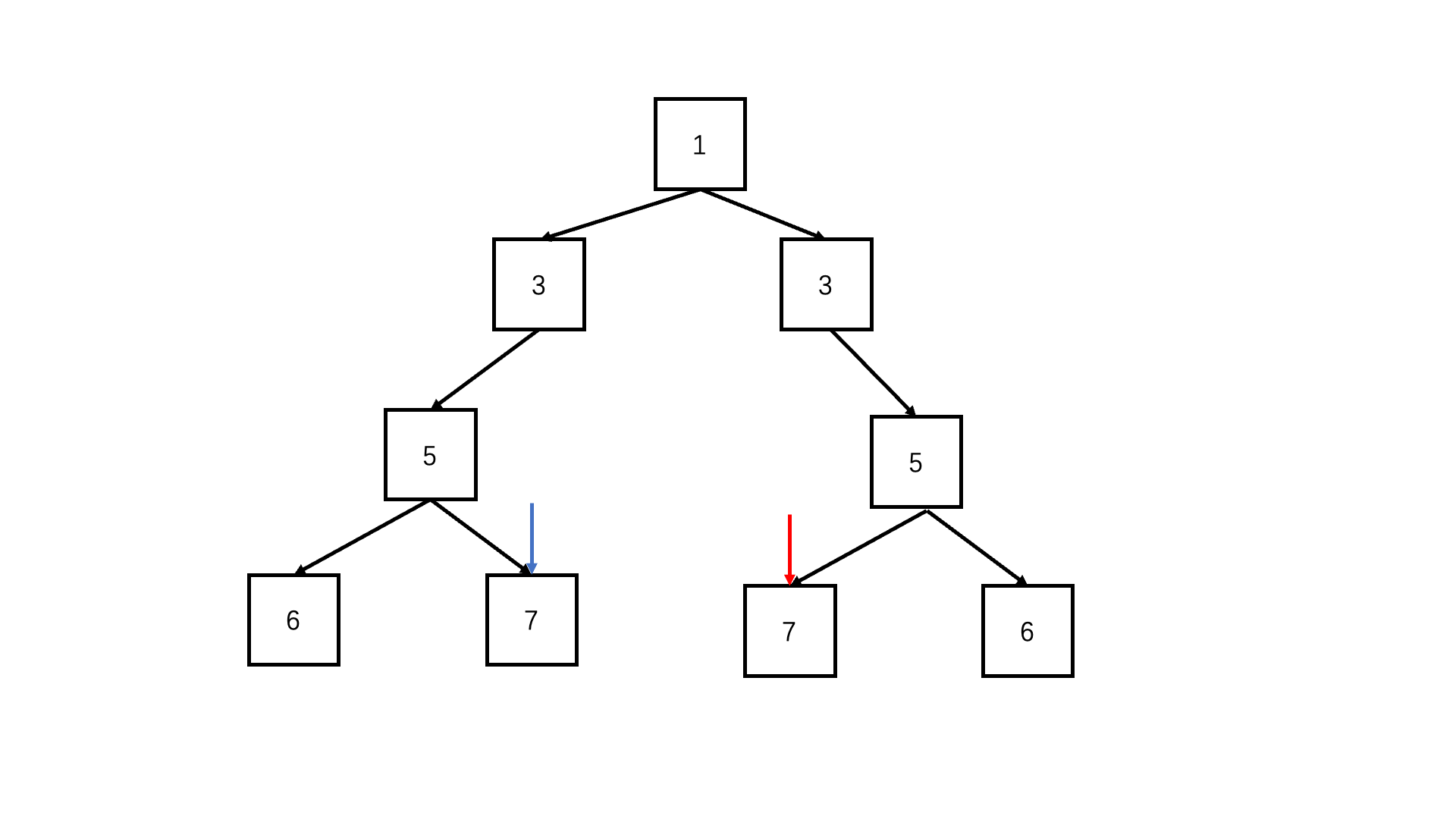
};判断对称二叉树
递归deep(left.left, right.right) && deep(left.right, right.left)
/* function TreeNode(x) {this.val = x;this.left = null;this.right = null;
} */
let flag = true;
function deep(left, right) {if (!left && !right) return true; //可以两个都为空if (!right||!left|| left.val !== right.val) {//只有一个为空或者节点值不同,必定不对称return false;}return deep(left.left, right.right) && deep(left.right, right.left); //每层对应的节点进入递归比较
}
function isSymmetrical(pRoot) {return deep(pRoot, pRoot);
}
module.exports = {isSymmetrical: isSymmetrical,
};
翻转/生成镜像二叉树
递归交换左右
先序遍历
/** function TreeNode(x) {* this.val = x;* this.left = null;* this.right = null;* }*/
/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pRoot TreeNode类 * @return TreeNode类*/
function Mirror( pRoot ) {function traversal(root){if(root===null) return ;//交换左右孩子let temp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = temp;traversal(root.left);traversal(root.right);return root;}return traversal(pRoot);// write code here
}
module.exports = {Mirror : Mirror
};两节点的最近公共祖先
如果从两个节点往上找,每个节点都往上走,一直走到根节点,那么根节点到这两个节点的连线肯定有相交的地方,
如果从上往下走,那么最后一次相交的节点就是他们的最近公共祖先节点。
递归后序遍历
/** function TreeNode(x) {* this.val = x;* this.left = null;* this.right = null;* }*//**** @param root TreeNode类* @param o1 int整型* @param o2 int整型* @return int整型*/
function dfs(root, o1, o2) {if (root == null || root.val == o1 || root.val == o2) {return root;}//递归遍历左子树let left = dfs(root.left, o1, o2);//递归遍历右子树let right = dfs(root.right, o1, o2);//如果left、right都不为空,那么代表o1、o2在root的两侧,所以root为他们的公共祖先if (left && right) return root;//如果left、right有一个为空,那么就返回不为空的那一个return left != null ? left : right;
}构造二叉树
从中序与前/后序遍历序列构造二叉树
//前
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {if (!preorder.length) return null;const rootVal = preorder.shift(); // 从前序遍历的数组中获取中间节点的值, 即数组第一个值const index = inorder.indexOf(rootVal); // 获取中间节点在中序遍历中的下标const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); // 创建中间节点root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(0, index), inorder.slice(0, index)); // 创建左节点root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index), inorder.slice(index + 1)); // 创建右节点return root;
};
//后
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {if (!inorder.length) return null;const rootVal = postorder.pop(); // 从后序遍历的数组中获取中间节点的值, 即数组最后一个值let rootIndex = inorder.indexOf(rootVal); // 获取中间节点在中序遍历中的下标const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); // 创建中间节点root.left = buildTree(inorder.slice(0, rootIndex), postorder.slice(0, rootIndex)); // 创建左节点root.right = buildTree(inorder.slice(rootIndex + 1), postorder.slice(rootIndex)); // 创建右节点return root;
};最大二叉树:二叉树的根是数组中的最大元素(递归定义)
var constructMaximumBinaryTree = function (nums) {const BuildTree = (arr, left, right) => {if (left > right)return null;let maxValue = -1;let maxIndex = -1;for (let i = left; i <= right; ++i) {if (arr[i] > maxValue) {maxValue = arr[i];maxIndex = i;}}let root = new TreeNode(maxValue);root.left = BuildTree(arr, left, maxIndex - 1);root.right = BuildTree(arr, maxIndex + 1, right);return root;}let root = BuildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);return root;
};二叉搜索树:左<根<右(按中序遍历有序的树)
删除二叉搜索树中的节点
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }*/
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {number} key* @return {TreeNode}*/
var deleteNode = function(root, key) {if (!root) return null;if (key > root.val) {root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);return root;} else if (key < root.val) {root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);return root;} else {// 场景1: 该节点是叶节点if (!root.left && !root.right) {return null}// 场景2: 有一个孩子节点不存在if (root.left && !root.right) {return root.left;} else if (root.right && !root.left) {return root.right;}// 场景3: 左右节点都存在const rightNode = root.right;// 获取最小值节点const minNode = getMinNode(rightNode);// 将待删除节点的值替换为最小值节点值root.val = minNode.val;// 删除最小值节点root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val);return root;}
};
function getMinNode(root) {while (root.left) {root = root.left;}return root;
}修剪二叉搜索树
修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L)
var trimBST = function (root,low,high) {if(root === null) {return null;}if(root.val < low) {let right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);return right;}if(root.val > high) {let left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);return left;}root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);return root;}有序数组转换为平衡二叉搜索树
left, right比arr.slice高效
Math.floor(left + (right - left) / 2)
var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) {const buildTree = (Arr, left, right) => {if (left > right)return null;let mid = Math.floor(left + (right - left) / 2);let root = new TreeNode(Arr[mid]);root.left = buildTree(Arr, left, mid - 1);root.right = buildTree(Arr, mid + 1, right);return root;}return buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
};最值、差值->有序数组的差值、最值
二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
二叉搜索树转换为累加树
一个有序数组[2, 5, 13],求从后到前的累加数组,也就是[20, 18, 13]
累加的顺序是右中左,所以我们需要反中序遍历这个二叉树,然后顺序累加
’东哥带你刷二叉树(思路篇) | labuladong 的算法笔记

![[VC++]圆形进度条](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f021c165bafac29476a7596f31711f05.gif)