目录
数据结构——迷宫问题求解::
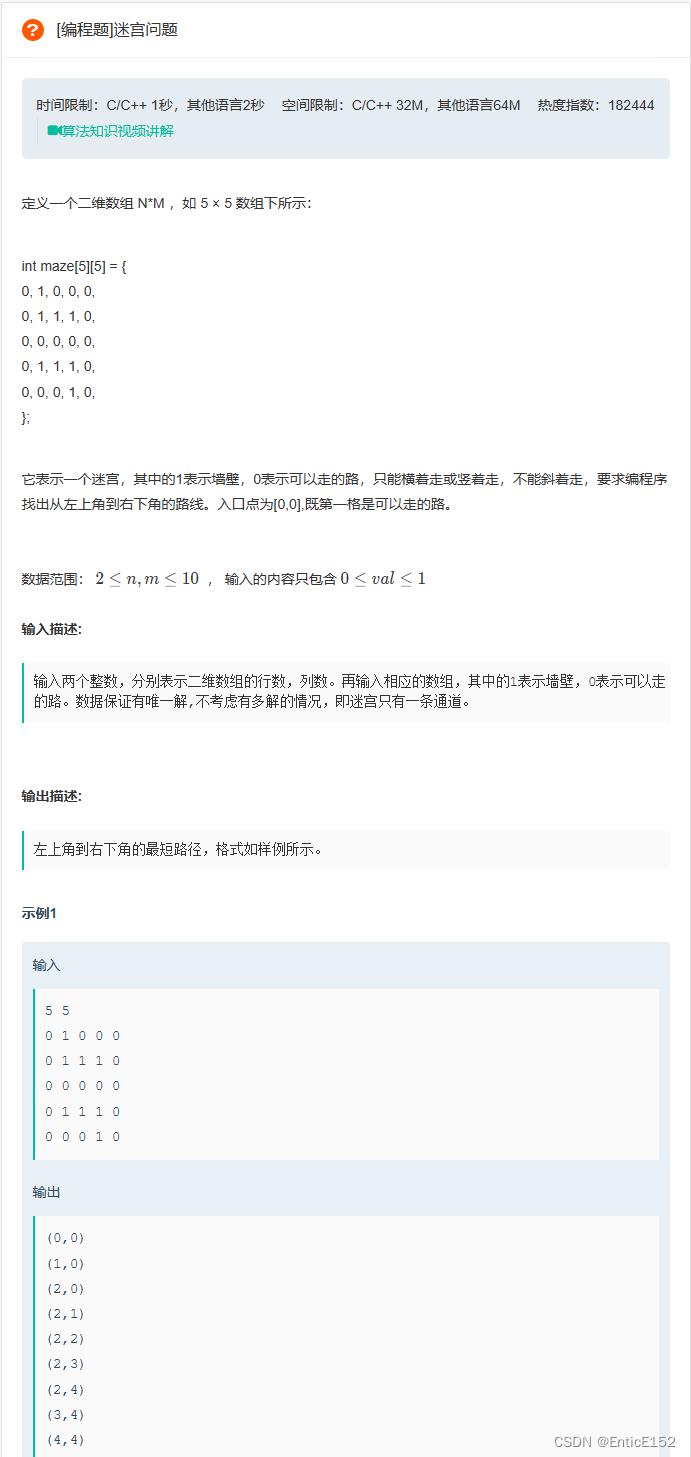
1.迷宫问题
2.迷宫最短路径问题
数据结构——迷宫问题求解::
1.迷宫问题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct Point
{int row;int col;
}PT;
typedef PT STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//数据结构建议不要直接访问结构体数据,一定要通过函数接口访问
//解耦:高内聚,低耦合
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!StackEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);//为空不能访问栈顶元素assert(!StackEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}
ST path;
void PrintPath(ST* ps)
{ST rPath;StackInit(&rPath);while (!StackEmpty(ps)){StackPush(&rPath, StackTop(ps));StackPop(ps);}while (!StackEmpty(&rPath)){PT top = StackTop(&rPath);printf("(%d,%d)\n", top.row, top.col);StackPop(&rPath);}StackDestory(&rPath);
}
bool IsPass(int** maze, int N, int M, PT pos)
{if (pos.row >= 0 && pos.row < N&& pos.col >= 0 && pos.col < M&& maze[pos.row][pos.col] == 0){return true;}else{return false;}
}
bool GetMazePath(int** maze, int N, int M, PT cur)
{StackPush(&path, cur);//如果走到出口if (cur.row == N - 1 && cur.col == M - 1){return true;}//探测cur位置上下左右四个方向PT next;maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 2;//探测上next = cur;next.row -= 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))return true;}//探测下next = cur;next.row += 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))return true;}//探测左next = cur;next.col -= 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))return true;}//探测右next = cur;next.col += 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))return true;}StackPop(&path);return false;
}
int main()
{int N = 0;int M = 0;while (scanf("%d %d", &N, &M) != EOF){//动态开辟二维数组int** maze = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){maze[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * M);}//二维数组的输入for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){for (int j = 0; j < M; j++){scanf("%d", &maze[i][j]);}}StackInit(&path);//PrintMaze(maze, N, M);PT entry = { 0,0 };if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, entry)){PrintPath(&path);}StackDestory(&path);//二维数组的销毁for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){free(maze[i]);maze[i] = NULL;}free(maze);maze = NULL;}return 0;
}2.迷宫最短路径问题


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct Point
{int row;int col;
}PT;
typedef PT STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//数据结构建议不要直接访问结构体数据,一定要通过函数接口访问
//解耦:高内聚,低耦合
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!StackEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);//为空不能访问栈顶元素assert(!StackEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}
ST path;
ST minPath;
void PrintPath(ST* ps)
{ST rPath;StackInit(&rPath);while (!StackEmpty(ps)){StackPush(&rPath, StackTop(ps));StackPop(ps);}while (StackSize(&rPath) > 1){PT top = StackTop(&rPath);printf("[%d,%d],", top.row, top.col);StackPop(&rPath);}PT top = StackTop(&rPath);printf("[%d,%d]\n", top.row, top.col);StackPop(&rPath);StackDestory(&rPath);
}
bool IsPass(int** maze, int N, int M, PT pos)
{if (pos.row >= 0 && pos.row < N&& pos.col >= 0 && pos.col < M&& maze[pos.row][pos.col] == 1){return true;}else{return false;}
}
void StackCopy(ST* ppath, ST* pcopy)
{pcopy->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * ppath->capacity);memcpy(pcopy->a, ppath->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ppath->top);pcopy->top = ppath->top;pcopy->capacity = ppath->capacity;
}
void GetMazePath(int** maze, int N, int M, PT cur, int P)
{StackPush(&path, cur);//如果走到出口if (cur.row == 0 && cur.col == M - 1){if (P >= 0 && StackEmpty(&minPath)|| StackSize(&path) < StackSize(&minPath)){StackDestory(&minPath);StackCopy(&path, &minPath);}}//探测cur位置上下左右四个方向PT next;maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 2;//探测上next = cur;next.row -= 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P - 3); }//探测下next = cur;next.row += 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P); }//探测左next = cur;next.col -= 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P - 1);}//探测右next = cur;next.col += 1;if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next)){GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P - 1);}maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 1;StackPop(&path);
}
int main()
{int N = 0;int M = 0;int P = 0;while (scanf("%d %d %d", &N, &M, &P) != EOF){//动态开辟二维数组int** maze = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){maze[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * M);}//二维数组的输入for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){for (int j = 0; j < M; j++){scanf("%d", &maze[i][j]);}}StackInit(&path);StackInit(&minPath);//PrintMaze(maze, N, M);PT entry = { 0,0 };GetMazePath(maze, N, M, entry, P);if (!StackEmpty(&minPath)){PrintPath(&minPath);}else{printf("Can not escape!\n");}StackDestory(&path);StackDestory(&minPath);//二维数组的销毁for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){free(maze[i]);maze[i] = NULL;}free(maze);maze = NULL;}return 0;
}


![[Java] 服务端消息推送汇总](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8835f3f4ddfe4a6e8dce02c4953924b5.png)