Netty P1 NIO 基础,网络编程
教程地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1py4y1E7oA
https://nyimac.gitee.io/2021/04/25/Netty%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/
1. 三大组件
1.1 Channel & Buffer
Channel 类似 Stream,它是读写数据的双向通道,可以从 Channel 将数据读入到 Buffer,也可以将 Buffer 的数据写入到 Channel 中;而 Stream 要么是输入,要么是输出。
常见的 Channel:
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
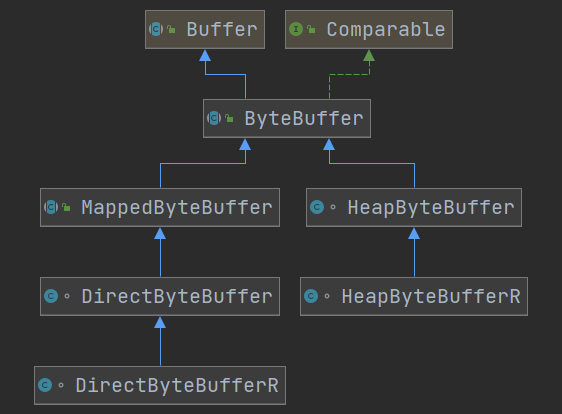
Buffer 用来缓冲读写数据,常见的 Buffer:
- ByteBuffer
- MappedByteBuffer
- DirectByteBuffer
- HeapByteBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- CharBuffer
1.2 Selector
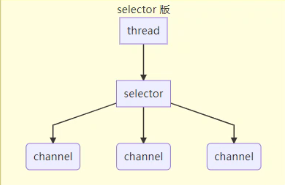
Selector 的作用就是配合一个线程来管理多个 Channel,获取这些 Channel 上发生的事件,这些 Channel 工作在非阻塞模式下,不会让线程吊死在一个 Channel 上。适合连接数特别多,但流量低的场景。
调用 Selector 的 select() 会阻塞直到 Channel 发生了读写就绪事件,这些事件发生,select 方法就会返回这些事件交给 Thread 来处理。
2. ByteBuffer
2.1 基本使用
- 向 Buffer 中写入数据,例如调用
channel.read(buffer)。 - 调用
buffer.filp()切换至读模式。 - 从 buffer 读取数据,例如调用
buffer.get()。 - 调用
buffer.clear()或者buffer.compact()切换至写模式。 - 重复 1~4 步骤。
@Slf4j
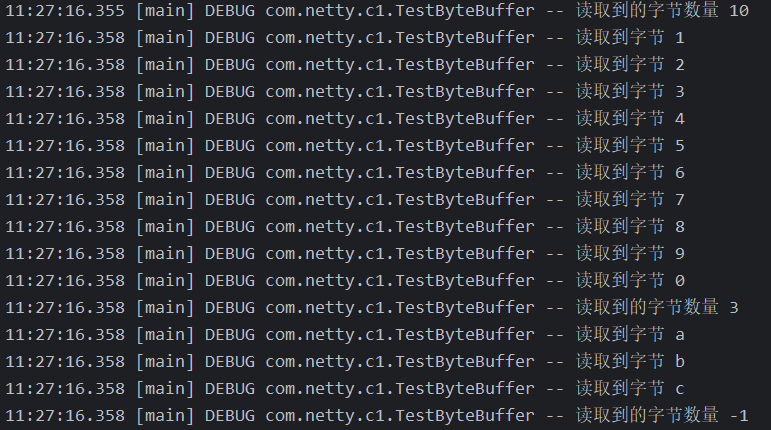
public class TestByteBuffer {public static void main(String[] args) {// FileChannel// 1. 输入输出流try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()) {// 准备缓冲区ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);// 从 Channel 读取数据,向 buffer 写入while (true) {int len = channel.read(buffer);log.debug("读取到的字节数量 {}", len);if (len == -1) {break;}// 切换读模式buffer.flip();while (buffer.hasRemaining()) { // 是否还有剩余未读数据byte b = buffer.get();log.debug("读取到字节 {}", (char) b);}// 切换至写模式buffer.clear();}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
2.2 结构
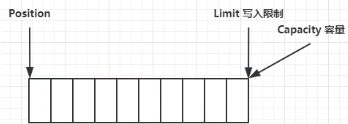
ByteBuffer 重要属性:
- capacity:缓冲区的容量。通过构造函数赋予,一旦设置,无法更改。
- position:下一个读写位置的索引(类似PC)。缓冲区的位置不能为负,并且不能大于 limit。
- limit:缓冲区的界限。位于limit 后的数据不可读写。缓冲区的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量。
- mark:记录当前 position 的值。position 被改变后,可以通过调用 reset() 方法恢复到 mark 的位置。
以上四个属性必须满足以下要求:
mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
初始状态:
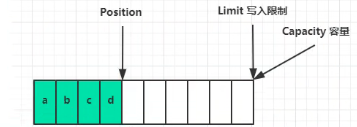
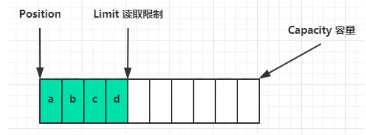
写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态:
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制:
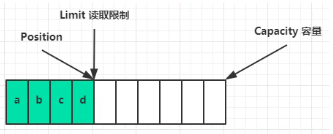
读取 4 个字节后,状态:
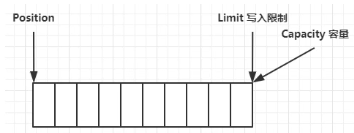
clear 动作发生后,状态:
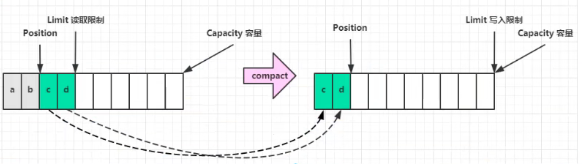
compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式:
2.3 方法演示
ByteBufferUtil 工具类
public class ByteBufferUtil {private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256];private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4];private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16];private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4];private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256];private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16];static {final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F];HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F];}int i;// Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddingsfor (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) {int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i;StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3);for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {buf.append(" ");}HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString();}// Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB).for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) {StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12);buf.append(StringUtil.NEWLINE);buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|');buf.append('|');HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString();}// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversionfor (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) {BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i);}// Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddingsfor (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) {int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i;StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding);for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {buf.append(' ');}BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString();}// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversionfor (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) {if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) {BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.';} else {BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i;}}}/*** 打印所有内容** @param buffer*/public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) {int oldlimit = buffer.limit();buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256);appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity());System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+");System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit);System.out.println(origin);buffer.limit(oldlimit);}/*** 打印可读取内容** @param buffer*/public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256);appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position());System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+");System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit());System.out.println(builder);}private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) {if (MathUtil.isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length+ ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')');}if (length == 0) {return;}dump.append(" +-------------------------------------------------+" +StringUtil.NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" +StringUtil.NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");final int startIndex = offset;final int fullRows = length >>> 4;final int remainder = length & 0xF;// Dump the rows which have 16 bytes.for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) {int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex;// Per-row prefix.appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex);// Hex dumpint rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16;for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);}dump.append(" |");// ASCII dumpfor (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);}dump.append('|');}// Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes.if (remainder != 0) {int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex;appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex);// Hex dumpint rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder;for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);}dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]);dump.append(" |");// Ascii dumpfor (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);}dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]);dump.append('|');}dump.append(StringUtil.NEWLINE +"+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");}private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) {if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) {dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]);} else {dump.append(StringUtil.NEWLINE);dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|');dump.append('|');}}public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) {return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);}
}
2.3.1 put 方法
用于向 Buffer 中写数据:
public class TestByteBufferReadWrite {public static void main(String[] args) {ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);buffer.put((byte) 0x61); // 'a'ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);buffer.put(new byte[]{'b', 'c', 'd'});ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);buffer.flip();System.out.println(buffer.get());ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);buffer.compact();ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);buffer.put(new byte[]{'e', 'f'});ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);}
}
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [1], limit: [10]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |a......... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [4], limit: [10]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 62 63 64 00 00 00 00 00 00 |abcd...... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
97
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [1], limit: [4]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 62 63 64 00 00 00 00 00 00 |abcd...... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [3], limit: [10]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
// compact 后下标为 3 的 position 位置的数据并不会清空,因为切换为写模式,写入的时候会直接覆盖
|00000000| 62 63 64 64 00 00 00 00 00 00 |bcdd...... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [10]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 62 63 64 65 66 00 00 00 00 00 |bcdef..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+2.3.2 分配空间 allocate
public class TestByteBufferReadWrite {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(ByteBuffer.allocate(10).getClass());System.out.println(ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10).getClass());}
}
class java.nio.HeapByteBuffer
class java.nio.DirectByteBuffer
java.nio.HeapByteBuffer:java 堆内存,读写效率较低,收到 GC 的影响java.nio.DirectByteBuffer:直接内存,读写效率高(少一次拷贝),不会受到 GC 的影响,分配效率低(因为要调用操作系统的方法),可能会造成内存泄漏
2.3.3 向 Buffer 写入数据
- 调用 channel 的 read 方法:
- 调用 buffer 自己的 put 方法
int len = channel.read(buffer); // 将 channel 内的数据读取到 buffer 中
buffer.put((byte) 127);
2.3.4 从 Buffer 读取数据
- 调用 channel 的 write 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 get 方法
int len = channel.write(buffer); // 将 buffer 中的内容写入到 channel 中
byte b = buffer.get();
get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据:
- 可以调用
rewind方法将 position 重新置为0 - 或者调用
get(int i)方法获取索引i的内容,它不会移动读指针
rewind() 使用:
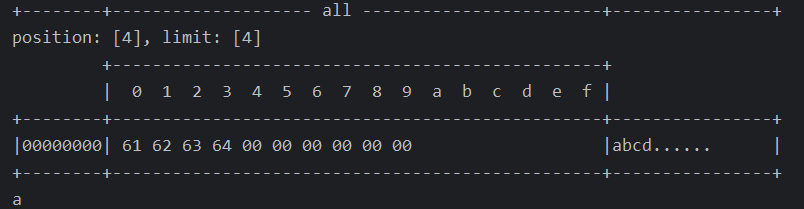
public class TestByteBufferRead {public static void main(String[] args) {ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);buffer.put("abcd".getBytes());buffer.flip(); // 切换到读模式// rewind 从头开始读buffer.get(new byte[buffer.limit()]);ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);buffer.rewind();System.out.println((char) buffer.get());}
}
get(int i) 使用:
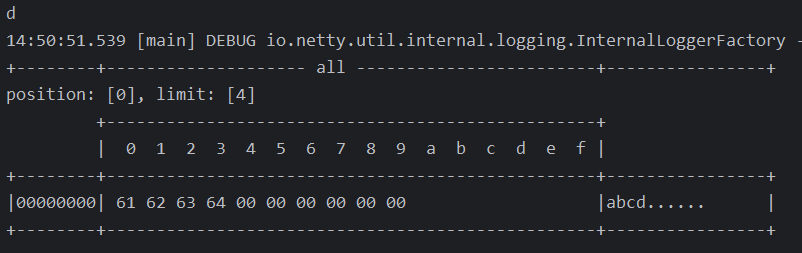
public class TestByteBufferRead {public static void main(String[] args) {ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);buffer.put("abcd".getBytes());buffer.flip(); // 切换到读模式System.out.println((char) buffer.get(3));ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);}
}
2.3.5 mark 和 reset
mark 做一个标记,记录 position 的位置,reset 是将 position 的位置重置到 mark 的位置。
public class TestByteBufferRead {public static void main(String[] args) {ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);buffer.put("abcd".getBytes());buffer.flip(); // 切换到读模式System.out.println((char) buffer.get());System.out.println((char) buffer.get());buffer.mark(); // 记录当前的position的值 2System.out.println((char) buffer.get());System.out.println((char) buffer.get());buffer.reset();// 将 position 置回到 2 这个位置System.out.println((char) buffer.get());System.out.println((char) buffer.get());}
}

2.3.6 字符串和 ByteBuffer 相互转换
public class TestByteBufferString {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 字符串转为 ByteBuffer, 使用后默认还是写模式ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);buffer1.put("hello".getBytes());ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);// 2. Charset,使用后直接切换为读模式ByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer2);// 3. wrap,使用后直接切换为读模式ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer3);// 4. Charset decode 将 buffer 转换为字符串String str1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString();System.out.println(str1);// 5. 因为没切换到读模式,所以什么都读取不到String str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();System.out.println(str2);}
}
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [16]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |hello...........|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]+-------------------------------------------------+| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
hello2.4 分散读,集中取
2.4.1 分散读
分散读取,有一个文本文件 words.txt
onetwothree
public class TestScatteringReads {public static void main(String[] args) {try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words.txt", "r").getChannel()) {ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);ByteBuffer b3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});b1.flip();b2.flip();b3.flip();ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(b1);ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(b2);ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(b3);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}

2.4.2 集中写
public class TestGatheringWrites {public static void main(String[] args) {ByteBuffer b1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");ByteBuffer b2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");ByteBuffer b3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好");try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words2.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
2.5 粘包半包分析
现象
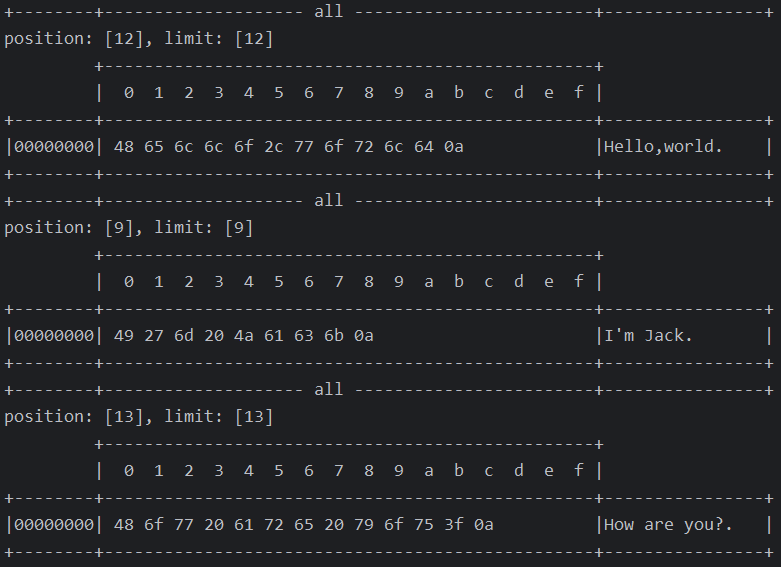
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔,但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有 3 条为:
Hello,world\nI’m Jack\nHow are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (粘包,半包)
Hello,world\nI’m Jack\nHow are you?\n
粘包
发送方在发送数据时,并不是一条一条地发送数据,而是将数据整合在一起(增加传输效率),当数据达到一定的数量后再一起发送。这就会导致多条信息被放在一个缓冲区中被一起发送出去。
半包
接收方的缓冲区的大小是有限的,当接收方的缓冲区满了以后,就需要将信息截断,等缓冲区空了以后再继续放入数据。这就会发生一段完整的数据最后被截断的现象。
解决办法
- 通过
get(index)方法遍历ByteBuffer,遇到分隔符时进行处理。注意:get(index)不会改变position的值- 记录该段数据长度,以便于申请对应大小的缓冲区
- 将缓冲区的数据通过
get()方法写入到target中
- 调用
compact方法切换模式,因为缓冲区中可能还有未读的数据
public class TestByteBufferExam {public static void main(String[] args) {ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);source.put("Hello,world\nI'm Jack\nHo".getBytes());split(source);source.put("w are you?\n".getBytes());split(source);}private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {source.flip();for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {// 找到一条完整消息if (source.get(i) == '\n') {int length = i + 1 - source.position();// 将完整消息存入到新的 ByteBuffer 对象中ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);// 从 source 读,向 target 写for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {target.put(source.get());}ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(target);}}source.compact();}
}
3. 网络编程
3.1 阻塞 vs 非阻塞
3.1.1 阻塞

Server:
@Slf4j
public class Server {@SneakyThrowspublic static void main(String[] args) {// 使用 nio 来理解阻塞模式,单线程// 0. ByteBufferByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);// 1. 创建服务器ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();// 2. 绑定端口ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));// 3. 连接集合List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();while (true) {// 4. accept 建立与客户端的连接,SocketChannel 用来与客户端之间通信log.debug("等待客户端连接...");SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept(); // 阻塞方法,线程停止运行,直到建立连接log.debug("客户端连接成功!!!, {}", sc);channels.add(sc);for (SocketChannel channel : channels) {// 5. 接受客户端发送的数据log.debug("等待客户端发送数据..., {}", channel);channel.read(buffer); // 阻塞方法,线程停止运行,直到客户端发送新的数据buffer.flip();ByteBufferUtil.debugRead(buffer);buffer.clear();log.debug("客户端发送数据成功!!!, {}", channel);}}}
}
客户端:
public class Client {@SneakyThrowspublic static void main(String[] args) {SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));sc.write(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello"));System.out.println("waiting。。。。");sc.close();}
}
3.1.2 非阻塞
- 可以通过
ServerSocketChannel的configureBlocking(false)方法将获得连接设置为非阻塞的。此时若没有连接,accept会返回null。 - 可以通过
SocketChannel的configureBlocking(false)方法将从通道中读取数据设置为非阻塞的。若此时通道中没有数据可读,read会返回-1。
@Slf4j
public class Server {@SneakyThrowspublic static void main(String[] args) {// 使用 nio 来理解阻塞模式,单线程// 0. ByteBufferByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);// 1. 创建服务器ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();// 2. 绑定端口ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));// 3. 连接集合List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();while (true) {// 4. accept 建立与客户端的连接,SocketChannel 用来与客户端之间通信log.debug("等待客户端连接...");// 设置为非阻塞模式,没有连接时返回null,不会阻塞线程ssc.configureBlocking(false);SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();if (sc != null) {log.debug("客户端连接成功!!!, {}", sc);channels.add(sc);}for (SocketChannel channel : channels) {// 5. 接受客户端发送的数据log.debug("等待客户端发送数据..., {}", channel);// 设置为非阻塞模式,若通道中没有数据,会返回0,不会阻塞线程channel.configureBlocking(false);int read = channel.read(buffer);if (read > 0) {buffer.flip();ByteBufferUtil.debugRead(buffer);buffer.clear();log.debug("客户端发送数据成功!!!, {}", channel);}}}}
}
这样写存在一个问题,因为设置为了非阻塞,会一直执行 while(true) 中的代码,CPU一直处于忙碌状态,会使得性能变低,所以实际情况中不使用这种方法处理请求。
3.1.3 Selector 处理 accept
多路复用
单线程可以配合 Selector 完成对多个 Channel 可读写事件的监控,这称之为多路复用。
- 多路复用仅针对网络 IO,普通文件 IO 无法利用多路复用
- 如果不用 Selector 的非阻塞模式,线程大部分时间都在做无用功,而 Selector 能够保证
- 有可连接事件时才去连接
- 有可读事件才去读取
- 有可写事件才去写入(限于网络传输能力,
Channel未必时时可写,一旦Channel可写,会触发Selector的可写事件)
@Slf4j
public class Server {@SneakyThrowspublic static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 创建 selector,管理多个 channelSelector selector = Selector.open();ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();ssc.configureBlocking(false);// 2. 建立 selector 和 channel 的联系(注册)// selectionKey:时间发生后,通过它可以知道事件和哪个 channel 的事件// OP_ACCEPT 表示只关注 accept 事件SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);log.debug("注册 key: {}", sscKey);ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();while (true) {// 3. select 方法,没有事件发生,线程阻塞,有事件,线程才会恢复运行// select 在事件未处理时,不会阻塞;事件发生后要么处理,要么取消,不能置之不理selector.select();// 4. 处理事件, selectedKeys 内部包含了所有发生的事件Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();while (iter.hasNext()) {SelectionKey key = iter.next();log.debug("key: {}", key);ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();log.debug("{}", sc);// key.cancel();}}}
}
3.1.4 处理 read 事件
@Slf4j
public class Server {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1. 创建 selector,管理多个 channelSelector selector = Selector.open();ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();ssc.configureBlocking(false);// 2. 建立 selector 和 channel 的联系(注册)// selectionKey:时间发生后,通过它可以知道事件和哪个 channel 的事件// OP_ACCEPT 表示只关注 accept 事件SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);log.debug("注册 key: {}", sscKey);ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();while (true) {// 3. select 方法,没有事件发生,线程阻塞,有事件,线程才会恢复运行// select 在事件未处理时,不会阻塞;事件发生后要么处理,要么取消,不能置之不理selector.select();// 4. 处理事件, selectedKeys 内部包含了所有发生的事件Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();while (iter.hasNext()) {SelectionKey key = iter.next();// 当处理完一个事件后,一定要调用迭代器的remove方法移除对应事件,否则会出现错误。iter.remove();log.debug("key: {}", key);// 5. 区分事件类型if (key.isAcceptable()) {ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();sc.configureBlocking(false);sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);log.debug("{}", sc);} else if (key.isReadable()) {try {SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);// 正常断开返回 -1int read = channel.read(buffer);if (read == -1) {key.cancel();} else if (read > 0) {buffer.flip();ByteBufferUtil.debugRead(buffer);buffer.clear();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();// 因为客户端断开了,因此需要将 key 取消(从 selector 的 keys 集合中真正删除 key)key.cancel();}}}}}
}