基本概念

反射中的四个类

Class类
Java文件在被编译之后,生成了.class文件,JVM此时解读.class文件,将其解析为java.lang.Class
对象,在程序运行时每个java文件就最终变成了Class类对象的一个实例。通过反射机制应用这个
实例就可以获得甚至添加这个类的属性和动作。
方法
获得类相关方法
| 方法 | 用途 |
| getClassLoader() | 获得类的加载器 |
| getDeclaredClasses() | 返回一个数组,数组中包含该类中所有类和接口类的对象(包括私有的) |
| forName(String className) | 根据类名返回类的对象 |
| newInstance() | 创建类的实例 |
| getName() | 获得类的完整路径的名字 |
获得类属性的方法
| 方法 | 用途 |
| getField(String name) | 获得某个公有的属性对象 |
| getFields() | 获得所有公有的属性对象 |
| getDeclaredField(String name) | 获得某个属性对象 |
| getDeclaredFields() | 获得所有属性对象 |
获得类中构造器相关的方法
| 方法 | 用途 |
| getConstructor(Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类中与参数类型匹配的公有构造方法 |
| getConstructors() | 获得该类的所有公有构造方法 |
| getDeclaredConstructor(Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类中与参数类型匹配的构造方法 |
| getDeclaredConstructors() | 获得该类所有构造方法 |
获得类中方法相关的方法
| 方法 | 用途 |
| getMethod(String name, Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类某个公有的方法 |
| getMethods() | 获得该类所有公有的方法 |
| getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类某个方法 |
| getDeclaredMethods() | 获得该类所有方法 |
加了Declared就可以获得不只是公有的对象,还能获得私有的等等
获取Class对象的三种方式
1.使用Class.forName("类的全路径名")
2.使用.class方法
3.使用类对象的getClass()方法
class Student {//私有属性nameprivate String name = "bit";//公有属性agepublic int age = 18;//不带参数的构造方法public Student(){System.out.println("Student()");}private Student(String name,int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;System.out.println("Student(String,name)");}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
public class Test {/*Class对象 只有一个*/public static void main(String[] args) {Class<?> c1 = null;try {c1 = Class.forName("demo1.Student");} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}Class<?> c2 = Student.class;Student student = new Student();Class<?> c3 = student.getClass();System.out.println(c1 == c2);System.out.println(c1 == c3);}
}
反射的使用
接下来我们开始使用反射,我们依旧反射上面的Student类,把反射的逻辑写到另外的类当中进行理解
创建对象
public class ReflectClassDemo {public static void reflectNewInstance() {Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("demo1.Student");Student student = (Student)classStudent.newInstance();System.out.println(student);}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);//newInstance 是受查异常,要加多这一行进行排查} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}} ![]()
反射私有的构造方法,并根据构造方法修改类的私有变量
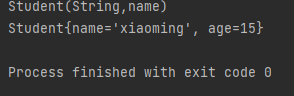
public static void reflectPrivateConstructor() {Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("demo1.Student");//获得构造方法Constructor<?> constructor = classStudent.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);//根据Student类的构造方法来修改name和age变量Student student = (Student)constructor.newInstance("xiaoming",15);System.out.println(student);}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);//newInstance 是受查异常,要加多这两行进行排查} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}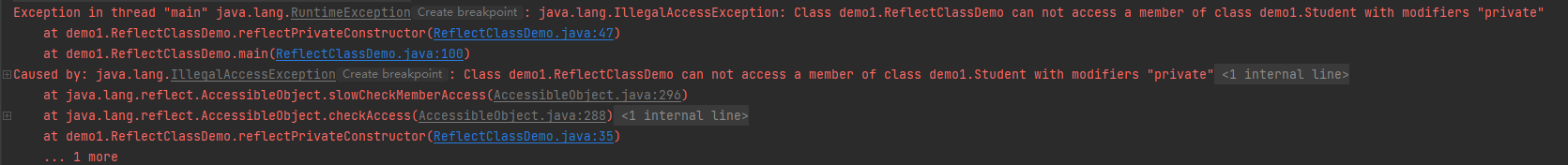
Constructor<?> constructor = classStudent.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
在这一行中我们要访问Student私有的成员变量,但是程序不知道我们要这么干就直接阻拦报错,所以我们需要写下面这行代码告诉系统我们确实要这么干。
constructor.setAccessible(true);
反射私有属性(不用构造方法直接修改私有属性的值)
public static void reflectPrivateField() {Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("demo1.Student");Field field = classStudent.getDeclaredField("name");field.setAccessible(true);Student student = (Student)classStudent.newInstance();field.set(student,"caocao");System.out.println(student);}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}反射私有方法
public static void reflectPrivateMethod() {Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("demo1.Student");Method method = classStudent.getDeclaredMethod("function",String.class);method.setAccessible(true);Student student = (Student)classStudent.newInstance();method.invoke(student,"我是一个反射的参数!");}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}总结
优点:
1. 对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法 2. 增加程序的灵活性和扩展性,降低耦合性,提高自适应能力
3. 反射已经运用在了很多流行框架如: Struts、 Hibernate、Spring 等等。
缺点:
1. 使用反射会有效率问题。会导致程序效率降低。具体参考这里: 大家都说 Java 反射效率低,你知道原因在哪里么_慕课手记 2. 反射技术绕过了源代码的技术,因而会带来维护问题。反射代码比相应的直接代码更复杂 。