Sentinel基础知识
资源
1、官方网址:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/
2、os-china: https://www.oschina.net/p/sentinel?hmsr=aladdin1e1
3、github: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel
一、软件简介
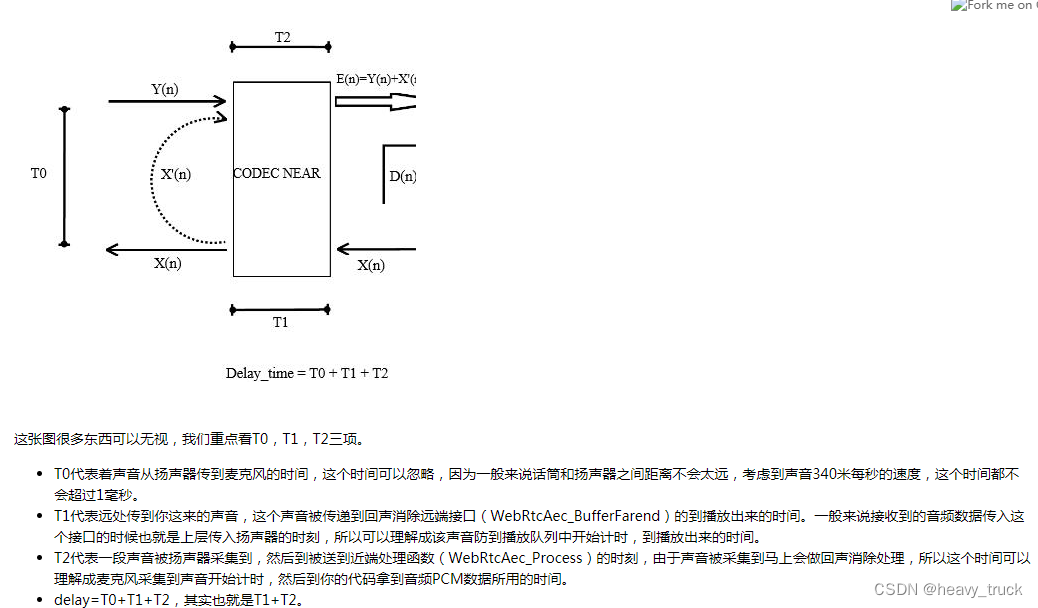
Sentinel 是面向分布式服务架构的高可用流量防护组件,主要以流量为切入点,从限流、流量整形、熔断降级、系统负载保护、热点防护等多个维度来帮助开发者保障微服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 具有以下特性:
- 丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
- 完备的实时监控:Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
- 广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架 / 库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
- 完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展接口。您可以通过实现扩展接口来快速地定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等。
Sentinel 的开源生态:
Sentinel 的历史
- 2012 年,Sentinel 诞生,主要功能为入口流量控制。
- 2013-2017 年,Sentinel 在阿里巴巴集团内部迅速发展,成为基础技术模块,覆盖了所有的核心场景。Sentinel 也因此积累了大量的流量归整场景以及生产实践。
- 2018 年,Sentinel 开源,并持续演进。
- 2019 年,Sentinel 朝着多语言扩展的方向不断探索,推出 C++ 原生版本,同时针对 Service Mesh 场景也推出了 Envoy 集群流量控制支持,以解决 Service Mesh 架构下多语言限流的问题。
- 2020 年,推出 Sentinel Go 版本,继续朝着云原生方向演进。
Sentinel 基本概念
资源
资源是 Sentinel 的关键概念。它可以是 Java 应用程序中的任何内容,例如,由应用程序提供的服务,或由应用程序调用的其它应用提供的服务,甚至可以是一段代码。在接下来的文档中,我们都会用资源来描述代码块。
只要通过 Sentinel API 定义的代码,就是资源,能够被 Sentinel 保护起来。大部分情况下,可以使用方法签名,URL,甚至服务名称作为资源名来标示资源。
规则
围绕资源的实时状态设定的规则,可以包括流量控制规则、熔断降级规则以及系统保护规则。所有规则可以动态实时调整。
Sentinel 功能和设计理念
流量控制
什么是流量控制
流量控制在网络传输中是一个常用的概念,它用于调整网络包的发送数据。然而,从系统稳定性角度考虑,在处理请求的速度上,也有非常多的讲究。任意时间到来的请求往往是随机不可控的,而系统的处理能力是有限的。我们需要根据系统的处理能力对流量进行控制。Sentinel 作为一个调配器,可以根据需要把随机的请求调整成合适的形状,如下图所示:
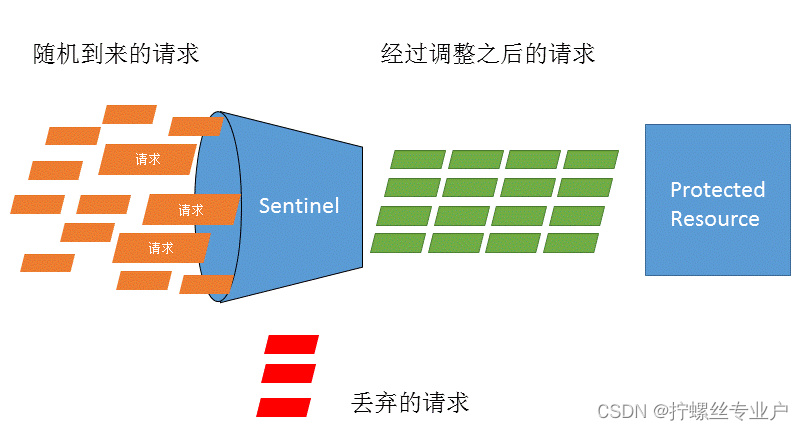
流量控制设计理念
流量控制有以下几个角度:
- 资源的调用关系,例如资源的调用链路,资源和资源之间的关系;
- 运行指标,例如 QPS、线程池、系统负载等;
- 控制的效果,例如直接限流、冷启动、排队等。
Sentinel 的设计理念是让您自由选择控制的角度,并进行灵活组合,从而达到想要的效果。
熔断降级
什么是熔断降级
除了流量控制以外,及时对调用链路中的不稳定因素进行熔断也是 Sentinel 的使命之一。由于调用关系的复杂性,如果调用链路中的某个资源出现了不稳定,可能会导致请求发生堆积,进而导致级联错误。
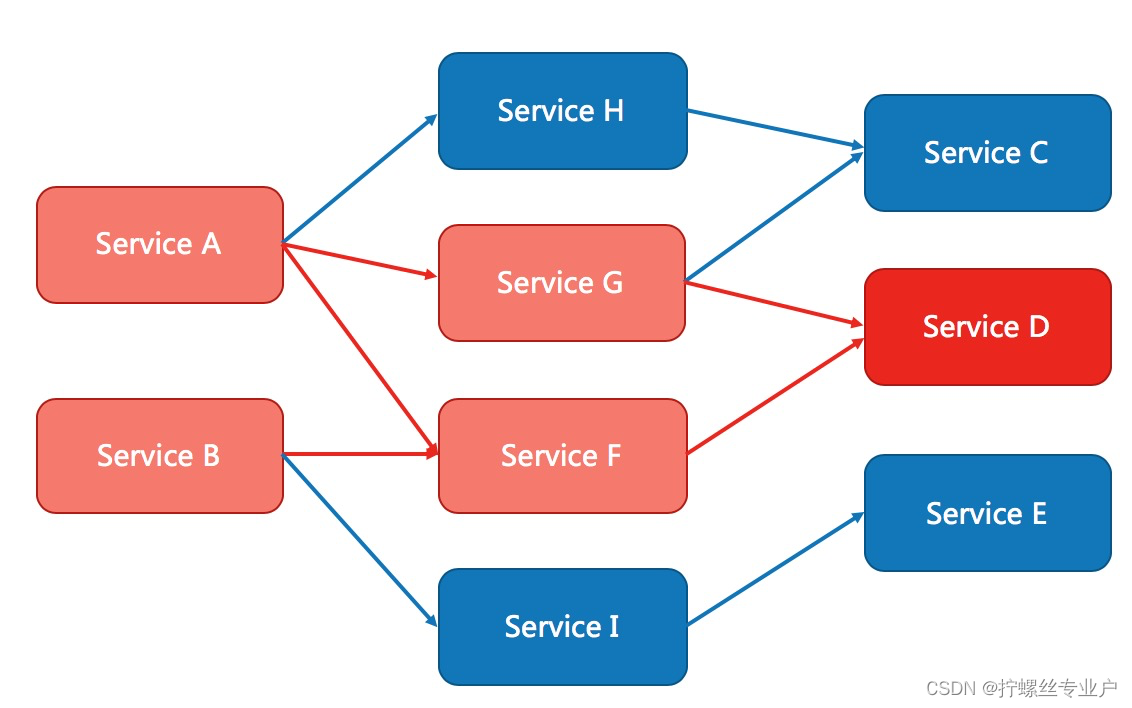
Sentinel 和 Hystrix 的原则是一致的:当检测到调用链路中某个资源出现不稳定的表现,例如请求响应时间长或异常比例升高的时候,则对这个资源的调用进行限制,让请求快速失败,避免影响到其它的资源而导致级联故障。
熔断降级设计理念
在限制的手段上,Sentinel 和 Hystrix 采取了完全不一样的方法。
Hystrix 通过 线程池隔离 的方式,来对依赖(在 Sentinel 的概念中对应 资源)进行了隔离。这样做的好处是资源和资源之间做到了最彻底的隔离。缺点是除了增加了线程切换的成本(过多的线程池导致线程数目过多),还需要预先给各个资源做线程池大小的分配,并且对于一些使用了 ThreadLocal 的场景来说会有问题(如 Spring 事务)。
Sentinel 对这个问题采取了两种手段:
- 通过并发线程数进行限制
和资源池隔离的方法不同,Sentinel 通过限制资源并发线程的数量,来减少不稳定资源对其它资源的影响。这样不但没有线程切换的损耗,也不需要您预先分配线程池的大小。当某个资源出现不稳定的情况下,例如响应时间变长,对资源的直接影响就是会造成线程数的逐步堆积。当线程数在特定资源上堆积到一定的数量之后,对该资源的新请求就会被拒绝。堆积的线程完成任务后才开始继续接收请求。
- 针对慢调用和异常对资源进行降级
除了对并发线程数进行控制以外,Sentinel 还可以根据响应时间和异常等不稳定因素来快速对不稳定的调用进行熔断。当依赖的资源出现响应时间过长后,所有对该资源的访问都会被直接拒绝,直到过了指定的时间窗口之后才重新渐进式地恢复。
系统自适应保护
Sentinel 同时提供系统维度的自适应保护能力。防止雪崩,是系统防护中重要的一环。当系统负载较高的时候,如果还持续让请求进入,可能会导致系统崩溃,无法响应。在集群环境下,网络负载均衡会把本应这台机器承载的流量转发到其它的机器上去。如果这个时候其它的机器也处在一个边缘状态的时候,这个增加的流量就会导致这台机器也崩溃,最后导致整个集群不可用。
针对这个情况,Sentinel 提供了对应的保护机制,让系统的入口流量和系统的负载达到一个平衡,保证系统在能力范围之内处理最多的请求。
Sentinel 是如何工作的
Sentinel 的主要工作机制如下:
- 对主流框架提供适配或者显示的 API,来定义需要保护的资源,并提供设施对资源进行实时统计和调用链路分析。
- 根据预设的规则,结合对资源的实时统计信息,对流量进行控制。同时,Sentinel 提供开放的接口,方便您定义及改变规则。
- Sentinel 提供实时的监控系统,方便您快速了解目前系统的状态。
二、快速开始
参考资料:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html
1. 引入 Sentinel 依赖
如果您的应用使用了 Maven,则在 pom.xml 文件中加入以下代码即可:
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId><artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId><version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
如果您未使用依赖管理工具,请到 Maven Center Repository 直接下载 JAR 包。
2. 定义资源
资源 是 Sentinel 中的核心概念之一。最常用的资源是我们代码中的 Java 方法。 当然,您也可以更灵活的定义你的资源,例如,把需要控制流量的代码用 Sentinel API SphU.entry("HelloWorld") 和 entry.exit() 包围起来即可。在下面的例子中,我们将 System.out.println("hello world"); 作为资源(被保护的逻辑),用 API 包装起来。参考代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {// 配置规则.initFlowRules();while (true) {// 1.5.0 版本开始可以直接利用 try-with-resources 特性try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("HelloWorld")) {// 被保护的逻辑System.out.println("hello world");} catch (BlockException ex) {// 处理被流控的逻辑System.out.println("blocked!");}}
}
完成以上两步后,代码端的改造就完成了。
您也可以通过我们提供的 注解支持模块,来定义我们的资源,类似于下面的代码:
@SentinelResource("HelloWorld")
public void helloWorld() {// 资源中的逻辑System.out.println("hello world");
}
这样,helloWorld() 方法就成了我们的一个资源。注意注解支持模块需要配合 Spring AOP 或者 AspectJ 一起使用。
3. 定义规则
接下来,通过流控规则来指定允许该资源通过的请求次数,例如下面的代码定义了资源 HelloWorld 每秒最多只能通过 20 个请求。
private static void initFlowRules(){List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();rule.setResource("HelloWorld");rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);// Set limit QPS to 20.rule.setCount(20);rules.add(rule);FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
完成上面 3 步,Sentinel 就能够正常工作了。更多的信息可以参考 使用文档。
4. 检查效果
Demo 运行之后,我们可以在日志 ~/logs/csp/${appName}-metrics.log.xxx 里看到下面的输出:
|--timestamp-|------date time----|--resource-|p |block|s |e|rt
1529998904000|2018-06-26 15:41:44|hello world|20|0 |20|0|0
1529998905000|2018-06-26 15:41:45|hello world|20|5579 |20|0|728
1529998906000|2018-06-26 15:41:46|hello world|20|15698|20|0|0
1529998907000|2018-06-26 15:41:47|hello world|20|19262|20|0|0
1529998908000|2018-06-26 15:41:48|hello world|20|19502|20|0|0
1529998909000|2018-06-26 15:41:49|hello world|20|18386|20|0|0
其中 p 代表通过的请求, block 代表被阻止的请求, s 代表成功执行完成的请求个数, e 代表用户自定义的异常, rt 代表平均响应时长。
可以看到,这个程序每秒稳定输出 “hello world” 20 次,和规则中预先设定的阈值是一样的。
更详细的说明可以参考: 如何使用
更多的例子可以参考: Sentinel Demo 集锦
5. 启动 Sentinel 控制台
Sentinel 开源控制台支持实时监控和规则管理。接入控制台的步骤如下:
(1)下载控制台 jar 包并在本地启动:可以参见 此处文档。
(2)客户端接入控制台,需要:
- 客户端需要引入 Transport 模块来与 Sentinel 控制台进行通信。您可以通过
pom.xml引入 JAR 包:
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId><artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId><version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
- 启动时加入 JVM 参数
-Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=consoleIp:port指定控制台地址和端口。更多的参数参见 启动参数文档。 - 确保应用端有访问量
完成以上步骤后即可在 Sentinel 控制台上看到对应的应用,机器列表页面可以看到对应的机器:
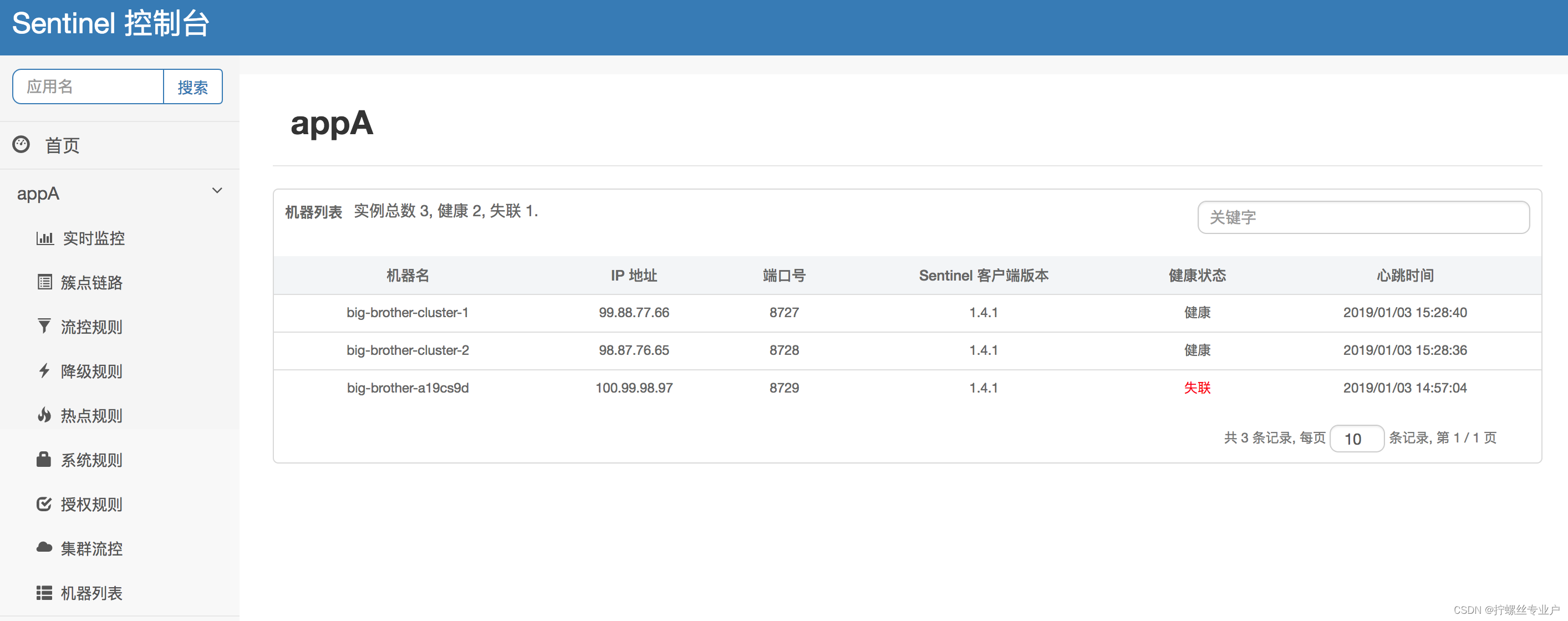
详细介绍和使用文档可参考:Sentinel 控制台文档。
三、Sentinel 核心类解析
ProcessorSlotChain
Sentinel 的核心骨架,将不同的 Slot 按照顺序串在一起(责任链模式),从而将不同的功能(限流、降级、系统保护)组合在一起。slot chain 其实可以分为两部分:统计数据构建部分(statistic)和判断部分(rule checking)。核心结构:
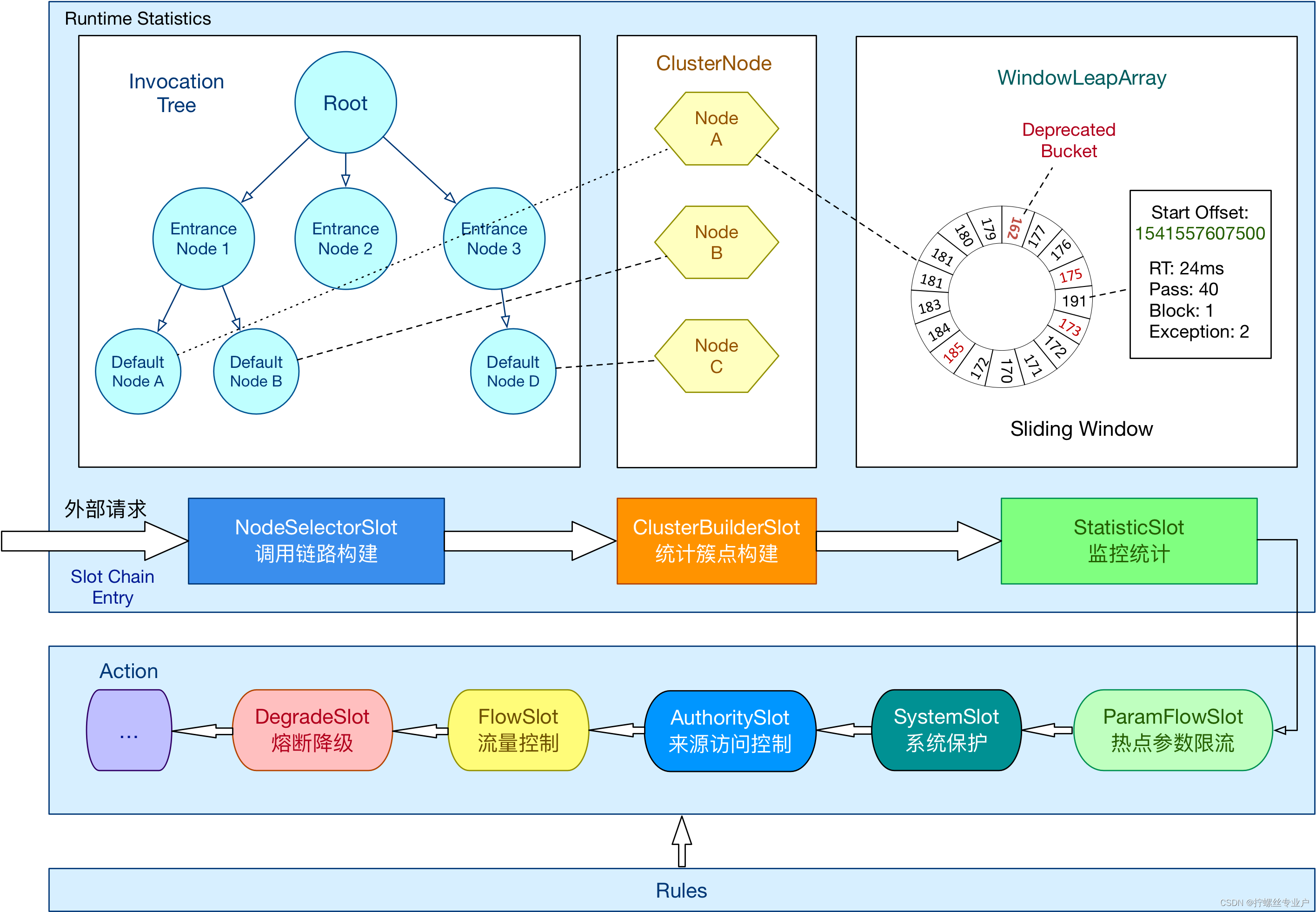
目前的设计是 one slot chain per resource,因为某些 slot 是 per resource 的(比如 NodeSelectorSlot)。
Context
Context 代表调用链路上下文,贯穿一次调用链路中的所有 Entry。Context 维持着入口节点(entranceNode)、本次调用链路的 curNode、调用来源(origin)等信息。Context 名称即为调用链路入口名称。
Context 维持的方式:通过 ThreadLocal 传递,只有在入口 enter 的时候生效。由于 Context 是通过 ThreadLocal 传递的,因此对于异步调用链路,线程切换的时候会丢掉 Context,因此需要手动通过 ContextUtil.runOnContext(context, f) 来变换 context。
Entry
每一次资源调用都会创建一个 Entry。Entry 包含了资源名、curNode(当前统计节点)、originNode(来源统计节点)等信息。
CtEntry 为普通的 Entry,在调用 SphU.entry(xxx) 的时候创建。特性:Linked entry within current context(内部维护着 parent 和 child)
需要注意的一点:CtEntry 构造函数中会做调用链的变换,即将当前 Entry 接到传入 Context 的调用链路上(setUpEntryFor)。
资源调用结束时需要 entry.exit()。exit 操作会过一遍 slot chain exit,恢复调用栈,exit context 然后清空 entry 中的 context 防止重复调用。
Node
Sentinel 里面的各种种类的统计节点:
StatisticNode:最为基础的统计节点,包含秒级和分钟级两个滑动窗口结构。DefaultNode:链路节点,用于统计调用链路上某个资源的数据,维持树状结构。ClusterNode:簇点,用于统计每个资源全局的数据(不区分调用链路),以及存放该资源的按来源区分的调用数据(类型为StatisticNode)。特别地,Constants.ENTRY_NODE节点用于统计全局的入口资源数据。EntranceNode:入口节点,特殊的链路节点,对应某个 Context 入口的所有调用数据。Constants.ROOT节点也是入口节点。
构建的时机:
EntranceNode在ContextUtil.enter(xxx)的时候就创建了,然后塞到 Context 里面。NodeSelectorSlot:根据 context 创建DefaultNode,然后 set curNode to context。ClusterBuilderSlot:首先根据 resourceName 创建ClusterNode,并且 set clusterNode to defaultNode;然后再根据 origin 创建来源节点(类型为StatisticNode),并且 set originNode to curEntry。
几种 Node 的维度(数目):
ClusterNode的维度是 resourceDefaultNode的维度是 resource * context,存在每个 NodeSelectorSlot 的map里面EntranceNode的维度是 context,存在 ContextUtil 类的contextNameNodeMap里面- 来源节点(类型为
StatisticNode)的维度是 resource * origin,存在每个 ClusterNode 的originCountMap里面
StatisticSlot
StatisticSlot 是 Sentinel 最为重要的类之一,用于根据规则判断结果进行相应的统计操作。
entry 的时候:依次执行后面的判断 slot。每个 slot 触发流控的话会抛出异常(BlockException 的子类)。若有 BlockException 抛出,则记录 block 数据;若无异常抛出则算作可通过(pass),记录 pass 数据。
exit 的时候:若无 error(无论是业务异常还是流控异常),记录 complete(success)以及 RT,线程数-1。
记录数据的维度:线程数+1、记录当前 DefaultNode 数据、记录对应的 originNode 数据(若存在 origin)、累计 IN 统计数据(若流量类型为 IN)。
四、核心代码阅读
1、DefaultController
下面加载rule的代码会创建流量控制器:
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules); // ref-1 来源于示例代码
创建的控制器如下所示:
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleUtil.java 文件private static TrafficShapingController generateRater(/*@Valid*/ FlowRule rule) {// 判断流控级别if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {switch (rule.getControlBehavior()) {case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP:return new WarmUpController(rule.getCount(), rule.getWarmUpPeriodSec(),ColdFactorProperty.coldFactor);case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER:return new RateLimiterController(rule.getMaxQueueingTimeMs(), rule.getCount());case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP_RATE_LIMITER:return new WarmUpRateLimiterController(rule.getCount(), rule.getWarmUpPeriodSec(),rule.getMaxQueueingTimeMs(), ColdFactorProperty.coldFactor);case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT:default:// Default mode or unknown mode: default traffic shaping controller (fast-reject).}}// 示例代码会创建默认的控制器return new DefaultController(rule.getCount(), rule.getGrade()); // ref-2
}
我们来看看默认的控制器里面都有什么?
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.DefaultController.java文件package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller;/*** Default throttling controller (immediately reject strategy).** @author jialiang.linjl* @author Eric Zhao*/
public class DefaultController implements TrafficShapingController {private static final int DEFAULT_AVG_USED_TOKENS = 0;private double count;private int grade;public DefaultController(double count, int grade) {this.count = count;this.grade = grade;}// 在示例代码的 SphU.entry("HelloWorld") 处会调用到这儿来@Overridepublic boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount) { // ref-3return canPass(node, acquireCount, false);}@Overridepublic boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);if (curCount + acquireCount > count) {if (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {long currentTime;long waitInMs;currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count);if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) {node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount);node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount);sleep(waitInMs);// PriorityWaitException indicates that the request will pass after waiting for {@link @waitInMs}.throw new PriorityWaitException(waitInMs);}}return false;}return true;}private int avgUsedTokens(Node node) { // ref-4 关键点:获取已经使用多的令牌if (node == null) {return DEFAULT_AVG_USED_TOKENS;}// node.passQps()底层使用滑动窗口计算当前每秒通过次数return grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD ? node.curThreadNum() : (int)(node.passQps());}private void sleep(long timeMillis) {try {Thread.sleep(timeMillis);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// Ignore.}}
}2、FlowSlot
Sentinal中的功能是由一个个插槽实现的,其中一个重要的插槽就是FlowSlot,代码如下所示:
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowSlot.java文件package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow;@Spi(order = Constants.ORDER_FLOW_SLOT)
public class FlowSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {private final FlowRuleChecker checker;public FlowSlot() {this(new FlowRuleChecker());}/*** Package-private for test.** @param checker flow rule checker* @since 1.6.1*/FlowSlot(FlowRuleChecker checker) {AssertUtil.notNull(checker, "flow checker should not be null");this.checker = checker;}// ref-5 在示例代码的 SphU.entry("HelloWorld") 处会调用到这儿来@Overridepublic void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);}void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized)throws BlockException {checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized); // ref-6}@Overridepublic void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);}private final Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider = new Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>>() {@Overridepublic Collection<FlowRule> apply(String resource) {// Flow rule map should not be null.Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap();return flowRules.get(resource);}};
}ref-6处的代码实际调用的地方如下所示:
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleChecker.java文件package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow;/*** Rule checker for flow control rules.** @author Eric Zhao*/
public class FlowRuleChecker {public void checkFlow(Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource,Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException {if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null) {return;}Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName());if (rules != null) {for (FlowRule rule : rules) {if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) {throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);}}}}public boolean canPassCheck(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node,int acquireCount) {return canPassCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, false);}public boolean canPassCheck(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,boolean prioritized) {String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();if (limitApp == null) {return true;}if (rule.isClusterMode()) {return passClusterCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);}return passLocalCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);}private static boolean passLocalCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,boolean prioritized) {Node selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node);if (selectedNode == null) {return true;}// 这儿会调用到上面创建的DefaultControllerreturn rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized);}// ....省略其他的代码
}
3、ProcessorSlotChain
接下来我们再看下把这些插槽串起来的ProcessorSlotChain类,代码如下:
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slotchain.ProcessorSlotChain.java文件package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slotchain;/*** Link all processor slots as a chain.** @author qinan.qn*/
public abstract class ProcessorSlotChain extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<Object> {/*** Add a processor to the head of this slot chain.** @param protocolProcessor processor to be added.*/public abstract void addFirst(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> protocolProcessor);/*** Add a processor to the tail of this slot chain.** @param protocolProcessor processor to be added.*/public abstract void addLast(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> protocolProcessor);
}Sentinel中提供了一个默认的实现,如下所示:
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slotchain.DefaultProcessorSlotChain.java文件package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slotchain;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.context.Context;/*** @author qinan.qn* @author jialiang.linjl*/
public class DefaultProcessorSlotChain extends ProcessorSlotChain {AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> first = new AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<Object>() {@Overridepublic void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)throws Throwable {super.fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);}@Overridepublic void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {super.fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);}};AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> end = first;@Overridepublic void addFirst(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> protocolProcessor) {protocolProcessor.setNext(first.getNext());first.setNext(protocolProcessor);if (end == first) {end = protocolProcessor;}}@Overridepublic void addLast(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> protocolProcessor) {end.setNext(protocolProcessor);end = protocolProcessor;}/*** Same as {@link #addLast(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot)}.** @param next processor to be added.*/@Overridepublic void setNext(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> next) {addLast(next);}@Overridepublic AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> getNext() {return first.getNext();}@Overridepublic void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)throws Throwable {first.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);}@Overridepublic void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {first.exit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);}}
其实就是构建了一个单向链表,把各个插槽(Slot)串起来了,并且这个单向链表有头、尾指针。
4、StatisticNode
这个是最基础的统计节点,代码如下所示:
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.node.StatisticNode.java文件 package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.node;/**
The statistic node keep three kinds of real-time statistics metrics:
1、metrics in second level (rollingCounterInSecond)
2、metrics in minute level (rollingCounterInMinute)
3、thread count
Sentinel use sliding window to record and count the resource statistics in real-time. The sliding window infrastructure behind the ArrayMetric is LeapArray.
case 1: When the first request comes in, Sentinel will create a new window bucket of a specified time-span to store running statics, such as total response time(rt), incoming request(QPS), block request(bq), etc. And the time-span is defined by sample count.0 100ms+-------+--→ Sliding Windows^|requestSentinel use the statics of the valid buckets to decide whether this request can be passed. For example, if a rule defines that only 100 requests can be passed, it will sum all qps in valid buckets, and compare it to the threshold defined in rule.
case 2: continuous requests0 100ms 200ms 300ms+-------+-------+-------+-----→ Sliding Windows^|requestcase 3: requests keeps coming, and previous buckets become invalid0 100ms 200ms 800ms 900ms 1000ms 1300ms+-------+-------+ ...... +-------+-------+ ...... +-------+-----→ Sliding Windows^|requestThe sliding window should become:300ms 800ms 900ms 1000ms 1300ms+ ...... +-------+ ...... +-------+-----→ Sliding Windows^|request*/
public class StatisticNode implements Node {/*** Holds statistics of the recent {@code INTERVAL} milliseconds. The {@code INTERVAL} is divided into time spans* by given {@code sampleCount}.*/private transient volatile Metric rollingCounterInSecond = new ArrayMetric(SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT,IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);/*** Holds statistics of the recent 60 seconds. The windowLengthInMs is deliberately set to 1000 milliseconds,* meaning each bucket per second, in this way we can get accurate statistics of each second.*/private transient Metric rollingCounterInMinute = new ArrayMetric(60, 60 * 1000, false);/*** The counter for thread count.*/private LongAdder curThreadNum = new LongAdder();/*** The last timestamp when metrics were fetched.*/private long lastFetchTime = -1;@Overridepublic Map<Long, MetricNode> metrics() {// The fetch operation is thread-safe under a single-thread scheduler pool.long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();currentTime = currentTime - currentTime % 1000;Map<Long, MetricNode> metrics = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();List<MetricNode> nodesOfEverySecond = rollingCounterInMinute.details();long newLastFetchTime = lastFetchTime;// Iterate metrics of all resources, filter valid metrics (not-empty and up-to-date).for (MetricNode node : nodesOfEverySecond) {if (isNodeInTime(node, currentTime) && isValidMetricNode(node)) {metrics.put(node.getTimestamp(), node);newLastFetchTime = Math.max(newLastFetchTime, node.getTimestamp());}}lastFetchTime = newLastFetchTime;return metrics;}@Overridepublic List<MetricNode> rawMetricsInMin(Predicate<Long> timePredicate) {return rollingCounterInMinute.detailsOnCondition(timePredicate);}private boolean isNodeInTime(MetricNode node, long currentTime) {return node.getTimestamp() > lastFetchTime && node.getTimestamp() < currentTime;}private boolean isValidMetricNode(MetricNode node) {return node.getPassQps() > 0 || node.getBlockQps() > 0 || node.getSuccessQps() > 0|| node.getExceptionQps() > 0 || node.getRt() > 0 || node.getOccupiedPassQps() > 0;}@Overridepublic void reset() {rollingCounterInSecond = new ArrayMetric(SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT, IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);}@Overridepublic long totalRequest() {return rollingCounterInMinute.pass() + rollingCounterInMinute.block();}@Overridepublic long blockRequest() {return rollingCounterInMinute.block();}@Overridepublic double blockQps() {return rollingCounterInSecond.block() / rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();}@Overridepublic double previousBlockQps() {return this.rollingCounterInMinute.previousWindowBlock();}@Overridepublic double previousPassQps() {return this.rollingCounterInMinute.previousWindowPass();}@Overridepublic double totalQps() {return passQps() + blockQps();}@Overridepublic long totalSuccess() {return rollingCounterInMinute.success();}@Overridepublic double exceptionQps() {return rollingCounterInSecond.exception() / rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();}@Overridepublic long totalException() {return rollingCounterInMinute.exception();}@Overridepublic double passQps() {return rollingCounterInSecond.pass() / rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();}@Overridepublic long totalPass() {return rollingCounterInMinute.pass();}@Overridepublic double successQps() {return rollingCounterInSecond.success() / rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();}@Overridepublic double maxSuccessQps() {return (double) rollingCounterInSecond.maxSuccess() * rollingCounterInSecond.getSampleCount()/ rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();}@Overridepublic double occupiedPassQps() {return rollingCounterInSecond.occupiedPass() / rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();}@Overridepublic double avgRt() {long successCount = rollingCounterInSecond.success();if (successCount == 0) {return 0;}return rollingCounterInSecond.rt() * 1.0 / successCount;}@Overridepublic double minRt() {return rollingCounterInSecond.minRt();}@Overridepublic int curThreadNum() {return (int)curThreadNum.sum();}@Overridepublic void addPassRequest(int count) {rollingCounterInSecond.addPass(count);rollingCounterInMinute.addPass(count);}@Overridepublic void addRtAndSuccess(long rt, int successCount) {rollingCounterInSecond.addSuccess(successCount);rollingCounterInSecond.addRT(rt);rollingCounterInMinute.addSuccess(successCount);rollingCounterInMinute.addRT(rt);}@Overridepublic void increaseBlockQps(int count) {rollingCounterInSecond.addBlock(count);rollingCounterInMinute.addBlock(count);}@Overridepublic void increaseExceptionQps(int count) {rollingCounterInSecond.addException(count);rollingCounterInMinute.addException(count);}@Overridepublic void increaseThreadNum() {curThreadNum.increment();}@Overridepublic void decreaseThreadNum() {curThreadNum.decrement();}@Overridepublic void debug() {rollingCounterInSecond.debug();}@Overridepublic long tryOccupyNext(long currentTime, int acquireCount, double threshold) {double maxCount = threshold * IntervalProperty.INTERVAL / 1000;long currentBorrow = rollingCounterInSecond.waiting();if (currentBorrow >= maxCount) {return OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout();}int windowLength = IntervalProperty.INTERVAL / SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT;long earliestTime = currentTime - currentTime % windowLength + windowLength - IntervalProperty.INTERVAL;int idx = 0;/** Note: here {@code currentPass} may be less than it really is NOW, because time difference* since call rollingCounterInSecond.pass(). So in high concurrency, the following code may* lead more tokens be borrowed.*/long currentPass = rollingCounterInSecond.pass();while (earliestTime < currentTime) {long waitInMs = idx * windowLength + windowLength - currentTime % windowLength;if (waitInMs >= OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) {break;}long windowPass = rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowPass(earliestTime);if (currentPass + currentBorrow + acquireCount - windowPass <= maxCount) {return waitInMs;}earliestTime += windowLength;currentPass -= windowPass;idx++;}return OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout();}@Overridepublic long waiting() {return rollingCounterInSecond.waiting();}@Overridepublic void addWaitingRequest(long futureTime, int acquireCount) {rollingCounterInSecond.addWaiting(futureTime, acquireCount);}@Overridepublic void addOccupiedPass(int acquireCount) {rollingCounterInMinute.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount);rollingCounterInMinute.addPass(acquireCount);}
}底层最核心的是滑动窗口的实现,代码如下所示:
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.base.LeapArray.java文件package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.base;/*** <p>* Basic data structure for statistic metrics in Sentinel.* </p>* <p>* Leap array use sliding window algorithm to count data. Each bucket cover {@code windowLengthInMs} time span,* and the total time span is {@link #intervalInMs}, so the total bucket amount is:* {@code sampleCount = intervalInMs / windowLengthInMs}.* </p>** @param <T> type of statistic data* @author jialiang.linjl* @author Eric Zhao* @author Carpenter Lee*/
public abstract class LeapArray<T> {protected int windowLengthInMs;protected int sampleCount;protected int intervalInMs;private double intervalInSecond;protected final AtomicReferenceArray<WindowWrap<T>> array;/*** The conditional (predicate) update lock is used only when current bucket is deprecated.*/private final ReentrantLock updateLock = new ReentrantLock();/*** The total bucket count is: {@code sampleCount = intervalInMs / windowLengthInMs}.** @param sampleCount bucket count of the sliding window* @param intervalInMs the total time interval of this {@link LeapArray} in milliseconds*/public LeapArray(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {AssertUtil.isTrue(sampleCount > 0, "bucket count is invalid: " + sampleCount);AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs > 0, "total time interval of the sliding window should be positive");AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs % sampleCount == 0, "time span needs to be evenly divided");this.windowLengthInMs = intervalInMs / sampleCount;this.intervalInMs = intervalInMs;this.intervalInSecond = intervalInMs / 1000.0;this.sampleCount = sampleCount;this.array = new AtomicReferenceArray<>(sampleCount);}/*** Get the bucket at current timestamp.** @return the bucket at current timestamp*/public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow() {return currentWindow(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis());}/*** Create a new statistic value for bucket.** @param timeMillis current time in milliseconds* @return the new empty bucket*/public abstract T newEmptyBucket(long timeMillis);/*** Reset given bucket to provided start time and reset the value.** @param startTime the start time of the bucket in milliseconds* @param windowWrap current bucket* @return new clean bucket at given start time*/protected abstract WindowWrap<T> resetWindowTo(WindowWrap<T> windowWrap, long startTime);private int calculateTimeIdx(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) {long timeId = timeMillis / windowLengthInMs;// Calculate current index so we can map the timestamp to the leap array.return (int)(timeId % array.length());}protected long calculateWindowStart(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) {return timeMillis - timeMillis % windowLengthInMs;}// ***********滑动窗口最核心的实现************/*** Get bucket item at provided timestamp.** @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds* @return current bucket item at provided timestamp if the time is valid; null if time is invalid*/public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return null;}int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);// Calculate current bucket start time.long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);/** Get bucket item at given time from the array.** (1) Bucket is absent, then just create a new bucket and CAS update to circular array.* (2) Bucket is up-to-date, then just return the bucket.* (3) Bucket is deprecated, then reset current bucket.*/while (true) {WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);if (old == null) {/** B0 B1 B2 NULL B4* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp* ^* time=888* bucket is empty, so create new and update** If the old bucket is absent, then we create a new bucket at {@code windowStart},* then try to update circular array via a CAS operation. Only one thread can* succeed to update, while other threads yield its time slice.*/WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {// Successfully updated, return the created bucket.return window;} else {// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.Thread.yield();}} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {/** B0 B1 B2 B3 B4* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp* ^* time=888* startTime of Bucket 3: 800, so it's up-to-date** If current {@code windowStart} is equal to the start timestamp of old bucket,* that means the time is within the bucket, so directly return the bucket.*/return old;} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {/** (old)* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4* |_______||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___* ... 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 timestamp* ^* time=1676* startTime of Bucket 2: 400, deprecated, should be reset** If the start timestamp of old bucket is behind provided time, that means* the bucket is deprecated. We have to reset the bucket to current {@code windowStart}.* Note that the reset and clean-up operations are hard to be atomic,* so we need a update lock to guarantee the correctness of bucket update.** The update lock is conditional (tiny scope) and will take effect only when* bucket is deprecated, so in most cases it won't lead to performance loss.*/if (updateLock.tryLock()) {try {// Successfully get the update lock, now we reset the bucket.return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);} finally {updateLock.unlock();}} else {// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.Thread.yield();}} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {// Should not go through here, as the provided time is already behind.return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));}}}/*** Get the previous bucket item before provided timestamp.** @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds* @return the previous bucket item before provided timestamp*/public WindowWrap<T> getPreviousWindow(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return null;}int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis - windowLengthInMs);timeMillis = timeMillis - windowLengthInMs;WindowWrap<T> wrap = array.get(idx);if (wrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(wrap)) {return null;}if (wrap.windowStart() + windowLengthInMs < (timeMillis)) {return null;}return wrap;}/*** Get the previous bucket item for current timestamp.** @return the previous bucket item for current timestamp*/public WindowWrap<T> getPreviousWindow() {return getPreviousWindow(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis());}/*** Get statistic value from bucket for provided timestamp.** @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds* @return the statistic value if bucket for provided timestamp is up-to-date; otherwise null*/public T getWindowValue(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return null;}int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);WindowWrap<T> bucket = array.get(idx);if (bucket == null || !bucket.isTimeInWindow(timeMillis)) {return null;}return bucket.value();}/*** Check if a bucket is deprecated, which means that the bucket* has been behind for at least an entire window time span.** @param windowWrap a non-null bucket* @return true if the bucket is deprecated; otherwise false*/public boolean isWindowDeprecated(/*@NonNull*/ WindowWrap<T> windowWrap) {return isWindowDeprecated(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(), windowWrap);}public boolean isWindowDeprecated(long time, WindowWrap<T> windowWrap) {return time - windowWrap.windowStart() > intervalInMs;}/*** Get valid bucket list for entire sliding window.* The list will only contain "valid" buckets.** @return valid bucket list for entire sliding window.*/public List<WindowWrap<T>> list() {return list(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis());}public List<WindowWrap<T>> list(long validTime) {int size = array.length();List<WindowWrap<T>> result = new ArrayList<WindowWrap<T>>(size);for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i);if (windowWrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(validTime, windowWrap)) {continue;}result.add(windowWrap);}return result;}/*** Get all buckets for entire sliding window including deprecated buckets.** @return all buckets for entire sliding window*/public List<WindowWrap<T>> listAll() {int size = array.length();List<WindowWrap<T>> result = new ArrayList<WindowWrap<T>>(size);for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i);if (windowWrap == null) {continue;}result.add(windowWrap);}return result;}/*** Get aggregated value list for entire sliding window.* The list will only contain value from "valid" buckets.** @return aggregated value list for entire sliding window*/public List<T> values() {return values(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis());}public List<T> values(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return new ArrayList<T>();}int size = array.length();List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(size);for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i);if (windowWrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(timeMillis, windowWrap)) {continue;}result.add(windowWrap.value());}return result;}/*** Get the valid "head" bucket of the sliding window for provided timestamp.* Package-private for test.** @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds* @return the "head" bucket if it exists and is valid; otherwise null*/WindowWrap<T> getValidHead(long timeMillis) {// Calculate index for expected head time.int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis + windowLengthInMs);WindowWrap<T> wrap = array.get(idx);if (wrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(wrap)) {return null;}return wrap;}/*** Get the valid "head" bucket of the sliding window at current timestamp.** @return the "head" bucket if it exists and is valid; otherwise null*/public WindowWrap<T> getValidHead() {return getValidHead(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis());}/*** Get sample count (total amount of buckets).** @return sample count*/public int getSampleCount() {return sampleCount;}/*** Get total interval length of the sliding window in milliseconds.** @return interval in second*/public int getIntervalInMs() {return intervalInMs;}/*** Get total interval length of the sliding window.** @return interval in second*/public double getIntervalInSecond() {return intervalInSecond;}public void debug(long time) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();List<WindowWrap<T>> lists = list(time);sb.append("Thread_").append(Thread.currentThread().getId()).append("_");for (WindowWrap<T> window : lists) {sb.append(window.windowStart()).append(":").append(window.value().toString());}System.out.println(sb.toString());}public long currentWaiting() {// TODO: default method. Should remove this later.return 0;}public void addWaiting(long time, int acquireCount) {// Do nothing by default.throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
}到这里基本上Sentinel核心的代码就分析完了。