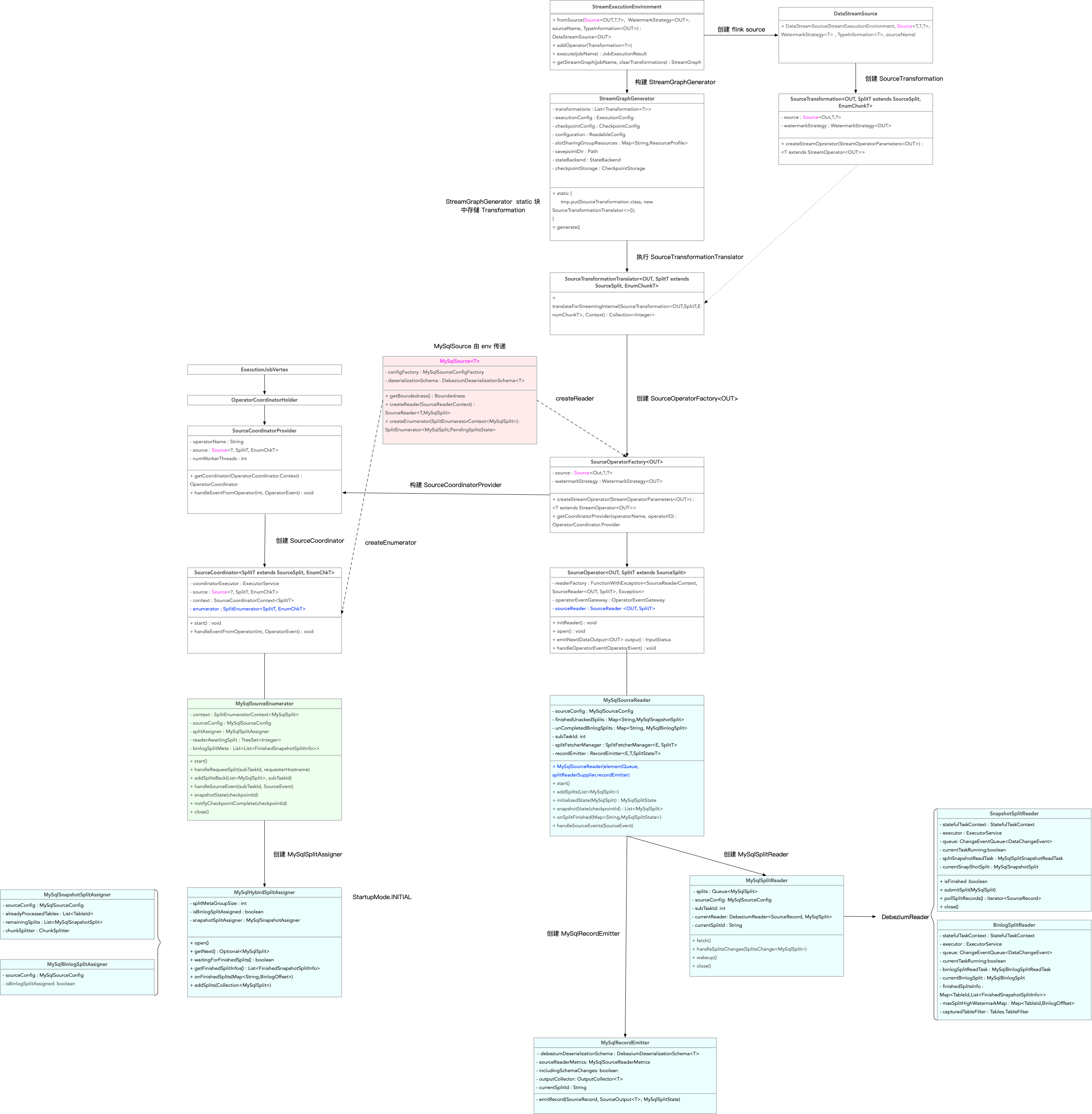
在普通的网页开发中,JavaScript由于安全性的考虑,通常是无法直接获取到客户端的磁盘路径的。浏览器出于隐私和安全原因对此类信息进行了限制。
在浏览器环境下,JavaScript主要通过Web APIs来与浏览器进行交互,而这些API通常受到浏览器的安全策略的限制。文件系统信息是被认为是敏感的信息,因此浏览器不提供直接访问客户端磁盘路径的API。所以要使用electron属性来获取。
第一步:
electron分为主进程和渲染进程,主进程就是使用electron的特性属性api,渲染进程就是我们的代码,比如vue页面代码这种。
首先我们要把项目用electron启动起来,具体怎么启动看我上一篇博客
启动完成后,找到项目文件中的backgroun.js文件,这是electron主进程的文件
把以下代码加进去
import { app, protocol, BrowserWindow ,ipcMain,ipcRenderer,dialog} from 'electron'
const fs = require('fs');
app.on('ready', async () => {// if (isDevelopment && !process.env.IS_TEST) {// // Install Vue Devtools// try {// await installExtension(VUEJS_DEVTOOLS)// } catch (e) {// console.error('Vue Devtools failed to install:', e.toString())// }// }createWindow()// 新增:在主进程中处理打开保存图片对话框的请求ipcMain.handle('dialog:saveImage', async (event, dataURL) => {return saveImage(dataURL);});
})// 将保存图片的逻辑封装成一个函数
async function saveImage(dataURL) {let base64 = dataURL.replace(/^data:image\/\w+;base64,/, '');let dataBuffer = Buffer.from(base64, 'base64');const options = {title: 'Save Image',buttonLabel: '保存', // 自定义保存按钮的文字defaultPath: 'image.jpg', // 默认文件名filters: [{ name: 'Images', extensions: ['jpg', 'png', 'gif'] }]};const { canceled, filePath } = await dialog.showSaveDialog(options);if (canceled) {return null; // 用户取消保存文件时返回 null} else {// 将 dataURL 保存到 filePath 的逻辑代码fs.writeFile(filePath, dataBuffer, function (err) {if (err) {console.error(err, '保存失败');} else {console.log(filePath, '保存成功');}});return filePath; // 返回用户选择的文件路径}
}- 在 Electron 应用程序启动后,创建了窗口(
createWindow函数应该是在代码中其他位置定义的)。 - 通过
ipcMain.handle方法,为名为 'dialog:saveImage' 的事件注册了一个处理函数,用于处理保存图片对话框的请求。当渲染进程发送 'dialog:saveImage' 事件时,主进程将会执行saveImage函数。 saveImage函数封装了保存图片的逻辑。首先将 Data URL 转换为 Buffer 格式,然后通过dialog.showSaveDialog方法展示保存对话框,用户选择保存路径后,将图片文件保存到指定路径。-
在
saveImage函数中: - 首先通过
dataURL.replace和Buffer.from将 Data URL 转换成了 Buffer 格式。 - 然后使用
dialog.showSaveDialog方法展示保存对话框,用户选择保存路径后,通过fs.writeFile方法将 Buffer 写入文件。 - 最后根据保存成功或失败,返回相应的结果给渲染进程。
fs 是 Node.js 核心模块中的一个模块,全称为 File System(文件系统)。这个模块提供了一系列用于处理文件和文件系统的方法,可以用于读取文件、写入文件、创建目录、删除文件等操作。通过 fs 模块,你可以在 Node.js 程序中对文件和文件系统进行各种操作,包括读写文件、文件夹的操作等。
在 Electron 应用程序中,由于可以利用 Node.js 的能力,因此可以在主进程中使用 fs 模块来处理文件和文件系统相关的操作,比如在上面的代码中就使用了 fs.writeFile 方法来将图片保存到指定路径。
这是最终background.js文件的代码:
'use strict'import { app, protocol, BrowserWindow ,ipcMain,ipcRenderer,dialog} from 'electron'
import { createProtocol } from 'vue-cli-plugin-electron-builder/lib'
// import installExtension, { VUEJS_DEVTOOLS } from 'electron-devtools-installer'
const isDevelopment = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
const fs = require('fs');// Scheme must be registered before the app is ready
protocol.registerSchemesAsPrivileged([{ scheme: 'app', privileges: { secure: true, standard: true } }
])async function createWindow() {// Create the browser window.const win = new BrowserWindow({width: 800,height: 600,webPreferences: {// Use pluginOptions.nodeIntegration, leave this alone// See nklayman.github.io/vue-cli-plugin-electron-builder/guide/security.html#node-integration for more infonodeIntegration: process.env.ELECTRON_NODE_INTEGRATION,contextIsolation: !process.env.ELECTRON_NODE_INTEGRATION}})win.maximize()if (process.env.WEBPACK_DEV_SERVER_URL) {// Load the url of the dev server if in development modeawait win.loadURL(process.env.WEBPACK_DEV_SERVER_URL)if (!process.env.IS_TEST) win.webContents.openDevTools()} else {createProtocol('app')// Load the index.html when not in developmentwin.loadURL('app://./index.html')}
}// Quit when all windows are closed.
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {// On macOS it is common for applications and their menu bar// to stay active until the user quits explicitly with Cmd + Qif (process.platform !== 'darwin') {app.quit()}
})app.on('activate', () => {// On macOS it's common to re-create a window in the app when the// dock icon is clicked and there are no other windows open.if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) createWindow()
})// This method will be called when Electron has finished
// initialization and is ready to create browser windows.
// Some APIs can only be used after this event occurs.
app.on('ready', async () => {// if (isDevelopment && !process.env.IS_TEST) {// // Install Vue Devtools// try {// await installExtension(VUEJS_DEVTOOLS)// } catch (e) {// console.error('Vue Devtools failed to install:', e.toString())// }// }createWindow()// 新增:在主进程中处理打开保存图片对话框的请求ipcMain.handle('dialog:saveImage', async (event, dataURL) => {return saveImage(dataURL);});
})// Exit cleanly on request from parent process in development mode.
if (isDevelopment) {if (process.platform === 'win32') {process.on('message', (data) => {if (data === 'graceful-exit') {app.quit()}})} else {process.on('SIGTERM', () => {app.quit()})}
}// 将保存图片的逻辑封装成一个函数
async function saveImage(dataURL) {let base64 = dataURL.replace(/^data:image\/\w+;base64,/, '');let dataBuffer = Buffer.from(base64, 'base64');const options = {title: 'Save Image',buttonLabel: '保存', // 自定义保存按钮的文字defaultPath: 'image.jpg', // 默认文件名filters: [{ name: 'Images', extensions: ['jpg', 'png', 'gif'] }]};const { canceled, filePath } = await dialog.showSaveDialog(options);if (canceled) {return null; // 用户取消保存文件时返回 null} else {// 将 dataURL 保存到 filePath 的逻辑代码fs.writeFile(filePath, dataBuffer, function (err) {if (err) {console.error(err, '保存失败');} else {console.log(filePath, '保存成功');}});return filePath; // 返回用户选择的文件路径}
}第二步:
去渲染进程里写相关代码,也就是你的.vue文件
//保存画布图片saveCanvasBackground() {if (this.image.url == '') return// 获取 canvas 元素和 Fabric 对象const canvas = document.getElementById("label-canvas");const fabricObj = this.fabricObj;// 将 canvas 内容保存为图片数据 URLconst dataURL = canvas.toDataURL({format: "png", // 保存的图片格式quality: 0.8, // 图片质量});//想主进程发送打开保存图片选项框请求ipcRenderer.invoke('dialog:saveImage', dataURL).then(response => {console.log(response, 'sssss');if (response) {// 接口// setsaveImage({// img:response// }).then(res=>{// console.log(res,'保存成功接口');// }).catch(err=>{// console.log(err,'保存失败接口');// })} else {//用户取消}}).catch(err => {console.error(err);});// 创建一个 Blob 对象// const byteCharacters = atob(dataURL.split(",")[1]);// const byteNumbers = new Array(byteCharacters.length);// for (let i = 0; i < byteCharacters.length; i++) {// byteNumbers[i] = byteCharacters.charCodeAt(i);// }// const byteArray = new Uint8Array(byteNumbers);// const blob = new Blob([byteArray], { type: "image/png" });// // 创建一个下载链接// const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob);// // 创建一个下载按钮并触发点击// const a = document.createElement("a");// a.style.display = "none";// a.href = url;// a.download = "saved_image.png"; // 设置下载的文件名// document.body.appendChild(a);// a.click();// // 释放对象 URL,避免内存泄漏// window.URL.revokeObjectURL(url);},这段代码是在渲染进程中使用 ipcRenderer.invoke 方法向主进程发送了一个名为 'dialog:saveImage' 的请求,同时传递了一个名为 dataURL 的参数。当主进程处理完这个请求后,渲染进程会接收到相应的结果。
在这段代码中,使用了 ipcRenderer.invoke 方法来发送请求,并通过 Promise 对象处理响应。如果主进程成功处理了请求并返回了结果,会执行 then 中的代码,如果出现错误,会执行 catch 中的代码。
在 then 中的代码中,首先会打印出返回的 response,然后根据返回的结果进行相应的处理。如果 response 存在,表示图片保存成功,可以处理接口请求或其他逻辑;如果 response 不存在,表示用户取消了保存操作,可以做出相应的反应。
整体来说,这段代码的作用是在渲染进程中向主进程发送保存图片选项框的请求,并根据主进程返回的结果进行相应的处理。
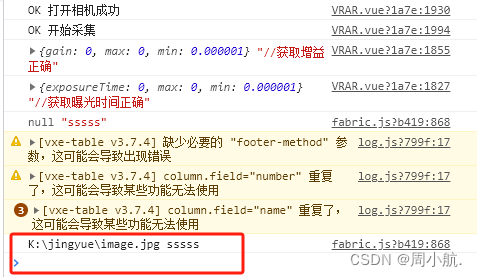
以上红色框内就是运行过后获取出来当前保存图片的磁盘路径!
双击点赞!!!!