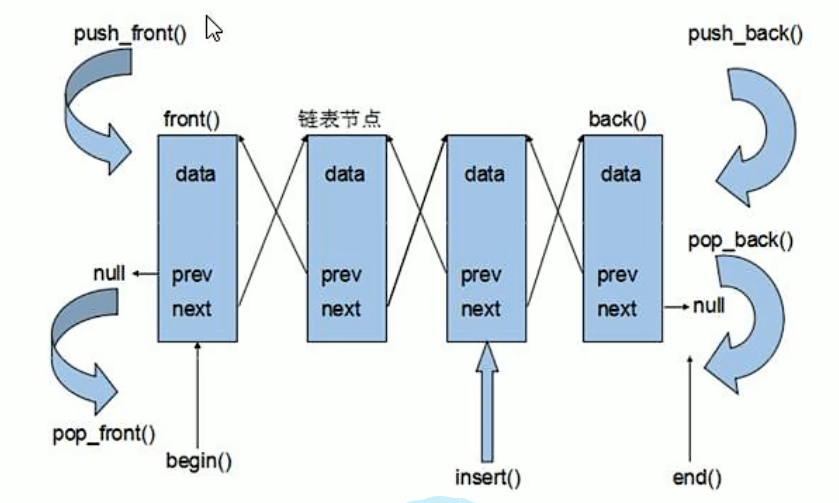
前言
堆是一种重要的数据结构,因此应该熟练掌握。
一、堆的基本概念
堆的基本:
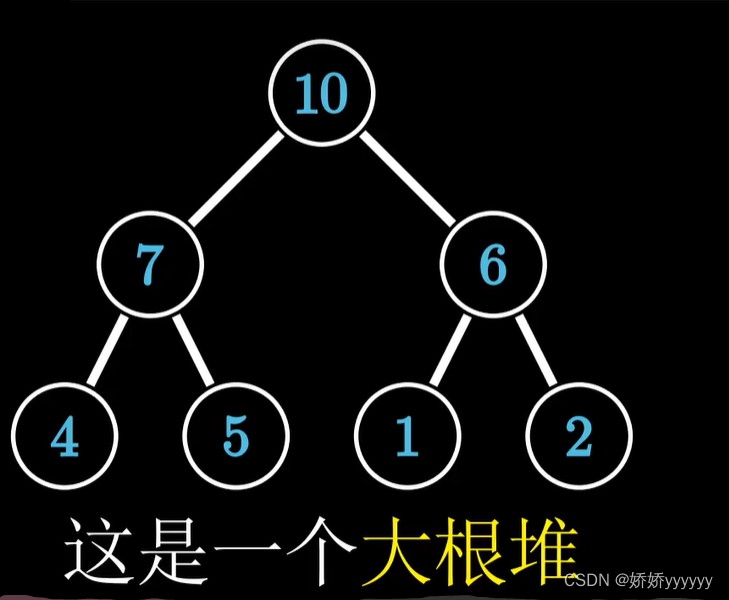
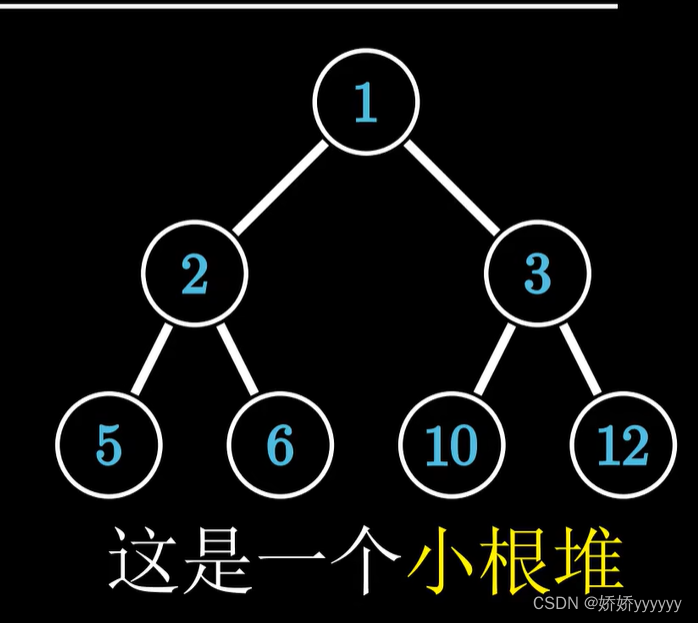
堆的结构实际上是一棵完全二叉树,堆可以分为大根堆和小根堆
大根堆:
小根堆:
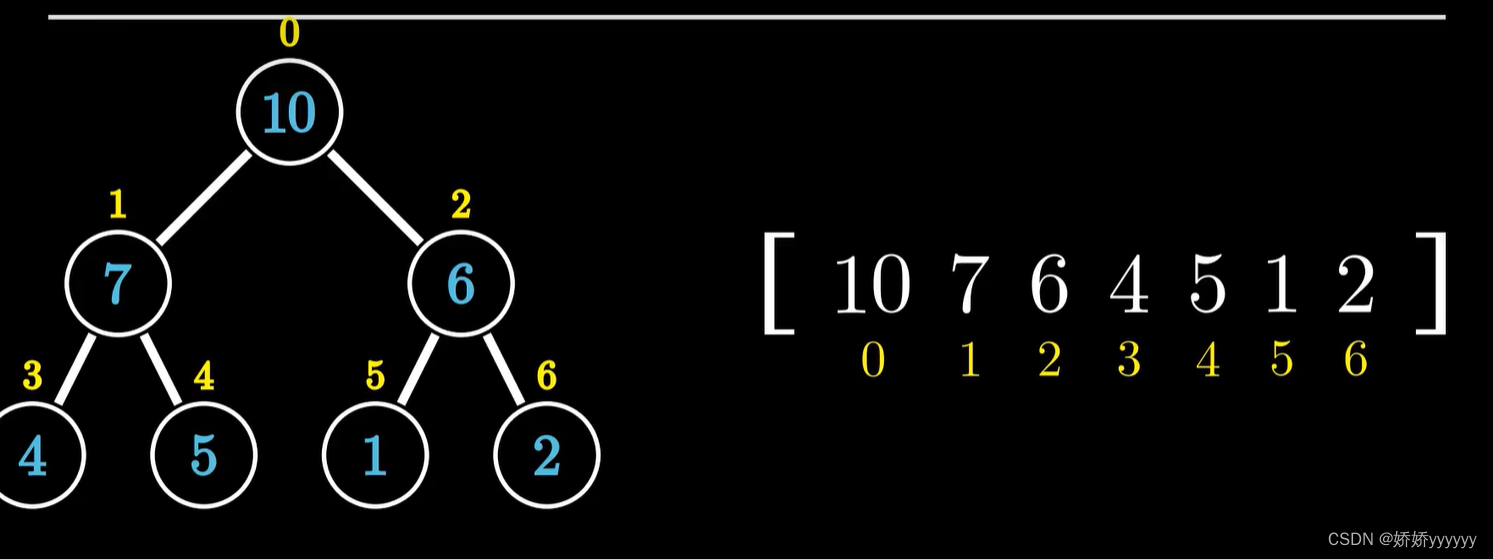
堆的储存:
若节点小标为i,则左子节点下标为2i+1,右子节点下标为2i+2。
堆的基本操作(模板):
//down模板:#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
int h[N],siz;
int n,m;
void down(int x)
{int t=x;if(2*x<=siz && h[2*x]<h[t]) t=2*x;if(2*x+1<=siz && h[2*x+1]<h[t]) t=2*x+1;if(x!=t){swap(h[x],h[t]);down(t);}
}//up模板:void up(int x)
{while(x/2 &&h[x]<h[x/2]){headswap(x/2,x);x/=2;}STL:
定义大根堆:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int> >q;
int main(){q.push(1);q.push(2);cout<<q.top();return 0;
}
或:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int>q;
int main(){q.push(1);q.push(2);cout<<q.top();return 0;
}定义小根堆:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> >q;
int main(){q.push(1);q.push(2);cout<<q.top();return 0;
}二、典型例题
1.例题:
2.AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N];//堆
int ph[N], hp[N];
int siz;
void heap_swap(int a,int b) {swap(ph[hp[a]],ph[hp[b]]);swap(hp[a],hp[b]);swap(h[a],h[b]);
}void down(int u) {int t = u;if (u * 2 <= siz && h[u * 2] < h[t]) {t = u * 2;//比左儿子}if (u * 2 + 1 <= siz && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) {t = u * 2 + 1;//比右儿子}if (u != t) {heap_swap(u, t);down(t);}
}void up(int u) {while (u / 2 && h[u / 2] > h[u]) {heap_swap(u / 2, u);u /= 2;}
}int main () {int n, m = 0;scanf("%d", &n);while (n --) {char op[10];int k, x;scanf("%s", op);if (!strcmp(op,"I")) {scanf("%d", &x);siz++;m++;ph[m] = siz, hp[siz] = m;h[siz] = x;up(siz);}else if (!strcmp(op,"PM")) {printf("%d\n", h[1]);}else if (!strcmp(op,"DM")) {heap_swap(1, siz);siz--;down(1);}else if (!strcmp(op,"D")) {scanf("%d", &k);k = ph[k];heap_swap(k, siz);siz--;down(k), up(k);}else {scanf("%d%d", &k, &x);k = ph[k];h[k] = x;down(k), up(k);}}return 0;
}