我们知道Java中的基本数据类型有以下几种
char占用2个字节
boolean占用1个字节或者4个字节(稍后解释)
byte占用1个字节
short占用2个字节
int占用4个字节
long占用8个字节
float占用4个字节
double占用8个字节
char a = 'a';
boolean b = false;
int c = 1;
......
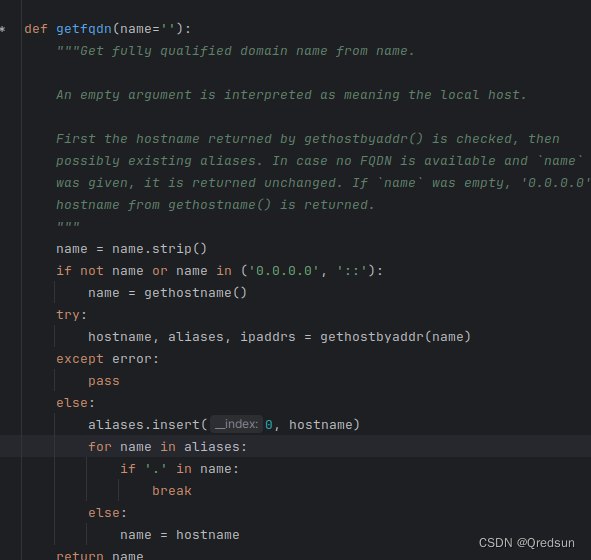
当我们在对这些基本数据类型操作时,JVM会帮我们生成字节码指令,举个例子
public class BasicDataType {public static void main(String[] args) {int a = 1;int b = 2;int c = a + b;}
}我们使用javac BasicDataType.java命令编译生成class,然后我们再通过javap -v BasicDataTyple.class命令来查看下生成的字节码,重点观察红色方框中的内容
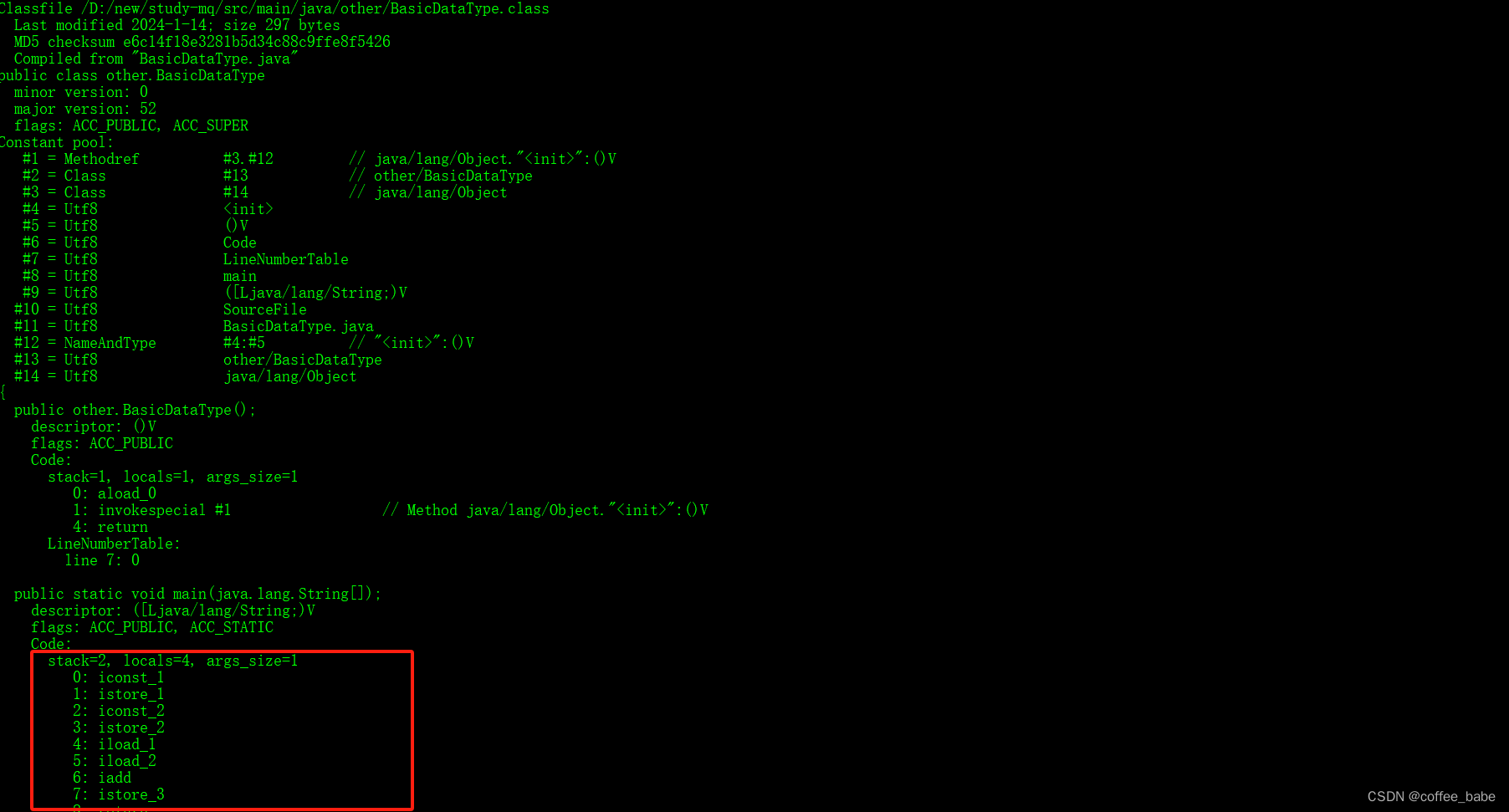
接着我再来简单介绍iconst iadd
iconst
表示我们定义了一个int类型的常量,其中i表示int类型,
iadd
表示两个int类型变量进行相加
同理其他的基本类型也有相应的指令,具体对应关系如下
- l 代表long
- s代表short
- b代表byte
- c代表char
- f代表float
- d代表double
看到这里,你可能会有疑问? 为什么没有boolean类型?当时我也有这样的疑问,会不会是资料写错了,抱着怀疑的态度去思考问题,我们再来将代码做一些调整再来观察
public class BasicDataType {public static void main(String[] args) {boolean testBool = false;boolean[] testBoolArray = new boolean[10];testBoolArray[0] = true;}
}javac BasicDataType.java
javap -v BasicDataType.class
重点关注下这个部分
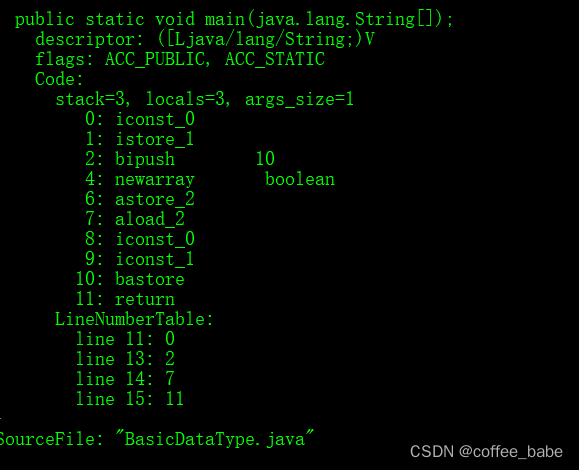
看到这里你可能会大吃一惊,iconst 不是操作int类型的嘛,我明明操作的是boolean类型,怎么是int类型的字节码操作。
通过查询官方字节码指令集:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se8/html/jvms-6.html#jvms-6.5.bastore
The arrayref must be of type reference and must refer to an array whose components are of type byte or of type boolean. The index and the value must both be of type int. The arrayref, index, and value are popped from the operand stack. The int value is truncated to a byte and stored as the component of the array indexed by index.
官方是这样描述boolean类型数组的,翻译过来的意思就是在操作boolean数组类型的时候,它的index索引值以及存储的值(也就是数组中的元素)都必须是int类型,对于boolean数组来说,会对int类型做截断让其占用1个字节的存储空间
总结来说就是,使用boolean数组类型,它的占用空间是一个字节,当我们单独使用boolean类型的时候,它其实被当作int类型了,那么也就是4个字节
结论我们已经知道了,接下来我们来谈谈为什么要这样处理?JVM为什么要使用int类型来表示boolean类型的字节码操作,为什么不用byte或者short,这样还可以在空间上节省一些
使用int类型的原因:
对于当下32位的处理器来说,
一次处理数据是32位(这里不是指的是32/64位操作系统),而是CPU硬件层面)的高效存取的数据,
虽然定义了boolean类型,
但是JVM只对它提工了非常有限的支持,
JVM中没有任何供boolean专用的字节码指令