文章目录
一、损失函数的概念
二、Pytorch内置损失函数
1. nn.CrossEntropyLoss
2. nn.NLLLoss
3. nn.NLLLoss2d
4. nn.BCELoss
5. nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss
6. nn.L1Loss
7. nn.MSELoss
8. nn.SmoothL1Loss
9. nn.PoissonNLLLoss
10. nn.KLDivLoss
11. nn.MarginRankingLoss
12. nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss
13. nn.SoftMarginLoss
14. nn.MultilabelSoftMarginLoss
15. nn.MultiMarginLoss
16. nn.TripletMarginLoss
17. nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss
18. nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss
19. nn.CTCLoss
一、损失函数的概念
损失函数(loss function):衡量模型输出与真实标签的差异。
损失函数也叫代价函数(cost function)/ 准测(criterion)/ 目标函数(objective function)/ 误差函数(error function)。
二、Pytorch内置损失函数
1. nn.CrossEntropyLoss
功能:交叉熵损失函数,用于多分类问题。这个损失函数结合了nn.LogSoftmax和nn.NLLLoss的计算过程。通常用于网络最后的分类层输出
主要参数:
- weight:各类别的loss设置权值
- ignore_index:忽略某个类别
- reduction:计算模式,可为 none /sum /mean:
①. none:逐个元素计算
②. sum:所有元素求和,返回标量
③. mean:加权平均,返回标量
nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction=‘mean’)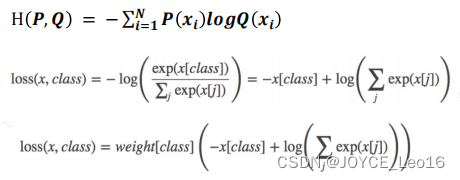
用法示例:
# Example of target with class indices
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3, dtype=torch.long).random_(5)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()
# Example of target with class probabilities
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5).softmax(dim=1)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()2. nn.NLLLoss
功能:负对数似然损失函数,当网络的最后一层是nn.LogSoftmax时使用。用于训练 C 个类别的分类问题
主要参数:
- weight:各类别的loss设置权值,必须是一个长度为 C 的 Tensor
- ignore _index:设置一个目标值, 该目标值会被忽略, 从而不会影响到 输入的梯度
- reduction :计算模式,可为none /sum /mean
①. none:逐个元素计算
②. sum:所有元素求和,返回标量
③. mean:加权平均,返回标量
nn.NLLLoss(weight=None,size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean')![]()
用法示例:
m = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
loss = nn.NLLLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([1, 0, 4])
output = loss(m(input), target)3. nn.NLLLoss2d
功能:对于图片输入的负对数似然损失. 它计算每个像素的负对数似然损失。它是nn.NLLLoss的二维版本。适用于图像相关的任务,比如像素级任务或分割
torch.nn.NLLLoss2d(weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')4. nn.BCELoss
功能:二元交叉熵损失函数,用于二分类问题。计算的是目标值和预测值之间的交叉熵。
注意事项:输入值取值在 [0,1]
主要参数:
- weight:各类别的loss设置权值
- ignore_index:忽略某个类别
- reduction:计算模式,可为none /sum /mean
①. none:逐个元素计算
②. sum:所有元素求和,返回标量
③. mean:加权平均,返回标量
torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None, size_average=None,reduce=None, reduction='mean')用法示例:
m = nn.Sigmoid()
loss = nn.BCELoss()
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
output = loss(m(input), target)5. nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss
功能:结合了nn.Sigmoid层和nn.BCELoss的损失函数,用于二分类问题,尤其在预测值没有经过nn.Sigmoid层时
注意事项:网络最后不加sigmoid函数
主要参数:
- pos_weight:正样本的权值
- weight:各类别的loss设置权值
- ignore_index:忽略某个类别
- reduction:计算模式,可为none /sum /mean
①. none:逐个元素计算
②. sum:所有元素求和,返回标量
③. mean:加权平均,返回标量
nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)用法示例:
loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
output = loss(input, target)6. nn.L1Loss
功能:L1损失函数,也称为最小绝对偏差(LAD)。它是预测值和真实值之间差的绝对值的和
主要参数:
- reduction:计算模式,可为none /sum /mean
①. none:逐个元素计算
②. sum:所有元素求和,返回标量
③. mean:加权平均,返回标量
torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction='mean')用法示例:
loss = nn.L1Loss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5)
output = loss(input, target)7. nn.MSELoss
功能:均方误差损失函数,计算预测值和真实值之间差的平方的平均值,用于回归问题。
主要参数:
- reduction:计算模式,可为none /sum /mean
①. none:逐个元素计算
②. sum:所有元素求和,返回标量
③. mean:加权平均,返回标量
torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')用法示例:
loss = nn.MSELoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5)
output = loss(input, target)8. nn.SmoothL1Loss
功能:平滑L1损失,也称为Huber损失,主要用于回归问题,尤其是当预测值与目标值差异较大时,比起L1损失更不易受到异常值的影响
- size_average
- reduce
- reduction
- beta
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='mean')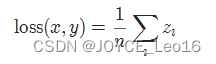
其中,
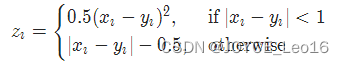
用法示例:
loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5)
output = loss(input, target)9. nn.PoissonNLLLoss
功能:泊松负对数似然损失,适用于计数或事件率预测,其中预测的是事件发生的平均率
主要参数:
- log_inpput:输入是否为对数形式,决定计算公式
- full:计算所有loss,默认为False
- eps:修正项,避免log(input)为nan
torch.nn.PoissonNLLLoss(log_input=True, full=False, eps=1e-08, reduction='mean')用法示例:
loss = nn.PoissonNLLLoss()
log_input = torch.randn(5, 2, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(5, 2)
output = loss(log_input.exp(), target)10. nn.KLDivLoss
功能::KL散度损失,用于衡量两个概率分布之间的差异。通常用于模型输出与某个目标分布或另一个模型输出之间的相似性度量
注意事项:需提前将输入计算 log-probabilities,如通过nn.logsoftmax()
主要参数:
- reduction:none / sum / mean / batchmean
①. batchmean:batchsize维度求平均值
②. none:逐个元素计算
③. sum:所有元素求和,返回标量
④. mean:加权平均,返回标量
torch.nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='mean')用法示例:
loss = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='batchmean')
input = torch.log_softmax(torch.randn(5, 10), dim=1)
target = torch.softmax(torch.randn(5, 10), dim=1)
output = loss(input, target)11. nn.MarginRankingLoss
功能:边缘排序损失,用于排序学习任务,它鼓励正例的得分比负例的得分更高一个边界值
注意事项:该方法计算两组数据之间的差异,返回一个 n*n 的loss 矩阵
主要参数:
- margin:边界值,x1和x2之间的差异值
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
①. y=1时,希望x1比x2大,当x1>x2时,不产生loss
②. y=-1时,希望x2比x1大,当x2>x1时,不产生loss
torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean')用法示例:
loss = nn.MarginRankingLoss()
input1 = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
input2 = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3).sign()
output = loss(input1, input2, target)12. nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss
功能:多标签边缘损失,用于多标签分类问题,其中每个类别的损失是独立计算的。
举例:四分类任务,样本x属于0类或3类
主要参数:
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
torch.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(reduction='mean')对于mini-batch(小批量) 中的每个样本按如下公式计算损失:

用法示例:
loss = nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([[3, 0, -1, -1, -1],[1, 3, -1, -1, -1],[1, 2, 3, -1, -1]])
output = loss(input, target)13. nn.SoftMarginLoss
功能:软边缘损失,用于二分类任务,是逻辑回归损失的平滑版本。
主要参数:
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
torch.nn.SoftMarginLoss(reduction='mean')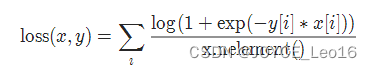
用法示例:
loss = nn.SoftMarginLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([-1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.float)
output = loss(input, target)14. nn.MultilabelSoftMarginLoss
功能:多标签软边缘损失,用于多标签分类问题,它是每个标签的二元交叉熵损失的加权版本
主要参数:
- weight:各类别的loos设置权值
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
torch.nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean')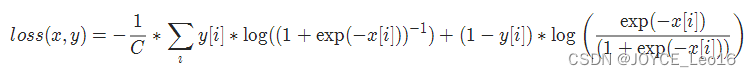
用法示例:
loss = nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3, 5).random_(2)
output = loss(input, target)15. nn.MultiMarginLoss
功能:多类别边缘损失,是SVM(支持向量机)的一个变种,用于多类别分类问题。
主要参数:
- p:可选1或2
- weight:各类别的loos设置权值
- margin:边界值
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss(p=1, margin=1.0, weight=None, reduction='mean')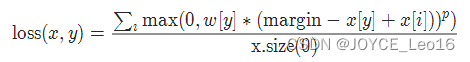
用法示例:
loss = nn.MultiMarginLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([1, 0, 4])
output = loss(input, target)16. nn.TripletMarginLoss
功能:三元组边缘损失,用于度量学习,其中学习的是输入样本之间的相对距离。人脸验证中常用
主要参数:
- p:范数的阶,默认为2
- margin:边界值
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
和孪生网络相似,具体例子:给一个A,然后再给B、C,看看B、C谁和A更像。

torch.nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2.0, eps=1e-06, swap=False, reduction='mean')![]()
其中,
![]()
用法示例:
loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2)
anchor = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
positive = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
negative = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
output = loss(anchor, positive, negative)17. nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss
功能:铰链嵌入损失,用于学习基于距离的相似性,当两个输入被认为是不相似的时,会惩罚它们的距离。常用于非线性embedding和半监督学习
注意事项:输入x 应为两个输入之差的绝对值
主要参数:
- margin:边界值
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0, reduction='mean')用法示例:
loss = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([1, -1, 1])
output = loss(input, target)18. nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss
功能:余弦嵌入损失,用于学习输入之间的余弦相似性,适用于确定两个输入是否在方向上是相似的
主要参数:
- margin:可取值[-1, 1],推荐为 [0,0.5]
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean')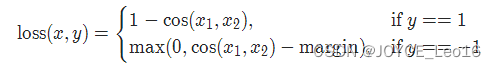
用法示例:
loss = nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss()
input1 = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
input2 = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([1, -1, 1])
output = loss(input1, input2, target)19. nn.CTCLoss
功能:连接时序分类(CTC)损失,用于无对齐或序列到序列问题,如语音或手写识别。
主要参数:
- blank:blank label
- zero_infinity:无穷大的值或梯度置0
- reduction:计算模式,可为none / sum / mean
torch.nn.CTCLoss(blank=0, reduction='mean')用法示例:
T = 50 # Input sequence length
C = 20 # Number of classes (including blank)
N = 16 # Batch size
S = 30 # Target sequence length of longest target in batch
S_min = 10 # Minimum target length, for demonstration purposes
# Initialize random batch of input vectors, for *size = (T,N,C)
input = torch.randn(T, N, C).log_softmax(2).detach().requires_grad_()
# Initialize random batch of targets (0 = blank, 1:C = classes)
target = torch.randint(low=1, high=C, size=(N, S), dtype=torch.long)
input_lengths = torch.full(size=(N,), fill_value=T, dtype=torch.long)
target_lengths = torch.randint(low=S_min, high=S, size=(N,), dtype=torch.long)
loss = nn.CTCLoss()
output = loss(input, target, input_lengths, target_lengths)在实际的代码实现中,你需要根据你的模型和数据来调整输入和目标张量的尺寸。
参考:https://yolov5.blog.csdn.net/article/details/123441628
参考:深度学习爱好者




![[晓理紫]每日论文分享(有中文摘要,源码或项目地址)-大模型、扩散模型、视觉导航](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f1dd0c7581f94db3825c7b4d5c72e502.jpeg#pic_center)