1 Beautiful说明
BeautifulSoup库是灵活又方便的网页解析库,处理高效,支持多种解析器。利用它不用编写正则表达式即可方便地实线网页信息的提取。
安装
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
解析库
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html.parser”) | Python的内置标准库、执行速度适中 、文档容错能力强 | Python 2.7.3 or 3.2.2)前的版本中文容错能力差 |
| lxml HTML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “lxml”) | 速度快、文档容错能力强 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “xml”) | 速度快、唯一支持XML的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html5lib”) | 最好的容错性、以浏览器的方式解析文档、生成HTML5格式的文档 | 速度慢、不依赖外部扩展 |
2 基本使用
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(soup.prettify()) # 格式化代码,自动补全
print(soup.title.string) # 得到title标签里的内容

报错:

3 标签选择器
选择元素
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
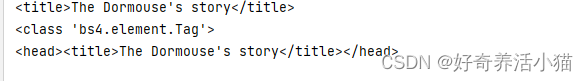
print(soup.title) # 选择了title标签
print(type(soup.title)) # 查看类型
print(soup.head)
获取名称
获得标签的名称:
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(soup.title.name)

获取属性
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(soup.p.attrs['name'])#获取p标签中,name这个属性的值
print(soup.p['name'])#另一种写法,比较直接

获取内容
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(soup.p.string)

嵌套选择
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(soup.head.title.string)

子节点和子孙节点
contents方式
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(soup.p.contents) # 获取指定标签的子节点,类型是list
输出结果:
['\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>, '\n', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, ' \n and\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ']Process finished with exit code 0child方式
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
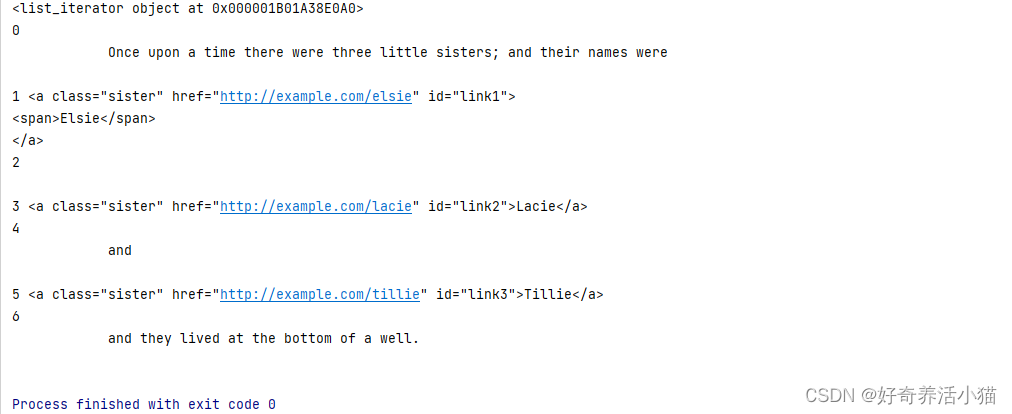
print(soup.p.children)#获取指定标签的子节点的迭代器对象
for i,children in enumerate(soup.p.children):#i接受索引,children接受内容print(i,children)
2为空,是因为标签与标签之间空一行
子孙节点
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
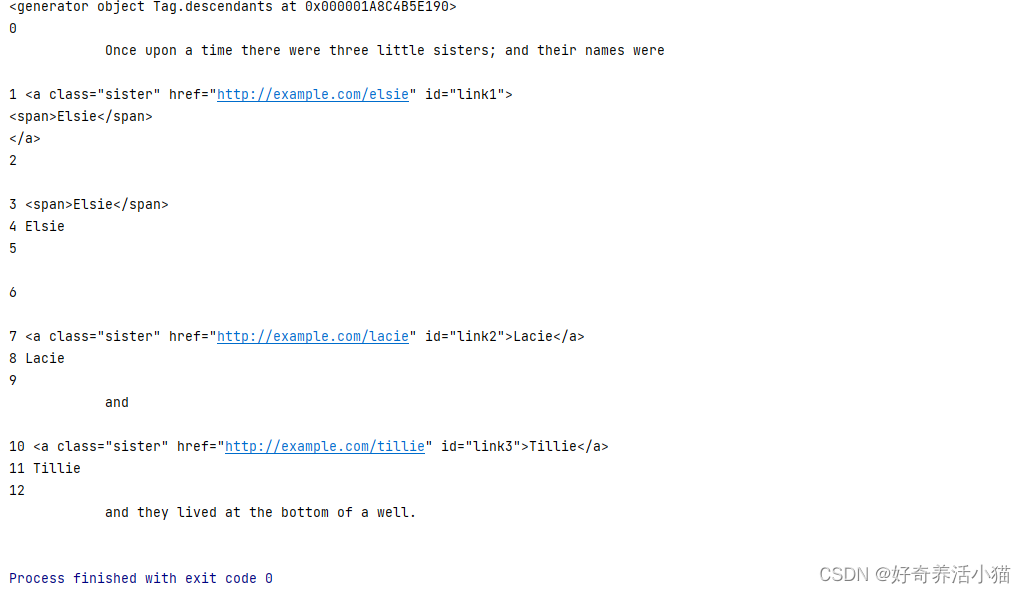
print(soup.p.descendants)#获取指定标签的子孙节点的迭代器对象
for i,child in enumerate(soup.p.descendants):#i接受索引,child接受内容print(i,child)
父节点和祖先节点
parent
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(soup.a.parent)#获取指定标签的父节点
打印出了a节点的父节点:p标签

parents
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.parents)))#获取指定标签的祖先节点
输出结果:
[(0, <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>), (1, <body>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>), (2, <html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body></html>), (3, <html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body></html>)]Process finished with exit code 0
兄弟节点
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p>
"""from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # 传入解析器:lxml
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings)))#获取指定标签的后面的兄弟节点
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.previous_siblings)))#获取指定标签的前面的兄弟节点
输出结果:
[(0, '\n'), (1, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>), (2, ' \n and\n '), (3, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>), (4, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ')]
[(0, '\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ')]Process finished with exit code 0
4 标准选择器
find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
可根据标签名、属性、内容查找文档。
name
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all('ul')) # 查找所有ul标签下的内容
print(type(soup.find_all('ul')[0])) # 查看其类型

嵌套地查找标签下的子标签:
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.find_all('ul'):print(ul.find_all('li'))

attrs
通过属性进行元素的查找:
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
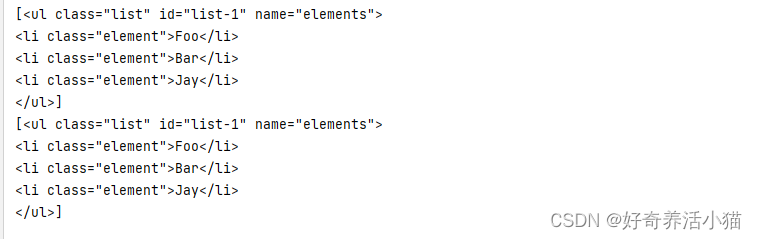
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'id': 'list-1'})) # 传入的是一个字典类型,也就是想要查找的属性
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'name': 'elements'}))
特殊类型的参数查找:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(id='list-1'))#id是个特殊的属性,可以直接使用
print(soup.find_all(class_='element')) #class是关键字所以要用class_
text
根据文本内容来进行选择:
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(text='Foo'))#查找文本为Foo的内容,但是返回的不是标签
text在做内容匹配的时候比较方便,但是在做内容查找的时候并不是太方便。
其他方式
find
find用法和findall一模一样,但是返回的是找到的第一个符合条件的内容输出。find_parents(), find_parent()
find_parents()返回所有祖先节点,find_parent()返回直接父节点。find_next_siblings() ,find_next_sibling()
1返回后面的所有兄弟节点,2返回后面的第一个兄弟节点find_previous_siblings(),find_previous_sibling()
1返回前面所有兄弟节点…find_all_next(),find_next()
1返回节点后所有符合条件的节点,2返回后面第一个符合条件的节点find_all_previous()和find_previous()
同理。
5 CSS选择器
通过select()直接传入CSS选择器即可完成选择
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.select('.panel .panel-heading')) # .代表class,中间需要空格来分隔
print(soup.select('ul li')) # 选择ul标签下面的li标签
print(soup.select('#list-2 .element')) # '#'代表id。这句的意思是查找id为"list-2"的标签下的,class=element的元素
print(type(soup.select('ul')[0])) # 打印节点类型

层层嵌套的选择:
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.select('ul'):print(ul.select('li'))

获取属性
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupsoup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.select('ul'):print(ul['id']) # 用[ ]即可获取属性print(ul.attrs['id']) # 另一种写法

获取内容
html = '''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for li in soup.select('li'):print(li.get_text())

6 总结
- 推荐使用lxml解析库,必要时使用html.parser
- 标签选择筛选功能弱但是速度快
- 建议使用find()、find_all() 查询匹配单个结果或者多个结果
- 如果对CSS选择器熟悉建议使用select()
- 记住常用的获取属性和文本值的方法