题目:
138. 随机链表的复制
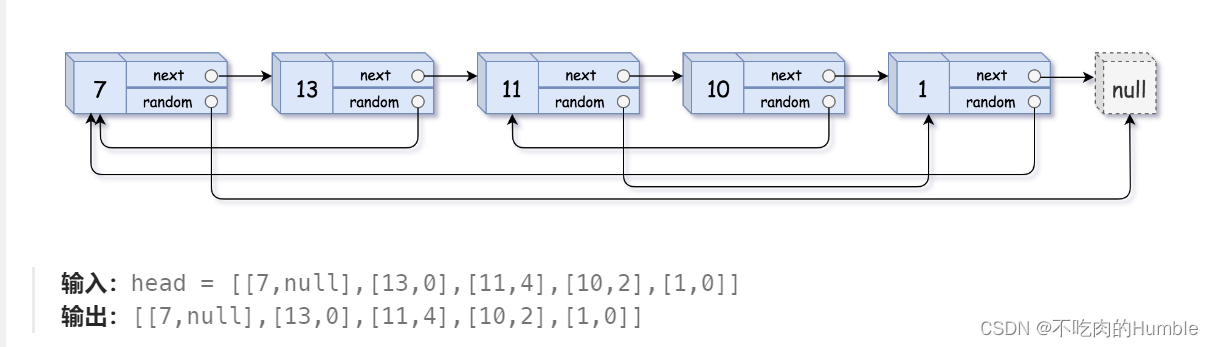
给你一个长度为
n的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针random,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。要求:构造这个链表的 深拷贝
深拷贝应该正好由
n个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的next指针和random指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。注意:复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点

示例:
思路一:暴力求解
1.拷贝链表
2.处理拷贝链表每个节点的random指针,这里封装一个函数来实现~
通过分析,思路一的时间复杂度应该是O(N^2),这是一种很直观的思路,下面我们来实现
1.拷贝链表,代码如下:
struct Node *copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)),*p;p = copy;struct Node *cur = head;//cur指向原链表的头节点while(cur!=NULL){struct Node *curcopy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));curcopy->val=cur->val;curcopy->random=NULL;copy->next=curcopy;//copy是curcopy的前驱,起着拷贝链表的连接作用copy = copy->next;//copy往后走cur=cur->next;//cur往后走}copy->next=NULL;//当cur = NULL后的处理
2.处理拷贝链表每个节点的random指针,代码如下:
cur=head;//让在第一步使用过的cur回到原链表的头copy=p->next;//让在第一步使用过的copy来到拷贝链表的头while(cur!=NULL){if(cur->random==NULL){copy->random=NULL;}else{//find函数是用来找到random指向的节点copy->random=find(head,p->next,cur->random);}copy=copy->next;cur=cur->next;}find函数的实现代码如下:
//find函数找到random指向的节点//head为原链表的头,copy为拷贝链表的头,dest为目标
struct Node* find(struct Node* head,struct Node* copy,struct Node* dest)
{while(head!=dest){head=head->next;copy=copy->next;}return copy;
}下面我们将第一步与第二步的代码整合起来,就形成完整的代码
struct Node* find(struct Node* head,struct Node* copy,struct Node* dest);
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head){if(head == NULL) return NULL;struct Node *copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)),*p;p = copy;struct Node *cur = head;while(cur!=NULL){struct Node *curcopy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));curcopy->val=cur->val;curcopy->random=NULL;copy->next=curcopy;copy = copy->next;cur=cur->next;}copy->next=NULL;cur=head;copy=p->next;while(cur!=NULL){if(cur->random==NULL){copy->random=NULL;}else{copy->random=find(head,p->next,cur->random);}copy=copy->next;cur=cur->next;}return p->next;//返回拷贝链表的头
}//find函数找到random指向的节点
struct Node* find(struct Node* head,struct Node* copy,struct Node* dest)
{while(head!=dest){head=head->next;copy=copy->next;}return copy;
}
虽然时间复杂度为O(N^2),但力扣居然给过了

不过这里要说的是,这样暴力的思路往往不是面试官心中的答案,所以下面我们来看一下更优的思路二
思路二:

1.插入拷贝节点在原节点的后面
2.控制拷贝节点的random
copy -> random = cur ->random->next(这句是精华)
3.解下拷贝节点,同时恢复原链表的指向
思路二的巧妙就在于它在建立拷贝链表时就和原链表有了联系,有了这种联系,之后处理random指针就能更高效,直接就能找到、、
我们看一下思路二的时间复杂度,已经变成了O(N),这就非常的nice
下面我们就来实现这个思路
第一步:插入拷贝节点在原节点的后面,代码如下
struct Node* cur = head;//cur在原节点的头while (cur != NULL)//第一步{struct Node* copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copy->val = cur->val;//插入copy->next = cur->next;cur->next = copy;//继续往下cur = copy->next;}第二步:控制拷贝节点的random,代码如下
cur = head;//恢复cur到原节点的头while (cur != NULL) //第二步{struct Node* curcopy = cur->next;//拷贝节点if (cur->random == NULL) curcopy->random = NULL;elsecurcopy->random =cur->random->next;cur = curcopy->next;}第三步:解下拷贝节点使其成为独立的链表,同时恢复原链表的指向,代码如下
cur = head;//恢复cur到原节点的头//第三步struct Node* copyhead=NULL,*copytail=NULL;//定义拷贝链表的头和尾while (cur != NULL){struct Node* curcopy = cur->next;struct Node* curnext = curcopy->next;// curnext是原链表cur的下一个节点//通过尾插使拷贝节点成为独立的链表if(copyhead == NULL)//处理头copyhead = copytail = curcopy;else //处理其他情况{copytail->next = curcopy;copytail = copytail->next;}cur->next= curnext;//恢复原链表的指向cur = curnext;//cur往后走}下面我们将这三步的代码整合起来,就形成完整的代码
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head){if (head == NULL) return NULL;struct Node* cur = head;//cur在原节点的头while (cur != NULL)//第一步{struct Node* copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copy->val = cur->val;//插入copy->next = cur->next;cur->next = copy;//继续往下cur = copy->next;}cur = head;//恢复cur到原节点的头while (cur != NULL) //第二步{struct Node* curcopy = cur->next;//拷贝节点if (cur->random == NULL) curcopy->random = NULL;elsecurcopy->random =cur->random->next;cur = curcopy->next;}cur = head;//第三步struct Node* copyhead=NULL,*copytail=NULL;while (cur != NULL){struct Node* curcopy = cur->next;struct Node* curnext = curcopy->next;// curnext是原链表cur的下一个节点if(copyhead == NULL)copyhead = copytail = curcopy;else {copytail->next = curcopy;copytail = copytail->next;}cur->next= curnext;//恢复原链表cur = curnext;}return copyhead;//返回拷贝链表的头
}代码走起来

就过了
好啦,到此为止,今天的随机链表的复制问题就结束啦,如果文中分析,题解代码有不足的地方欢迎大家在评论区讨论和指正
让我们在接下来的时间里一起学习,一起进步吧~