重学SpringBoot3-内容协商机制
- ContentNegotiationConfigurer接口
- 配置内容协商
- URL参数
- Accept头
- 使用Url扩展名
- 自定义内容协商格式
- 步骤1: 注册自定义媒体类型
- 步骤2: 实现`HttpMessageConverter`接口
- 步骤3: 使用自定义`HttpMessageConverter`
- 注意点
在 Spring Boot 3 中,内容协商(Content Negotiation)是一个非常重要的概念,特别是在构建 RESTful API 时。内容协商机制允许客户端和服务器就如何交换资源的数据格式达成协议。简单来说,它允许客户端通过请求头指定它们希望接收响应的格式(如 JSON,XML 等),服务器基于这些信息来决定以什么格式返回数据。
ContentNegotiationConfigurer接口
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ContentNegotiationConfigurer
ContentNegotiationConfigurer 是 Spring 框架中的一个接口,用于自定义内容协商策略,主要通过以下几种方式来实现:
- URL参数: 通过 URL 参数来指定响应格式,例如,
?format=json。 - Accept头: 通过
Accept请求头来指定希望接收的响应类型,这是HTTP规范推荐的方式。 - 扩展名: 通过 URL 的扩展名来指定响应的格式。例如,
.json表示希望响应为 JSON 格式,.xml表示希望响应为 XML 格式。
配置内容协商
在 Spring Boot 3 中,你可以在 application.properties 或 application.yml 文件中进行基本的内容协商配置:
# 开启基于请求参数的内容协商功能,默认此功能不开启
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-parameter=true
# 指定内容协商时使用的参数名。默认是 format
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.parameter-name=mediaType
# 用于设置支持的内容协商(Content Negotiation)的媒体类型
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.json=application/json
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.xml=application/xml
或者通过配置类来实现更复杂的逻辑,没错,就是之前讲过的通过重新 WebMvcConfigurer 接口方法实现自定义配置:
public interface WebMvcConfigurer {default void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {}// 其他方法
}
以下是一个示例,演示如何通过配置类来配置内容协商策略:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {configurer.favorParameter(true).parameterName("mediaType").ignoreAcceptHeader(false).useRegisteredExtensionsOnly(false).defaultContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).mediaType("json", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).mediaType("xml", MediaType.APPLICATION_XML);}
}
在这个配置中:
favorParameter(true):允许使用 URL 参数进行内容协商。parameterName("mediaType"):指定 URL 参数的名称。ignoreAcceptHeader(false):不忽略Accept头,即同时支持Accept头和URL参数。useRegisteredExtensionsOnly(false):不仅仅基于已注册的扩展进行格式匹配。defaultContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON):设置默认的响应类型为JSON。mediaType("json", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)和mediaType("xml", MediaType.APPLICATION_XML):注册 URL 扩展名到 MIME 类型的映射。
注意,如果要支持输出 XML 需要 pom 文件引入 jackson 包:
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId><artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId></dependency>
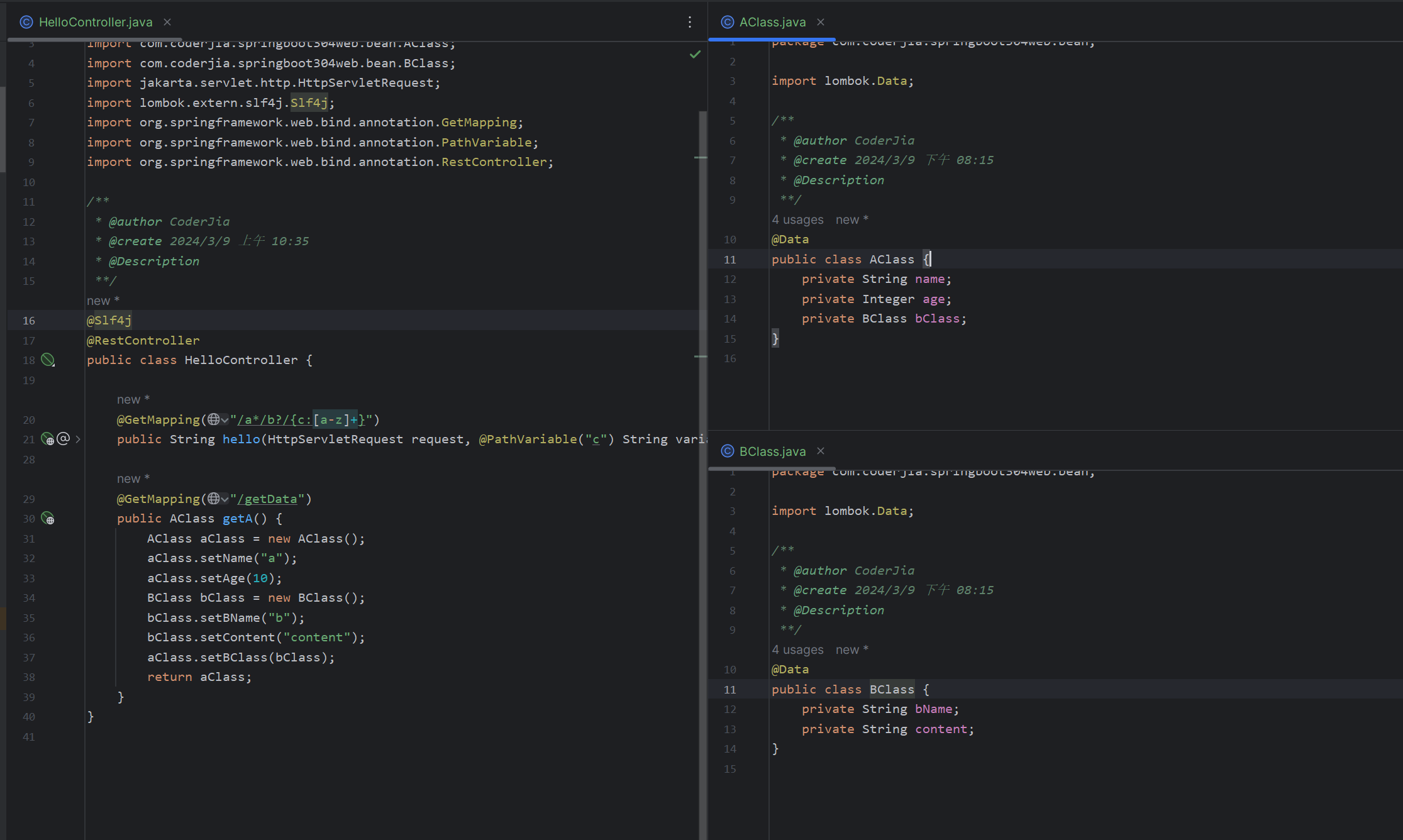
URL参数
需要携带查询字符串
?mediaType=

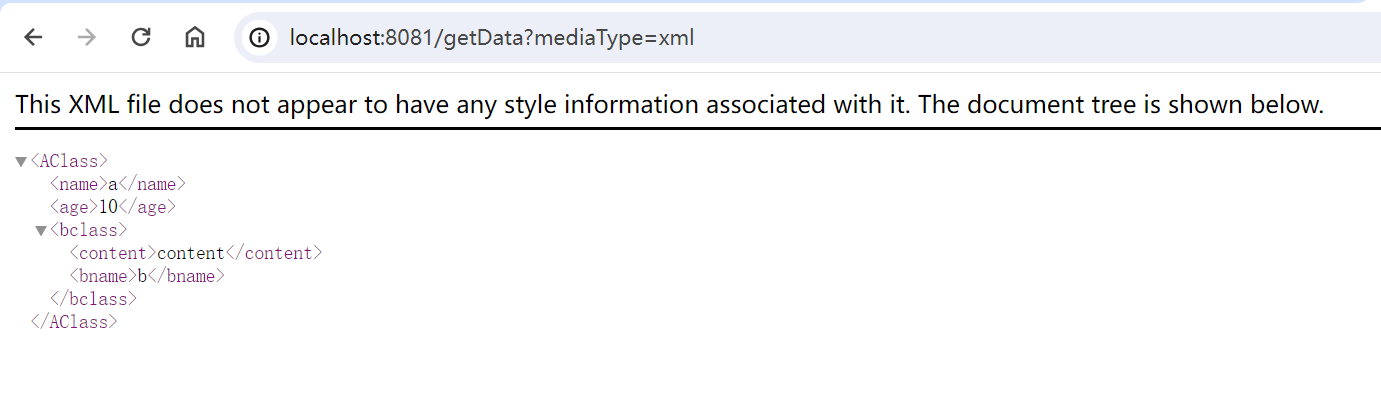
Accept头
修改请求头使用 postman 或者 apifox 工具。
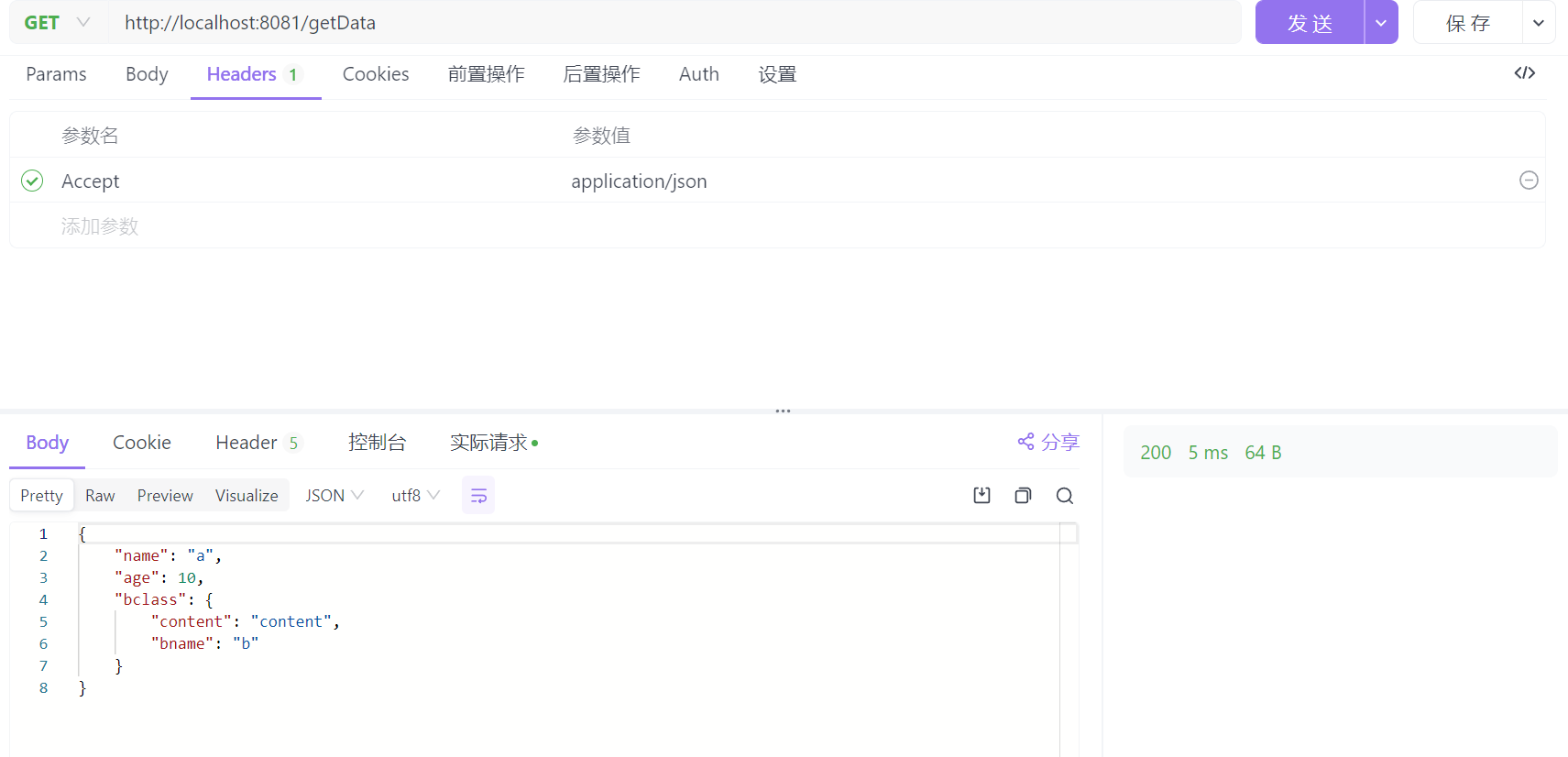

使用Url扩展名
从Spring Framework 5.3开始,官方推荐使用其他内容协商机制(如请求头
Accept)而非扩展名,因为路径扩展可能会引起一些安全和使用上的问题。因此,在实际应用中,建议评估使用扩展名方式的必要性。
配置了基于扩展名的内容协商,配置文件已经不支持这种配置,所有改成新建配置类的方式:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {configurer.favorPathExtension(true).favorParameter(false).ignoreAcceptHeader(false).useRegisteredExtensionsOnly(true).mediaType("json", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).mediaType("xml", MediaType.APPLICATION_XML);}
}



自定义内容协商格式
自定义内容协商格式主要涉及到两个方面:一是自定义支持的媒体类型(Media Types),二是自定义对这些媒体类型的处理。
在 Spring Boot 3 中,自定义内容协商格式通常需要以下几个步骤:
- 注册自定义媒体类型:你可以通过配置类来注册自定义的媒体类型,让 Spring MVC 知道你打算支持哪些额外的格式。
- 实现
HttpMessageConverter接口:对于每种你想支持的媒体类型,你需要提供一个相应的HttpMessageConverter实现,用于序列化和反序列化数据。 - 配置 Spring MVC 以使用你的自定义
HttpMessageConverter:最后,你需要在 Spring MVC 配置中注册你的HttpMessageConverter实现,以确保Spring MVC 会使用它们进行请求和响应的处理。
步骤1: 注册自定义媒体类型
假设你想添加对 application/yaml 这种媒体类型的支持,首先需要在配置类中注册这种媒体类型:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {configurer.mediaType("yaml", MediaType.valueOf("application/x-yaml"));}
}
或者使用配置文件:
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml=application/x-yaml
还需要引入 Jackson 库的 YAML 数据格式支持:
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId><artifactId>jackson-dataformat-yaml</artifactId>
</dependency>
步骤2: 实现HttpMessageConverter接口
接下来,需要创建一个 HttpMessageConverter 实现,用于处理 YAML 格式的数据。这里需要实现 read 和 write 方法,分别用于反序列化和序列化数据。例如,使用 YamlMapper(这是一个假设的类,实际上你可能需要使用例如SnakeYAML之类的库):
package com.coderjia.springboot304web.config;import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLMapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpInputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.HttpOutputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.AbstractHttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotWritableException;import java.io.IOException;/*** @author CoderJia* @create 2024/3/9 下午 10:32* @Description**/
public class YamlHttpMessageConverter extends AbstractHttpMessageConverter<Object> {private final YAMLMapper yamlMapper = new YAMLMapper();public YamlHttpMessageConverter() {super(MediaType.valueOf("application/x-yaml"));}@Overrideprotected boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {// 这里简化了实现,实际上你可能需要更复杂的逻辑来决定你的converter支持哪些类return true;}@Overrideprotected Object readInternal(Class<?> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {// 从HttpInputMessage中读取并解析YAML格式的数据return yamlMapper.readValue(inputMessage.getBody(), clazz);}@Overrideprotected void writeInternal(Object object, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {// 将给定的对象写入HttpOutputMessage的body中yamlMapper.writeValue(outputMessage.getBody(), object);}
}步骤3: 使用自定义HttpMessageConverter
最后,需要在 Spring MVC 配置中注册这个新的 HttpMessageConverter。这通常是在一个配置类中完成,通过重写 configureMessageConverters方法:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {configurer.mediaType("yaml", MediaType.valueOf("application/x-yaml"));}@Overridepublic void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {converters.add(new YamlHttpMessageConverter());}}
这样,当客户端请求以 application/x-yaml 格式接收数据时(比如,通过设置Accept: application/x-yaml头),Spring MVC 就会使用你的 YamlHttpMessageConverter 来序列化响应数据为YAML格式:
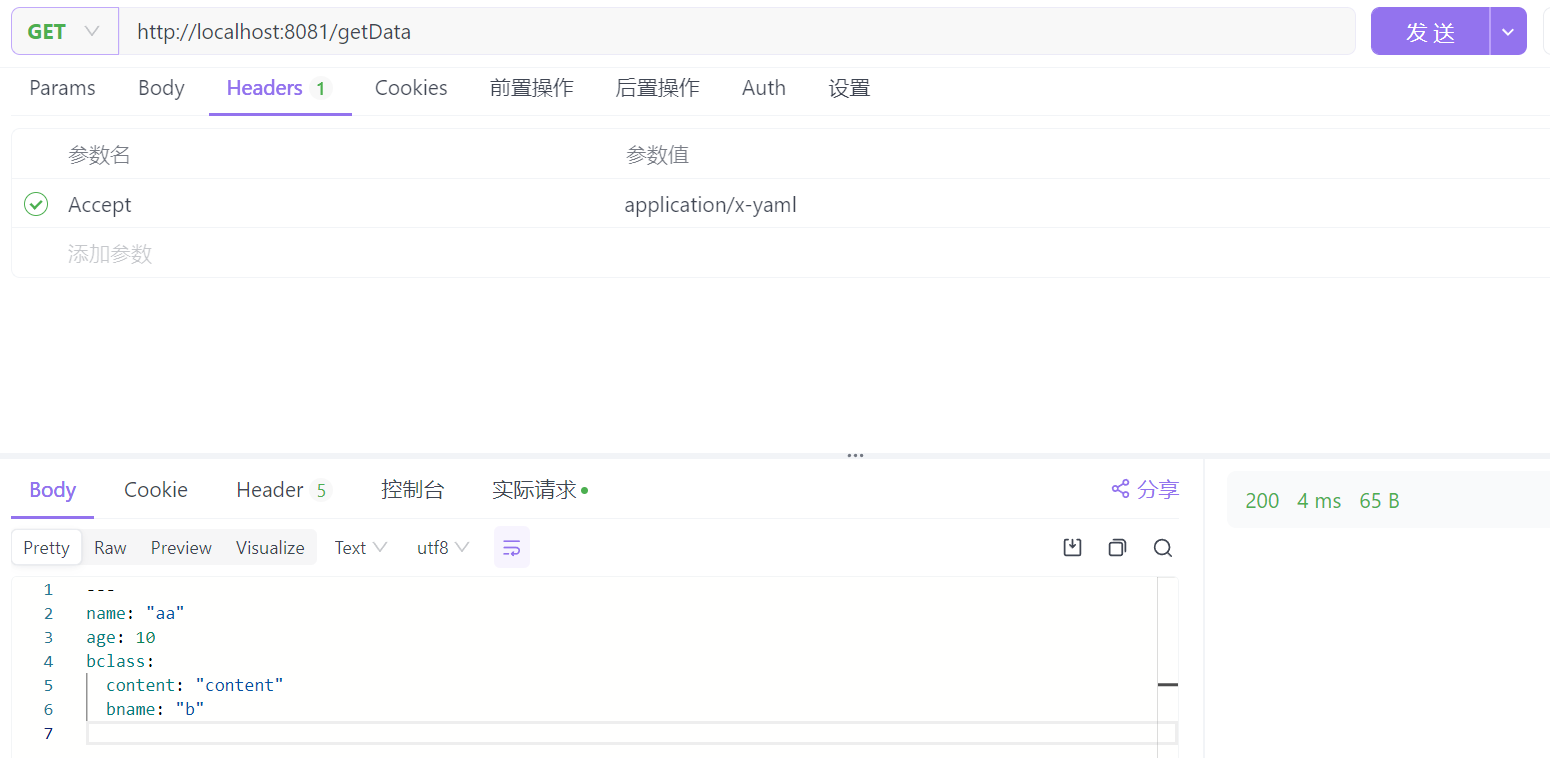
注意点
内容协商的配置和实现方式可能因 Spring Boot 版本的不同而略有变化。上述示例适用于 Spring Boot 3,但在实际应用中,还需要根据具体的需求和环境来调整配置。