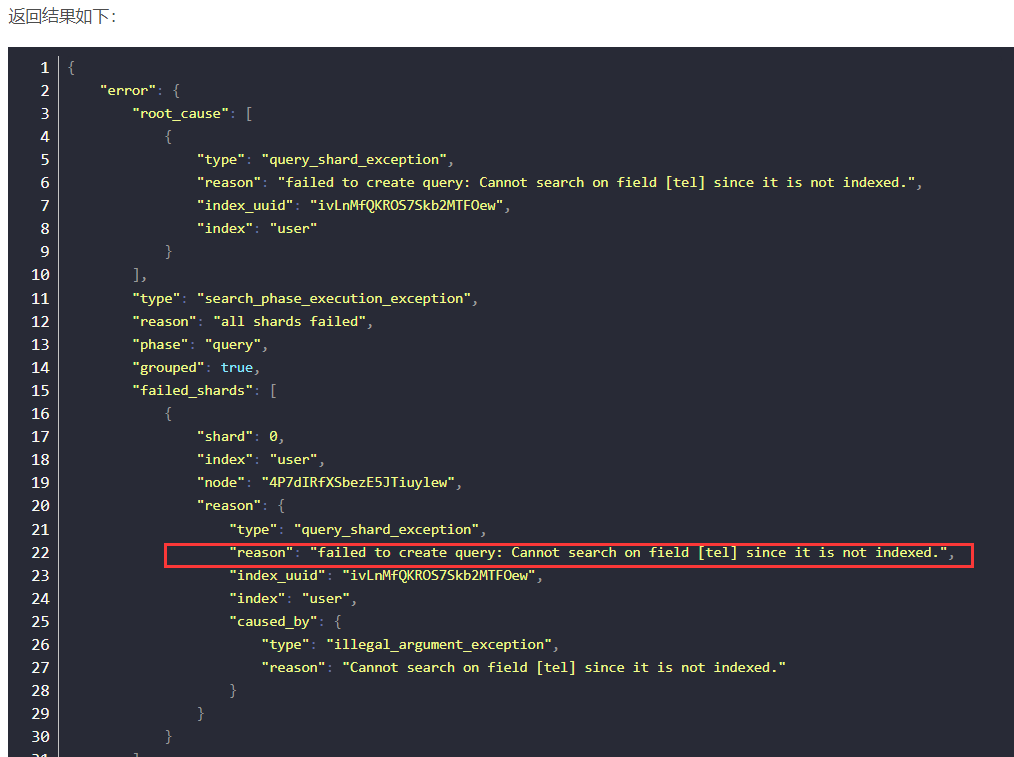
113路径总和 II
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
思路:
题目最终输出的是路径,因此用BFS遍历的时候,需要记录走到每个节点的路径;
又因为路径和是要等于某个目标值的,因此也需要记录目标和。
⇒ 走到每个节点时需要记录 该结点的路径和路径和。
⇒ BFS 里queue 记录 的节点 [ node , [ node.val],node.val]
function TreeNode(val, left, right) {this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : valthis.left = left === undefined ? null : leftthis.right = right === undefined ? null : right
}// 根据数组创建一颗树
const createTree = (arr) => {const len = arr.lengthif (len === 0) return nullconst root = new TreeNode(arr[0]) // 根节点const queue = [root] // 用于存储每一层的节点let i = 1 // 当前节点在数组中的索引while (i < len) {const node = queue.shift() // 取出当前层的第一个节点const leftVal = arr[i++] // 左子节点的值const rightVal = arr[i++] // 右子节点的值if (leftVal !== null) {const leftNode = new TreeNode(leftVal)node.left = leftNodequeue.push(leftNode) // 将左子节点添加到队列中}if (rightVal !== null) {const rightNode = new TreeNode(rightVal)node.right = rightNodequeue.push(rightNode) // 将右子节点添加到队列中}}return root
}let arr = [5, 4, 8, 11, null, 13, 4, 7, 2, null, null, 5, 1]
let root = createTree(arr)
// console.log(root) // 输出树的结构/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {number} targetSum* @return {number[][]}*/
var pathSum = function (root, targetSum) {// 找出所有,遍历的时候记录路径,路径和,路径和用于判断是否满足条件let res = []if (!root) return reslet queue = [[root,[root.val],root.val]]while (queue.length) {const [node,path,pathSum] = queue.shift()// 满足条件保存。if (node.left === null && node.right === null && pathSum === targetSum) {res.push(path)}// 将临近的节点加入queueif (node.left) {queue.push([node.left, path.concat([node.left.val]), pathSum + node.left.val])}if (node.right) {queue.push([node.right, path.concat([node.right.val]), pathSum + node.right.val])}}return res
}注意:path.concat 返回的是数组,path.push返回的是数组的长度。
console.log([5].push(3)) // 返回的是长度。console.log([5].concat(3)) // [5, 3]let list = [5]list.push(2)console.log(list) // 返回的是 [5,2]二、二叉树标记将路径和中分的点
从根到叶子节点的通路上,有个节点可以把通路上的节点平分成两部分,将其标记,统计整棵树上的所有节点和减去标记节点的和
如图,绿色的即为标记的点,
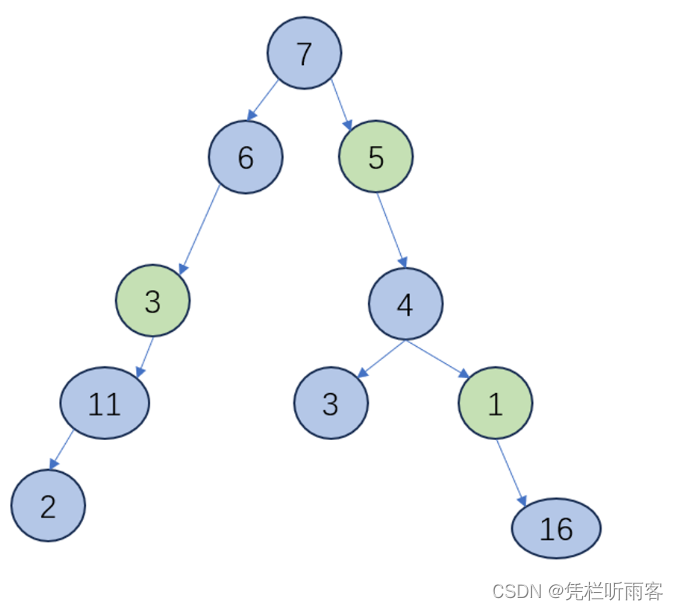
节点3上边为 6+7=13,下边为11+2=13,因此将3标记
节点5上边为7,下边有4+3 = 7,因此标记
节点1上边为7+5+4 = 16,下边为16,标记
思路:
BFS遍历每个节点,如果某个节点是所在路径的中间点,那么该节点的前缀和是所在路径和-该节点的值后剩余数的 一半,因此对于每个节点来说,都需要记录前缀和、路径和以及该节点的值。
因为树上可能会出现值一样的不同节点,因此visitedMap 需要保存的key是节点,而不能是节点的值。
function TreeNode(val, left, right) {this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : valthis.left = left === undefined ? null : leftthis.right = right === undefined ? null : right
}// 根据数组创建一颗树
const createTree = (arr) => {const len = arr.lengthif (len === 0) return nullconst root = new TreeNode(arr[0]) // 根节点const queue = [root] // 用于存储每一层的节点let i = 1 // 当前节点在数组中的索引while (i < len) {const node = queue.shift() // 取出当前层的第一个节点const leftVal = arr[i++] // 左子节点的值const rightVal = arr[i++] // 右子节点的值if (leftVal !== null) {const leftNode = new TreeNode(leftVal)node.left = leftNodequeue.push(leftNode) // 将左子节点添加到队列中}if (rightVal !== null) {const rightNode = new TreeNode(rightVal)node.right = rightNodequeue.push(rightNode) // 将右子节点添加到队列中}}return root
}let arr = [7, 6, 5, 3, null, 4, null, 11, null, 1, 3, 2, null, 16, null]
let root = createTree(arr)const bisectTreePath = (root) => {const queue = [[root, [root], root.val, [root.val]]]// 因为可能出现相同值的不同结点,如果map值存放值,就可能会遗漏。因此map的key存放树节点。let markedMap = new Map()const res = []while (queue.length > 0) {const [node, path, pathSum, pre] = queue.shift()markedMap.set(node, false)// 遇到叶子结点将结果保存。if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {res.push([path, pathSum, pre])}if (node.left !== null) {queue.push([node.left,path.concat(node.left),pathSum + node.left.val,pre.concat(pre.at(-1) + node.left.val)])}if (node.right !== null) {queue.push([node.right,path.concat(node.right),pathSum + node.right.val,pre.concat(pre.at(-1) + node.right.val)])}}for (let i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {const [path, pathSum, pre] = res[i]// console.log(path[0].val,11)for (let j = 0; j < pre.length - 1; j++) {if (pre[j] * 2 + path[j + 1].val === pathSum &&!markedMap.get(path[j + 1])) {markedMap.set(path[j + 1], true)}}}// 遍历markedMaplet sum = 0for (let [key, value] of markedMap) {if (value === false) {sum += key.val}}return sum
}console.log(bisectTreePath(root))