三、字节码技术
1、类文件结构
一个简单的 HelloWorld.java
package com.mysite.jvm.t5;
// HelloWorld 示例
public class HelloWorld {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("hello world");}
}
执行 javac -parameters -d . HellowWorld.java
编译为 HelloWorld.class 后是这个样子的:
[root@localhost ~]# od -t xC HelloWorld.class
0000000 ca fe ba be 00 00 00 34 00 23 0a 00 06 00 15 09
0000020 00 16 00 17 08 00 18 0a 00 19 00 1a 07 00 1b 07
0000040 00 1c 01 00 06 3c 69 6e 69 74 3e 01 00 03 28 29
0000060 56 01 00 04 43 6f 64 65 01 00 0f 4c 69 6e 65 4e
0000100 75 6d 62 65 72 54 61 62 6c 65 01 00 12 4c 6f 63
0000120 61 6c 56 61 72 69 61 62 6c 65 54 61 62 6c 65 01
0000140 00 04 74 68 69 73 01 00 1d 4c 63 6e 2f 69 74 63
0000160 61 73 74 2f 6a 76 6d 2f 74 35 2f 48 65 6c 6c 6f
0000200 57 6f 72 6c 64 3b 01 00 04 6d 61 69 6e 01 00 16
0000220 28 5b 4c 6a 61 76 61 2f 6c 61 6e 67 2f 53 74 72
0000240 69 6e 67 3b 29 56 01 00 04 61 72 67 73 01 00 13
0000260 5b 4c 6a 61 76 61 2f 6c 61 6e 67 2f 53 74 72 69
0000300 6e 67 3b 01 00 10 4d 65 74 68 6f 64 50 61 72 61
0000320 6d 65 74 65 72 73 01 00 0a 53 6f 75 72 63 65 46
0000340 69 6c 65 01 00 0f 48 65 6c 6c 6f 57 6f 72 6c 64
0000360 2e 6a 61 76 61 0c 00 07 00 08 07 00 1d 0c 00 1e
0000400 00 1f 01 00 0b 68 65 6c 6c 6f 20 77 6f 72 6c 64
0000420 07 00 20 0c 00 21 00 22 01 00 1b 63 6e 2f 69 74
0000440 63 61 73 74 2f 6a 76 6d 2f 74 35 2f 48 65 6c 6c
0000460 6f 57 6f 72 6c 64 01 00 10 6a 61 76 61 2f 6c 61
0000500 6e 67 2f 4f 62 6a 65 63 74 01 00 10 6a 61 76 61
0000520 2f 6c 61 6e 67 2f 53 79 73 74 65 6d 01 00 03 6f
0000540 75 74 01 00 15 4c 6a 61 76 61 2f 69 6f 2f 50 72
0000560 69 6e 74 53 74 72 65 61 6d 3b 01 00 13 6a 61 76
0000600 61 2f 69 6f 2f 50 72 69 6e 74 53 74 72 65 61 6d
0000620 01 00 07 70 72 69 6e 74 6c 6e 01 00 15 28 4c 6a
0000640 61 76 61 2f 6c 61 6e 67 2f 53 74 72 69 6e 67 3b
0000660 29 56 00 21 00 05 00 06 00 00 00 00 00 02 00 01
0000700 00 07 00 08 00 01 00 09 00 00 00 2f 00 01 00 01
0000720 00 00 00 05 2a b7 00 01 b1 00 00 00 02 00 0a 00
0000740 00 00 06 00 01 00 00 00 04 00 0b 00 00 00 0c 00
0000760 01 00 00 00 05 00 0c 00 0d 00 00 00 09 00 0e 00
0001000 0f 00 02 00 09 00 00 00 37 00 02 00 01 00 00 00
0001020 09 b2 00 02 12 03 b6 00 04 b1 00 00 00 02 00 0a
0001040 00 00 00 0a 00 02 00 00 00 06 00 08 00 07 00 0b
0001060 00 00 00 0c 00 01 00 00 00 09 00 10 00 11 00 00
0001100 00 12 00 00 00 05 01 00 10 00 00 00 01 00 13 00
0001120 00 00 02 00 14
根据 JVM 规范,类文件结构如下
ClassFile {u4 magic; // 魔数 4 byteu2 minor_version; // 最小版本号 2 byteu2 major_version; // 最大版本号 2 byteu2 constant_pool_count;// 常量池数量cp_info constant_pool[constant_pool_count-1]; // 常量池内容u2 access_flags; // 访问修饰符u2 this_class; // 自己的类名信息u2 super_class; // 父类信息u2 interfaces_count;// 接口数量u2 interfaces[interfaces_count]; //接口u2 fields_count; // 成员变量数量field_info fields[fields_count]; // 成员变量内容u2 methods_count; // 方法数量method_info methods[methods_count]; // 方法内容u2 attributes_count; // 其他的属性信息attribute_info attributes[attributes_count];
}
1)魔数
0~3 字节,表示它是否是【class】类型的文件
0000000 ca fe ba be 00 00 00 34 00 23 0a 00 06 00 15 09
2)版本
4~7字节,表示类的版本 00 34(52)表示 Java 8
0000000 ca fe ba be 00 00 00 34 00 23 0a 00 06 00 15 09
3)常量池
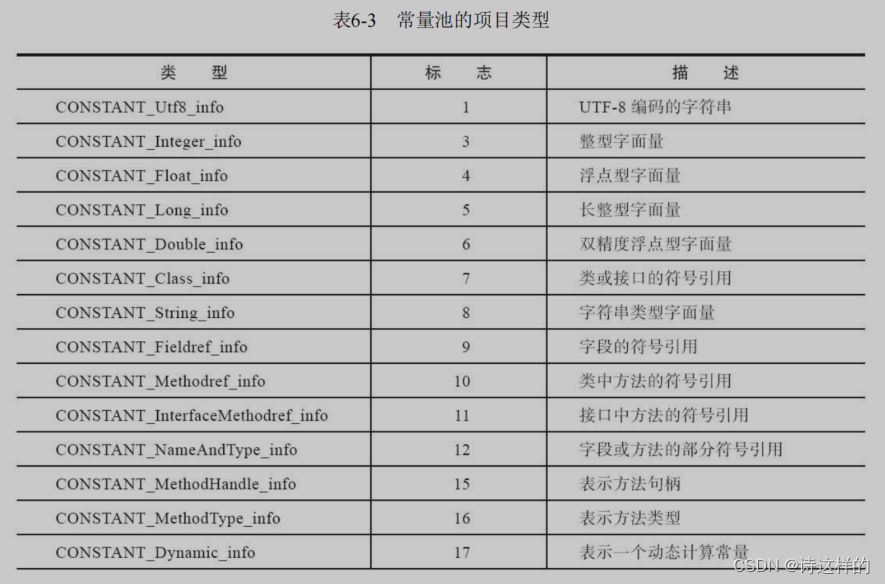
详细见《深入理解深入理解Java虚拟机:JVM高级特性与最佳实践(第3版) (周志明) 》- p303
或
详细见Java虚拟机规范参考文档
2、字节码指令
1)入门
2)javap 工具
通过 javap 工具反编译 class 文件
javap -v ./Demo.class
3)图解方法执行流程
3.1 原始 java 代码
package cn.itcast.jvm.t3.bytecode;
/**
* 演示 字节码指令 和 操作数栈、常量池的关系
*/
public class Demo3_1 {public static void main(String[] args) {int a = 10;int b = Short.MAX_VALUE + 1;int c = a + b;System.out.println(c);}
}
3.2 编译后的字节码文件
[root@localhost ~]# javap -v Demo3_1.class
Classfile /root/Demo3_1.class
Last modified Jul 7, 2019; size 665 bytes
MD5 checksum a2c29a22421e218d4924d31e6990cfc5
Compiled from "Demo3_1.java"
public class cn.itcast.jvm.t3.bytecode.Demo3_1
minor version: 0
major version: 52
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #7.#26 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Class #27 // java/lang/Short
#3 = Integer 32768
#4 = Fieldref #28.#29 //
java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#5 = Methodref #30.#31 // java/io/PrintStream.println:(I)V
#6 = Class #32 // cn/itcast/jvm/t3/bytecode/Demo3_1
#7 = Class #33 // java/lang/Object
#8 = Utf8 <init>
#9 = Utf8 ()V
#10 = Utf8 Code
#11 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#12 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#13 = Utf8 this
#14 = Utf8 Lcn/itcast/jvm/t3/bytecode/Demo3_1;
#15 = Utf8 main
#16 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
#17 = Utf8 args
#18 = Utf8 [Ljava/lang/String;
#19 = Utf8 a
#20 = Utf8 I
#21 = Utf8 b
#22 = Utf8 c
#23 = Utf8 MethodParameters
#24 = Utf8 SourceFile
#25 = Utf8 Demo3_1.java
#26 = NameAndType #8:#9 // "<init>":()V
#27 = Utf8 java/lang/Short
#28 = Class #34 // java/lang/System
#29 = NameAndType #35:#36 // out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#30 = Class #37 // java/io/PrintStream
#31 = NameAndType #38:#39 // println:(I)V
#32 = Utf8 cn/itcast/jvm/t3/bytecode/Demo3_1
#33 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#34 = Utf8 java/lang/System
#35 = Utf8 out
#36 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#37 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream
#38 = Utf8 println
#39 = Utf8 (I)V
{
public cn.itcast.jvm.t3.bytecode.Demo3_1();descriptor: ()Vflags: ACC_PUBLICCode:stack=1, locals=1, args_size=10: aload_01: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."
<init>":()V4: returnLineNumberTable:line 6: 0LocalVariableTable:Start Length Slot Name Signature0 5 0 this Lcn/itcast/jvm/t3/bytecode/Demo3_1;
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)Vflags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATICCode:stack=2, locals=4, args_size=10: bipush 102: istore_13: ldc #3 // int 327685: istore_26: iload_17: iload_28: iadd9: istore_310: getstatic #4 // Field
java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;13: iload_314: invokevirtual #5 // Method
java/io/PrintStream.println:(I)V17: returnLineNumberTable:line 8: 0line 9: 3line 10: 6line 11: 10line 12: 17LocalVariableTable:Start Length Slot Name Signature0 18 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;3 15 1 a I6 12 2 b I10 8 3 c I
MethodParameters:
Name Flags
args
}
3.3 常量池载入运行时常量池
超出了整数的范围的存储在运行时常量池中,未超出和字节码指令放在一起。
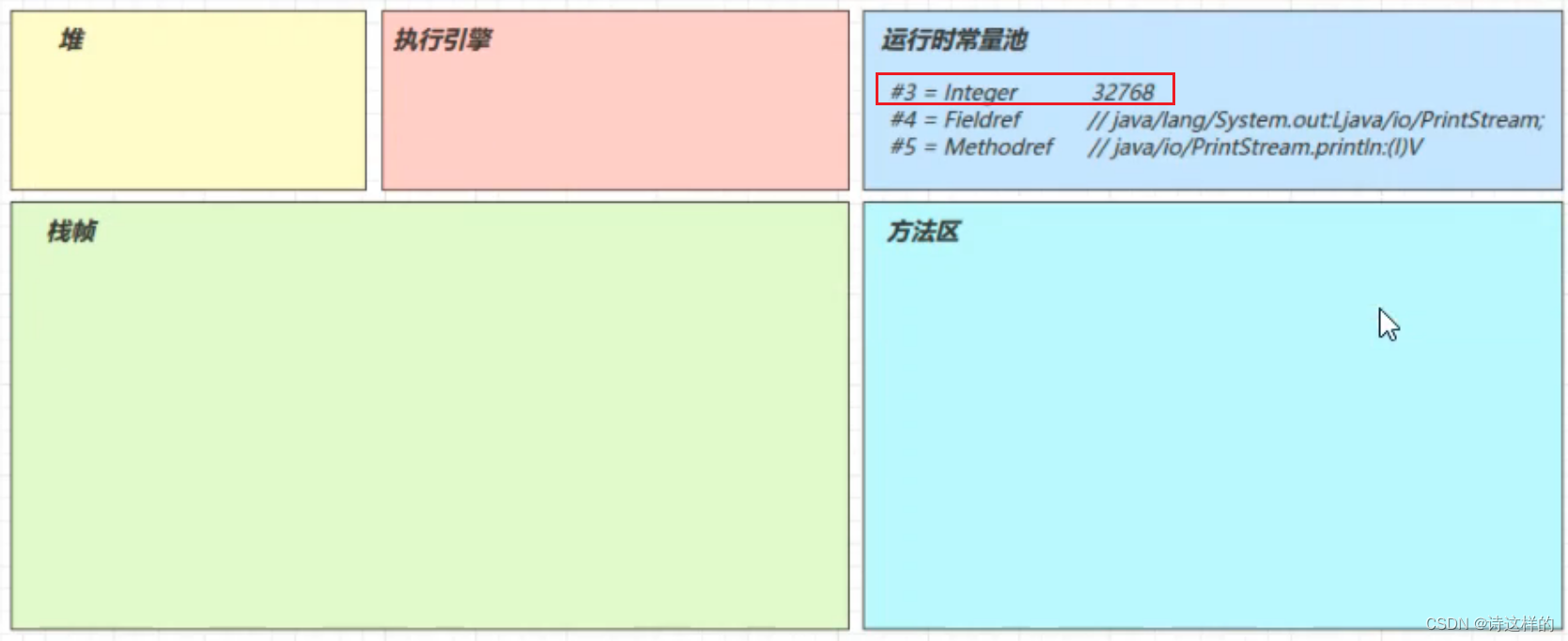
3.4 方法字节码载入方法区
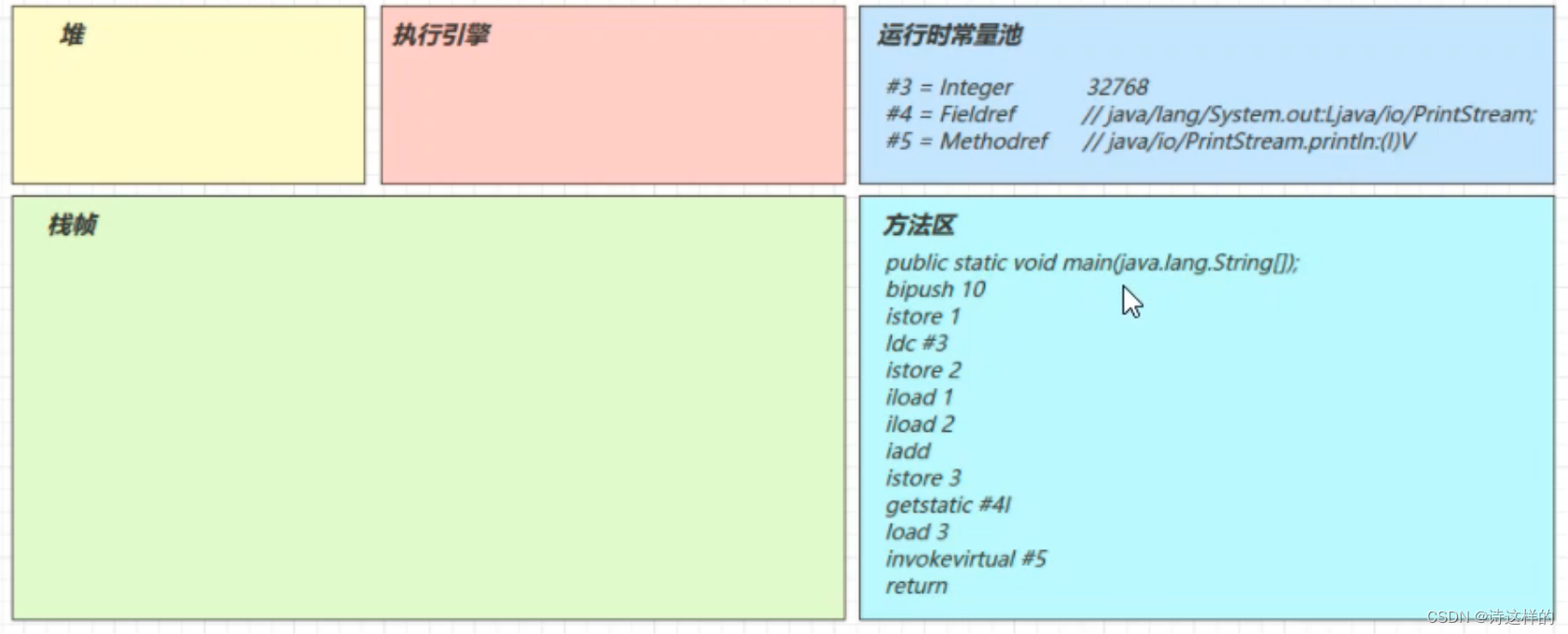
3.5main 线程开始运行,分配栈帧内存
(stack = 2, locals = 4)
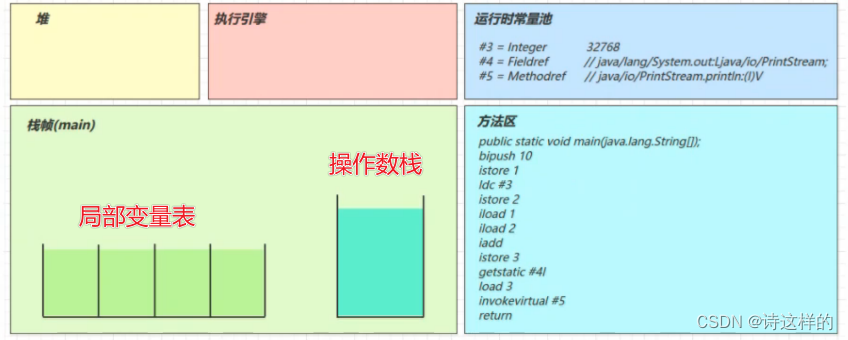
3.6执行引擎开始执行字节码
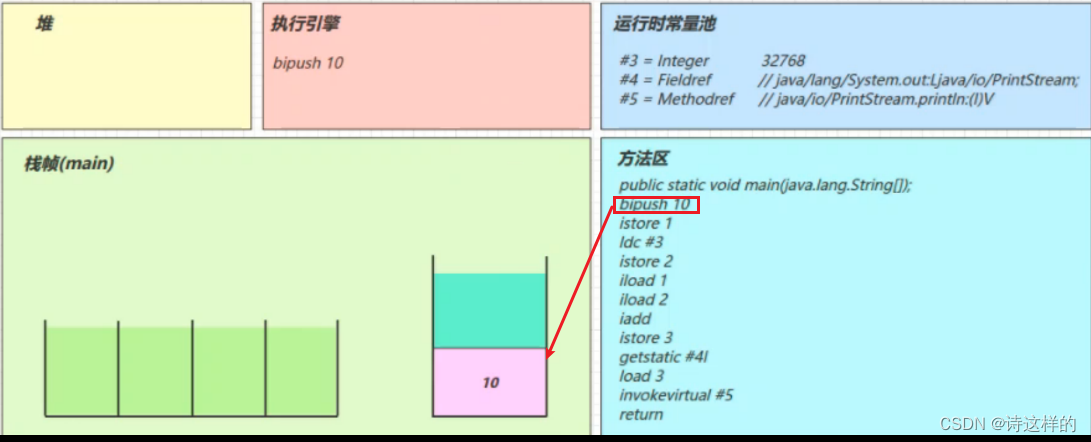
bipush 10
- 将一个 byte 压入操作数栈(其长度会补齐 4 个字节),类似的指令还有
- sipush 将一个 short 压入操作数栈(其长度会补齐 4 个字节)
- ldc 将一个 int 压入操作数栈
- ldc2_w 将一个 long 压入操作数栈(分两次压入,因为 long 是 8 个字节)
- 这里小的数字都是和字节码指令存在一起,超过 short 范围的数字存入了常量池
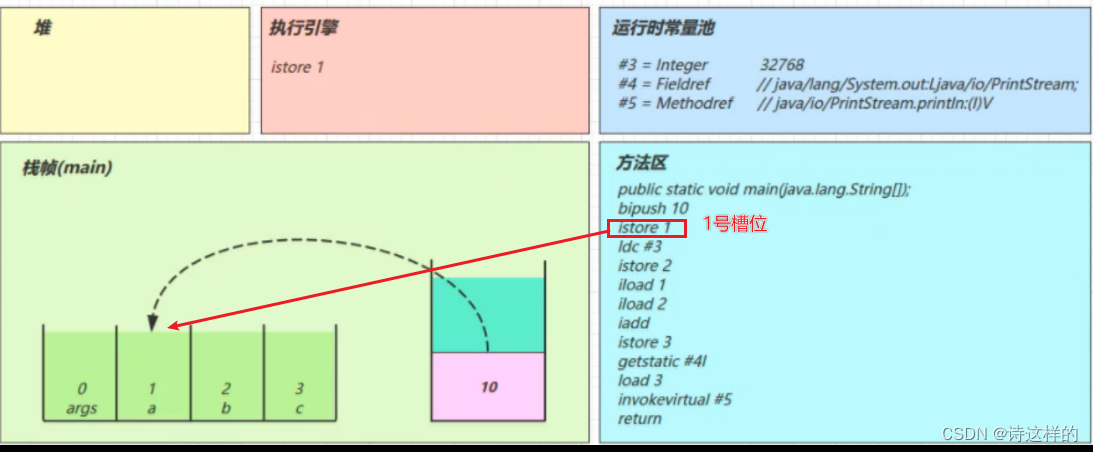
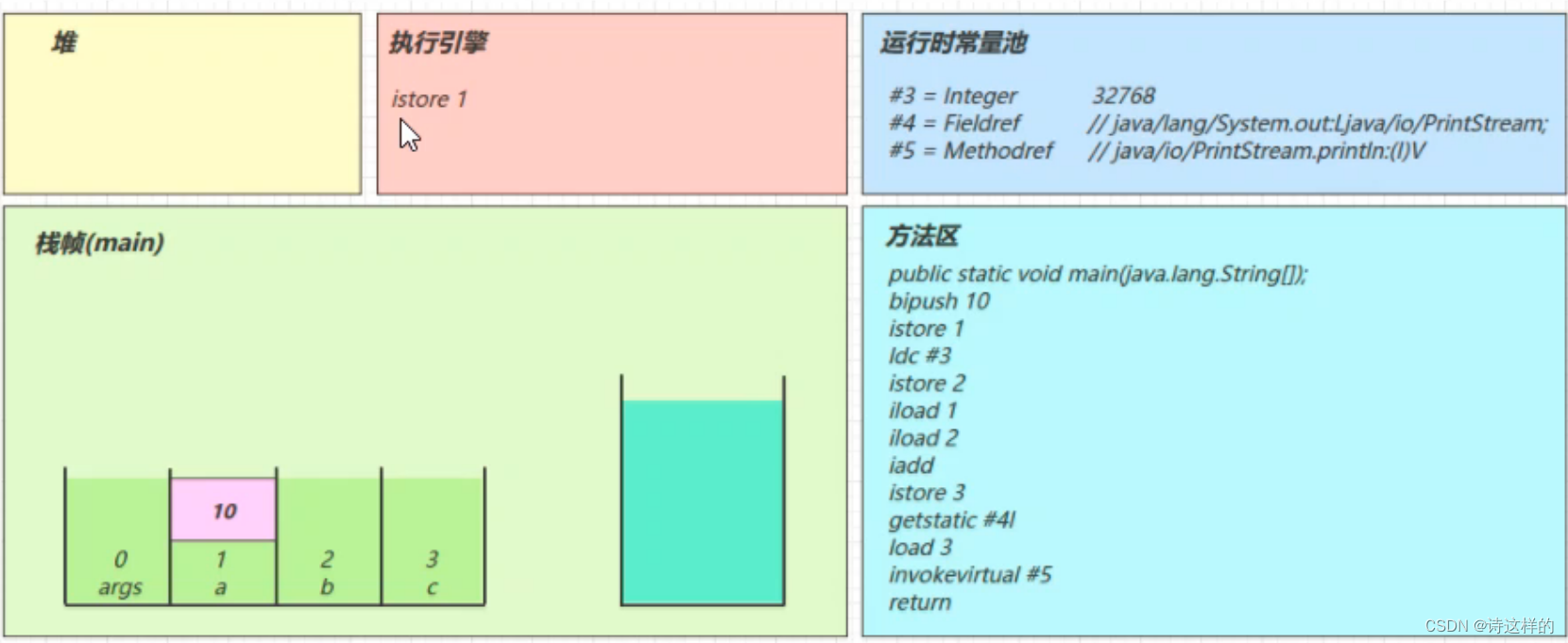
istore_1
- 将操作数栈顶数据弹出,存入局部变量表的 slot 1
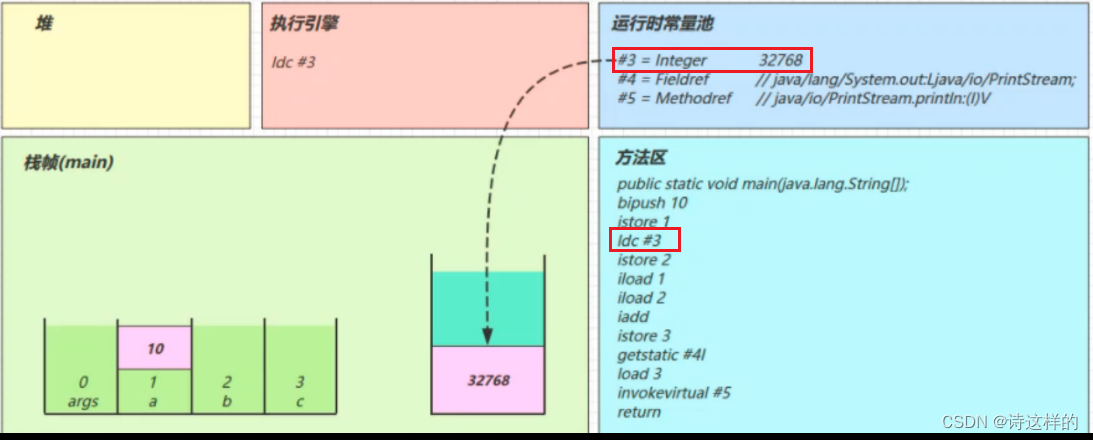
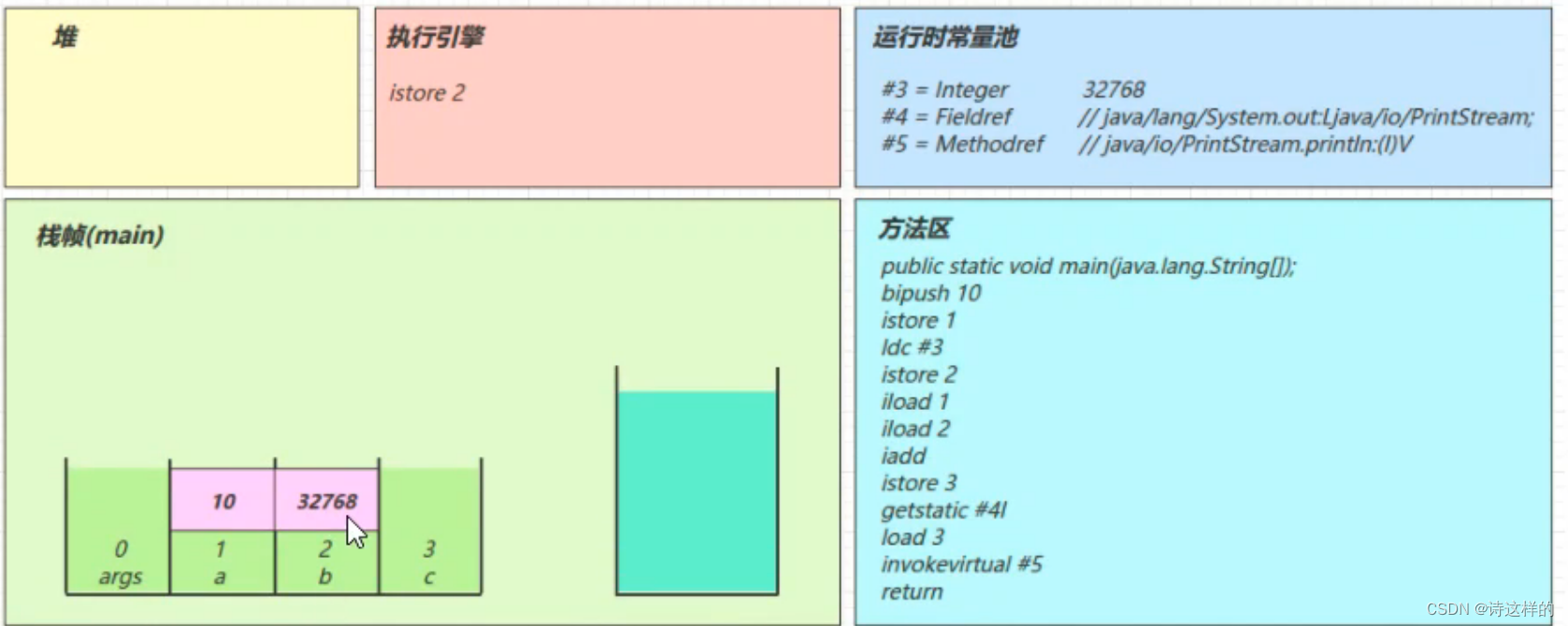
ldc #3
- 从常量池加载 #3 数据到操作数栈
- 注意 Short.MAX_VALUE 是 32767,所以 32768 = Short.MAX_VALUE + 1 实际是在编译期间计算好的
istore_2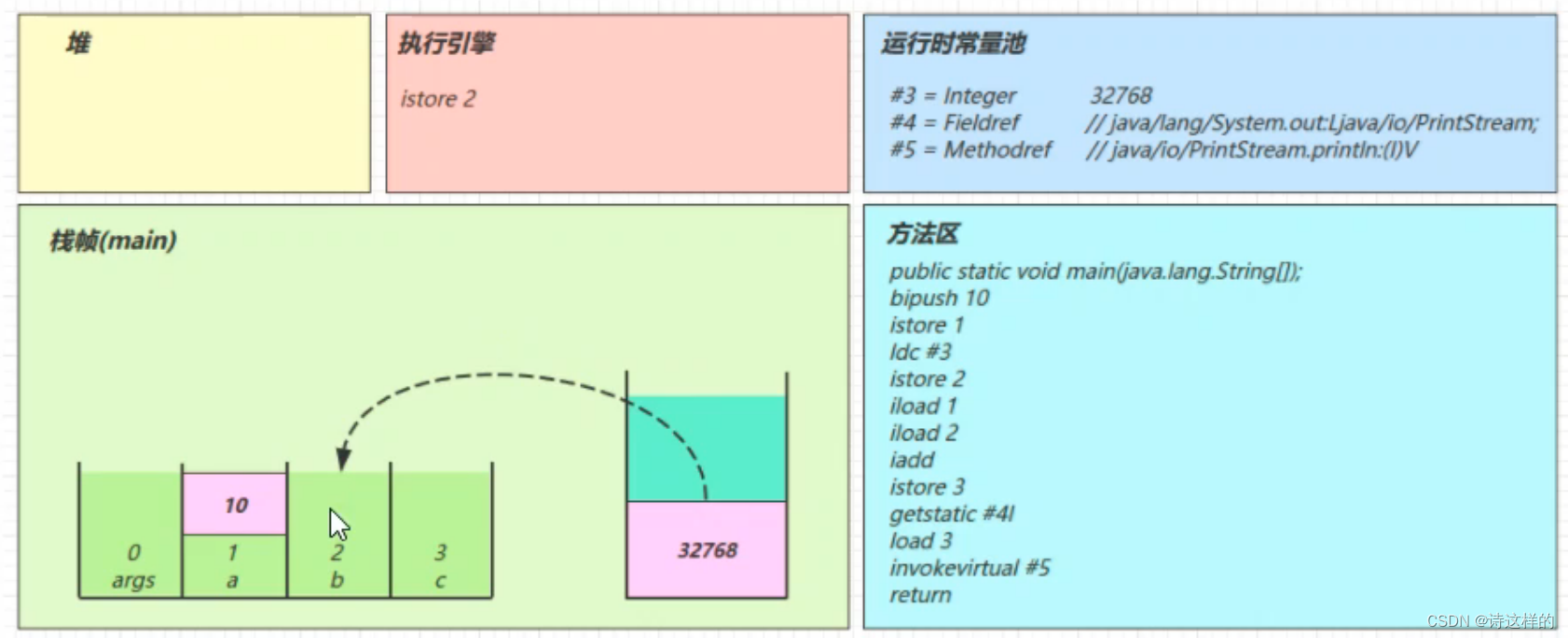
iload_1
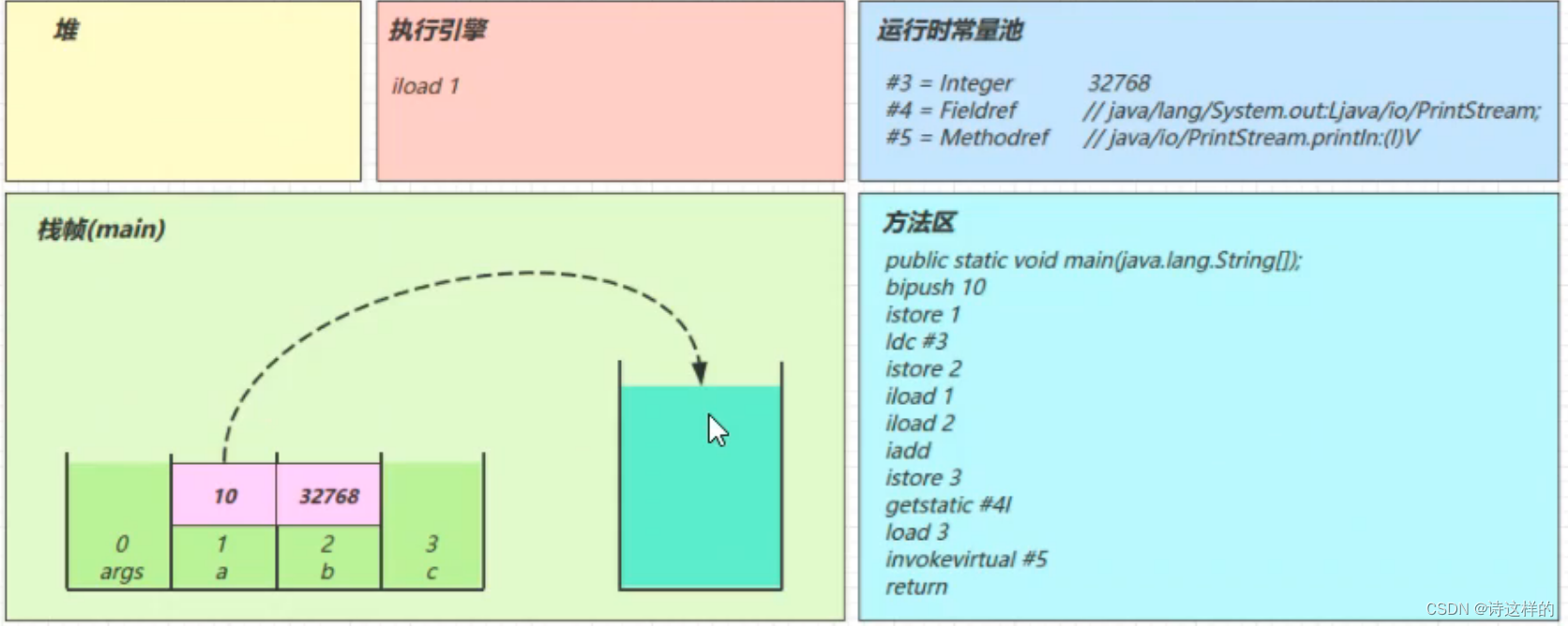
iload_2
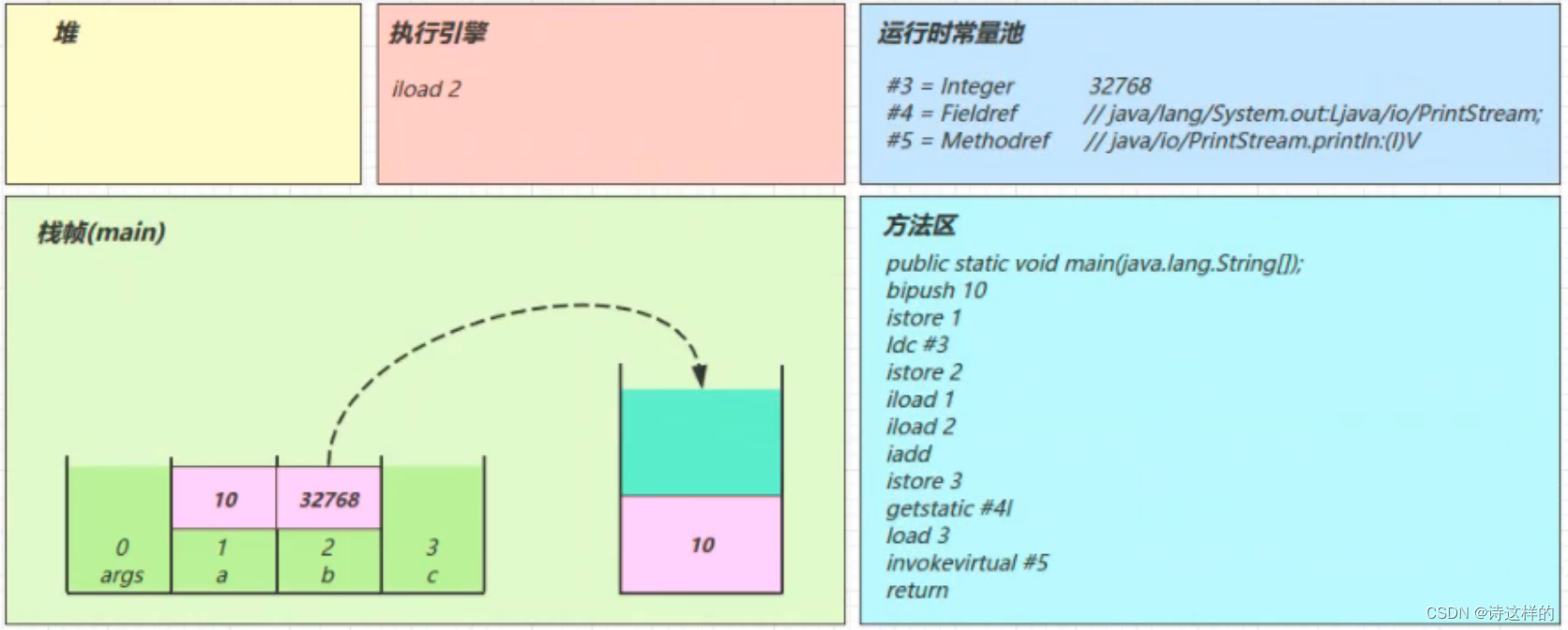
iadd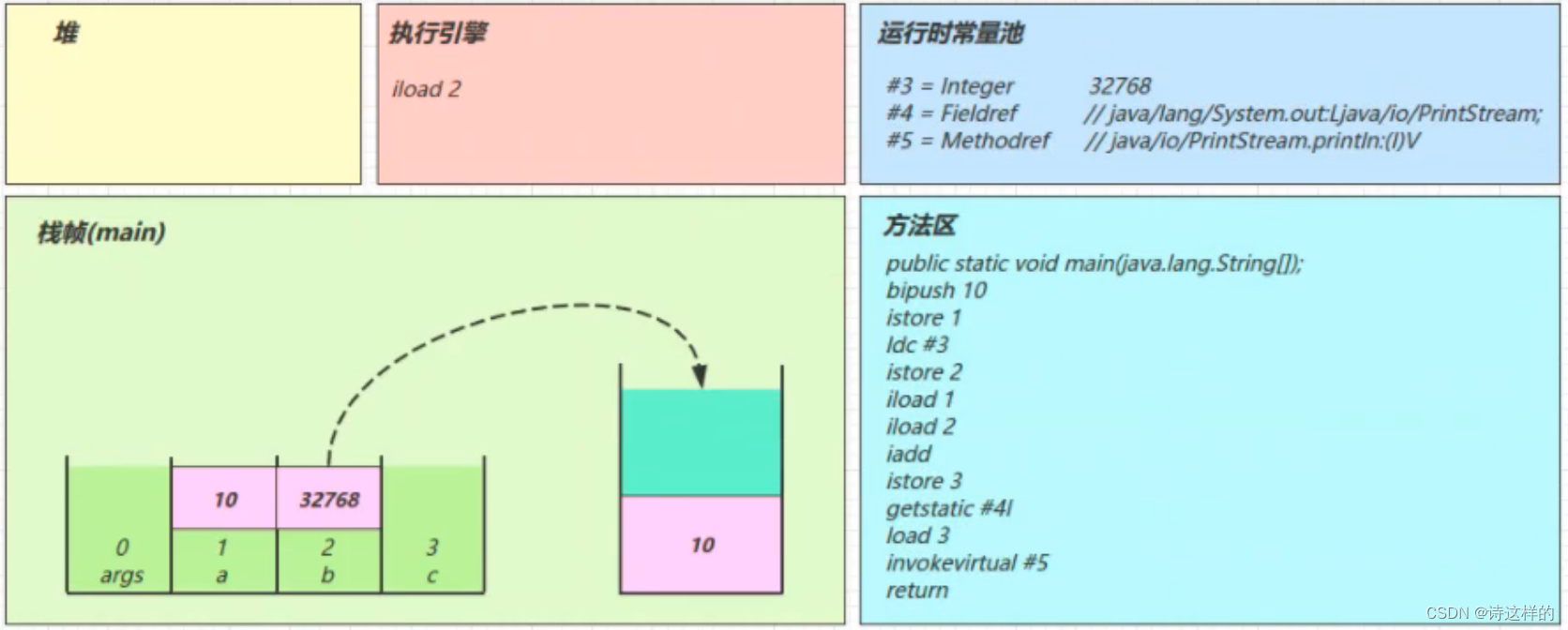
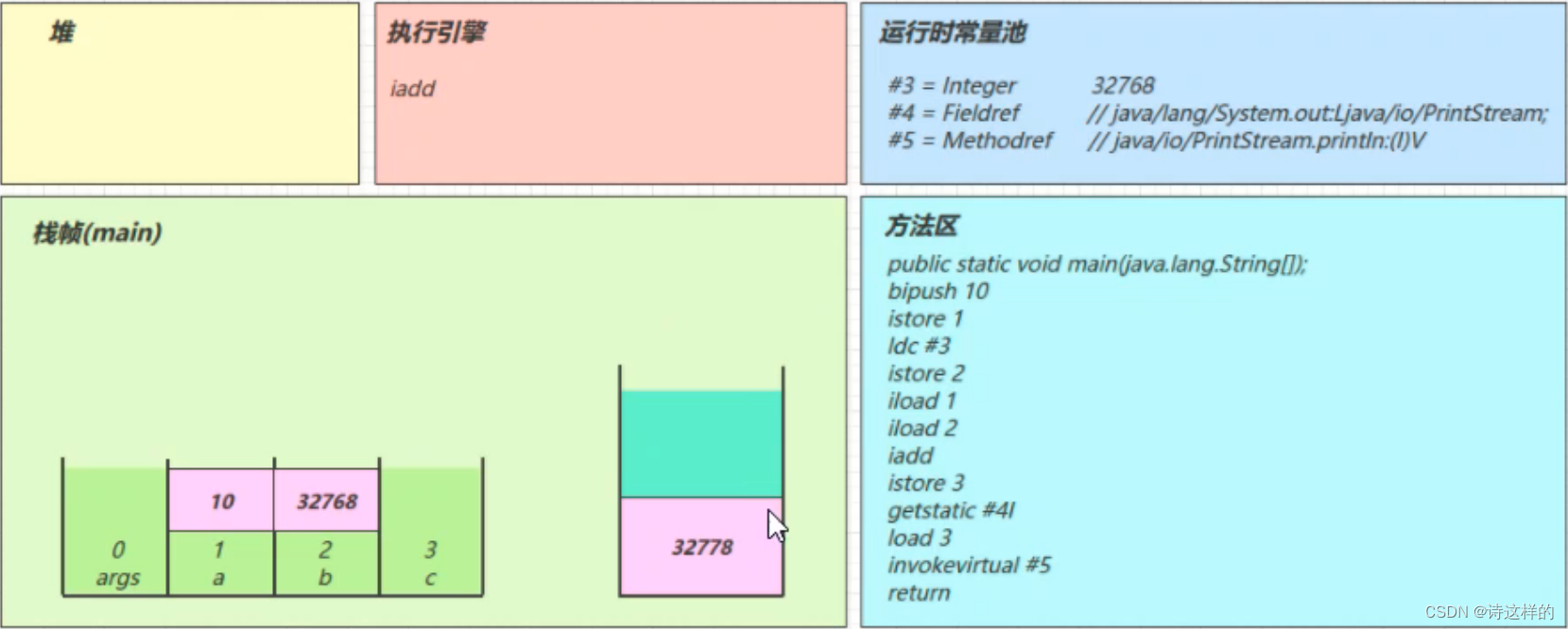
getstatic #4
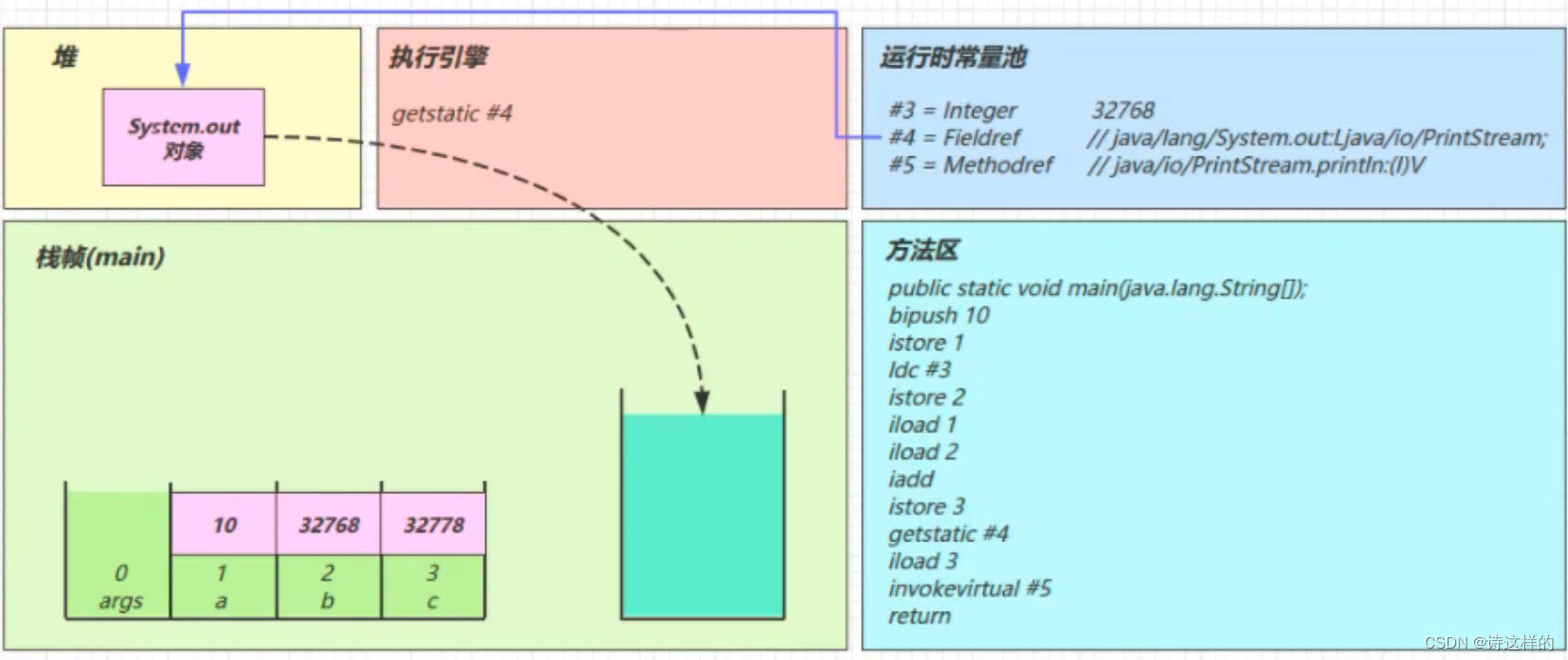
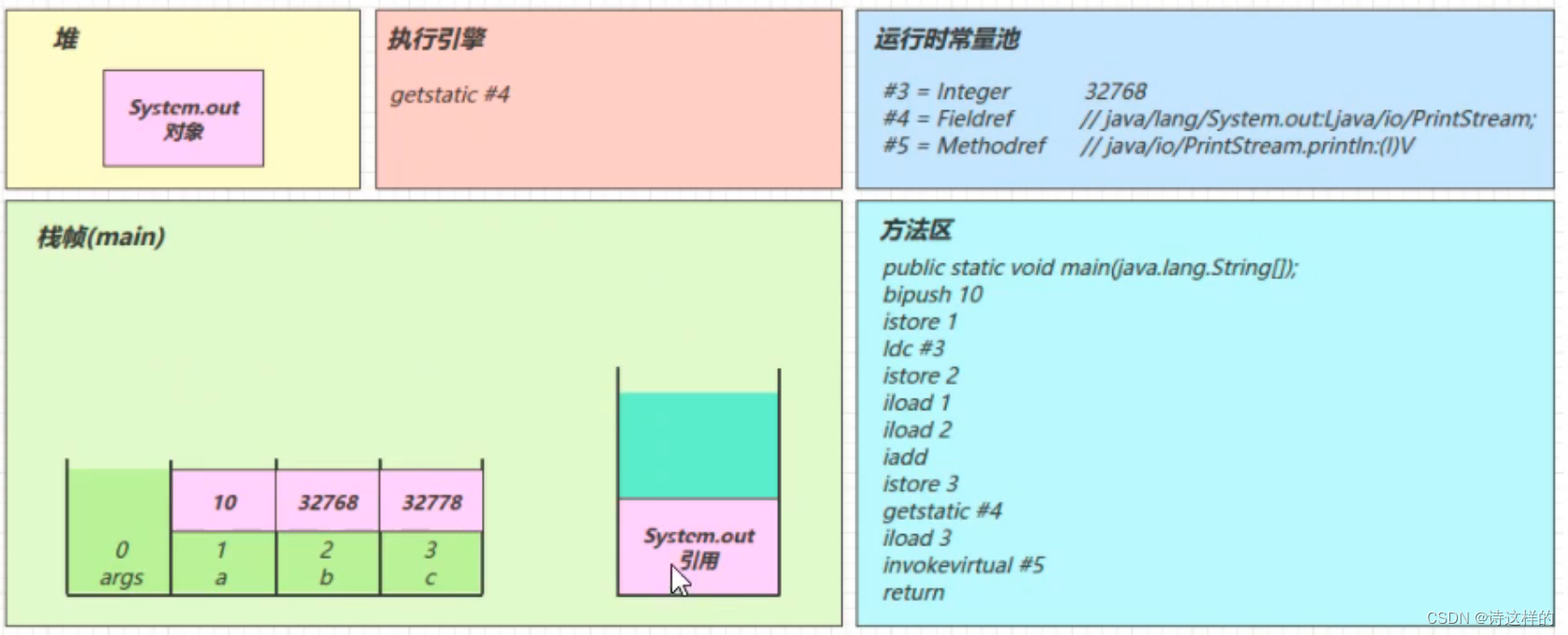
iload_3
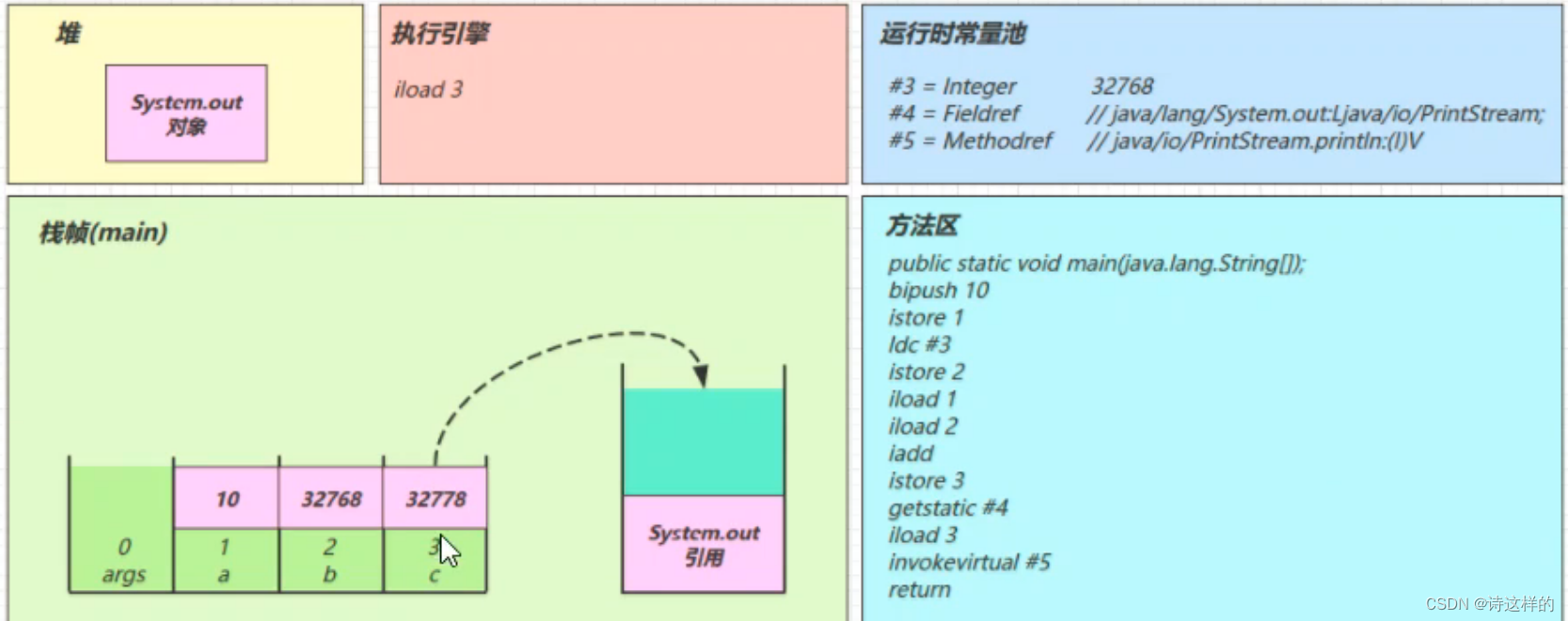
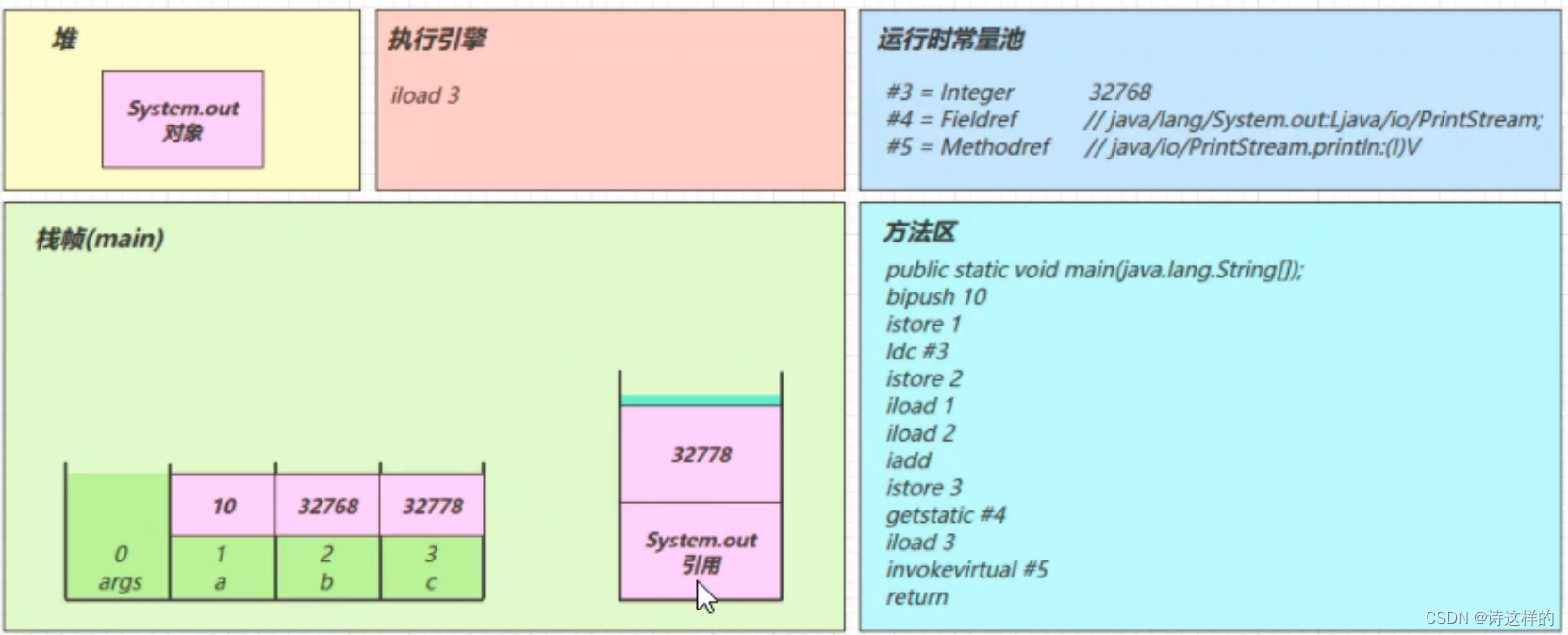
invokevirtual #5
- 找到常量池 #5 项
- 定位到方法区 java/io/PrintStream.println:(I)V 方法
- 生成新的栈帧(分配 locals、stack等)
- 传递参数,执行新栈帧中的字节码
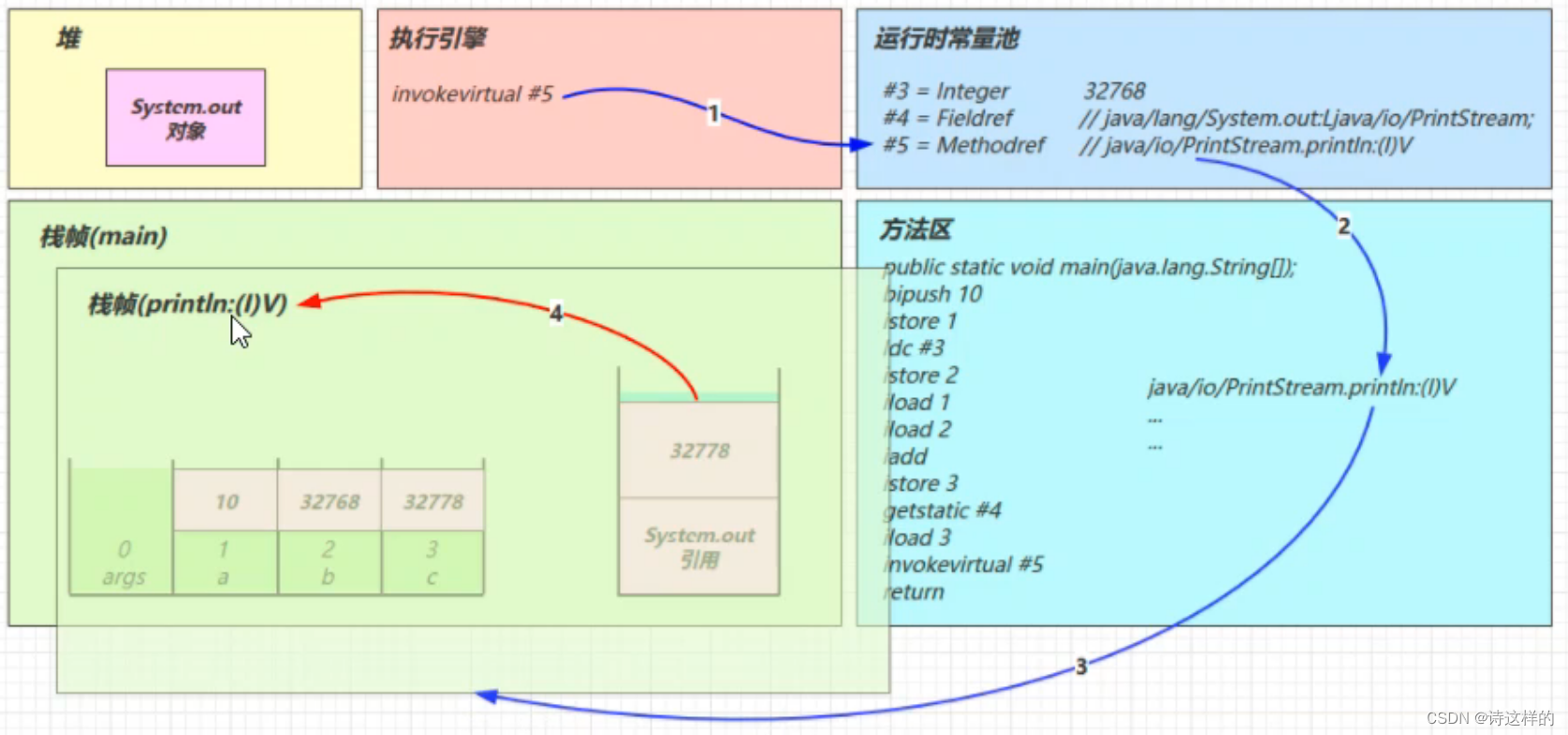
- 执行完毕,弹出栈帧
- 清除 main 操作数栈内容
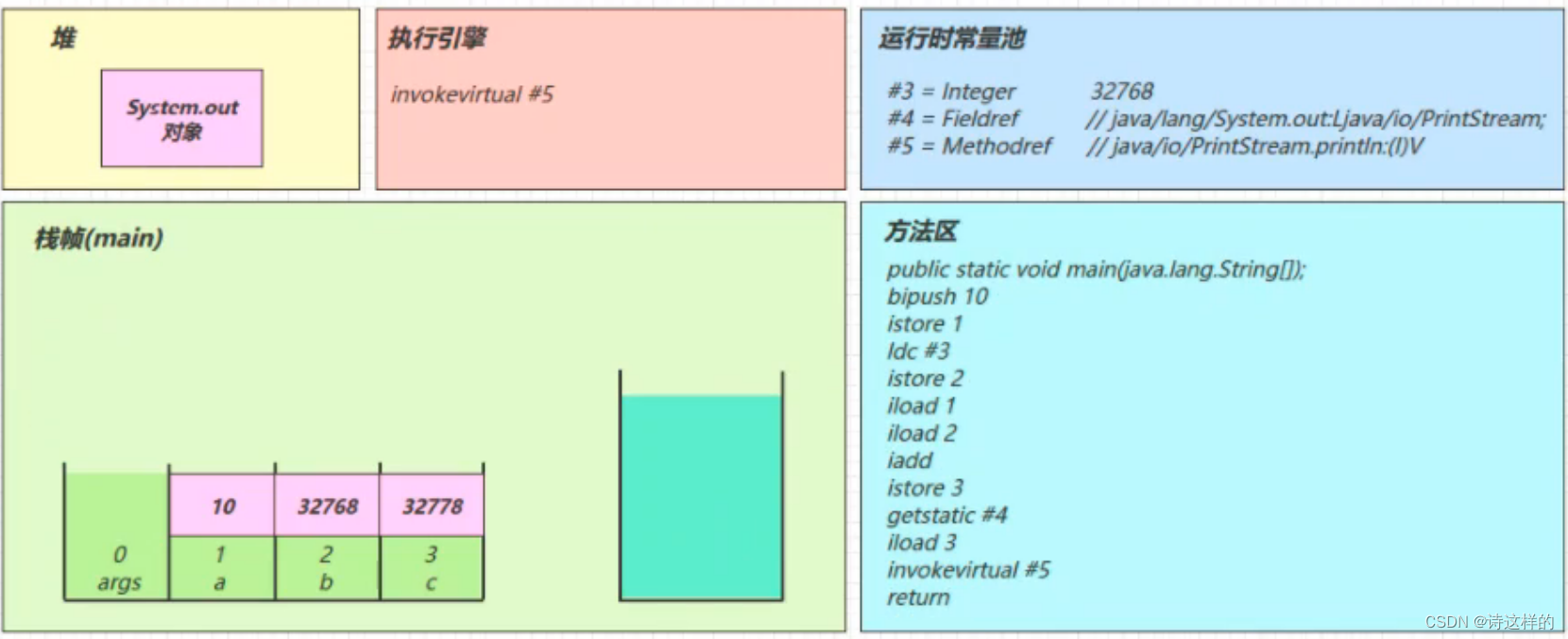
return
- 完成 main 方法调用,弹出 main 栈帧
- 程序结束
4)构造方法
4.1 <cinit>()V
public class Demo3_8_1 {static int i = 10;static {i = 20;}static {i = 30;}
}
编译器会按从上至下的顺序,收集所有 static 静态代码块和静态成员赋值的代码,合并为一个特殊的方法 <cinit>()V :
0: bipush 10
2: putstatic #2 // Field i:I
5: bipush 20
7: putstatic #2 // Field i:I
10: bipush 30
12: putstatic #2 // Field i:I
15: return
<cinit>()V 方法会在类加载的初始化阶段被调用
2)<init>()V
public class Demo3_8_2 {private String a = "s1";{b = 20;}private int b = 10;{a = "s2";}public Demo3_8_2(String a, int b) {this.a = a;this.b = b;}public static void main(String[] args) {Demo3_8_2 d = new Demo3_8_2("s3", 30);System.out.println(d.a);System.out.println(d.b);}
}
编译器会按从上至下的顺序,收集所有 {} 代码块和成员变量赋值的代码,形成新的构造方法,但原始构
造方法内的代码总是在最后
public cn.itcast.jvm.t3.bytecode.Demo3_8_2(java.lang.String, int);
descriptor: (Ljava/lang/String;I)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=3, args_size=3
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // super.<init>()V
4: aload_0
5: ldc #2 // <- "s1"
7: putfield #3 // -> this.a
10: aload_0
11: bipush 20 // <- 20
13: putfield #4 // -> this.b
16: aload_0
17: bipush 10 // <- 10
19: putfield #4 // -> this.b
22: aload_0
23: ldc #5 // <- "s2"
25: putfield #3 // -> this.a
28: aload_0 // ------------------------------
29: aload_1 // <- slot 1(a) "s3" |
30: putfield #3 // -> this.a |
33: aload_0 |
34: iload_2 // <- slot 2(b) 30 |
35: putfield #4 // -> this.b --------------------
38: return
LineNumberTable: ...
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 39 0 this Lcn/itcast/jvm/t3/bytecode/Demo3_8_2;
0 39 1 a Ljava/lang/String;
0 39 2 b I
MethodParameters: ...
5)方法调用
public class Demo3_9 {public Demo3_9() { }private void test1() { }private final void test2() { }public void test3() { }public static void test4() { }public static void main(String[] args) {Demo3_9 d = new Demo3_9();d.test1();d.test2();d.test3();d.test4();Demo3_9.test4();}
}
字节码:
0: new #2 // class cn/itcast/jvm/t3/bytecode/Demo3_9
3: dup
4: invokespecial #3 // Method "<init>":()V
7: astore_1
8: aload_1
9: invokespecial #4 // Method test1:()V
12: aload_1
13: invokespecial #5 // Method test2:()V
16: aload_1
17: invokevirtual #6 // Method test3:()V
20: aload_1
21: pop
22: invokestatic #7 // Method test4:()V
25: invokestatic #7 // Method test4:()V
28: return
- new 是创建【对象】,给对象分配堆内存,执行成功会将【对象引用】压入操作数栈
- dup 是赋值操作数栈栈顶的内容,本例即为【对象引用】,为什么需要两份引用呢,一个是要配合 invokespecial 调用该对象的构造方法 “<init>”: ()V (会消耗掉栈顶一个引用),另一个要配合 astore_1 赋值给局部变量
- 最终方法(final),私有方法(private),构造方法都是由 invokespecial 指令来调用,属于静态绑定
- 普通成员方法是由 invokevirtual 调用,属于动态绑定,即支持多态
- 成员方法与静态方法调用的另一个区别是,执行方法前是否需要【对象引用】
- 比较有意思的是 d.test4(); 是通过【对象引用】调用一个静态方法,可以看到在调用
- invokestatic 之前执行了 pop 指令,把【对象引用】从操作数栈弹掉了😂
还有一个执行 invokespecial 的情况是通过 super 调用父类方法
6)多态的原理
当执行 invokevirtual 指令时,
- 先通过栈帧中的对象引用找到对象
- 分析对象头,找到对象的实际 Class
- Class 结构中有 vtable,它在类加载的链接阶段就已经根据方法的重写规则生成好了
- 查表得到方法的具体地址
- 执行方法的字节码
所以说多态中调用方法性能不如 invokespecial 和 invokestatic 指令 即私有方法、和带有 final 和 static 关键字的方法。
7)异常处理
try-catch
public class Demo3_11_1 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0;try {i = 10;} catch (Exception e) {i = 20;}}
}
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)Vflags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATICCode:stack=1, locals=3, args_size=10: iconst_01: istore_12: bipush 104: istore_15: goto 128: astore_29: bipush 2011: istore_112: returnException table:from to target type2 5 8 Class java/lang/ExceptionLineNumberTable: ...LocalVariableTable:Start Length Slot Name Signature9 3 2 e Ljava/lang/Exception;0 13 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;2 11 1 i IStackMapTable: ...MethodParameters: ...
}
- 可以看到多出来一个 Exception table 的结构,[from, to) 是前闭后开的检测范围,一旦这个范围内的字节码执行出现异常,则通过 type 匹配异常类型,如果一致,进入 target 所指示行号
- 8 行的字节码指令 astore_2 是将异常对象引用存入局部变量表的 slot 2 位置
finally
public class Demo3_11_4 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0;try {i = 10;} catch (Exception e) {i = 20;} finally {i = 30;}}
}
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)Vflags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATICCode:stack=1, locals=4, args_size=10: iconst_01: istore_1 // 0 -> i2: bipush 10 // try --------------------------------------4: istore_1 // 10 -> i |5: bipush 30 // finally |7: istore_1 // 30 -> i |8: goto 27 // return -----------------------------------11: astore_2 // catch Exceptin -> e ----------------------12: bipush 20 // |14: istore_1 // 20 -> i |15: bipush 30 // finally |17: istore_1 // 30 -> i |18: goto 27 // return -----------------------------------21: astore_3 // catch any -> slot 3 ----------------------22: bipush 30 // finally |24: istore_1 // 30 -> i |25: aload_3 // <- slot 3 |26: athrow // throw ------------------------------------27: returnException table:from to target type2 5 11 Class java/lang/Exception2 5 21 any // 剩余的异常类型,比如 Error11 15 21 any // 剩余的异常类型,比如 ErrorLineNumberTable: ...LocalVariableTable:Start Length Slot Name Signature12 3 2 e Ljava/lang/Exception;0 28 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;2 26 1 i IStackMapTable: ...MethodParameters: ...
可以看到 finally 中的代码被复制了 3 份,分别放入 try 流程,catch 流程以及 catch 剩余的异常类型流
程。
注意:如果在 finally 块中,直接 return 会吞掉异常 (字节码athrow 指令)。
8)synchronized
public class Demo3_13 {public static void main(String[] args) {Object lock = new Object();synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("ok");}}
}
Code:stack=2, locals=4, args_size=10: new #2 // class java/lang/Object3: dup // 复制一份栈顶,然后压入栈中。用于函数消耗4: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V7: astore_1 // 将栈顶的对象地址方法 局部变量表中 1 中8: aload_1 // 加载到操作数栈9: dup // 复制一份,放到操作数栈,用于加锁时消耗10: astore_2 // 将操作数栈顶元素弹出,暂存到局部变量表的 2 号槽位。这时操作数栈中有一份对象的引用11: monitorenter // 加锁12: getstatic #3 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;15: ldc #4 // String ok17: invokevirtual #5 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V20: aload_2 // 加载对象到栈顶21: monitorexit // 释放锁22: goto 30// 异常情况的解决方案 释放锁!25: astore_326: aload_227: monitorexit28: aload_329: athrow30: return// 异常表!Exception table:from to target type12 22 25 any25 28 25 anyLineNumberTable: ...LocalVariableTable:Start Length Slot Name Signature0 31 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;8 23 1 lock Ljava/lang/Object;